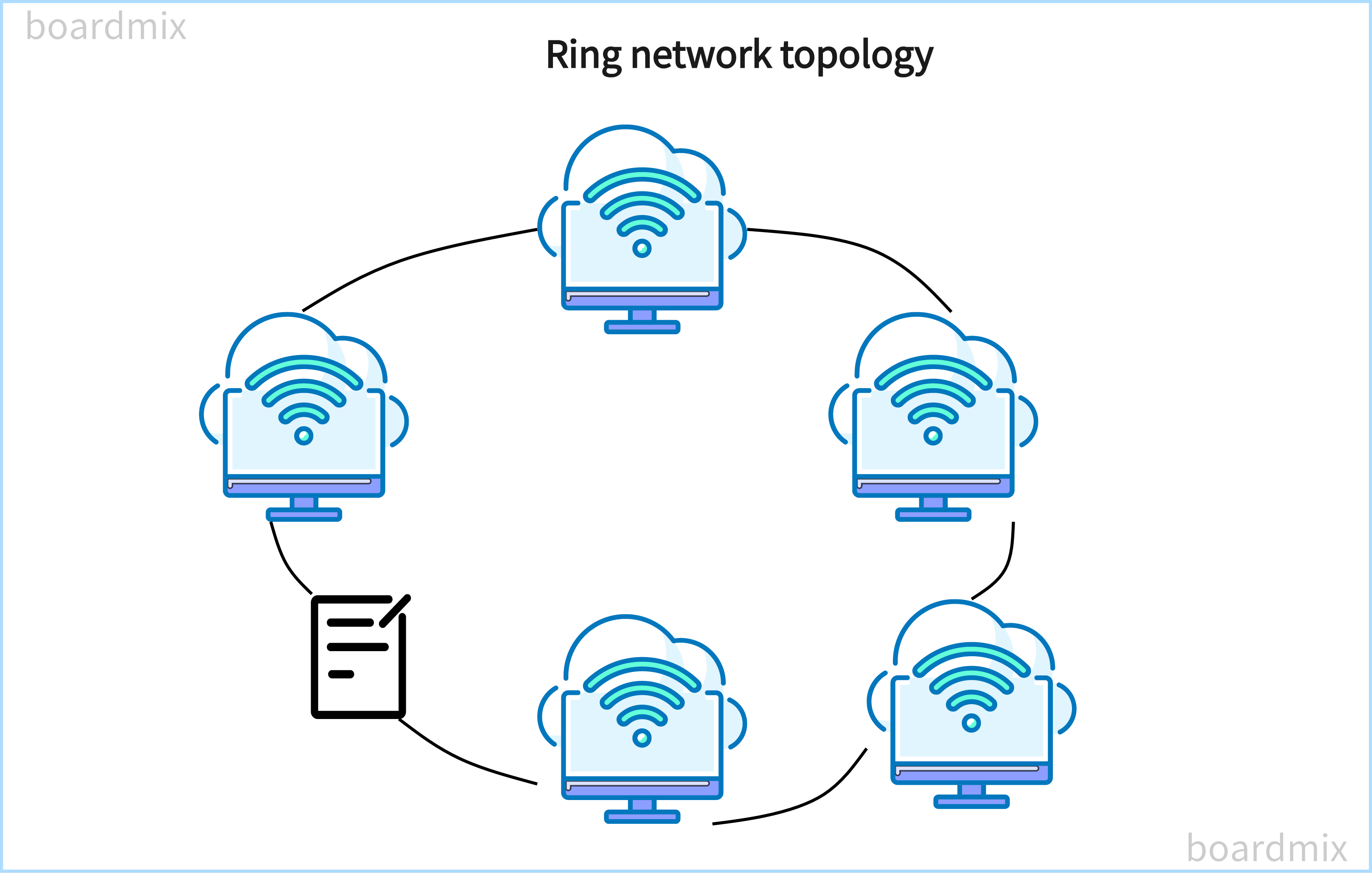
Visualizing a Ring Network Topology Diagram can be likened to drawing a perfect circle. It's about illustrating how each node connects in a circular pattern, ensuring efficient data transmission and network performance. Creating a clear and accurate visual representation that can guide network setup, management, and troubleshooting. Let's explore the art of visualizing connectivity through a Ring Network Topology Diagram.
What is Ring Network Topology
Ring network topology is a type of network configuration in which devices are connected in a circular loop. In this topology, each device is connected to its adjacent devices forming a closed loop. The data flows in only one direction around the ring, passing through each device until it reaches its destination. The ring network topology is suitable for small to medium-sized networks that require equal access and efficient data transfer. It is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and can be implemented using both wired and wireless connections.
Applications and Examples of Ring Network Topology
Exploring Ring Network Topology applications can be compared to studying the intricate design of a well-crafted piece of jewelry. It's about understanding how each node, like a gemstone, is connected in a circular pattern to ensure smooth and efficient data transmission. But this isn't just about appreciating the structure. Here are some applications and examples of ring network topology.
- Local Area Networks (LANs): Ring network topology is commonly used in LANs where devices are connected in a circular loop. This topology allows for efficient data transmission and provides fault tolerance as data can flow in both directions.
- Token Ring Networks: Token ring networks use a ring topology where devices pass a token to gain access to the network. This ensures fair access to the network and prevents data collisions. Token ring networks were widely used in the past but have been largely replaced by Ethernet.
- SONET/SDH Networks: Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) networks utilize ring topology for high-speed data transmission over optical fibers. These networks are commonly used for long-distance telecommunications and can provide high bandwidth and reliability.
- Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs): Some MANs use ring topology to connect multiple LANs or buildings within a city or metropolitan area. This allows for efficient data transfer between different locations and provides redundancy in case of link failures.
- FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface) Networks: FDDI networks use a dual-ring topology where data can be transmitted in both directions for increased fault tolerance. FDDI was commonly used for high-speed data transmission in backbone networks.
- Industrial Control Systems: In industrial environments, ring topology is often used for connecting various control devices and sensors. This allows for real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes and ensures reliable data transmission.
- Telecommunications Networks: Some telecommunications networks, such as synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) networks, use ring topology for high-speed data transmission between central offices and cell towers. This ensures reliable connectivity and efficient data transfer.
- Fiber Optic Networks: Ring topology is commonly used in fiber optic networks due to its ability to provide redundancy and fault tolerance. Multiple fibers can be used to create a ring, allowing for alternate paths in case of fiber breaks.
These are just a few examples of the applications and use cases of ring network topology. Each application has its own specific requirements, and the choice of topology depends on factors such as data transfer speeds, fault tolerance, and scalability.
Boardmix: Ring Network Topology Diagram Online Maker
Boardmix is a popular online tool that allows users to create ring network topology diagrams easily. With its intuitive interface and drag-and-drop functionality, users can quickly design and visualize their ring network topology.
Key Features of Boardmix
- Pre-designed Shapes: Boardmix provides a wide range of pre-designed shapes that represent various network devices and components. Users can simply drag and drop these shapes onto the canvas to create their network topology.
- Customization Options: Users can customize the appearance of their network diagram by changing colors, and line styles, and adding labels to the shapes. This helps in organizing and differentiating different network elements.
- Connection Tools: Boardmix offers tools to create connections between network devices, allowing users to define the link type, direction, and other parameters. These connections accurately represent the physical connections in the ring network.
- Collaboration and Sharing: Boardmix enables users to collaborate with team members by inviting them to edit or view the network diagram. Users can also share the diagram with others by generating a shareable link or exporting it as an image or PDF file.
- Real-Time Updates: Changes made by multiple users in real-time are automatically synced, ensuring everyone is working on the latest version of the diagram. This improves collaboration and eliminates the need for manual updates.
- Integration: Boardmix integrates with popular cloud storage services like Google Drive and Dropbox, making it easy to save and access diagrams from anywhere.
- Export and Printing: Users can export their ring network topology diagrams in various formats such as PNG, JPEG, SVG, or PDF. This allows for easy sharing or printing of the diagrams for presentations or documentation.
Boardmix is a user-friendly and efficient tool for creating ring network topology diagrams online. Whether you are a network administrator, IT professional, or student, Boardmix can help you design and visualize your network configurations with ease.
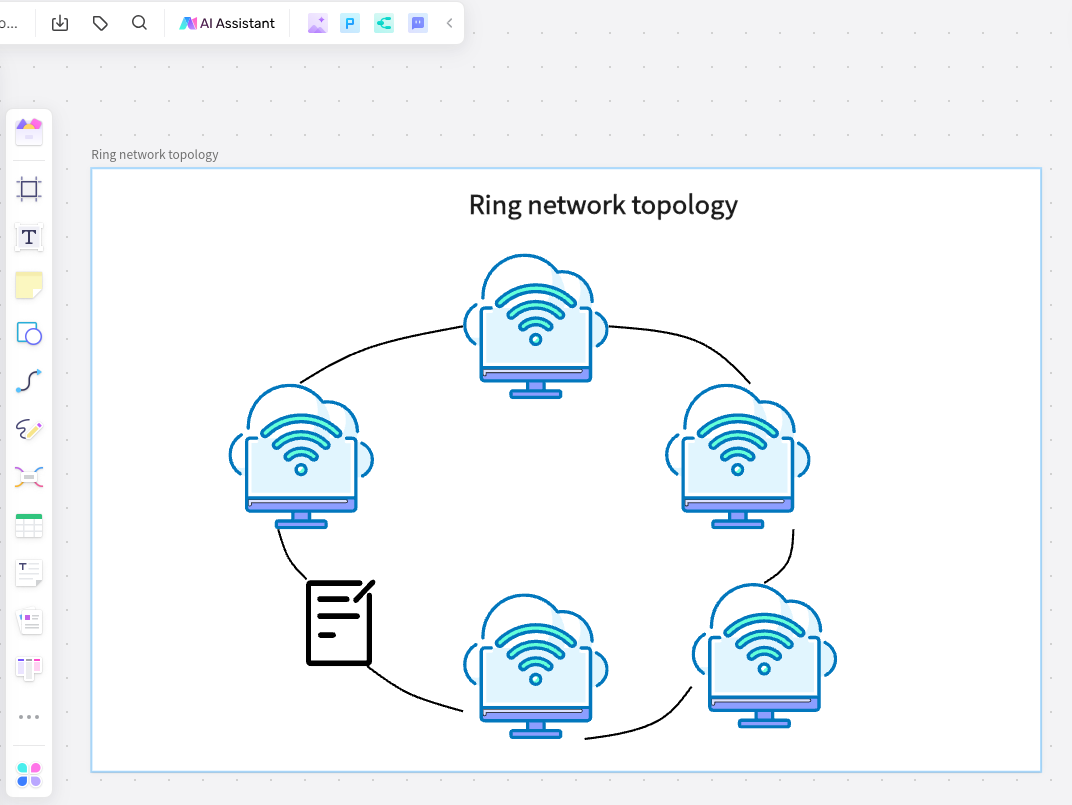
How to use Boardmix
Making a Ring Network Topology Diagram in Boardmix is simple. Here's a step-by-step guide.
- Login to Boardmix: Go to the Boardmix website and sign in to your account. If you don't have an account, you can create one for free.
- Create a New Diagram: Once you're logged in, click on the "New Board" button to start creating your ring network topology diagram. Or you can go to the Template library and search for topology templates to save time.
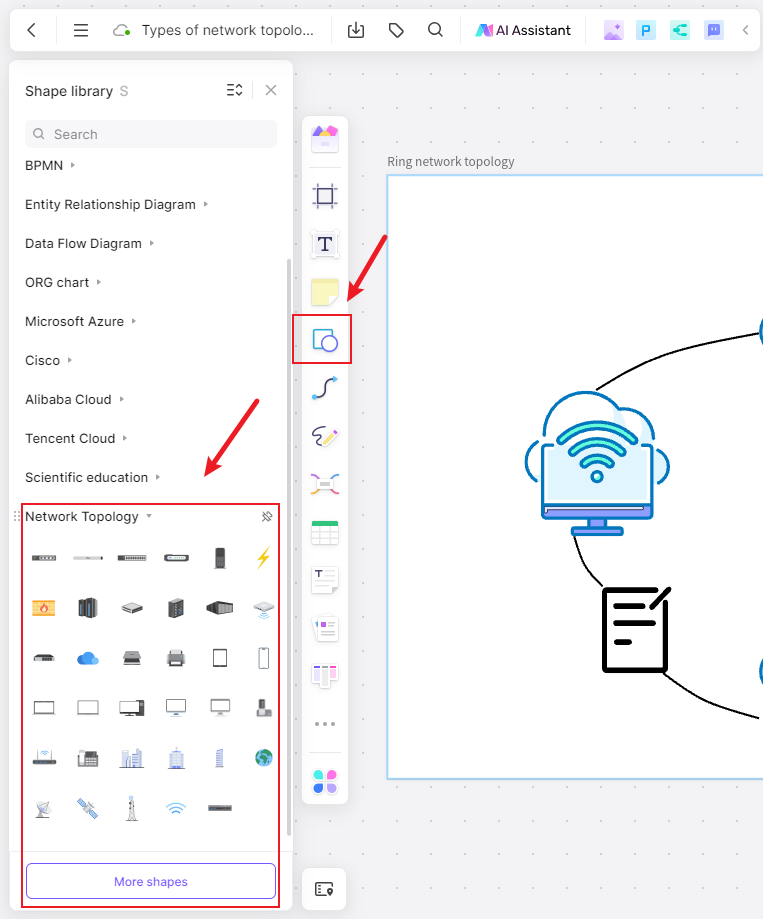
- Add Network Devices: Use the pre-designed shapes provided by Boardmix to add network devices to your diagram. You can find shapes for routers, switches, servers, computers, and other network components on the left navigation bar. Simply drag and drop the shapes onto the canvas.
- Connect the Devices: Use the connection tools in Boardmix to create connections between the network devices. Click on the connection tool and then click on the source device and the destination device to establish a connection. You can also define the link type, direction, and other parameters for each connection.
- Customize the Diagram: Boardmix allows you to customize the appearance of your diagram. You can change the colors and line styles of the shapes, add labels to the devices, and adjust the layout of the diagram.
- Collaborate and Share: If you're working on the diagram with a team, you can invite them to collaborate by sharing the diagram with them. Boardmix allows multiple users to edit the diagram in real-time, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Save and Export: Once you're done creating your ring network topology diagram, save your work. You can save it directly on Boardmix or export it as an image or PDF file. Boardmix supports various export formats like PNG, JPEG, SVG, and PDF.
That's it! You've successfully created a ring network topology diagram in Boardmix. This diagram can be used for documentation, troubleshooting, or communication purposes in your network management activities. If you have any further questions or need assistance, you can even ask the AI assistant of Boardmix.
Best Practices for Ring Network Topology
Adhering to the best practices of Ring Network Topology can optimize the performance and reliability of your network, facilitating smooth and efficient data transmission. Here are some best practices for implementing and managing a ring network topology.
- Redundancy: To ensure fault tolerance and minimize the impact of a single point of failure, it is important to have redundant links or multiple paths in the ring network. This allows for alternate paths in case of link failures, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity.
- Network Monitoring: Implement a robust network monitoring system to monitor the performance and health of the ring network constantly. This helps identify any issues or anomalies in real-time and allows for proactive troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Bandwidth Management: Depending on the specific requirements of the network, it is important to properly manage and allocate bandwidth to ensure efficient data transmission. This can be achieved through Quality of Service (QoS) and bandwidth prioritization.
- Scalability: Consider the future growth and expansion of the network when designing the ring topology. Ensure that the network can accommodate additional devices and increase traffic without compromising performance or reliability.
- Documentation and Labeling: Maintain accurate documentation of the network topology, including the location and configuration of devices, cables, and connections. Proper labeling of cables and devices makes troubleshooting and maintenance easier.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance activities such as cleaning connectors, checking cable integrity, and updating firmware/software to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the network.
- Security Measures: Implement appropriate security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and access control mechanisms to protect the ring network from unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Training and Education: Train and educate network administrators and users to ensure they are familiar with the ring network topology, its best practices, and proper handling of network equipment.
By following these best practices, you can effectively implement and manage a ring network topology that meets your organization's requirements for performance, reliability, and scalability.
Advantages and Limitations of Ring Network Topology
The ring network topology is a computer network configuration in which each device is connected to two other devices, forming a closed loop or ring. This topology can provide efficient and reliable network performance in some situations, but it also has some potential issues and limitations. Here are the advantages and limitations of the ring network topology.
Advantages of Ring Network Topology
- Equal Access: In a ring network topology, each device has equal access to the network. This means that all devices have the same transmission rights, resulting in fair and efficient data transfer.
- Efficient Data Transfer: Data flows in only one direction around the ring, passing through each device until it reaches its destination. This sequential transmission can lead to efficient data transfer and reduced network congestion.
- Simple Network Structure: The ring network topology is relatively simple in structure, making it easy to implement and maintain. This simplicity can save time and resources during network setup and troubleshooting.
Limitations of Ring Network Topology
- Single Point of Failure: One major limitation of the ring network topology is that if one device fails or is disconnected, the entire network can be affected. Since data transmission relies on each device in the loop to pass the data along, the failure of a single device can disrupt the entire network.
- Limited Scalability: Adding or removing devices from a ring network can be challenging and can disrupt the network. The ring structure limits the scalability of the network, making it less suitable for large networks that may require frequent changes or expansions.
- Difficult Troubleshooting: Identifying and troubleshooting issues in a ring network can be more complex compared to other topologies. If there is a problem in the network, finding the exact location of the issue can be difficult, as data flows in a closed loop.
It's important to consider these advantages and limitations when deciding whether to implement a ring network topology. Assessing your specific networking needs and considering factors such as reliability, scalability, and ease of troubleshooting can help you make an informed decision.
To Recap
In conclusion, visualizing connectivity through a Ring Network Topology Diagram is pivotal in comprehending the intricacies of network design. The advantages of Ring Network Topology, such as redundancy and reliability, are balanced by considerations of limitations like potential disruptions. Acknowledging these aspects is key to making informed decisions when designing network infrastructures. As we navigate the landscape of Ring Network Topology Diagrams, it's apparent that the visual representation of connectivity is essential. Boardmix, as an online collaborative teamwork tool, stands out as a reliable platform for creating Ring Network Topology Diagrams. Its user-friendly interface and collaborative features make it an accessible choice for professionals seeking to visualize and optimize ring networks. Boardmix is your partner in bringing visualizations to life—where connectivity meets collaboration seamlessly.