Divisional organizational structure allows companies to operate more flexibly and responsively, adapting to market demands and specific needs of different product lines or geographical regions, which plays a pivotal role in shaping a company's efficiency, communication, and overall success. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore divisional organizational structure, discuss its benefits, and provide insights into using templates for creating effective divisional structures in your business.
What is Divisional Organizational Structure?
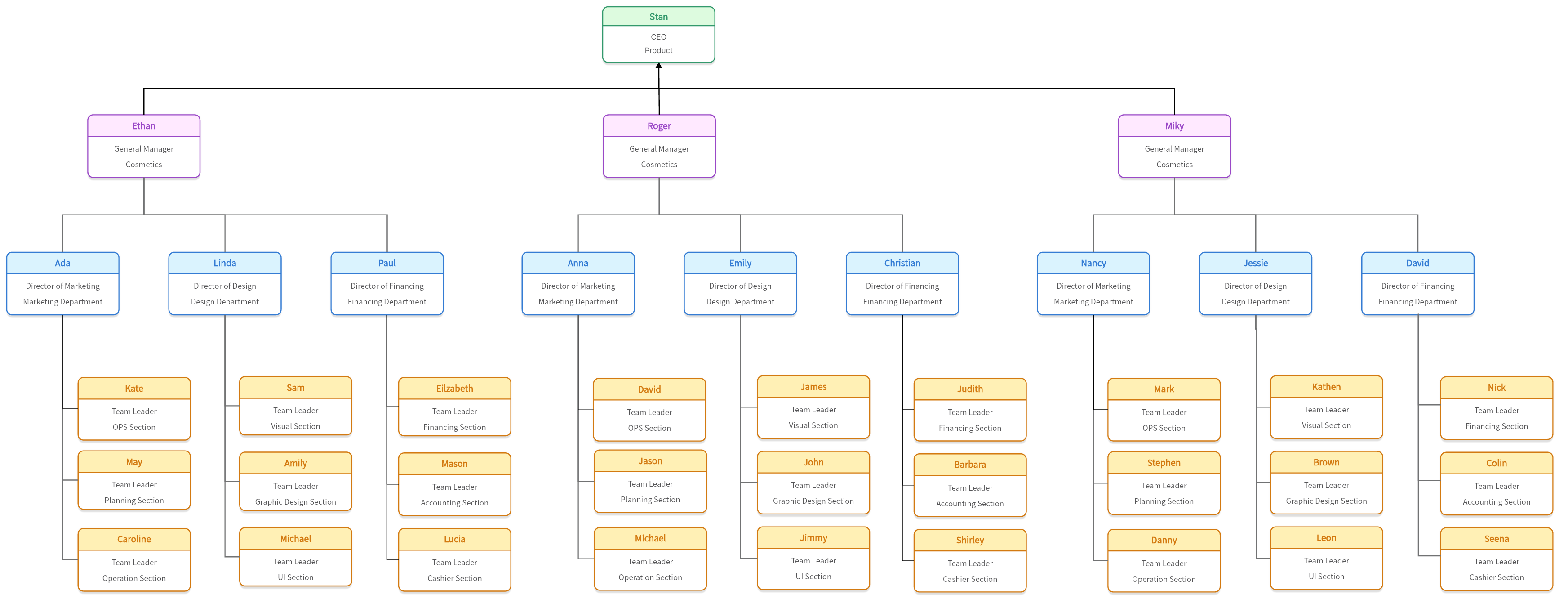
The divisional organizational structure is a type of organizational design that groups a company’s activities around products, services, customers, or geographic locations. Each division operates as a semi-autonomous entity, with its resources and objectives, yet remains aligned with the overarching goals of the organization. This structure is particularly advantageous for large corporations with diverse product lines or operations in multiple regions.
Key Characteristics of Divisional Organizational Structure:
Product-Based Divisions: Companies like Procter & Gamble or Johnson & Johnson have divisions based on product lines, such as beauty, healthcare, and household products. Each division focuses on specific products, and tailoring strategies to their market.
Geographic-Based Divisions: Multinational corporations like Coca-Cola use geographic divisions to manage operations in different regions, such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. This approach allows for strategies that are sensitive to regional market dynamics and cultural differences.
Customer-Based Divisions: Some companies, like banks or insurance firms, create divisions based on customer segments, such as retail customers, corporate clients, and small businesses. This ensures that the unique needs of each customer group are addressed effectively.
Market-Based Divisions: Businesses that cater to different markets, like technology firms, might segment their operations into divisions targeting various sectors, such as education, healthcare, and government.
Functional VS Divisional Organizational Structure?
Understanding the differences between functional and divisional organizational structures example is essential for businesses to choose the one that best suits their needs.
| 🔆🔆 |
Divisional Organizational Structure |
Functional Organizational Structure |
|
Responsibility |
Each division is responsible for all aspects of its specific focus area, including production, marketing, finance, and customer service. Divisional managers have comprehensive responsibility for the performance and outcomes of their divisions. | Employees within each department are responsible for tasks related to their specific functions. Department heads are accountable for the performance and output of their respective functions. |
| Autonomy of Decisions | Divisions operate with a high degree of autonomy, allowing managers to make decisions quickly and independently based on the needs and circumstances of their specific divisions. This decentralized decision-making enhances responsiveness and agility in addressing market demands and operational challenges. | Decision-making tends to be centralized within each department, with significant decisions made by department heads or higher-level management. This can lead to slower decision-making processes as approvals and coordination are required across different functions. |
| Cost | Divisional structures can be more expensive to maintain due to the duplication of resources and functions across divisions. Each division may have its own marketing team, finance department, and operational units, leading to increased overhead costs. | Generally, functional structures can be more cost-efficient due to the centralized nature of operations and the specialization of resources. |
| Appropriate Scenarios |
-Small to medium-sized companies with a limited range of products or services. -Organizations seeking to capitalize on functional expertise and specialization. -Environments where operational efficiency and consistency are critical, and the need for cross-functional coordination is relatively low. |
-Large corporations with diverse product lines, customer segments, or geographic operations. -Companies operating in dynamic markets where quick decision-making and flexibility are essential. -Businesses that require tailored strategies and operations to meet the unique needs of different divisions. |
Why does Company Use Divisional Organizational Structure?
Companies adopt a divisional organizational structure template for various strategic reasons, each contributing to enhanced business performance and market adaptability.
1. Enhanced Responsiveness and Flexibility
Divisional organizational structure templates operate as semi-autonomous entities, allowing them to respond swiftly to market changes, customer demands, and competitive pressures. For example, a company with product-based divisions can quickly adjust its marketing strategies for a specific product line without affecting the entire organization.
2. Improved Focus and Accountability
Each division has its own goals and resources, promoting a sense of ownership and accountability among division managers. This focus can drive better performance and innovation within each division. For instance, geographic divisions enable managers to tailor strategies to local markets, ensuring that regional preferences and trends are effectively addressed.
3. Tailored Strategies and Operations
Divisional structures allow for strategies that are tailored to the unique needs of different products, services, or regions. This targeted approach can enhance customer satisfaction and market penetration. A customer-based division in a financial institution can develop specialized services and marketing campaigns for retail customers, distinct from those designed for corporate clients.
4. Scalability
As companies grow, a divisional structure can accommodate expansion more easily. New divisions can be added without disrupting existing operations. A tech company expanding into new international markets can establish geographic divisions for each region, ensuring that local operations are managed effectively.
Divisional Organizational Structure Templates for Business
When creating a divisional organizational structure template, using well-designed templates can streamline the process and ensure clarity and efficiency. Creating an effective divisional organizational structure requires careful planning and design. Boardmix offers a variety of templates that can help businesses design, implement, and manage their divisional structures effectively.
1. Corporate Organizational Structure Template
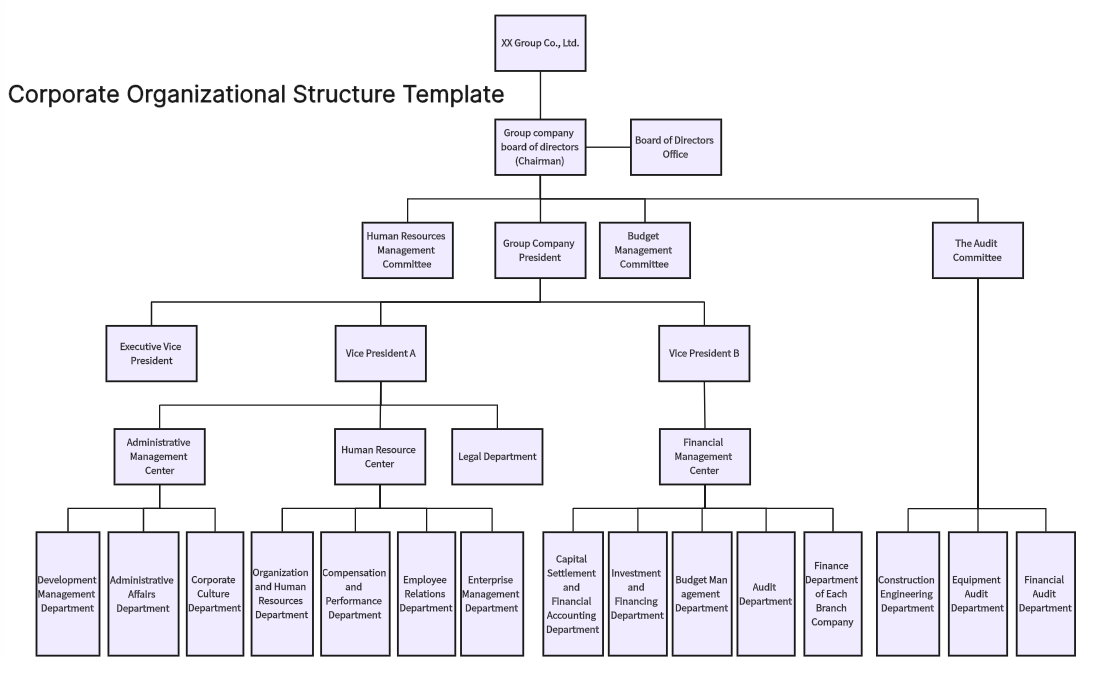
Division Headers: Sections for each division within the corporation, such as Product Divisions, Geographic Divisions, or Customer-Based Divisions.
Sub-Divisions: Further breakdown of divisions into sub-units or departments, such as marketing, finance, operations, and HR within each division.
Reporting Lines: Clear lines of authority and reporting relationships, showing who reports to whom within each division.
Roles and Responsibilities: Detailed descriptions of the roles and responsibilities of key positions within each division.
Applications:
Large Corporations: Ideal for large, diversified corporations with multiple product lines or geographical operations.
Strategic Planning: Useful for strategic planning and resource allocation, helping management visualize and optimize the structure.
Communication: Enhances internal communication and helps in onboarding new employees by providing a clear organizational roadmap.
2. Finance Organizational Structure Template
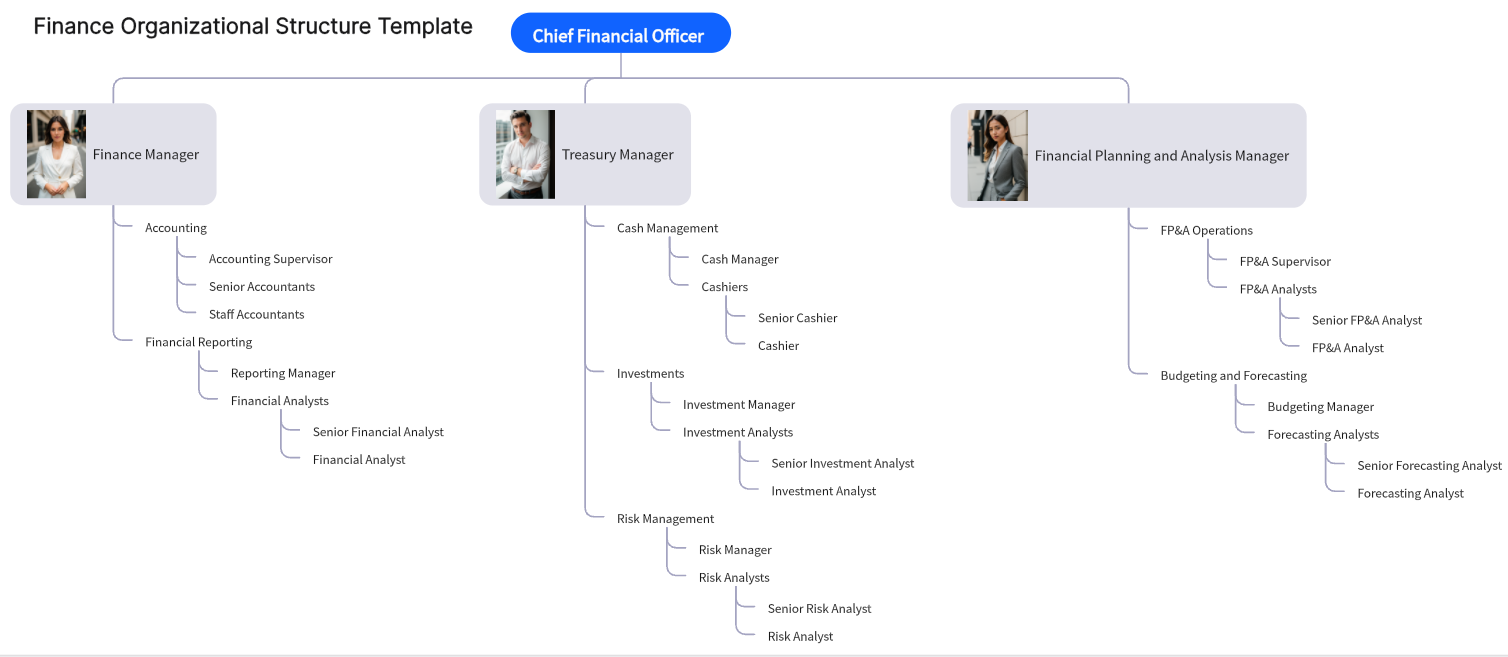
Division of Finance: Segments the finance department into divisions such as Accounting, Treasury, Risk Management, and Financial Planning & Analysis.
Roles: Details the roles within each segment, such as CFO, Controllers, Treasurers, Risk Analysts, and Financial Planners.
Reporting Structure: Shows the hierarchical reporting lines, indicating who reports to the CFO and other senior finance leaders.
Responsibilities: Outlines the responsibilities of each role, ensuring clarity on who handles specific financial tasks and decision-making.
Applications:
Finance Departments: Suitable for large companies with complex financial operations requiring detailed oversight and specialization.
Risk Management: Useful for identifying and managing financial risks through clear role definitions and responsibilities.
Budgeting and Planning: Facilitates effective financial planning and budgeting by delineating responsibilities for financial analysis and forecasting.
3. Business Ownership Organizational Chart
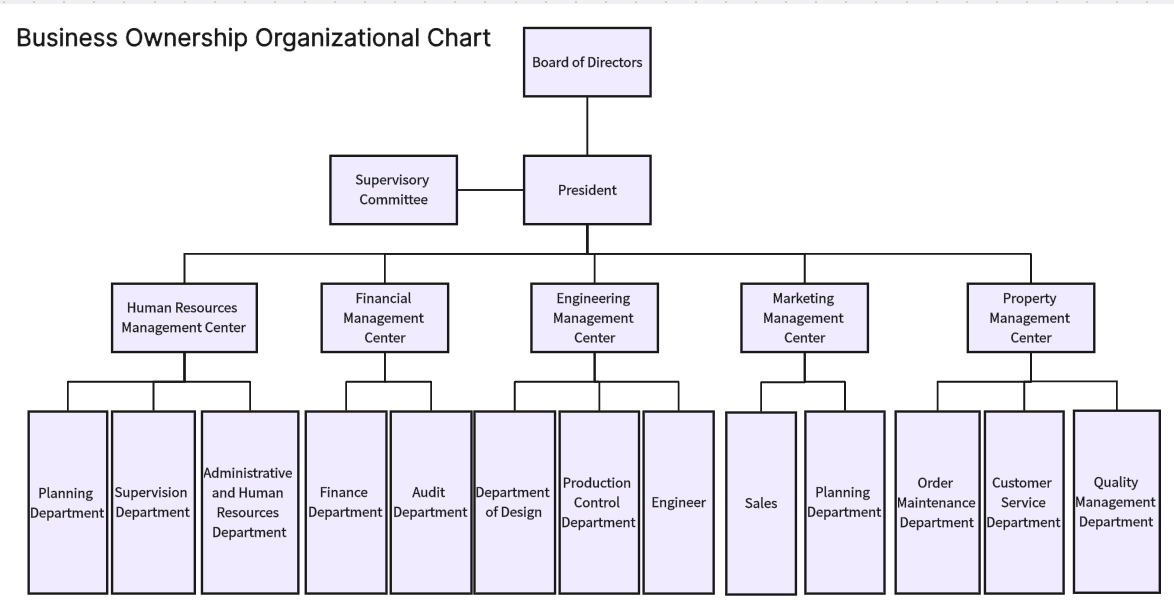
Ownership Levels: Visual representation of ownership stakes and levels within the business, including major shareholders and minority stakeholders.
Parent and Subsidiaries: Details of parent companies and their subsidiaries, including the percentage of ownership and control.
Board of Directors: Information on the board of directors, including roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines to shareholders.
Management Teams: Key management teams for each subsidiary or division, showing how ownership translates into operational control.
Applications:
Corporate Governance: Useful for corporate governance, ensuring clear oversight and control mechanisms.
Mergers and Acquisitions: Essential during mergers and acquisitions to visualize and plan the integration of ownership structures.
Investor Relations: Helps in communicating ownership and governance structures to investors and stakeholders.
4. Gaming Company Organizational Chart
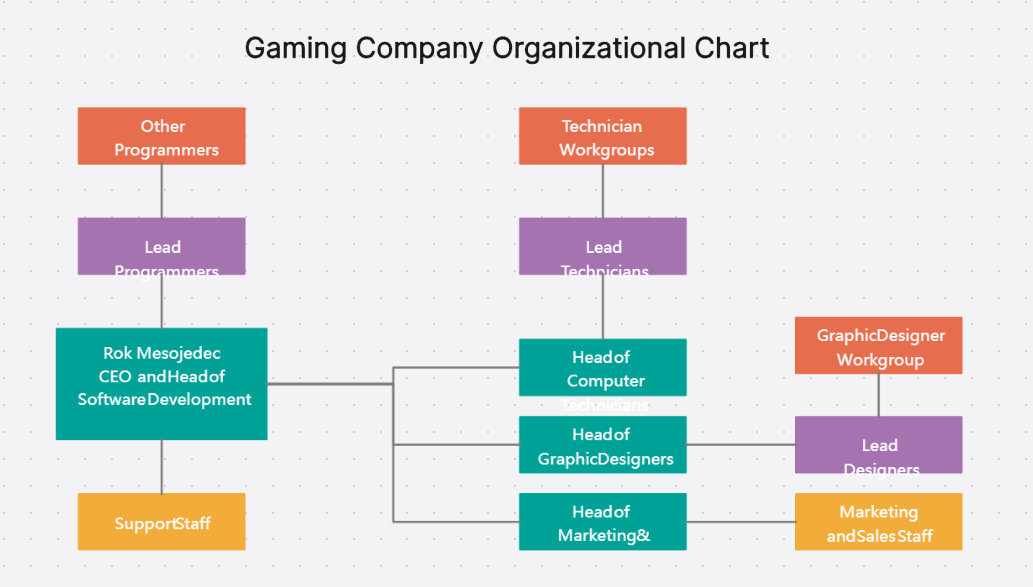
Divisions: Segments the gaming company into divisions such as Game Development, Marketing, Sales, and Customer Support.
Departments: Break down each division into specific departments like Design, Programming, Quality Assurance, and User Experience within Game Development.
Roles and Teams: Lists roles and teams within each department, such as Lead Designers, Programmers, QA Testers, and UX Specialists.
Project Teams: Shows project-specific teams, including cross-functional teams working on specific game titles or features.
Applications:
Game Development Studios: Ideal for game development studios, both large and small, to manage complex development projects.
Product Launches: Useful for planning and executing game launches, ensuring coordination between development, marketing, and sales.
Customer Support: Enhances customer support by clearly defining support roles and responsibilities, improving response times and customer satisfaction.
How to Create a Divisional Organizational Structure Using Boardmix?
Creating a divisional organizational structure in Boardmix is straightforward and efficient. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Define Your Divisions
Identify the basis for your divisions—whether by product, market, geography, or customer type. Clearly outline the scope and objectives of each division.
Step 2: Select a Template
Choose the appropriate template from Boardmix's library. For example, if your divisions are based on products, select the Product-Based Divisional Structure Template.
Step 3: Customize the Template
Adapt the template to fit your company's specific needs. Enter the names of your divisions, assign managers, and define the responsibilities and resources for each division.
Step 4: Add Details and Hierarchies
Include additional details such as sub-divisions, departments, and key roles within each division. Establish clear hierarchies and reporting lines to ensure accountability and communication.
Step 5: Review and Refine
Review the structure with your management team. Make any necessary adjustments to ensure it align with your company's strategic goals and operational needs.
Step 6: Implement and Monitor
Once finalized, implement the divisional structure within your organization. Use Boardmix to regularly monitor and update the structure as your company evolves and grows.
The divisional organizational structure offers businesses a flexible and responsive way to manage diverse product lines, customer segments, and geographic markets. By understanding the benefits and challenges of this structure, companies can make informed decisions about its implementation. Utilizing tools like Boardmix and its comprehensive templates can streamline the process, ensuring that your divisional structure is well-designed and effectively managed. With the right approach, a divisional organizational structure can drive business growth, enhance customer satisfaction, and improve overall organizational performance.









