The growth of Starbucks from a single coffee shop in Seattle to a multinational giant is nothing short of exceptional. But, how did they manage to maintain consistency in the taste of their coffees, reaching different corners of the world, without compromising on quality? A closer look at the company's value chain offers the answers.
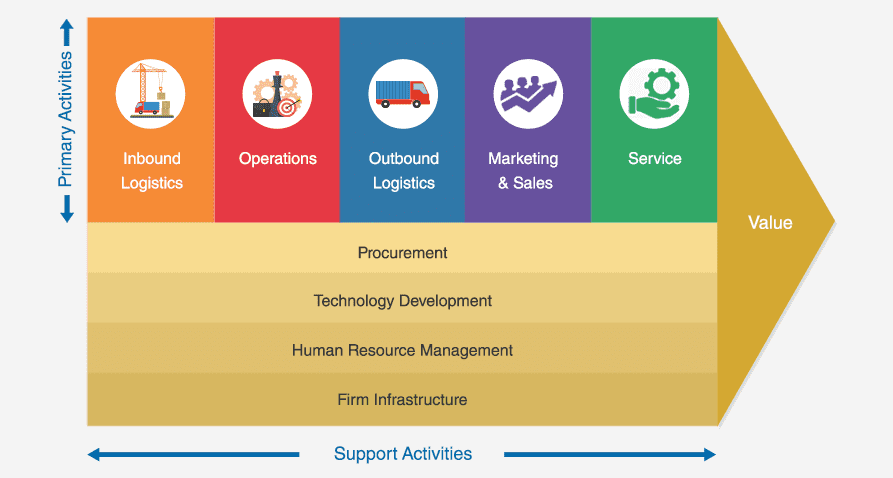
Primary Activities of Starbucks Value Chain
Primary activities in Starbucks’s value chain are critical because they directly deal with how Starbucks creates and sells its products. They directly generate revenue and include processes related to production, marketing, and customer service.
Inbound Logistics
The journey of a Starbucks coffee cup starts at its very source—the coffee growers. This initial stage of the value chain, the inbound logistics, is essential in maintaining Starbucks's signature taste and quality.
Starbucks has developed a comprehensive, direct relationship with coffee producers globally. These relationships are not just mere transactions; they are partnerships built on mutual respect and trust. Starbucks's Coffee and Farmer Equity (C.A.F.E) practices have ensured that their growers follow ethical and responsible growing methods, which accentuates the company's commitment to social responsibility.
An integral part of these inbound logistics is the quality inspection teams. Comprising of seasoned coffee specialists, these teams are on the ground, verifying that the coffee beans meet Starbucks's stringent quality requirements. From the size, color, and taste of the beans to the moisture content, every aspect undergoes rigorous checking. This careful scrutiny ensures that only the highest quality beans make their way to Starbucks roasteries.
Furthermore, Starbucks's inbound logistics involves sophisticated supply chain management. The company utilizes advanced forecasting tools and algorithms to predict demand accurately and ensure the efficient flow of raw materials from farms to their processing units. It helps Starbucks manage its inventory effectively and reduces unnecessary costs related to overstocking or understocking.
Operations
The second phase in Starbucks's value chain is operations. Here, the high-quality, responsibly-sourced green coffee beans are transformed into the coffee loved by millions around the world.
Starbucks operates numerous state-of-the-art roasting facilities worldwide. Each bean's roasting time is meticulously controlled to ensure the uniformity and consistency of their signature coffee taste. As per the data from 2020, Starbucks processed approximately 551 million pounds of coffee at its roasting facilities.
Post-roasting, the beans are packaged and prepared for distribution. Starbucks utilizes high-speed, automated packaging lines, reducing human error and enhancing efficiency.
The heart of Starbucks operations, however, lies within its stores. Each Starbucks store is strategically designed to evoke a warm, inviting atmosphere—a third place between home and work. With over 32,000 stores worldwide as of 2021, consistency in delivering this experience is crucial.
Starbucks ensures this through standardization. Each barista goes through rigorous training to learn the detailed process of making every drink on the menu. Starbucks' 'latte method' for instance, requires specific actions in a precise sequence - steam milk, then brew espresso, and finally pour the milk into the espresso.
Apart from drinks, Starbucks also serves an array of food items like sandwiches, pastries, and salads. In 2020, food sales represented about 20% of Starbucks's total revenue, highlighting its focus on diversifying its offerings.
Outbound Logistics
Following the roasting and packaging phase, the next vital cog in Starbucks's value chain is its outbound logistics. This process ensures that the freshly roasted coffee and other product offerings efficiently reach every Starbucks store worldwide.
To accomplish this, Starbucks has established an extensive distribution network. The company operates six primary distribution centers, three in the United States (York, PA; Carson City, NV; and Memphis, TN) and three in international locations (Amsterdam, Singapore, and Shanghai). Each center holds stock of green coffee beans from varied sources worldwide, providing the company a strategic advantage in distributing coffee with minimal time lapse.
Starbucks also embraces advanced logistics strategies to manage its complex supply chain efficiently. It leverages innovative technology to monitor inventory levels and manage order processing. The use of data analytics enables Starbucks to anticipate demand accurately, facilitating effective management of their inventory, both in their warehouses and retail outlets.
By 2021, Starbucks has reached more than 32,000 locations worldwide. Every single store, whether company-operated or licensed, needs a consistent supply of fresh coffee along with other merchandise. Starbucks's outbound logistics is adept at handling this daunting task while ensuring every outlet receives timely deliveries.
Additionally, Starbucks has taken environmentally-friendly measures in its outbound logistics too. The company uses energy-efficient vehicles for transportation and encourages its suppliers to do the same.
Marketing & Sales
Starbucks has achieved its unparalleled global recognition, not through traditional advertising channels, but rather by the inherent strength of its brand and customer experience. The company's approach to marketing and sales is a testament to its unique strategy.
Unlike other multinational corporations, Starbucks has always maintained a lower profile when it comes to advertising. As of 2019, the company reportedly spent only 1% of its revenue on advertising. Instead, it relies heavily on “word-of-mouth” marketing, allowing the high quality of their products and the Starbucks experience to create organic conversations and referrals among customers.
The 'Starbucks Experience', as coined by the company, is designed to transform a routine activity, drinking coffee, into a rich experience that uplifts the customer's day. This experience-centric approach is reflected in every element of Starbucks stores, from the design and ambiance to the customer service.
Further driving its sales is Starbucks's commitment to product innovation. With over 87,000 possible drink combinations and regular seasonal specials, Starbucks ensures its menu caters to a wide range of tastes and preferences. The introduction of non-dairy alternatives and 'healthier' options like the sous-vide egg bites reflects Starbucks's knack for evolving with customer preferences.
Leveraging technology has also played a critical role in their marketing and sales strategy. Starbucks's mobile app, introduced in 2011, quickly became a major revenue driver for the company, accounting for about 30% of their U.S. transactions as of 2020. This app, equipped with a loyalty program, mobile ordering, and personalized marketing offers, underscores Starbucks's focus on enhancing customer experience while driving sales.
Services
In Starbucks's value chain, the services component is crucial as it continually enhances and elevates the customer experience, ensuring Starbucks remains a favored choice for coffee lovers worldwide.
The baristas, the front-line employees of Starbucks, are central to this service aspect. Starbucks invests heavily in training its baristas, making sure they possess not just the knowledge and skills to prepare perfect beverages, but also the ability to connect with customers, enhancing the overall experience. This personalized approach to service adds a human touch that customers appreciate.
Moreover, Starbucks has established a robust customer feedback system. By encouraging customers to share their experiences and feedback, Starbucks ensures that it remains aligned with customer needs and expectations. This feedback process aids in developing new products and refining existing ones, allowing Starbucks to remain relevant in a rapidly evolving market.
Additionally, Starbucks’s commitment to its mobile technology enhances its service offering. The Starbucks app simplifies the purchasing process by providing features like mobile order & pay, rewards, and gift card functions. Starbucks was an early adopter of mobile payments and continues to evolve its digital capabilities, enriching the customer experience.
Starbucks also excels in its after-sales service. Any customer dissatisfied with their beverage can simply ask for it to be remade. Starbucks’s “Your drink should be perfect, every time. If not, let us know and we’ll make it right” policy speaks volumes about their dedication to customer satisfaction.
Support Activities of Starbucks Value Chain
In Starbucks's value chain, alongside primary activities, support activities also play a significant role in enhancing its value proposition. These activities include infrastructure, human resource management, technology development, and procurement.
Infrastructure
Starbucks's corporate infrastructure serves as the backbone of its global operations. It comprises all organizational structures, from its corporate headquarters to regional offices and individual stores.
Starbucks's impressive infrastructure facilitates smooth coordination and execution of business processes. Its administrative teams play a critical role in strategic planning, risk management, quality control, legal matters, finance and accounting operations. The infrastructure ensures that the company's core values and culture are uniformly communicated and upheld across its vast network.
Human Resource Management
Human resource management is crucial to Starbucks's success. The company values its employees, or 'partners', as it calls them, recognizing that they are integral to the Starbucks experience.
Starbucks is renowned for offering competitive wages and a comprehensive benefits package, including health insurance, retirement savings, stock options, and free college tuition for eligible employees. Such initiatives contribute to high employee satisfaction levels and low turnover rates, translating into consistent customer service delivery.
Technology Development
Starbucks leverages technology to augment its operational efficiency and customer experience. It uses data analytics for demand forecasting, inventory management, and personalizing marketing initiatives.
The company's pioneering mobile app is an excellent example of its technology deployment. By combining mobile payments, loyalty programs, and personalized offers into one platform, Starbucks has enhanced customer convenience and boosted sales. The company continually upgrades this digital platform, reinforcing its commitment to technological innovation.
Procurement
Finally, procurement forms a vital support activity. Starbucks follows ethical sourcing principles when procuring coffee beans from growers worldwide. Its Coffee and Farmer Equity (C.A.F.E) practices ensure that the company sources high-quality beans while promoting environmental sustainability and farmers' welfare.
Starbucks's procurement strategies also extend to securing best-quality milk, bakery products, equipment, and store furnishing materials. By maintaining stringent procurement standards, Starbucks safeguards the quality and consistency of its offerings.
Starbucks Value Chain Analysis Example
The essence of the Starbucks value chain can be better understood with a simple diagram. The diagram breaks down each process stage, providing a straightforward guide for business professionals who want to understand how Starbucks creates value.
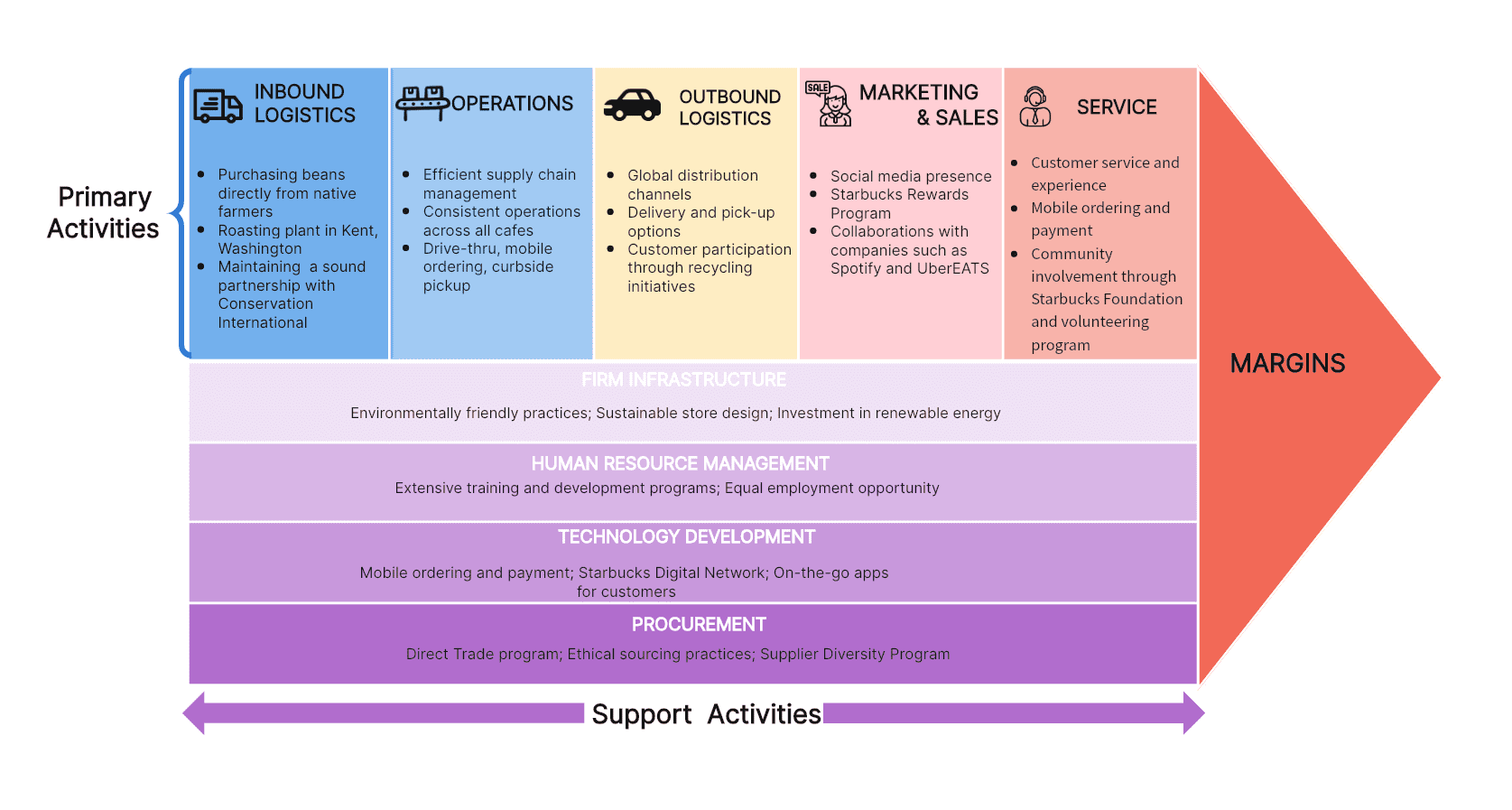
Key Takeaways
A deeper understanding of Starbucks’s value chain provides insights into how they consistently offer high-quality products. From a strong relationship with coffee growers to robust support activities like HR and technology, every step contributes to Starbucks's overall customer experience and brand strength.
If you wish to illustrate complex value chain analysis like this, consider using our whiteboard solution, Boardmix. With its pre-built value chain template, you can seamlessly visualize any value chain analysis in an easy-to-understand format. Visit us here for more details.