In today's fast-paced and digitally driven world, businesses and organizations are realizing the importance of understanding their customers on a deeper level. Empathy, the ability to understand and share the feelings of others, plays a crucial role in creating products and services that truly resonate with people. One powerful tool that has emerged to foster empathy is the "Empathy Map." This article explores the concept of empathy maps, their benefits, and how they can effectively enhance user experiences.
Part 1. What is an Empathy Map?
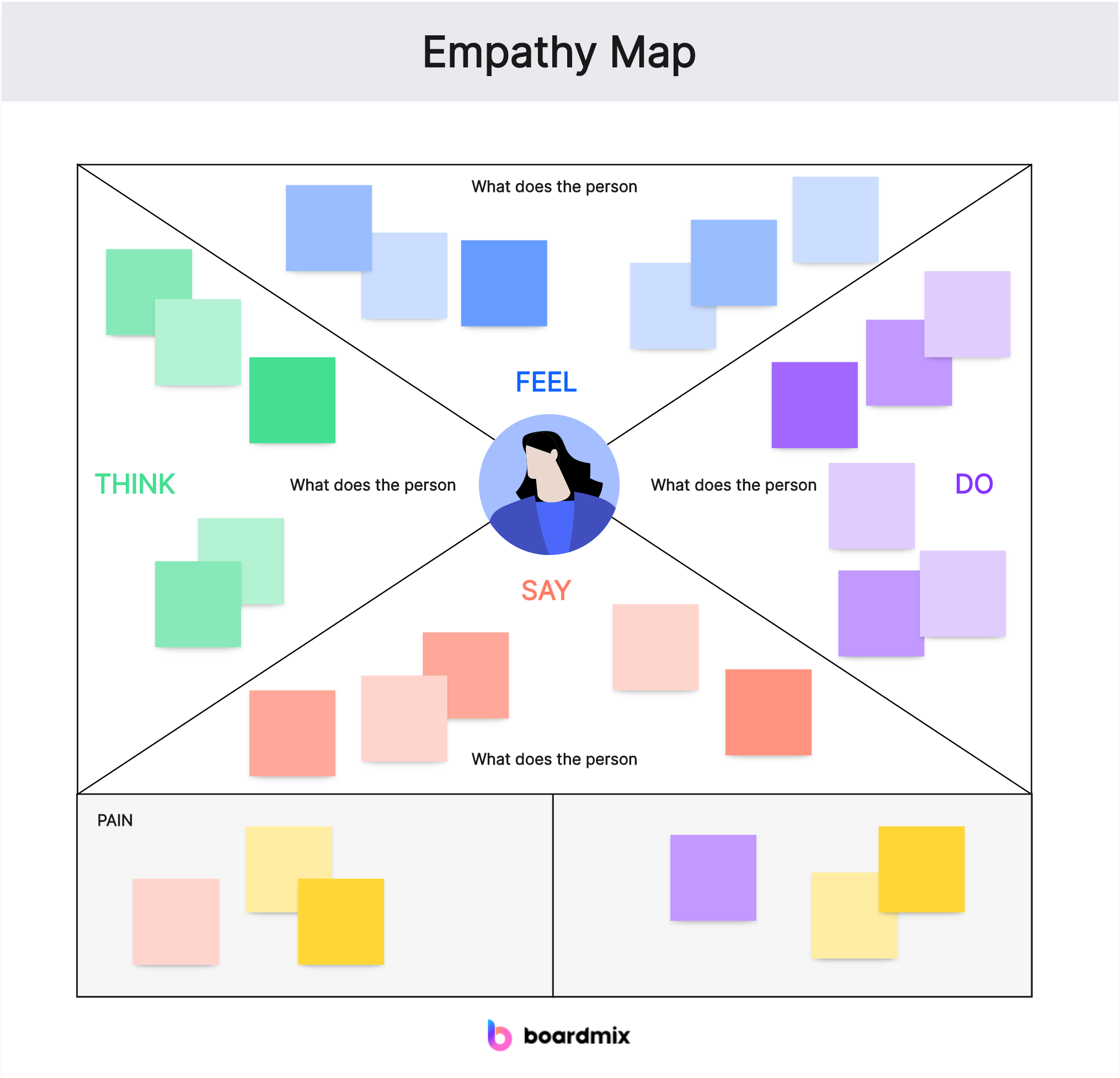
An empathy map is a visual representation of user experiences, emotions, and thoughts. It serves as a collaborative tool to help teams gain a deeper understanding of their target audience by creating a shared perspective. The map typically consists of four quadrants, each focusing on a specific aspect of the user's experience:
Seeing: This quadrant represents the observable elements of the user's experience. What can the user see? This may include their environment, physical surroundings, and any visual cues relevant to their experience.
Hearing: In this quadrant, teams explore the auditory aspects of the user's experience. What are the users hearing, both externally and internally? This could involve conversations, feedback, or even their own thoughts.
Saying/Doing: This quadrant delves into the explicit actions and verbal expressions of the user. What are they saying out loud? What actions are they taking? Understanding the explicit behaviors is essential for comprehending the user's mindset.
Thinking/Feeling: The final quadrant focuses on the internal aspects of the user's experience. What are they thinking? What emotions are they feeling? This provides insights into the user's motivations, fears, and aspirations.
Part 2. Why Need an Empathy Map
The use of an empathy map serves several important purposes in various fields, primarily focusing on understanding and empathizing with users or stakeholders. Here are the key purposes:
User-Centric Design: Empathy maps facilitate a deeper understanding of user needs, preferences, and pain points. This insight is crucial for designing products, services, or experiences that align with and address the genuine concerns of the target audience.
Improved Communication: Teams can use empathy maps as visual tools to enhance communication and collaboration. By having a shared representation of the user's experience, cross-functional teams can better align their efforts and work towards a common goal.
Informed Decision-Making: Empathy maps provide a holistic view of the user's journey, helping decision-makers make informed choices based on a nuanced understanding of user behaviors, motivations, and emotions.
Enhanced Innovation: By empathizing with users, teams can identify unmet needs and opportunities for innovation. This empathetic approach fosters creative problem-solving, encouraging teams to develop solutions that go beyond the obvious and truly address user requirements.
Persona Development: Empathy maps contribute to the creation and refinement of user personas. They help in building a comprehensive profile of the target audience, ensuring that design and marketing efforts are tailored to the specific characteristics and expectations of users.
Customer Satisfaction: Understanding users at a deeper level allows businesses to create products and services that resonate with their audience. This, in turn, leads to higher customer satisfaction as the offerings are better aligned with user expectations and preferences.
Continuous Improvement: Empathy maps are dynamic tools that can be regularly updated. This supports a culture of continuous improvement by incorporating new insights and adapting to changes in user behavior or market trends.
Empathy Building: Beyond the practical applications, empathy maps contribute to fostering a culture of empathy within organizations. Team members gain a better appreciation for the experiences and emotions of users, leading to more empathetic and compassionate interactions.
In summary, the primary purposes of using an empathy map are to foster user-centric design, improve communication within teams, make informed decisions, drive innovation, develop accurate user personas, enhance customer satisfaction, support continuous improvement, and cultivate empathy within the organizational culture.
Part 3. How to Build an Empathy Map
Building an empathy map involves a structured process of gathering and organizing insights about the user's experiences, emotions, and behaviors. Here's a step-by-step guide to creating an empathy map:
Define Your Target Persona:
- Identify the specific user or customer persona you want to understand better.
- Clearly define the demographics, behaviors, and characteristics of this persona.
Gather User Insights:
- Conduct user interviews, surveys, or observations to collect qualitative data.
- Focus on the user's experiences, emotions, thoughts, and behaviors related to the product or service.
Identify Key Touchpoints:
- Pinpoint the key touchpoints in the user journey where interactions with your product or service occur.
- Understand the user's experiences at each touchpoint.
Create Four Quadrants:
- Draw or use a template to create four quadrants on a large sheet of paper or a digital tool.
- Label the quadrants as "Seeing," "Hearing," "Saying/Doing," and "Thinking/Feeling."
Populate Each Quadrant:
- Seeing: What does the user see in their environment? Include visual cues, surroundings, and any relevant objects.
- Hearing: What are the auditory aspects of their experience? Include conversations, feedback, and any sounds that impact their experience.
- Saying/Doing: What explicit actions is the user taking? What are they saying out loud? Include both verbal and non-verbal expressions.
- Thinking/Feeling: Explore the internal aspects of the user's experience. What are they thinking, and what emotions are they feeling?
Use Visuals and Quotes:
- Incorporate visuals, symbols, or keywords to represent each aspect of the user's experience in the quadrants.
- Include direct quotes from users to capture their authentic voice and perspective.
Collaborate with Your Team:
- Building an empathy map is a collaborative effort. Involve team members from different disciplines to gain diverse insights.
- Use workshops or brainstorming sessions to fill in the map collectively.
Iterate and Refine:
- The empathy map is not a static document. Regularly update and refine it based on new insights, user feedback, or changes in the product/service.
Combine with User Personas:
- Integrate the empathy map with your user personas. The map can inform and enrich the characteristics of the personas, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the target audience.
Use Digital Tools:
- Consider using digital tools or software to create a more dynamic and shareable empathy map. This can facilitate easier collaboration, especially for remote teams.
Share and Communicate:
- Share the empathy map with relevant stakeholders, ensuring that the insights gained are disseminated across the organization.
- Use the empathy map as a reference point for decision-making, design, and communication strategies.
Remember, the goal is to create a visual representation that fosters a shared understanding of the user's experience within your team and organization. Regularly revisit and update the empathy map to keep it aligned with the evolving needs and behaviors of your users.
Part 4. What Is Empathy Map vs Persona Map?
Empathy maps and persona maps are both tools used in user-centered design, but they serve different purposes and focus on distinct aspects of the user experience. Here's a comparison between empathy maps and persona maps:
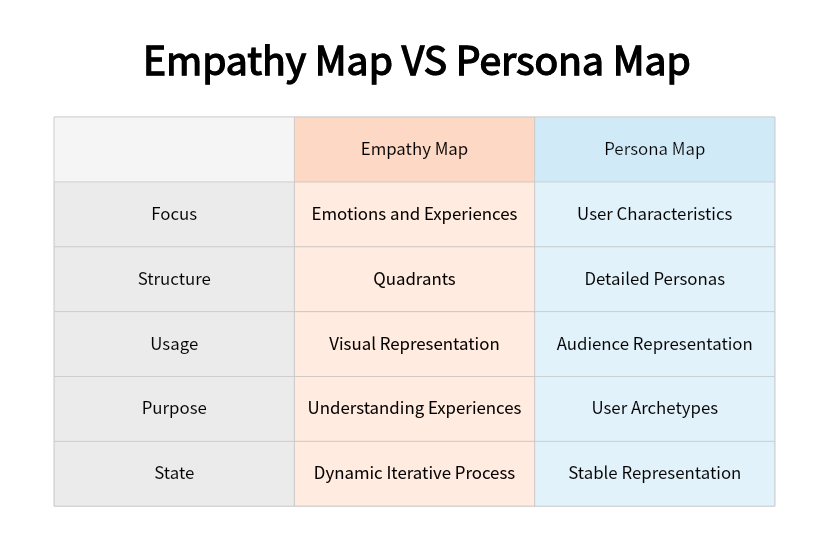
Empathy Map:
- Focus:
Emotions and Experiences: Empathy maps primarily focus on capturing the emotions, experiences, and behaviors of a specific user or target audience.
- Structure:
Quadrants: Empathy maps are often structured into four quadrants: Seeing, Hearing, Saying/Doing, and Thinking/Feeling. Each quadrant captures a different aspect of the user's experience.
- Usage:
Visual Representation: They provide a visual representation of the user's journey and help teams understand the user's perspective on a deeper level.
- Purpose:
Understanding Experiences: The main purpose of an empathy map is to foster empathy by helping teams understand what users see, hear, say, do, think, and feel during their interactions with a product or service.
- Dynamic:
Iterative Process: Empathy maps are often created iteratively, allowing for continuous updates based on new insights and changing user behaviors.
Persona Map:
- Focus:
User Characteristics: Persona maps focus on the demographic and psychographic characteristics of a fictional representation of the target user, known as a persona.
- Structure:
Detailed Personas: Persona maps typically include detailed information about the user, such as age, gender, job role, goals, challenges, and other relevant attributes.
- Usage:
Audience Representation: They serve as a tool for representing and understanding the different segments of the target audience. Each persona represents a group of users with similar traits.
- Purpose:
User Archetypes: Persona maps help teams create archetypal users, making it easier to design products and services that align with the needs and preferences of specific user groups.
- Static:
Stable Representation: Once created, persona maps are relatively stable and are not updated as frequently as empathy maps. They represent an idealized and somewhat static view of user characteristics.
Relationship:
Complementary Tools: Empathy maps and persona maps are often used together. Empathy maps provide a deep understanding of user experiences, while persona maps offer a broader view of user characteristics.
User-Centric Approach: Both tools contribute to a user-centric approach in design and development, ensuring that products and services are not only functional but also resonate with the target audience on an emotional and practical level.
In summary, while empathy maps delve into the user's experiences and emotions, persona maps focus on creating detailed user personas based on demographic and psychographic characteristics. Both tools play crucial roles in developing a comprehensive understanding of the target audience.
Part 5. Build Empathy Map with Boardmix
Boardmix's Empathy Map template is a powerful tool designed to help teams gain deeper insights into their customers' needs, wants, and challenges. This interactive online whiteboard tool allows you to visualize your customer's experience from their perspective, helping you understand their thoughts, feelings, and motivations. The Empathy Map template is easy to use and customizable, allowing teams of all sizes to collaborate in real-time and make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of the customer's journey. Unlike other online whiteboards, Boardmix focuses on providing an intuitive user experience with a wide range of templates that cater to various business needs.
Steps to Build Empathy Map with Boardmix
1. Start by opening Boardmix and selecting the 'Empathy Map template' from our extensive library of templates.
2. Invite your team members to join the board. With Boardmix, you can collaborate in real-time, no matter where you are located.
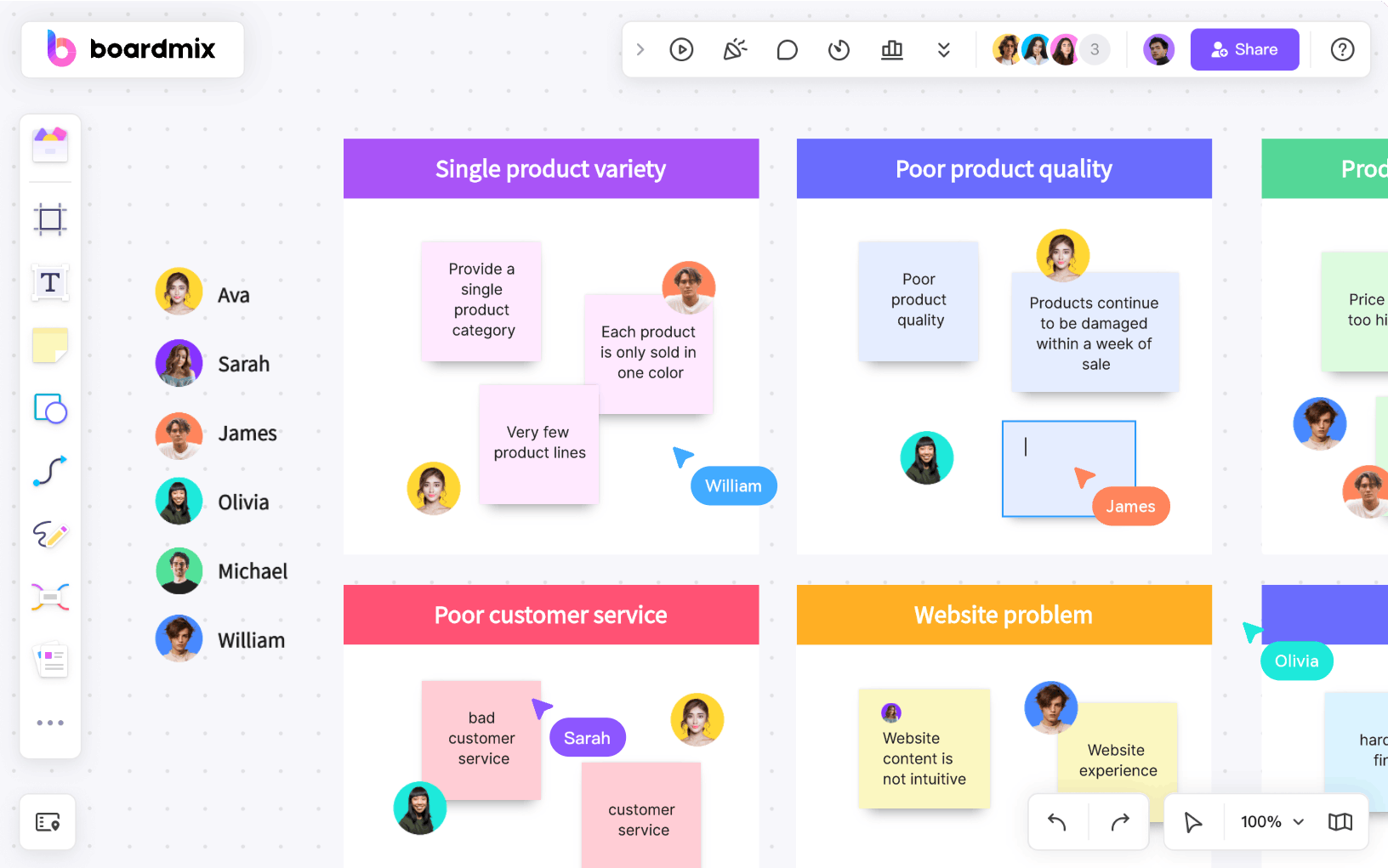
3. Begin filling out the sections of the Empathy Map: 'Says', 'Thinks', 'Does', and 'Feels'. This will help you visualize what your customer is experiencing at different stages.
4. Use sticky notes, text boxes, or drawing tools to add insights into each section. You can easily move, edit or delete these elements as your understanding evolves.
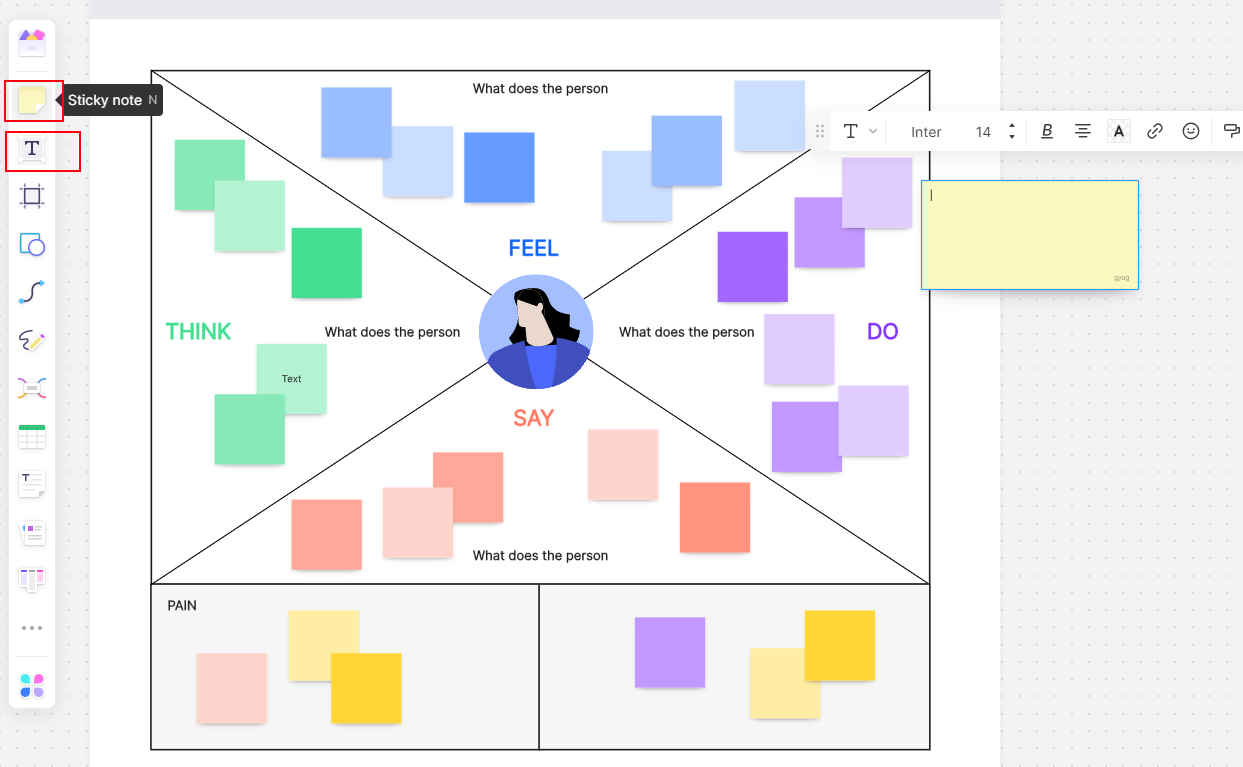
5. Once completed, use this visual tool to guide your decision-making process, ensuring it's aligned with your customer's needs and experiences.
Conclusion
Empathy maps are invaluable tools for organizations looking to create meaningful connections with their users. By fostering a deeper understanding of user experiences, emotions, and motivations, businesses can design products and services that truly resonate with their audience. Incorporating empathy maps into the development process not only enhances user satisfaction but also promotes a culture of empathy within cross-functional teams, ultimately driving innovation and success in the ever-evolving landscape of user-centric design.
Boardmix is the ultimate online whiteboard tool that brings your team's collaboration to a whole new level. With our wide range of intuitive and customizable templates, including the Empathy Map, you can visualize and understand your customer's journey like never before. Don't wait, start using Boardmix today and experience a seamless, real-time collaboration that drives meaningful insights and informed decision-making.