In the realm of goal setting, one method has consistently proven its worth across various sectors and industries – SMART goals. From enhancing individual productivity to driving organizational success, SMART goals provide a structured and effective framework for achieving meaningful objectives. This article explores what SMART goals are and their benefits for businesses.
What Are SMART Goals
SMART is an acronym for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. It represents a set of criteria that helps in establishing clear and achievable goals.

- Specific: The goal should clearly state what is to be achieved, by whom, where, and when it is to be achieved, and why that is the goal.
- Measurable: The goal should be quantifiable; that is, it should include a way to measure success.
- Achievable: The goal should be attainable given the available resources and existing constraints.
- Relevant: The goal should be aligned with other business goals to support the organization's overall strategy or mission.
- Time-bound: The goal should specify when it will be achieved.
Benefits of SMART Goals for Business
SMART goals are invaluable for businesses and bring a host of benefits:
- Clear Focus: SMART goals ensure that everyone knows exactly what the company aims to achieve. This eliminates confusion and allows employees at all levels to align their efforts towards these common objectives.
- Improved Decision Making: When goals are clear and tied into the overall business strategy, decision-making processes are significantly improved. Managers can easily prioritize tasks based on their relevance to the set SMART goals.
- Enhanced Motivation: When employees understand exactly what is expected of them, it increases their motivation to work towards achieving these goals. The measurable nature of SMART goals also allows for recognition of progress and success, further boosting employee motivation.
- Increased Efficiency: SMART goals promote efficiency by eliminating wasted effort on tasks that do not contribute to achieving the key objectives. They also encourage better use of resources, thus promoting overall business efficiency.
- Facilitates Monitoring and Control: With SMART goals, progress can be tracked and measured at regular intervals. This facilitates easy monitoring of progress and allows timely intervention if any deviations are noted.
SMART goals can drive significant improvements in productivity, efficiency, and overall business performance. Therefore, adopting a SMART goal approach can be a game-changer for many organizations seeking growth and success in their endeavors.
8 SMART Goals Examples for Business
Creating and implementing SMART goals can pave the way for a successful business journey. These eight examples across various departments highlight the effectiveness and flexibility of the SMART goals framework.
SMART Goals Example for Business Students
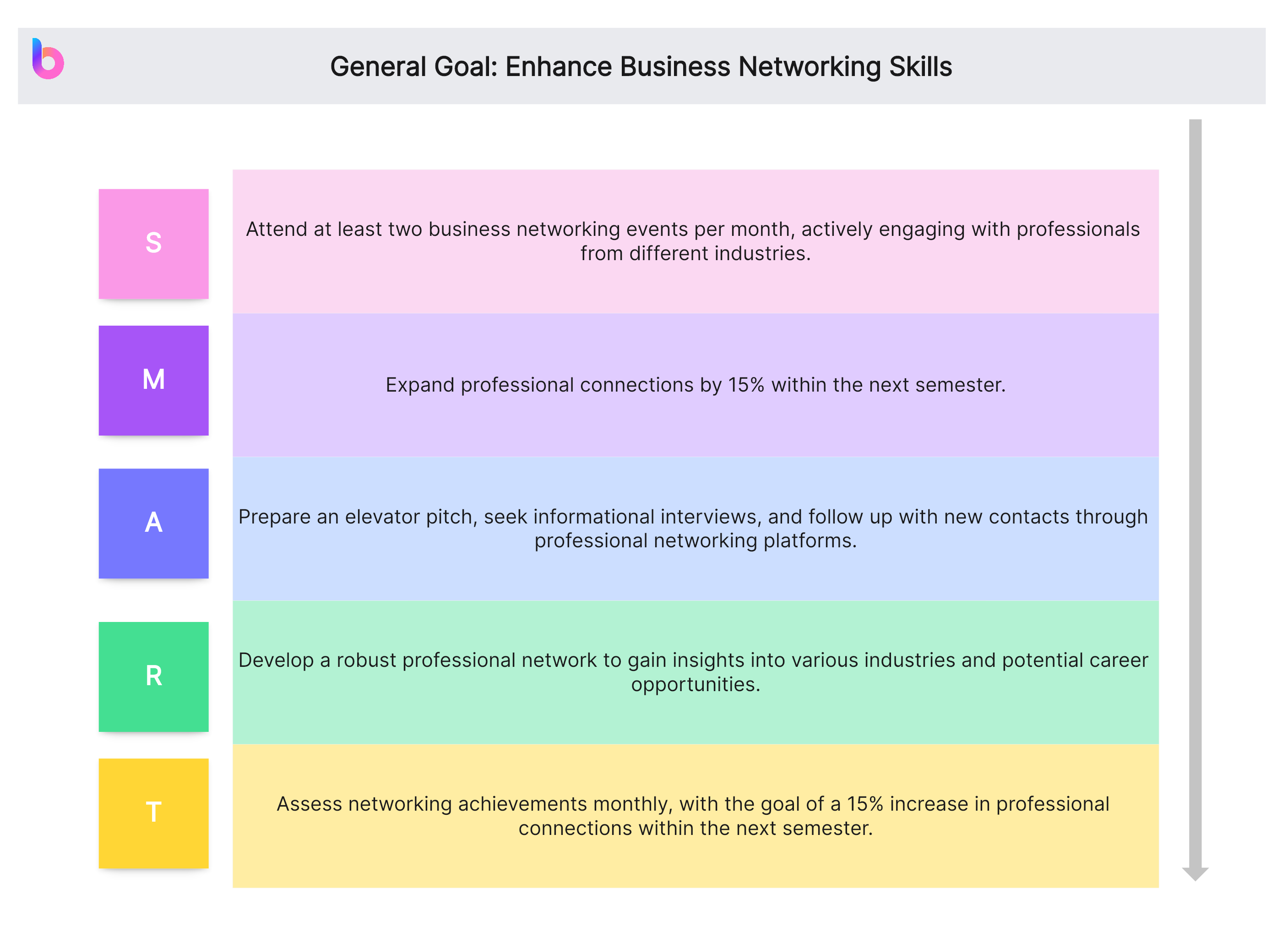
General Goal: Enhance Business Networking Skills
- Specific (S): Attend at least two business networking events per month, actively engaging with professionals from different industries.
- Measurable (M): Expand professional connections by 15% within the next semester.
- Achievable (A): Prepare an elevator pitch, seek informational interviews, and follow up with new contacts through professional networking platforms.
- Relevant (R): Develop a robust professional network to gain insights into various industries and potential career opportunities.
- Time-bound (T): Assess networking achievements monthly, with the goal of a 15% increase in professional connections within the next semester.
SMART Goals Example for Business Students
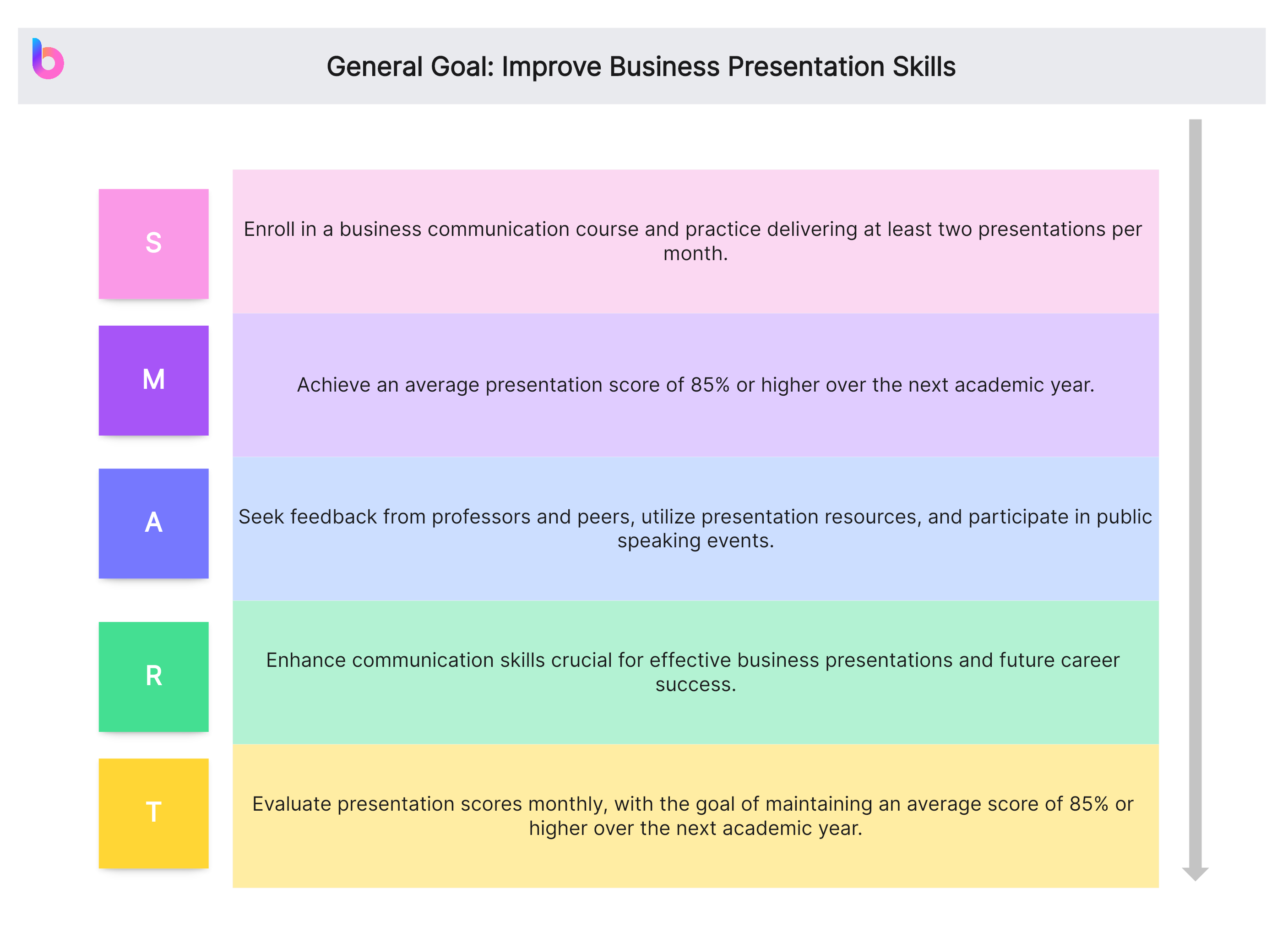
General Goal: Improve Business Presentation Skills
- Specific (S): Enroll in a business communication course and practice delivering at least two presentations per month.
- Measurable (M): Achieve an average presentation score of 85% or higher over the next academic year.
- Achievable (A): Seek feedback from professors and peers, utilize presentation resources, and participate in public speaking events.
- Relevant (R): Enhance communication skills crucial for effective business presentations and future career success.
- Time-bound (T): Evaluate presentation scores monthly, with the goal of maintaining an average score of 85% or higher over the next academic year.
SMART Goals Example for Business Analysts
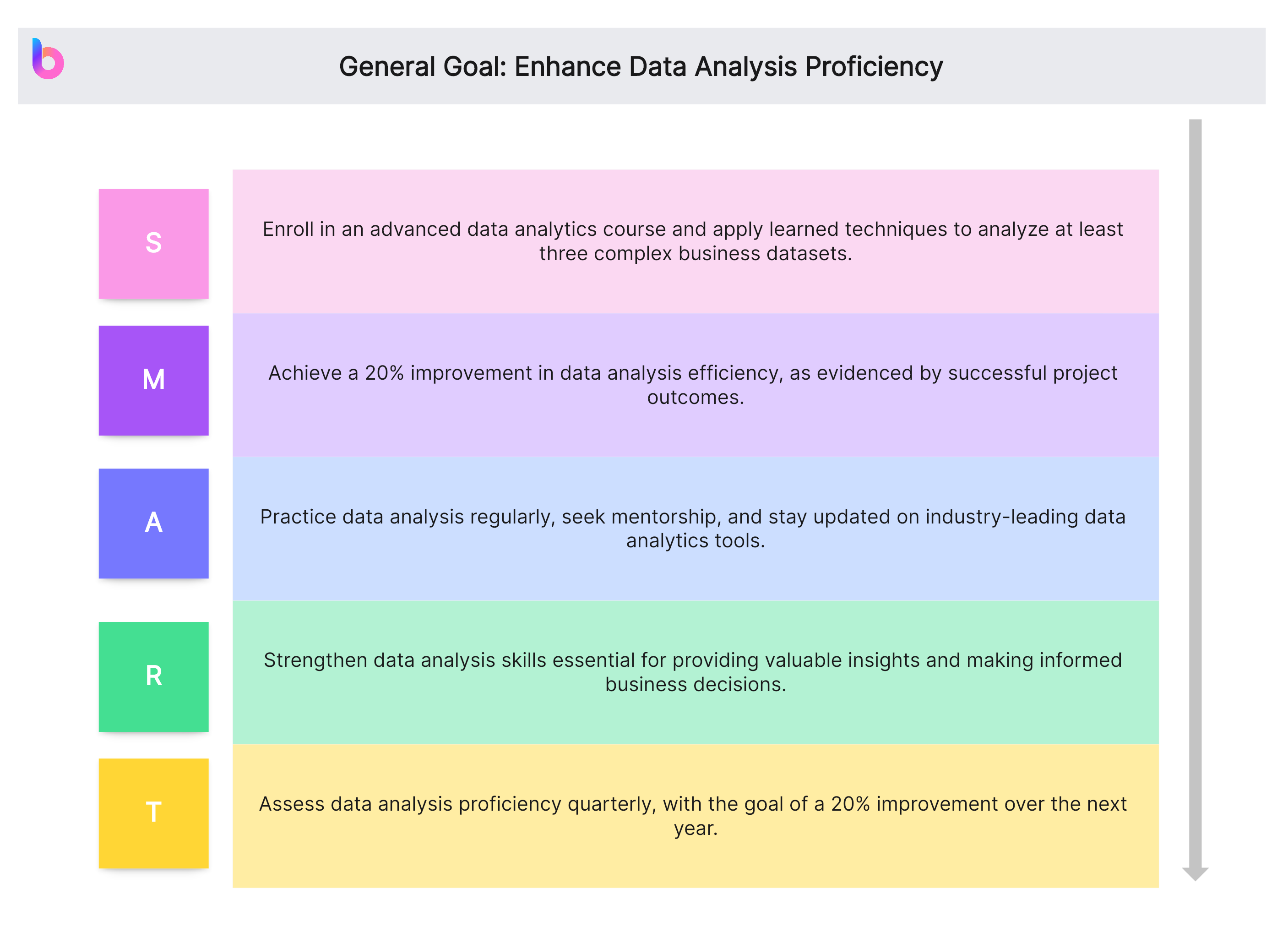
General Goal: Enhance Data Analysis Proficiency
- Specific (S): Enroll in an advanced data analytics course and apply learned techniques to analyze at least three complex business datasets.
- Measurable (M): Achieve a 20% improvement in data analysis efficiency, as evidenced by successful project outcomes.
- Achievable (A): Practice data analysis regularly, seek mentorship, and stay updated on industry-leading data analytics tools.
- Relevant (R): Strengthen data analysis skills essential for providing valuable insights and making informed business decisions.
- Time-bound (T): Assess data analysis proficiency quarterly, with the goal of a 20% improvement over the next year.
SMART Goals Example for Business Analysts
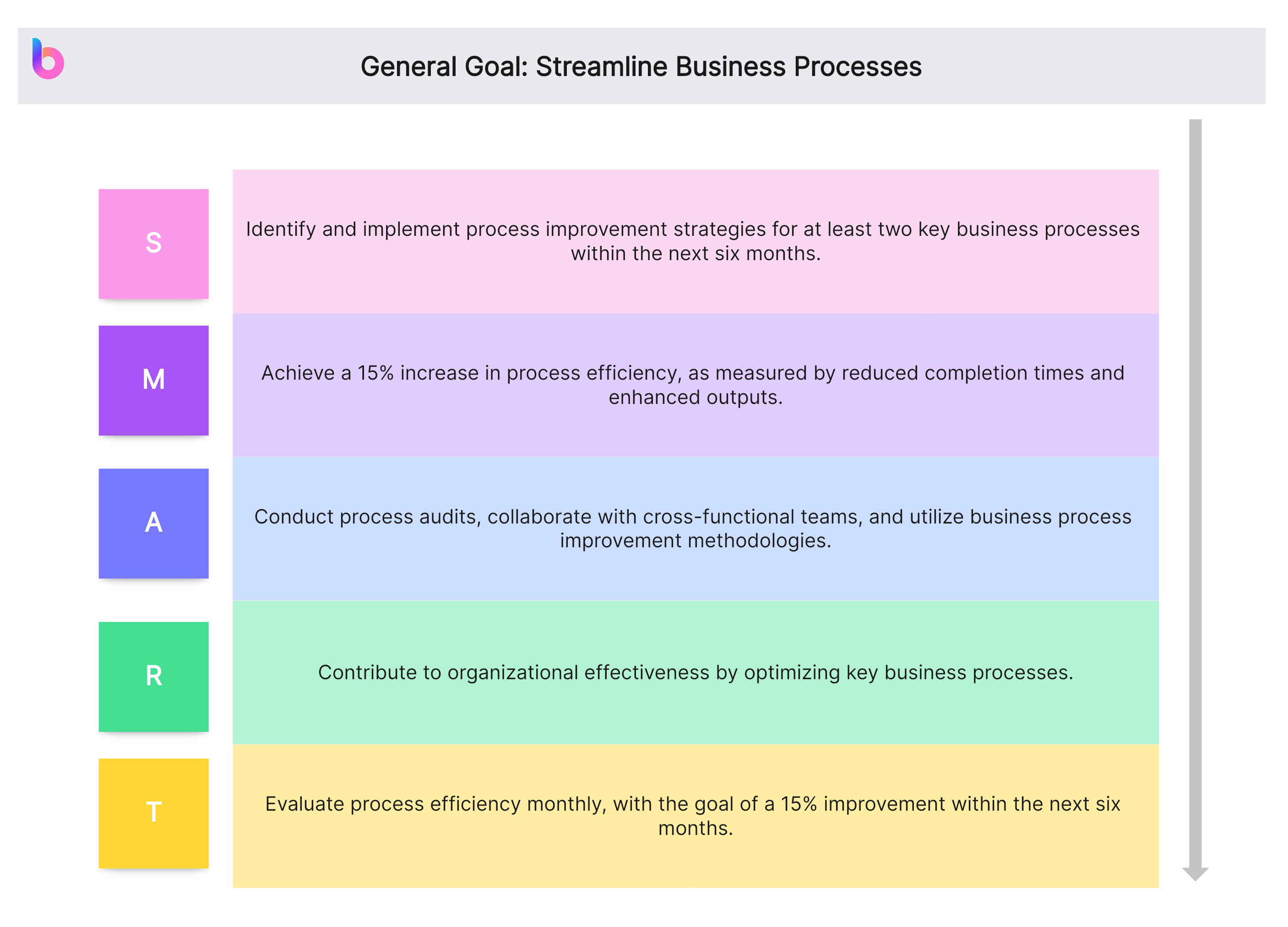
General Goal: Streamline Business Processes
- Specific (S): Identify and implement process improvement strategies for at least two key business processes within the next six months.
- Measurable (M): Achieve a 15% increase in process efficiency, as measured by reduced completion times and enhanced outputs.
- Achievable (A): Conduct process audits, collaborate with cross-functional teams, and utilize business process improvement methodologies.
- Relevant (R): Contribute to organizational effectiveness by optimizing key business processes.
- Time-bound (T): Evaluate process efficiency monthly, with the goal of a 15% improvement within the next six months.
SMART Goals Example for Business Planners
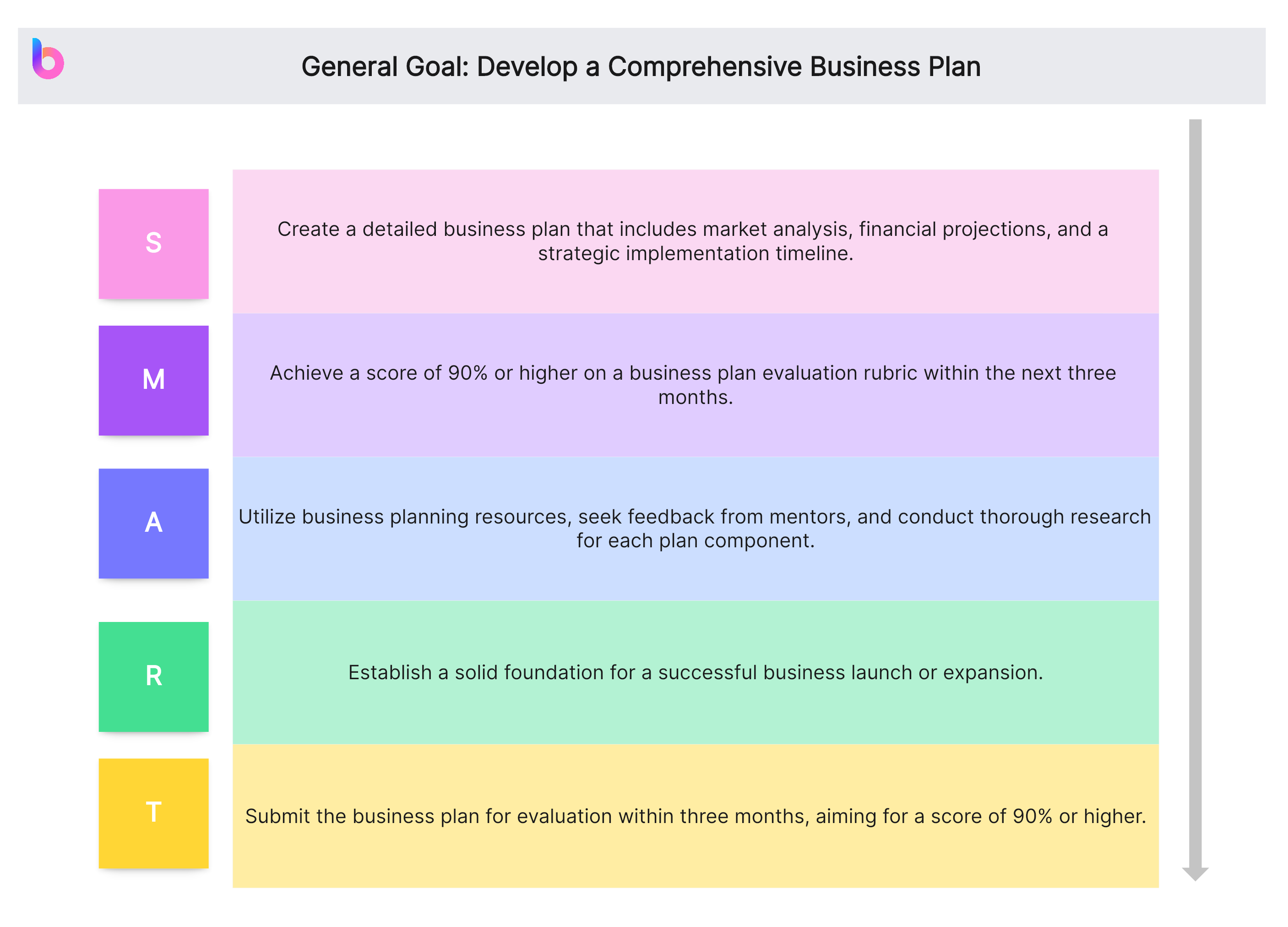
General Goal: Develop a Comprehensive Business Plan
- Specific (S): Create a detailed business plan that includes market analysis, financial projections, and a strategic implementation timeline.
- Measurable (M): Achieve a score of 90% or higher on a business plan evaluation rubric within the next three months.
- Achievable (A): Utilize business planning resources, seek feedback from mentors, and conduct thorough research for each plan component.
- Relevant (R): Establish a solid foundation for a successful business launch or expansion.
- Time-bound (T): Submit the business plan for evaluation within three months, aiming for a score of 90% or higher.
SMART Goals Example for Business Planners
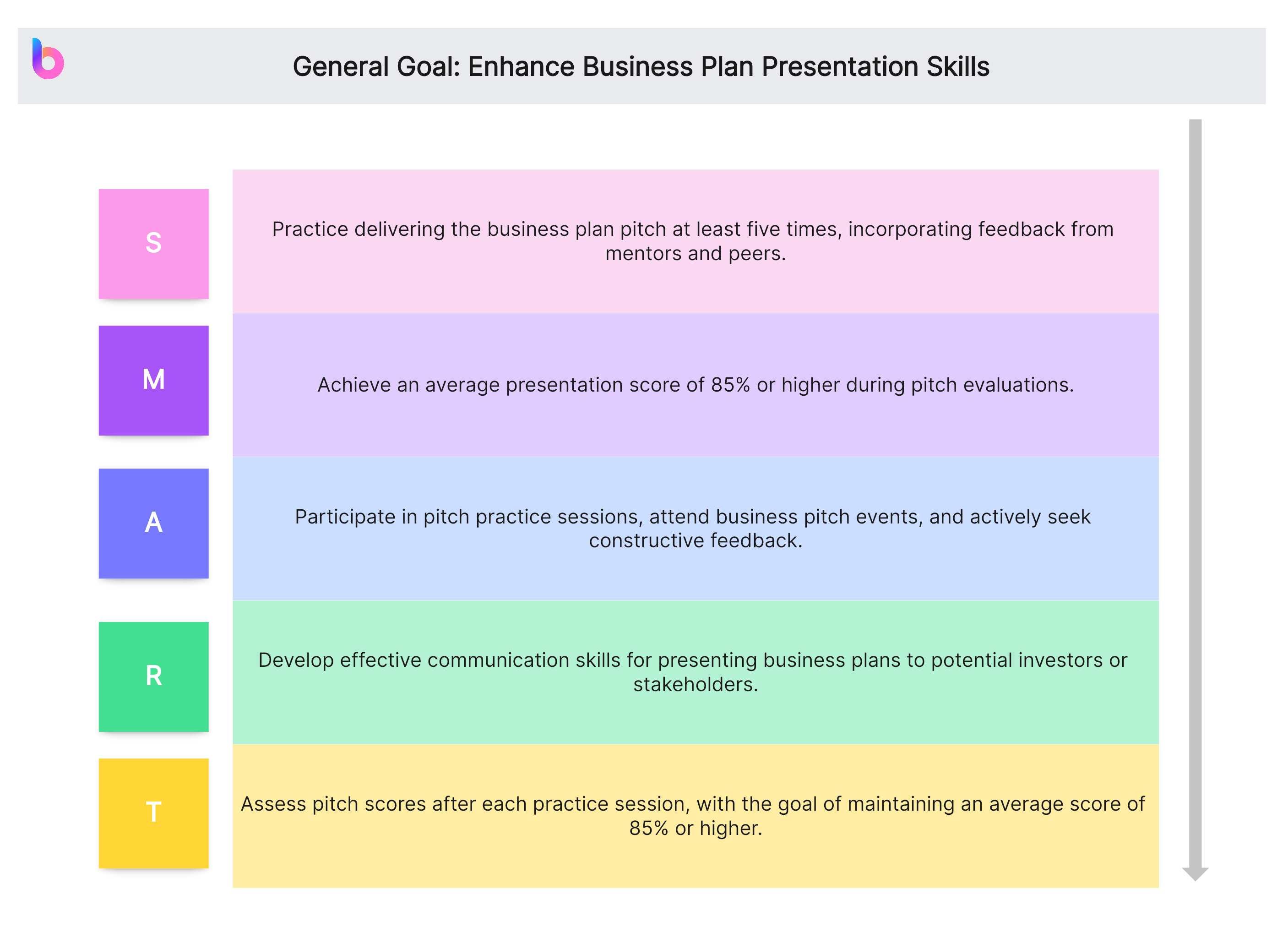
General Goal: Enhance Business Plan Presentation Skills
- Specific (S): Practice delivering the business plan pitch at least five times, incorporating feedback from mentors and peers.
- Measurable (M): Achieve an average presentation score of 85% or higher during pitch evaluations.
- Achievable (A): Participate in pitch practice sessions, attend business pitch events, and actively seek constructive feedback.
- Relevant (R): Develop effective communication skills for presenting business plans to potential investors or stakeholders.
- Time-bound (T): Assess pitch scores after each practice session, with the goal of maintaining an average score of 85% or higher.
SMART Goals Example for Small Business
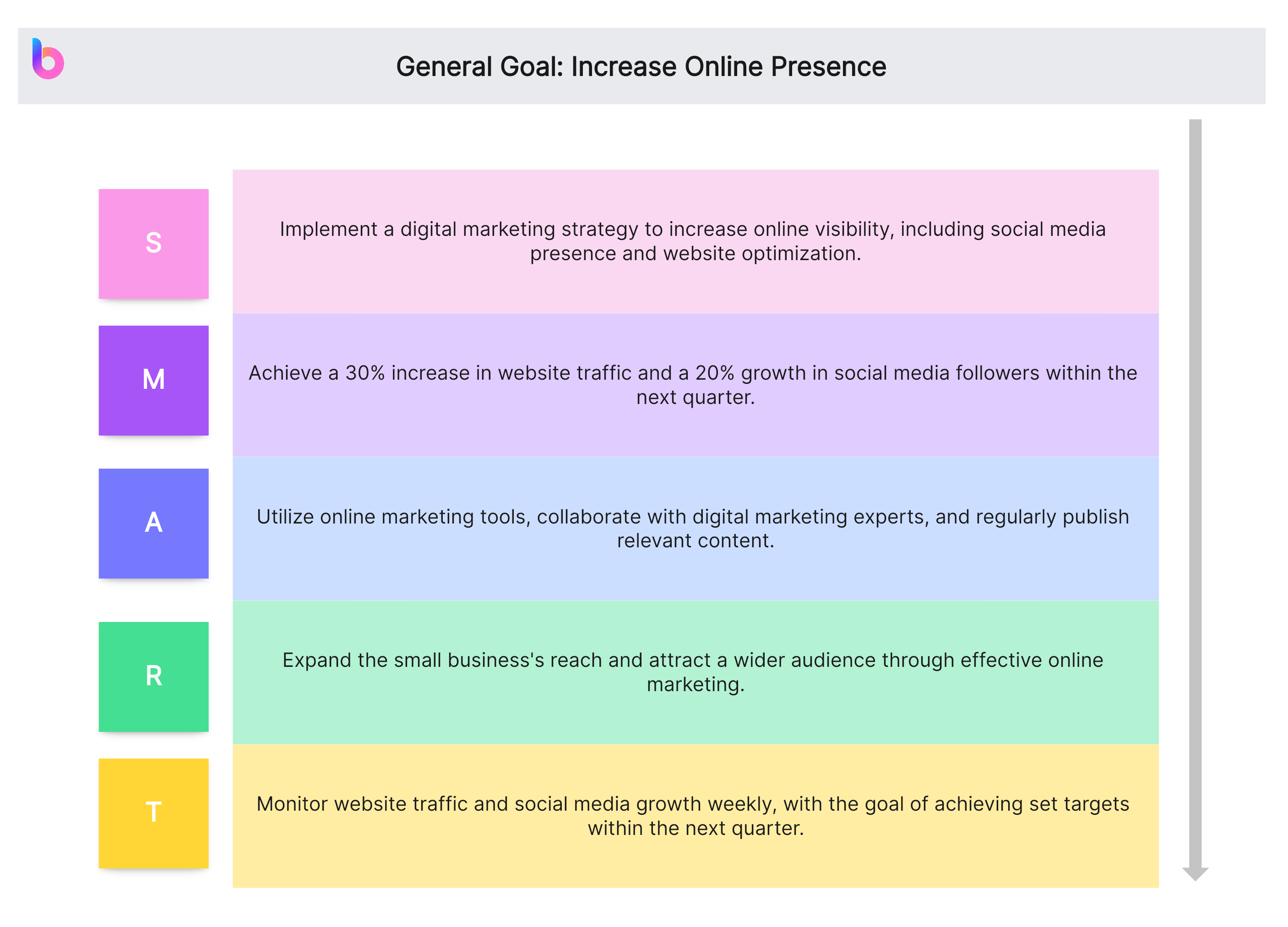
General Goal: Increase Online Presence
- Specific (S): Implement a digital marketing strategy to increase online visibility, including social media presence and website optimization.
- Measurable (M): Achieve a 30% increase in website traffic and a 20% growth in social media followers within the next quarter.
- Achievable (A): Utilize online marketing tools, collaborate with digital marketing experts, and regularly publish relevant content.
- Relevant (R): Expand the small business's reach and attract a wider audience through effective online marketing.
- Time-bound (T): Monitor website traffic and social media growth weekly, with the goal of achieving set targets within the next quarter.
SMART Goals Example for Small Business
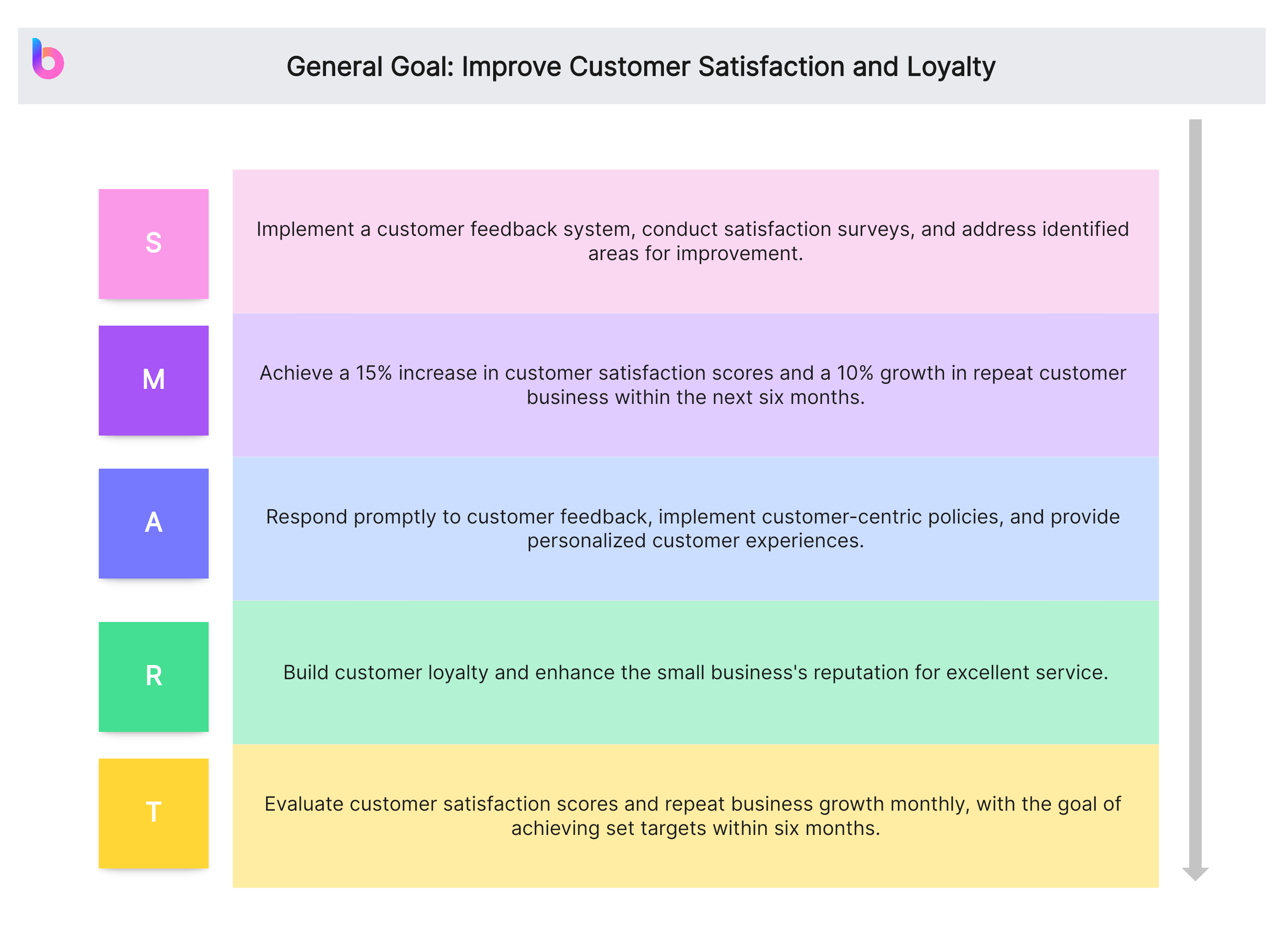
General Goal: Improve Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
- Specific (S): Implement a customer feedback system, conduct satisfaction surveys, and address identified areas for improvement.
- Measurable (M): Achieve a 15% increase in customer satisfaction scores and a 10% growth in repeat customer business within the next six months.
- Achievable (A): Respond promptly to customer feedback, implement customer-centric policies, and provide personalized customer experiences.
- Relevant (R): Build customer loyalty and enhance the small business's reputation for excellent service.
- Time-bound (T): Evaluate customer satisfaction scores and repeat business growth monthly, with the goal of achieving set targets within six months.
A Versatile SMART Goals Maker - Boardmix
In the business world, setting clear, achievable goals is an essential component of success. This process becomes even more effective and efficient with the right tools at our disposal. One such game-changer is Boardmix, a comprehensive and versatile SMART goals maker.
Boardmix is an innovative SMART goals maker designed to help users set, manage, and achieve their objectives. It combines cutting-edge technology with an intuitive user interface, creating a tool that makes goal setting not only easy but enjoyable.
This tool provides a seamless way to set SMART goals. It prompts users through each step with the help of pre-made SMART goals frameworks, ensuring each goal is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. With Boardmix, you can easily track progress towards your goals in real-time. This feature motivates users to keep pushing forward and gives them the satisfaction of seeing their progress.
Most importantly, Boardmix isn't just for individuals; it's also designed to foster teamwork. Teams can collaborate on shared goals, promoting effective communication and joint responsibility for success.
Extra Tip: How to Write Short-term and Long-term SMART Goals for Business Plan
Creating a business plan involves setting both short-term and long-term goals. By using the SMART framework, these goals can become the driving force that propels your business to success.
Writing Short-term SMART Goals
Short-term goals typically span a few weeks to a few months. They are the immediate targets that contribute to the long-term objectives of your business. Here's how to write short-term SMART goals:
- Specific: Define what you want to achieve in detail. For instance, instead of writing 'Increase sales,' you could write 'Increase online sales by 10% in the next quarter.'
- Measurable: Your goal should include a way to measure success. The 10% increase in online sales in the previous example is a measurable goal.
- Achievable: Ensure your goal is attainable with the resources at hand. If your online platform has limited reach, a 50% increase in online sales in the next quarter might not be achievable.
- Relevant: The goal should align with your business strategy. If your primary focus is on physical store sales, focusing on online sales might not be relevant.
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achieving the goal. In this case, it is 'in the next quarter.'
Writing Long-term SMART Goals
Long-term goals are broad, strategic objectives that take longer to achieve, usually spanning over several years. Here's how to write long-term SMART goals:
- Specific: Define your goal precisely. For instance, 'Expand business operations to two new cities within three years.'
- Measurable: Make sure there's a clear criterion to evaluate success. Here, success means operating in two new cities.
- Achievable: Your goal should stretch your capabilities but still be within reach. Do you have the resources to expand to two new cities within three years?
- Relevant: Ensure the goal fits into your larger business plan and overall mission. If expansion aligns with your plan to grow your business, then it's a relevant goal.
- Time-bound: Assign a timeframe for your goal. In this example, the timeframe is 'within three years.'
In both short-term and long-term planning, SMART goals offer a structure that guides progress and keeps businesses on track. By adopting this approach in your business plan, you can enhance focus, boost motivation, and ultimately drive your organization towards its strategic vision.