FBDs serve as indispensable tools in system design, providing a visual language to unravel intricate processes. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamentals of FBDs, explores their optimal applications, and decodes the symbols shaping their language. Whether you're a seasoned professional or a newcomer to system design, this guide is your key to mastering FBDs through the user-friendly features of Boardmix.
What Is a Functional Block Diagram
A Functional Block Diagram (FBD) stands as a potent visual tool, adept at illustrating the intricate functional relationships existing among diverse system components. Utilizing blocks to symbolize distinct functions or operations, and interconnected lines to delineate the flow of signals or data, FBDs play a pivotal role in the landscape of system design. These diagrams provide a lucid and succinct panorama of complex processes, offering designers and engineers a valuable medium for conceptualizing and communicating the interplay of functions within a system.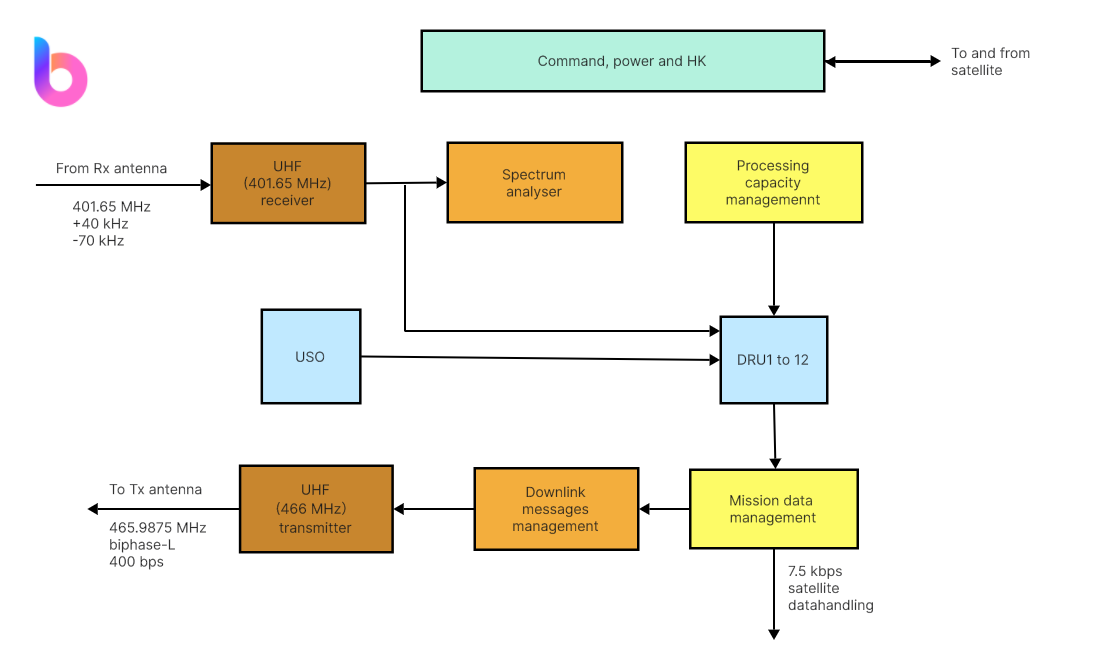
In essence, an FBD serves as a roadmap, guiding the design process and enabling effective communication among stakeholders involved in the development and optimization of intricate systems.
When to Use a Functional Block Diagram
The applications of Functional Block Diagrams (FBDs) span various fields, making them a versatile tool employed in engineering, electronics, and software development. These diagrams become invaluable when the objective is to grasp and articulate the intricate interactions and dependencies inherent within a system.
Particularly beneficial during the nascent phases of design and troubleshooting, FBDs offer a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving. By encapsulating the intricate relationships between system components, these diagrams facilitate a deeper understanding of system functionality. In the realm of engineering, FBDs prove instrumental in the initial stages of system conceptualization, providing a visual blueprint that aids engineers in comprehending the overall architecture and relationships between different functions.
Additionally, during troubleshooting endeavors, FBDs serve as a diagnostic tool, enabling practitioners to pinpoint issues and streamline the resolution process by visualizing the intricate web of interactions within the system. Therefore, whether in the realms of design or troubleshooting, the adaptability and clarity offered by FBDs make them an indispensable asset in navigating the complexities of diverse systems.
Functional Diagram Symbols
Functional diagram symbols are the visual building blocks of Functional Block Diagrams (FBDs), forming a standardized language for communication within these diagrams.
- Rectangles for Functions: Utilize rectangles as common symbols representing distinct functions or operations within the system. Each rectangle encapsulates a specific function, contributing to a visually simple representation of complex processes.
- Input and Output Arrows: Employ input and output arrows to denote the flow of data within the system. Inputs are represented by arrows entering a function, while outputs are symbolized by arrows emanating from a function. This visual distinction clarifies the direction of information exchange.
- Lines for Connections: Utilize lines as symbols to indicate connections between different functions, illustrating the interdependencies within the system. Lines visually establish relationships and contribute to a clear depiction of the overall structure.
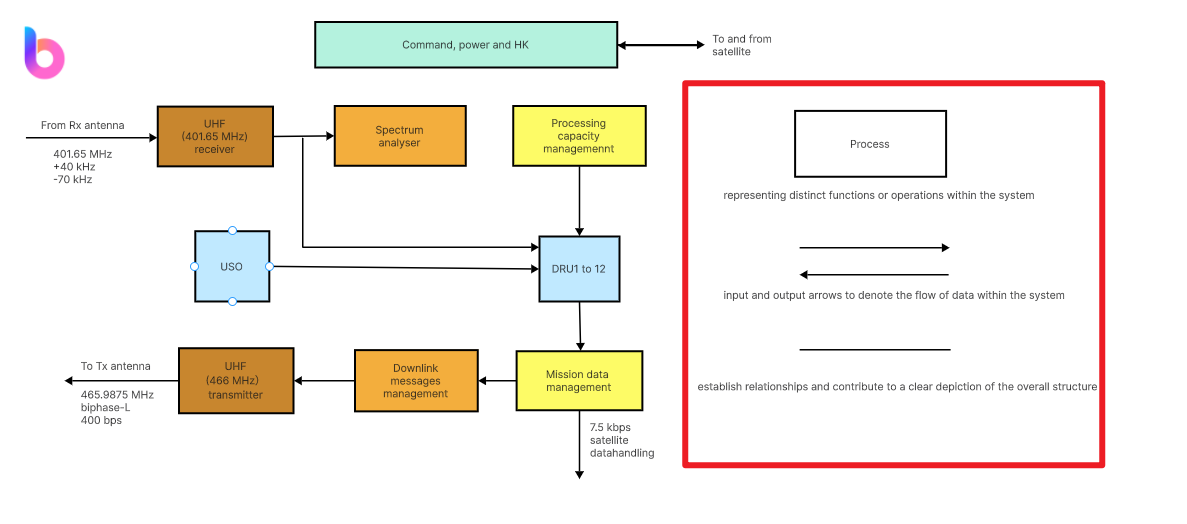
Mastering each step in interpreting and using these symbols enhances the efficiency of diagram creation, fostering precise and effective communication in the realm of system design and analysis.
Functional Block Types
Functional blocks, the fundamental components of Functional Block Diagrams (FBDs), exhibit diverse types, each serving a distinct purpose within system design. These encompass input and output blocks, processing blocks, and control blocks, with each category playing a crucial role in delineating the functions of a system.
Input and Output Blocks:
Input blocks represent entry points for external data or signals into the system, initiating the flow of information. Conversely, output blocks signify points where the system transmits data or signals to the external environment. Mastery of these blocks is essential for comprehending how information enters and exits the system.
Processing Blocks:
At the core of system functionality, processing blocks encapsulate functions that manipulate or transform incoming data. They serve as hubs for computations, transformations, or operations critical to the system's overall functionality. Understanding processing blocks is pivotal for grasping how raw data undergoes essential transformations within the system.
Control Blocks:
Control blocks exert authority over information flow within the system, regulating and managing the execution of functions. They ensure a coordinated and efficient operation, influencing the direction and pace of system processes. Proficiency in recognizing and comprehending control blocks is indispensable for understanding the governing mechanisms steering the system's course.
In essence, mastery of these block types enhances the ability to craft Functional Block Diagrams that are not only precise but also instrumental in effective system design and analysis.
How to Make a Functional Block Diagram Using Boardmix
Boardmix, an innovative data visualization platform, offers a comprehensive environment for crafting Functional Block Diagrams despite the absence of a specific template. Follow these detailed steps:

- Login and Board Creation: Begin by logging into Boardmix and creating a new board to organize your Functional Block Diagram.
- Data Entry and Import(if necessary): Input your functional data directly or seamlessly import it from other sources within Boardmix.If you have a lot of text or data, you will need to prepare and import it in advance.
- Block Creation: Utilize Boardmix's versatile tools to create blocks, representing different functions in your diagram.
- Connection Lines: Establish connections between blocks using lines to depict the flow of signals or data.
- Customization: Leverage Boardmix's diverse customization options to modify colors, labels, and other details to suit your preferences.
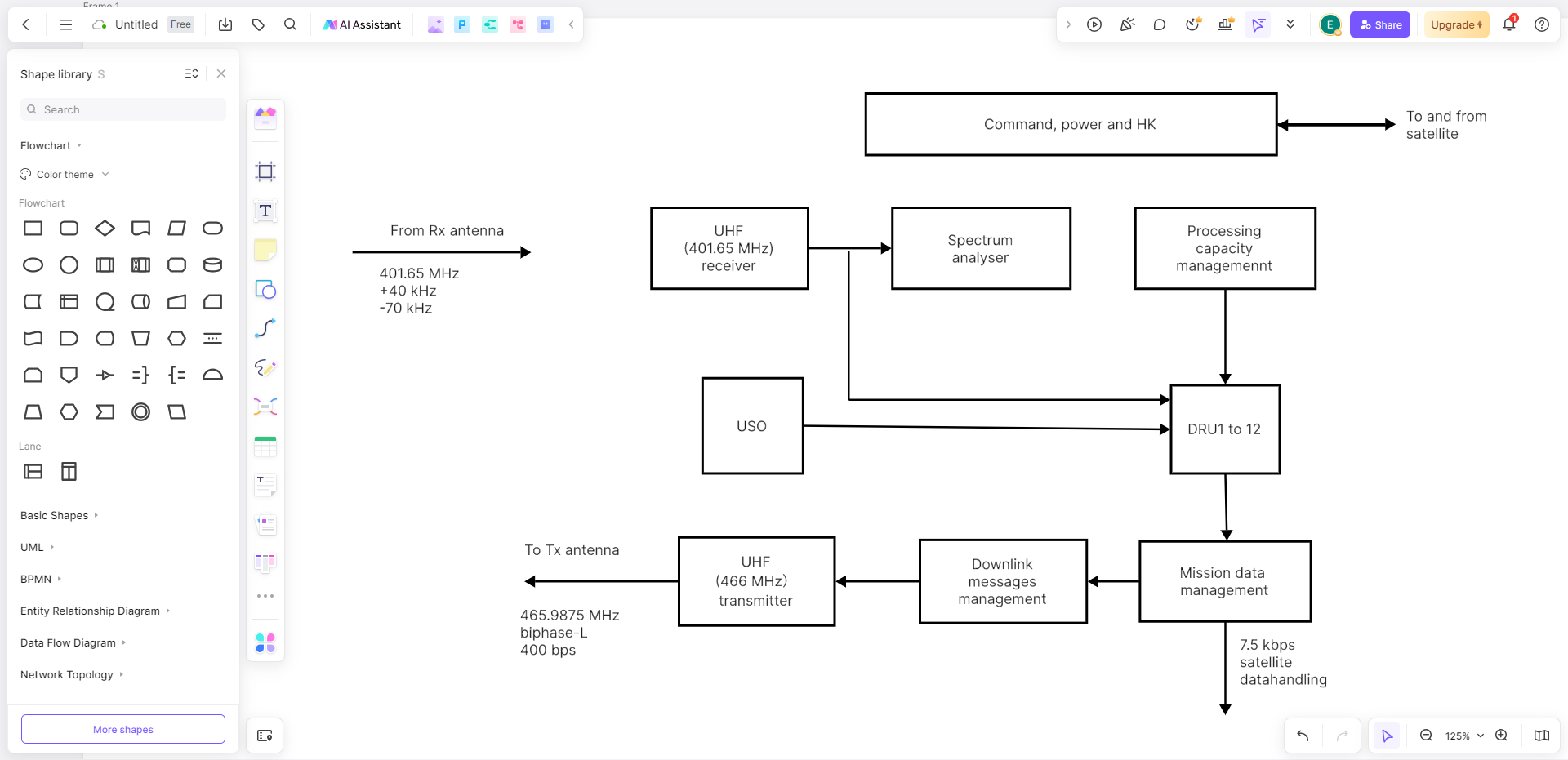
- Finalization: Before finalizing, use the preview feature to assess the visual impact of your Functional Block Diagram. Refine the diagram as needed to ensure effective communication.

- Share Your board: Once you are satisfied, share your board so that the carefully crafted functional block diagram can be saved and shared in Boardmix in real time.
Tips and Tricks on Making a Functional Block Diagram
Creating impactful Functional Block Diagrams (FBDs) demands more than just technical proficiency—it requires a strategic approach that prioritizes clarity, consistency, and visual appeal. Here are essential tips to enhance your FBD creation experience:
- Clarity is Key:
Focus on the clear arrangement of blocks and lines. Ensure a logical flow that aligns with the system's functionality, facilitating easy comprehension for stakeholders. A well-organized layout serves as the cornerstone for a comprehensible and effective diagram.
- Consistency Matters:
Maintain consistency in the usage of symbols throughout your diagram. A uniform representation of functions enhances the overall cohesion of the diagram, providing a professional and organized look. Consistency in layout, spacing, and symbol choice contributes to a visually harmonious diagram.
- Use Color Strategically:
Leverage color strategically to differentiate between different functions or highlight specific elements. Color can be a powerful tool to enhance visual hierarchy, guiding the viewer's attention to key components. Thoughtful use of color not only adds aesthetic appeal but also contributes to the clarity of your diagram.
By integrating these expert tips into your FBD creation process in Boardmix, you can elevate the quality and effectiveness of your diagrams. Whether you're aiming for enhanced communication, improved understanding, or a more professional presentation, these tips serve as invaluable guidelines to navigate the intricate landscape of Functional Block Diagram design.