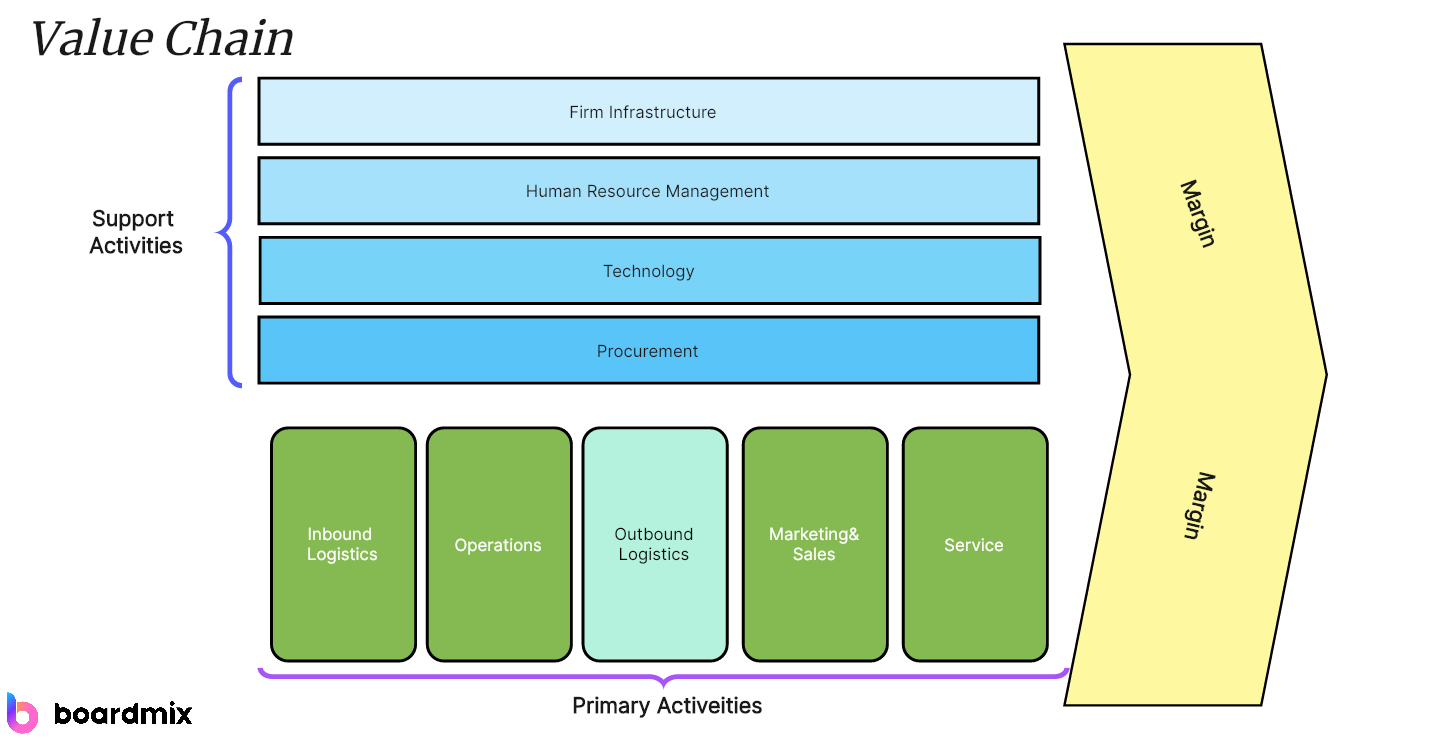
When you mention a global leader in digital technology innovation, Samsung comes to the forefront of the conversation. Founded in 1938 as a small trading company, the company has rapidly evolved and revolutionized various industries from fashion to semiconductors, plant construction to skyscraper construction, petrochemicals to life sciences. The journey towards this zenith of success was orchestrated with precision, thanks to its highly integrated Value Chain. This article will delve into Samsung's primary and secondary activities that drive its value chain.
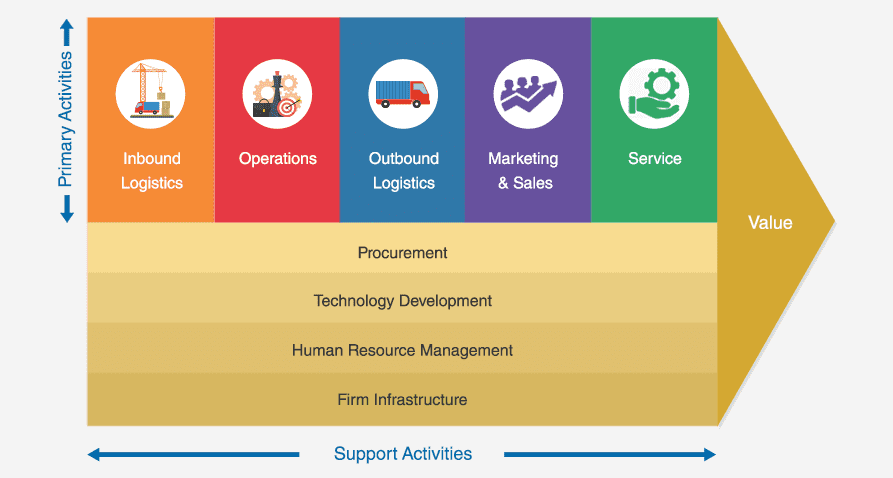
Primary Activities of Samsung's Value Chain
Samsung's Value Chain Primary Activities can be categorized into five key components:
Inbound Logistics
In the context of Samsung's success, a key cornerstone is its efficient and reliable Inbound Logistics. This process encompasses everything from the acquisition of raw materials to handling internal logistics and managing relationships with suppliers.
Samsung strategically selects suppliers who adhere to stringent quality standards and are capable of delivering the required materials on time. These suppliers play an integral role in the production process, providing the essential components needed to manufacture Samsung's wide array of electronics products. The company ensures a comprehensive verification process before engaging with suppliers to meet their high-quality standards.
Samsung also maintains a technologically advanced logistics system, enabling them to monitor and manage inventory levels effectively. Leveraging real-time tracking, the company ensures that the materials are not only transported safely but also reach the right place at the right time, thus preventing production lags.
Furthermore, Samsung has developed a systematic approach to handle internal logistics, which includes storage, transportation, and distribution of materials within the organization. They have strategically located warehouses that optimize space usage and reduce costs, thereby enhancing efficiency.
Through its proactive approach to managing inbound logistics, Samsung maintains a continuous flow of high-quality raw materials, allowing it to keep up with demand while maintaining stringent quality control. This strong foundational pillar significantly contributes to their ability to produce an impressive portfolio of innovative and high-quality products.
Operations
The Operations segment of Samsung's Value Chain sets the stage for the company's unprecedented manufacturing efficiency. Rooted in state-of-the-art technology, relentless innovation, and rigorous quality standards, it serves as the heartbeat of Samsung's production line.
Samsung's operations echo their ethos of 'Quality First'. Backed by its annual R&D expenditure of $17.7 billion in 2020 (as per Statista), the company continually innovates and upgrades its manufacturing processes. Its semiconductor plants, for instance, employ leading-edge Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography technology for chip fabrication, placing them at the forefront of semiconductor production.
Another pillar supporting Samsung's operational prowess is its globally dispersed manufacturing facilities. With around 61 facilities in 34 countries (as per Samsung), these strategically located factories help optimize production and supply chain efficiency, catering to market demands more responsively.
Sustainability also threads through Samsung's operations. According to its 2020 Sustainability Report, the company aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from its manufacturing sites by 70% by 2030 compared to 2018 levels. Their commitment extends to energy-efficient product design, with more than 90% of their products meeting the Energy Star certification standard in 2019.
Samsung's efficient operations also lie in lean management practices that streamline workflow, eliminate waste, and boost productivity. Their factories adopt the Six Sigma methodology, a set of techniques aimed at process improvement, contributing to an error rate as low as 1.6 per million opportunities.
Outbound Logistics
Outbound Logistics, the mechanism that ensures Samsung products reach the right place at the right time, is an essential part of Samsung's Value Chain. The process encompasses all aspects of getting finished products from the warehouse shelves to consumer hands.
At the heart of Samsung's outbound logistics is a sprawling, globally-integrated distribution network that delivers to over 200 countries. To support this massive operation, Samsung owns over 2,000 overseas corporations and approximately 230 logistics bases (as per their website).
The use of technology further strengthens Samsung's distribution strategy. The company uses advanced logistics systems that enable real-time tracking and management of product deliveries, reducing delays, and ensuring accurate shipments.
The magnitude of Samsung's outbound logistics is exemplified by their annual shipment volumes. For example, in 2019 alone, Samsung shipped over 295 million smartphones globally (according to IDC), highlighting their remarkable logistical capabilities.
Crucial to their successful outbound logistics is a customer-centric approach. Whether it's in the choice of trusted carriers for transportation or setting up logistics bases near high-demand areas, the goal is clear: get products into customer's hands as efficiently as possible.
Besides, Samsung has also tapped into e-commerce channels to improve its product reach, resulting in a year-on-year growth of approximately 50% in online sales in Q1 2020 (Samsung Newsroom).
Marketing & Sales
The Marketing & Sales aspect of Samsung's Value Chain is an integral engine that fuels its sustained market dominance and customer retention.
Samsung's marketing strategy is a perfect blend of extraordinary storytelling, innovative campaigns, and significant investments. In 2019, the brand spent a staggering $9.8 billion on advertising and promotions according to Statista, underscoring their commitment to maintaining a strong market presence.
Their "Do What You Can't" campaign is a prime example of how Samsung connects with its audience on an emotional level while subtly highlighting its cutting-edge product features. The campaign successfully increased their brand recall and boosted sales.
Samsung’s sales strategy revolves around a wide distribution network that spans both online and offline channels. It operates approximately 1,400 retail stores worldwide, allowing customers to have tangible experiences with their products. In contrast, their e-commerce platform caters to the burgeoning digital consumer base, contributing significantly to their global smartphone market share of 21.8% in 2020 (according to IDC).
Furthermore, Samsung embraces data-driven sales strategies. Utilizing advanced analytics and AI, the company identifies potential market trends and consumer preferences, which enable targeted sales and marketing initiatives. Their use of data contributed to a 30% increase in online sales in Q3 2020 compared to Q2 (Samsung Newsroom).
Services
As an integral part of Samsung's Value Chain, the Services provided by the company play a pivotal role in customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Samsung firmly believes that quality service goes beyond merely selling a product; it's about providing a holistic customer experience. To this end, they offer a multitude of services that range from device setup, troubleshooting, and product repair to recycling.
Understanding the need for instant solutions in our fast-paced world, Samsung offers real-time customer support through its 'Samsung Care+' service. This comprehensive support platform provides 24/7 assistance, addressing customer queries and issues effectively, thereby reducing downtime and enhancing user experience.
Additionally, Samsung's commitment to sustainable solutions extends to its services as well. Their Take Back & Recycling (TBR) program encourages customers to recycle electronic products responsibly, reflecting their stance on environmental consciousness.
The company also takes product service to the next level with its unique value-added services like 'Samsung Pay,' an innovative mobile payment service, and 'Samsung Health,' an app that assists customers in maintaining their fitness and wellness.
Samsung's in-store experiences further elevate their services. Their 'Samsung Experience Stores offer personalized product demonstrations and workshops for customers to better understand their devices and features.
Moreover, their 'Samsung Members App' provides exclusive content, community connections, expert support, and perks to the Samsung user community, thus creating a dynamic user engagement ecosystem.
Support Activities of Samsung's Value Chain
Support activities within Samsung's Value Chain play a critical role in fortifying its primary processes and achieving operational competency. This segment is constituted by four key areas - Firm Infrastructure, Human Resource Management, Technological Development, and Procurement.
Firm Infrastructure
Samsung’s organizational structure, governance, quality control, legal framework, and financial operations comprise its firm infrastructure. This solid infrastructure forms the backbone of the company's global operations. With a well-defined hierarchical structure, the company ensures effective communication and decision-making across multiple verticals. Additionally, Samsung’s robust financial health (with revenue of over $200 billion in 2020 as per Statista) substantiates its robust firm infrastructure.
Human Resource Management
With more than 260,000 employees globally, as reported by Samsung, effective HRM is pivotal for the company. Samsung’s talent acquisition and retention strategies focus on fostering innovation, diversity, and professional growth. Their various training and development programs such as the 'Global Competency Development Program' nurture employees' skills and prepare them for future roles. They also emphasize employee welfare with initiatives like 'Work-Life Balance Day'.
Technological Development
Samsung invests heavily in R&D to sustain technological advancement, as exemplified by its $17.7 billion investment in 2020 (Statista). Their extensive patent portfolio - more than 160,000 patents globally in 2019 - underscores their technological prowess. Samsung also incorporates emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and 5G across products and processes, reinforcing its technological dominance.
Procurement
Samsung's procurement policy is rooted in fairness, transparency, and sustainability. They collaborate with a network of global suppliers who meet their stringent quality and ethical standards. Moreover, through its 'Partner Collaboration Portal', Samsung maintains open communication with suppliers, ensuring process efficiency and strong relationships.
Samsung Value Chain Analysis Example
To further illustrate how all these pieces come together, here is a simplified Samsung value chain analysis diagram. This diagram provides a quick reference guide for business professionals looking to understand Samsung's value chain's intricate workings.
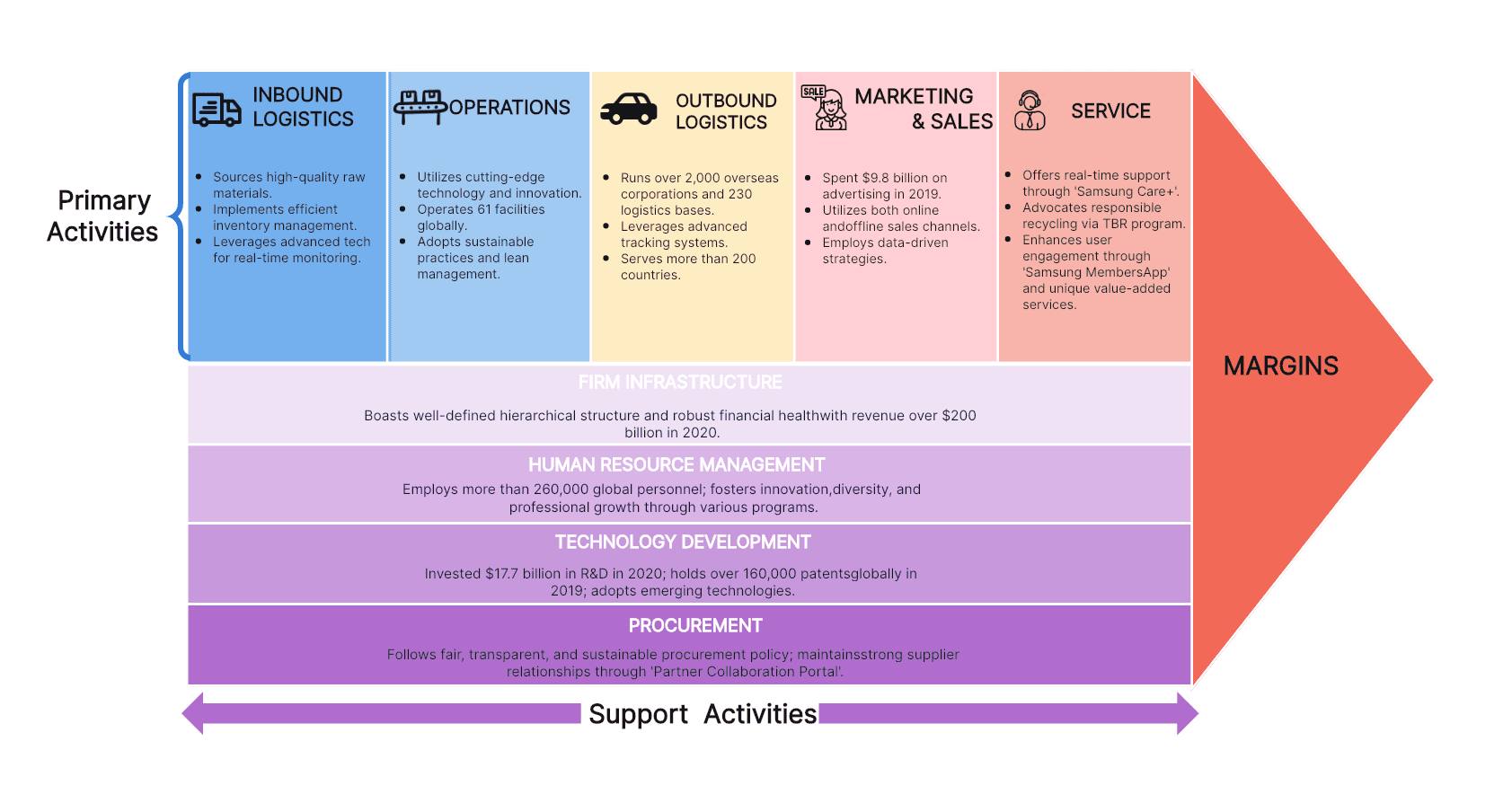
Key Takeaways
Samsung’s success can largely be attributed to its holistic approach to its value chain management. From building a robust infrastructure to investing in human resources and technology, Samsung ensures that every component of its value chain is fine-tuned for efficiency and productivity.
If you’re a business professional aiming to gain a deeper understanding of value chains and apply this knowledge to your operations, consider using a whiteboard solution like Boardmix. With a pre-built value chain template, you can map out your business processes easily and more effectively. Explore it here.