Agile retrospectives are a pivotal component in the realm of successful project management strategies. These retrospectives offer teams an invaluable platform to introspect their work methodologies, pinpoint strengths and weaknesses, and strategize for enhanced performance. This comprehensive guide will navigate you through the complex landscape of agile retrospectives, shedding light on its principles, stages, goals, and best practices. It aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to harness the full potential of agile retrospectives in driving continuous improvement and fostering a culture of transparency and collaboration within your team.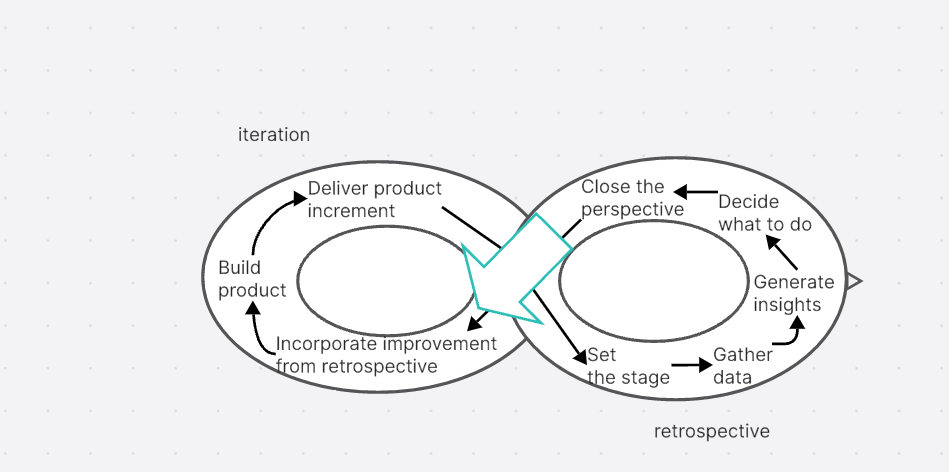
Part 1. What Is an Agile Retrospective?
An agile retrospective, often considered as the heartbeat of Scrum, is a dedicated meeting that takes place upon the completion of each sprint within the agile project management framework. This gathering serves as a reflective mirror for team members, enabling them to introspect their performance throughout the sprint. It's an open forum where successes are celebrated, challenges are dissected, and lessons learned are shared. More importantly, it's a catalyst for continuous improvement as it empowers teams to identify potential opportunities and devise actionable strategies for enhanced productivity in subsequent sprints.
Part 2. What Are the 5 Stages of the Retrospective?
The agile retrospective is structured around five distinct stages: Setting the Stage, Gathering Data, Generating Insights, Deciding What to Do, and Closing the Retrospective. Each stage serves a unique purpose and collectively they form a comprehensive framework for effective retrospection.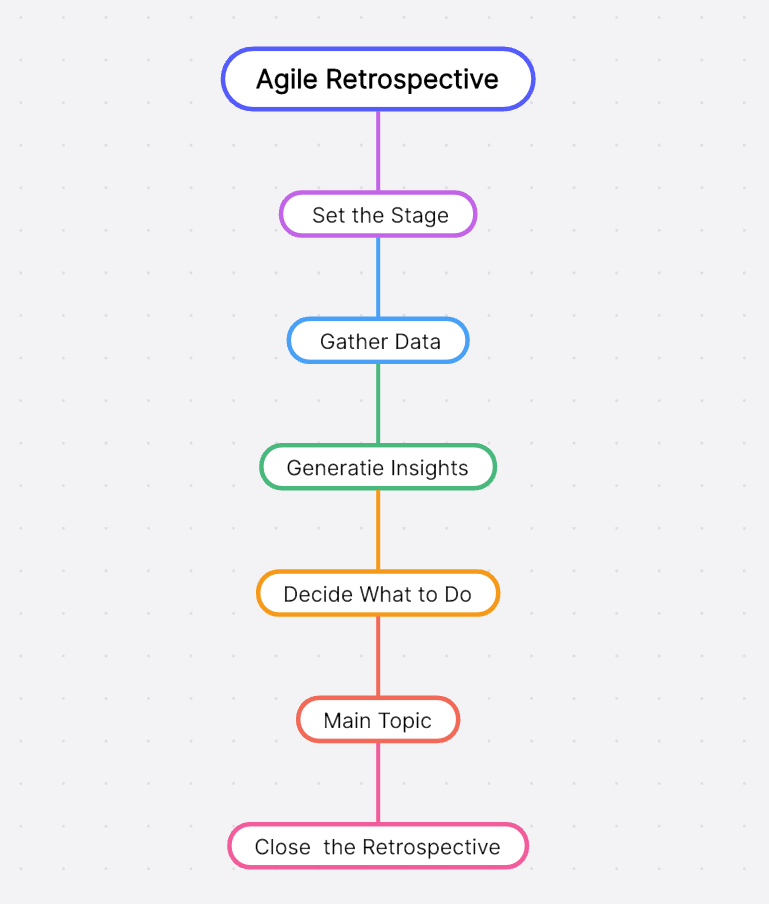
1. Setting the Stage: This initial phase sets the tone for the meeting. It's about creating an open and respectful environment where every team member feels comfortable sharing their thoughts.
2.. Gathering Data: Here, teams collect information about what happened during the sprint. This could be in terms of completed tasks, challenges faced, or unexpected events that occurred.
3. Generating Insights: In this stage, teams analyze the gathered data to identify patterns or trends. The goal is to understand why certain things happened and how they impacted the team's performance.
4. Deciding What to Do: Based on insights generated, teams decide on actions to improve their future sprints. These should be specific, achievable tasks that are assigned to individuals or sub-teams.
5. Closing the Retrospective: The final stage involves summarizing key points from the meeting and ensuring everyone is clear on next steps. It's also an opportunity to appreciate each other's contributions and close on a positive note.
Each stage plays a critical role in fostering transparency and understanding among team members about what worked well during the sprint and what areas need improvement for future iterations.
Part 3. What Is the Principle of Retrospective in Agile?
The cornerstone principle underpinning agile retrospectives is the pursuit of continuous improvement. This iterative process encourages teams to regularly pause and reflect on their performance, fostering a culture of introspection and learning. By consistently analyzing their actions, decisions, and outcomes, teams can swiftly identify any bottlenecks or issues that may have surfaced during the sprint. This proactive approach allows for immediate corrective measures to be implemented, minimizing the impact of such issues on the project's progress. In essence, agile retrospectives serve as a powerful tool in an organization's arsenal to drive ongoing enhancement in productivity, collaboration, and overall team performance.
Part 4. What Is the Goal of an Agile Retrospective?
The primary objective of an agile retrospective is to bolster team collaboration and operational efficiency. It acts as a reflective lens, enabling teams to identify and celebrate their triumphs, while also acknowledging and learning from their shortcomings during past sprints. But retrospectives go beyond mere identification; they are about transforming these insights into actionable plans for future sprints. By doing so, they foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement where each sprint is seen as an opportunity to perform better than the last. In essence, agile retrospectives are not just about making teams work together but making them work better together, thereby driving project success and overall organizational growth.
Part 5. Tips for Agile Retrospective
To conduct effective retrospectives, several key strategies can be employed.
Firstly, it's essential to cultivate a safe and inclusive environment that encourages open communication. This means fostering a culture of trust where team members feel comfortable sharing their thoughts, ideas, and concerns without fear of judgment or retribution.
Secondly, the focus should be on evaluating processes rather than individuals. Retrospectives are not about finger-pointing or blame games; they're about understanding how the team as a whole can improve. By concentrating on the process, teams can identify systemic issues that may be hindering performance and devise solutions to address them.
Lastly, it's crucial to ensure that follow-up actions resulting from the retrospective are clearly defined, assigned to appropriate team members, and diligently tracked. This ensures accountability and helps translate insights gained during the retrospective into tangible improvements in future sprints.
Part 6. Steps to Run an Agile Retrospective Meeting
Executing an effective retrospective is a multi-step process that requires careful planning and active participation from all team members.
Firstly, it's crucial to set clear objectives for the meeting. This provides a roadmap for the discussion and ensures everyone understands what the team hopes to achieve from the retrospective.
Secondly, gathering data about team performance during the sprint forms the basis of your discussion. This could involve reviewing completed tasks, identifying challenges encountered, or discussing unexpected events that may have impacted the sprint.
Thirdly, discussing insights gleaned from this data allows teams to delve deeper into their performance. It's an opportunity to identify patterns, understand root causes of issues, and celebrate successes.
The fourth step involves deciding on improvements based on these insights. The goal here is not just to identify what needs to change but also to formulate actionable strategies on how to effect these changes in future sprints.
Finally, closing with clear action items ensures everyone leaves the meeting with a clear understanding of their responsibilities moving forward. These should be specific tasks assigned to individuals or sub-teams and should be tracked until completion in subsequent sprints.
In essence, running an effective retrospective is a structured process that combines reflection with action - it's about understanding where you've been and charting a course for where you want to go next.
Part 7. How to Run an Agile Retrospective Meeting with Boardmix
Boardmix emerges as your ultimate online whiteboard solution, meticulously designed to foster seamless collaborative sessions, including agile retrospectives. It's more than just a tool; it's a virtual workspace that transcends geographical boundaries, enabling teams to brainstorm, strategize and reflect together in real-time. With its intuitive interface and robust features, Boardmix aims to redefine the way you collaborate, making your retrospective meetings more engaging, productive and insightful. Whether you're dissecting past sprints or planning for future ones, Boardmix stands as your reliable partner in facilitating effective communication and driving continuous improvement within your team.
Key features of Boardmix:
- Drawing Templates: A wide selection of templates for various meeting needs.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Enables simultaneous work on the same board from different locations.
- Interactive Tools: Includes sticky notes, markers, shapes and lines for effective expression of ideas.
- Easy Sharing and Accessibility: Boards can be shared via a link and accessed across devices.
- Secure and Private: Default privacy settings with user-controlled access to boards.
- Unlimited Boards: No limit on the number of boards you can create for brainstorming and collaboration.
- Revision History: Tracks changes over time with an option to revert back if necessary.
Here's how you can use Boardmix for your next retrospective:
Step 1: Sign up or login to Boardmix and go to workspace.
Step 2. Choose a template suitable for your meeting or start from scratch.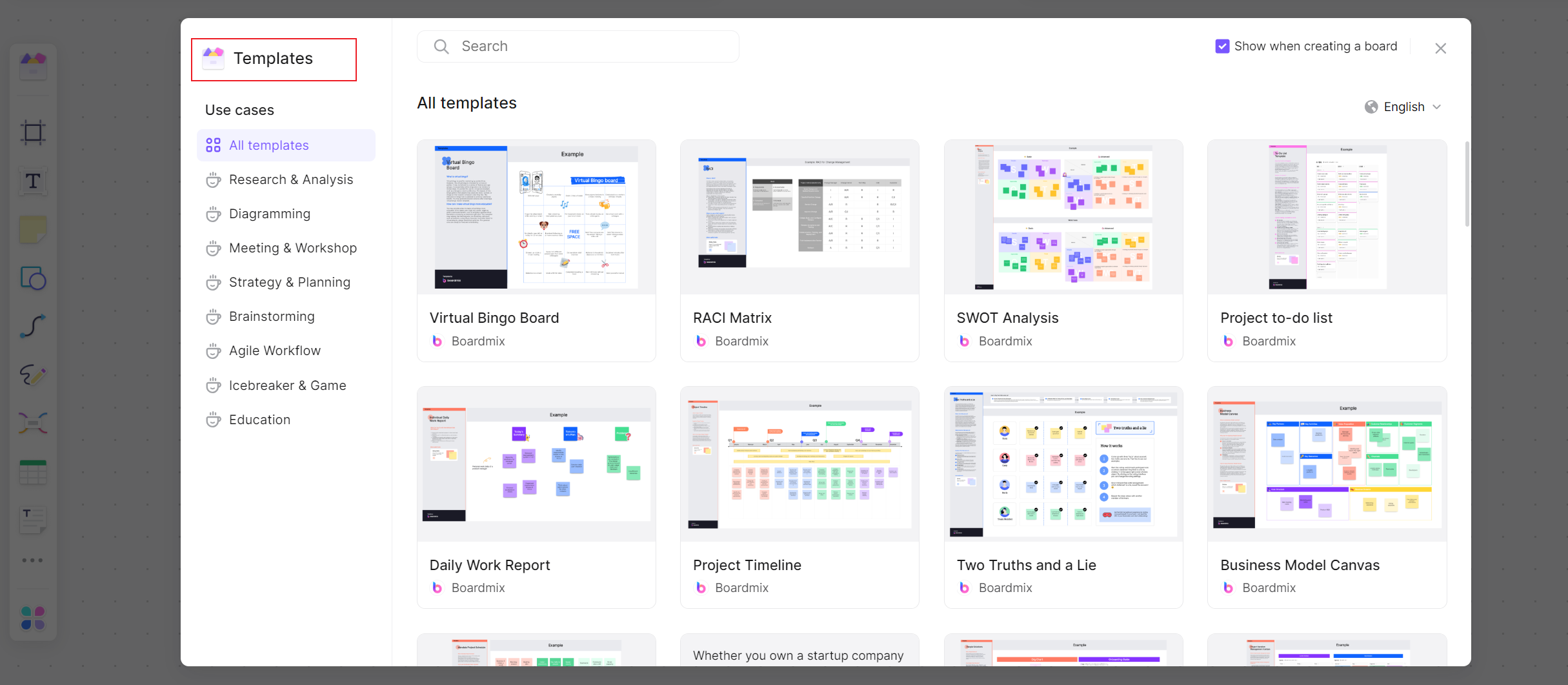
Step 3: Invite team members to join your board.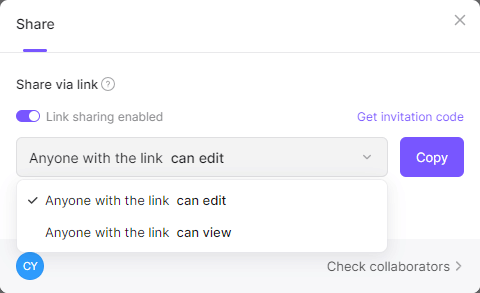
Step 4: Use tools provided by Boardmix such as sticky notes or markers during different stages of your retrospective.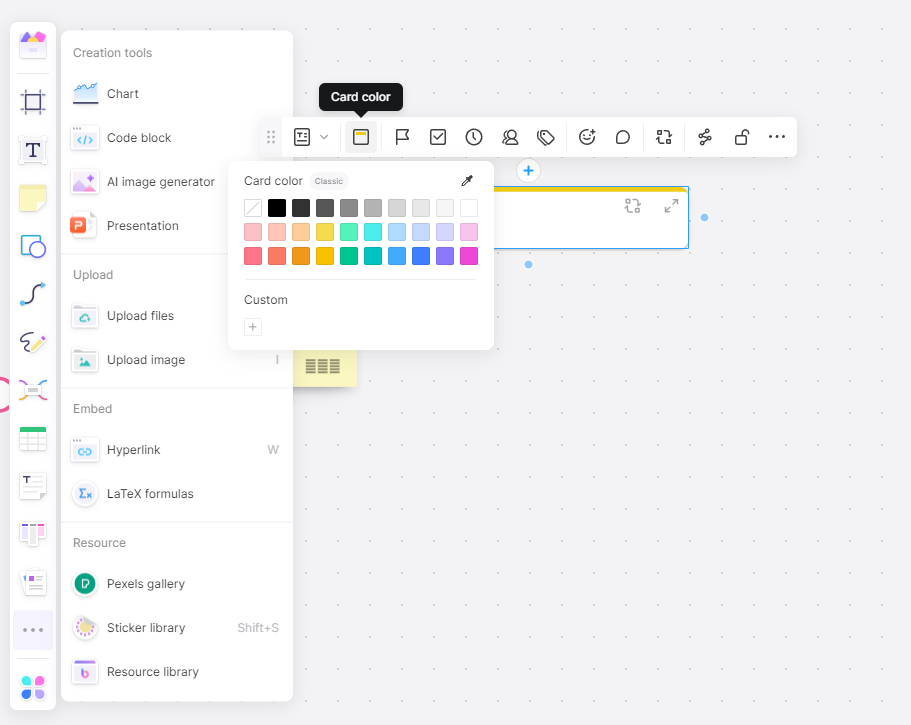
Step 5: Save your board at end of session so you can revisit it later or share it with others who couldn't attend.
Conclusion
Agile retrospectives are indeed a cornerstone of continuous improvement for teams operating within agile frameworks. They serve as a platform for reflection, learning, and proactive planning. With the advent of innovative tools like Boardmix, conducting these critical meetings has been transformed into an efficient and productive process. Boardmix, with its intuitive interface and robust features such as a variety of drawing templates, real-time collaboration, interactive tools, easy sharing and accessibility, secure environment, unlimited boards creation, and revision history tracking, empowers teams to conduct retrospectives in a more engaging and insightful manner. It's not just about making retrospectives easier; it's about making them more effective than ever before!