In an era characterized by rapidly changing environments, companies are seeking innovative ways to keep up with these changes. One of these ways is adopting a flat organizational structure. While this type of structure presents its own set of benefits, it isn't devoid of some drawbacks as well. In this article, we dive deep into understanding what flat organizational structures are, how they operate, their pros and cons, and how to implement them effectively.
What is a flat organizational structure?
In the business world, structure dictates how roles, power, and responsibilities are assigned and coordinated. One of the distinct and progressive organizational structures is the flat organizational structure.
At its core, a flat organizational structure, also referred to as a horizontal structure, or a level, is defined by fewer or no levels of middle management between staff and executives. This sort of structure puts emphasis on employee empowerment, with an intent to encourage a fast flow of communication and collaboration across departments.
The driving idea behind the adoption of a flat organizational structure is to simplify the operational process. By getting rid of excessive levels of bureaucracy, companies with a flat structure aim to make their operations more efficient and their personnel more productive.
It's worth noting that a flat organizational structure is not a one-size-fits-all. It tends to work better in smaller, dynamic organizations or companies that emphasize innovation. It gives more authority and responsibility to employees, driving them to learn and progress. But at the same time, it also demands higher self-responsibility from the staff as they are required to make decisions and perform tasks usually handled by middle management.
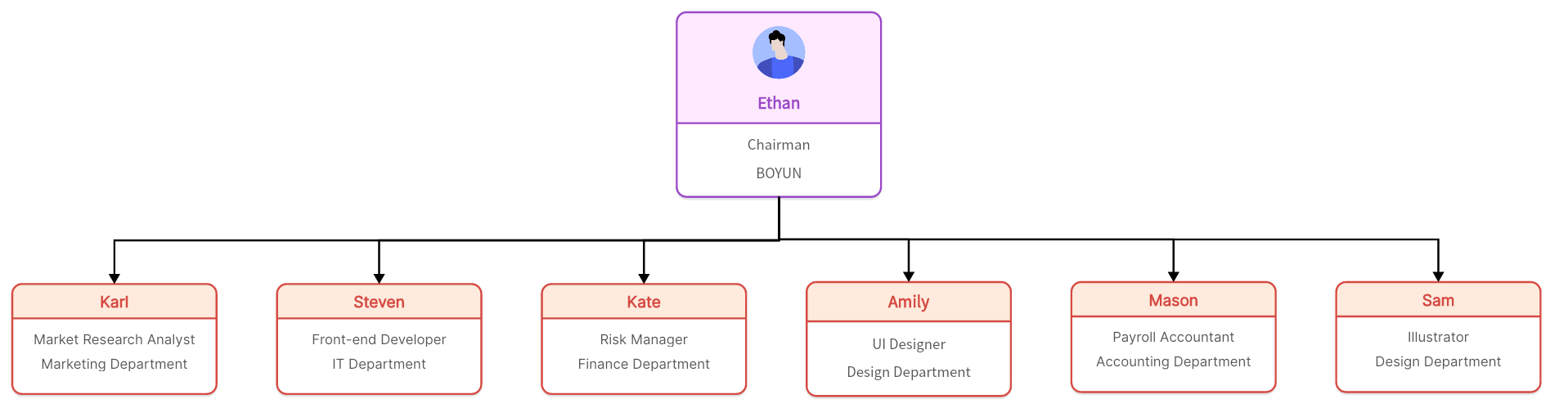
How does a flat organizational structure work?
Understanding how a flat organizational structure operates requires focusing on its key components: minimal hierarchy, broad roles, open communication, collaboration, and autonomy.
A minimal hierarchy is one of the most distinguishing features of a flat organization. Unlike traditional models, where directives pass through various managerial levels before reaching employees, in flat structures, there are typically just one or two levels separating the top executives from the rest of the team. This creates an environment where executives and employees often work side by side.
When it comes to roles, they are usually more broad and encompassing in flat organizations than in hierarchical ones. Employees might find themselves performing tasks that extend beyond their primary job descriptions. Such an approach allows them to learn new skills and contribute more significantly to the company's goals.
Open communication is another critical element of flat organizations. With fewer levels between staff and leadership, information can flow quickly in all directions – bottom-up and top-down. This not only enhances transparency but also allows for faster decision making.
The emphasis on collaboration is a characteristic feature of a flat organizational structure. Rather than working in silos, employees are encouraged to work together, fostering a sense of unity and team spirit.
Finally, with autonomy, employees in flat structures are typically empowered to make decisions that would traditionally be made by their supervisors. This freedom can lead to high levels of job satisfaction and engagement as employees have the space to exercise their creativity and feel more valued in their roles.
Benefits of Flat Organizational Structures
Flat organizational structures offer several benefits that can drive business success. Let's dive deeper into these advantages.
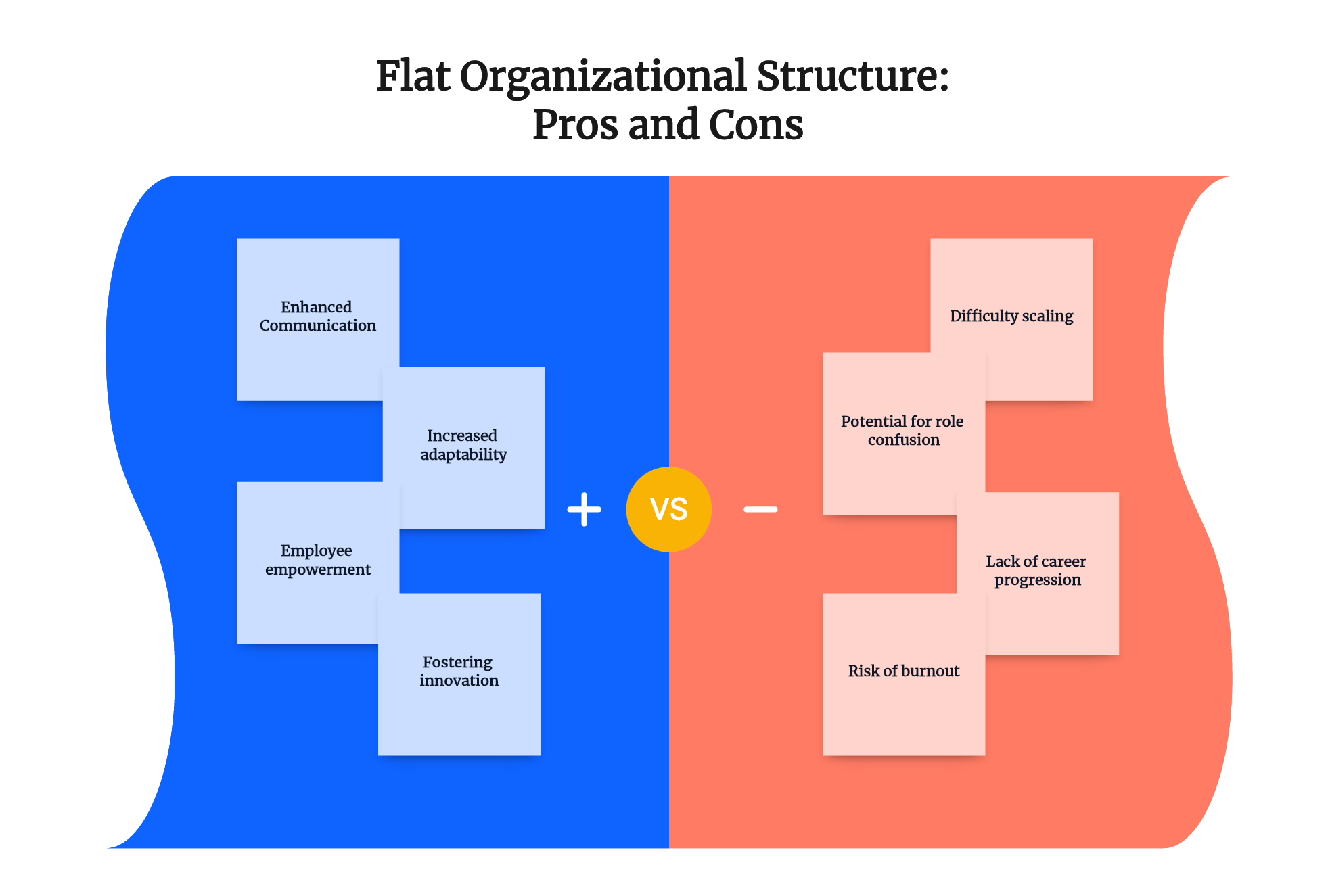
- Enhanced Communication:In a flat structure, with less hierarchy, information travels faster and more effectively. Decisions don't have to be passed through multiple layers of management, ensuring employees at all levels stay informed and engaged. Moreover, it encourages open dialogue and fosters a culture of transparency.
- Increased adaptability:Flat organizations are more flexible and agile. They can react swiftly to market changes or shifts in business strategy because the decision-making process is not bound by multiple layers of approval. The end result is a nimble organization that can stay ahead in a dynamic business environment.
- Employee empowerment:In a flat organizational structure, employees are granted more responsibility and autonomy in their roles. They're encouraged to take the initiative, propose ideas, and make decisions. This freedom can boost their confidence and productivity while fostering an entrepreneurial spirit within the company.
- Fostering innovation:A flat organizational structure promotes creativity and innovation. It provides employees the opportunity to share their ideas and feedback directly with the top management, sparking unique solutions and innovative approaches to business problems.
Drawbacks of Flat Organizational Structures
Despite the above benefits, flat organizational structures also present certain challenges. Understanding these drawbacks can help organizations better anticipate potential issues.
- Potential for role confusion:In flat organizations, job roles are typically broad and not strictly defined, which can lead to role confusion and overlapping responsibilities. Some employees might struggle with knowing what's expected of them, leading to decreased productivity and potential conflicts.
- Difficulty scaling:As a company grows, maintaining a flat structure might become challenging. Adding employees without adding managerial levels can cause a lack of clarity in decision-making, communication difficulties, and an imbalance in workloads.
- Risk of burnout:With more responsibility placed on each individual, there is an increased risk of employee burnout in flat organizations. Without sufficient support or delineation of roles, employees might feel overwhelmed by their workloads.
- Lack of career progression:Flat structures don't offer the typical managerial path that some employees may aspire to in their career progression. This lack of clear advancement opportunities could impact employee retention and recruitment efforts.
Tips for Using the Flat Organizational Structure
Transitioning to or efficiently using a flat organizational structure requires thoughtful strategy and diligent implementation. Here are some crucial tips to help businesses thrive in a flat organizational framework.
- Clear Communication:Emphasize open, honest, and transparent communication at all levels. This will not only make employees feel more valued but also improve efficiency, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding organizational objectives.
- Define Roles Clearly:To avoid confusion and potential conflicts, clearly define roles and responsibilities. Each team member should know their job scope and who to turn to if they need assistance or guidance.
- Foster a Collaborative Environment:Encourage employees to work together towards common goals. Teamwork not only enhances productivity but also nurtures a sense of belonging and commitment among the staff.
- Provide Adequate Support:Though employees in a flat structure often have more autonomy, they still require support from leaders. Be sure to provide necessary resources, training, and mentorship to ensure employees feel confident in their roles.
- Develop a Strong Company Culture:A strong and positive company culture can glue together a flat organization by aligning employees with the organization's values, goals, and mission. It also fosters employee loyalty and satisfaction.
- Consider Hybrid Structures:For larger companies, consider a hybrid structure which combines elements of both hierarchical and flat structures. This allows for flexibility and scalability, supporting growth while still maintaining many of the benefits of a flat structure.
- Respect Employee Work-Life Balance:With greater responsibility comes the risk of employee burnout. Ensure that while employees have the freedom to work flexibly, they're not burdened with unrealistic expectations that impede their work-life balance.
- Feedback Mechanism:Establish a regular feedback system where employees can share their thoughts, suggestions, or concerns freely. It helps in continual improvement and keeping everyone engaged.
Examples of flat organizational structure in different sectors
The concept of a flat organizational structure isn't purely theoretical, it has been effectively executed by several leading companies across the globe. These organizations, each with their own unique take on the flat structure, have leveraged it to promote innovation, flexibility, and employee satisfaction. Here are some illustrative examples of flat organizational structures operating successfully in various sectors.
- Valve Corporation:A pioneer in the gaming industry, Valve is famous for its non-hierarchical, flat organizational structure. Employees are free to choose their projects and teams without managerial directives. This structure has fostered a highly creative environment that has contributed to the creation of popular games like Half-Life and Portal. However, it's worth noting that such a structure has also faced criticism, particularly concerning clarity in decision-making processes and progression routes for employees.
- Gore-Tex:The innovative company behind Gore-Tex products operates with a 'lattice' structure which promotes direct communication among employees, disregarding formal chains of command. Rather than being managed, associates (as they are referred to within the company) are expected to commit to the fairness, freedom, and flexibility offered by the organization. It has also been highlighted that this model has helped in creating a high-trust environment that encourages innovation.
- Spotify:The Swedish music streaming giant is another great example of a company with a flat structure, but it has added its own twist. Spotify operates with 'squads', 'tribes', 'chapters', and 'guilds', creating a model that combines the best of hierarchical and flat structures. Each squad operates autonomously, fostering a culture of ownership and accountability.
Frequently asked questions about flat organizational structures
What is the difference between a flat and hierarchical organization?
A hierarchical organization has many levels of management and authority, while a flat organization reduces the number of levels, promoting more direct communication and quicker decision-making.
Are there any alternatives to a flat organizational structure?
Yes, there are several alternatives including the Functional structure, Matrix structure, Network structure, and Divisional structure. You can read more about these in our article 8 Types of Organizational Structures for Businesses.
Is Amazon a flat organization?
No, Amazon follows a more hierarchical structure with clearly defined roles and responsibilities, though it promotes a culture of rapid decision-making and ownership.