In today's dynamic business environment, an effective organizational structure is essential for the success of any company. An efficient structure can foster better communication, streamline the decision-making process, and improve productivity. One of the most common and well-established structures that companies across the globe utilize is the line-staff organizational structure. This article aims to delve deeper into what a line-staff structure entails, its working mechanism, potential benefits, drawbacks, and practical applications.
What is a Line-Staff Organizational Structure?
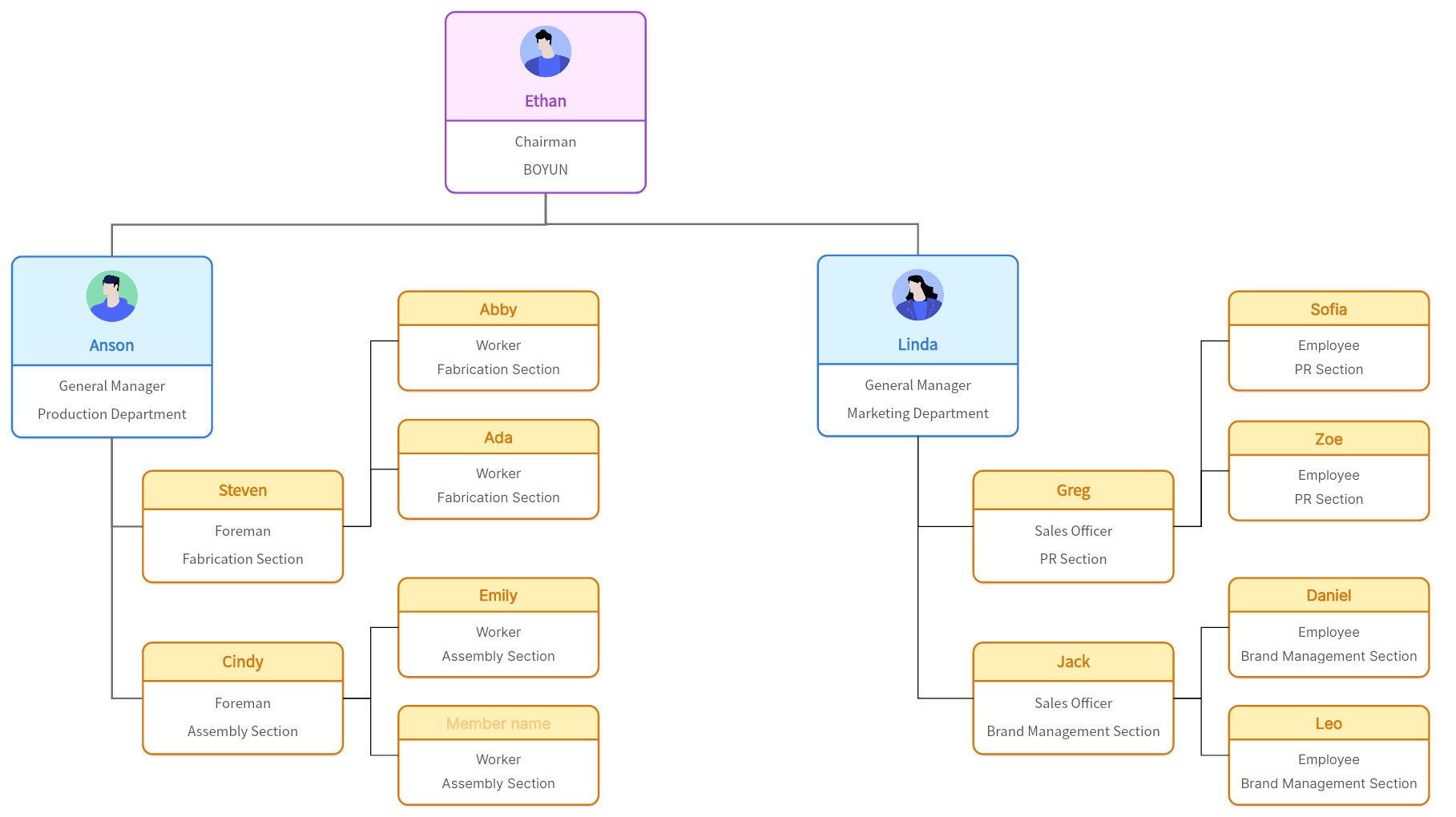
A line-staff organizational structure symbolizes a careful balance between traditional line positions and staff roles within an organization. In this type of structure, line positions represent the jobs directly responsible for fulfilling an organization's primary objective. They hold decision-making authority and perform activities that align directly with the company's mission and vision.
On the other hand, staff positions serve in a supporting capacity to these line roles. Their main function is to provide expertise, advice, and assistance to line personnel to ensure smooth operation. These roles may include specialized departments such as human resources, legal, public relations, or any other internal services that support line activities.
Though staff positions don't directly contribute to achieving the organization's main goals like the line positions, they hold equal significance. Their specialized knowledge and skills often offer a new perspective, leading to more efficient and effective decision-making within the organization.
How Does a Line-Staff Organizational Structure Work?
A line-staff organizational structure functions on a unique mechanism where authority and responsibilities are distinctly shared between line and staff positions.
Line positions construct the direct chain of command. Each individual within this chain possesses a distinct role, contributing towards achieving the company's objectives. These line roles might range from senior executives and middle managers to front-line employees. They are the frontline warriors driving the core operations of the organization.
While line positions might take the final decisions based on their authoritative position within the organizational chain, they don't operate in isolation. This is where staff positions step in.
Staff positions operate in an advisory capacity, providing specialized input and insights that help guide decision-making. They act as a reservoir of specialist knowledge within their respective domains. While they don't have direct authority to take critical decisions impacting an organization's goals like the line positions do, their inputs and suggestions are highly valued.
For example, consider a manufacturing company where line roles might include production managers and assembly line workers directly involved in product creation – a primary goal of the organization. Staff roles in such a setting might involve quality assurance personnel who, while not directly involved in product creation, play a pivotal role in ensuring product standards meet industry benchmarks.
This balance between decision-making line positions and supportive staff roles fosters an environment of cooperation within an organization. It facilitates well-rounded decision making, ensuring decisions aren't just focused on achieving primary goals but also take into consideration factors that might indirectly influence these goals.
Pros of a Line-Staff Organizational Structure
The line-staff organizational structure brings a plethora of advantages that can significantly enhance an organization's efficiency and productivity. The benefits it offers span across various areas of organizational operation.
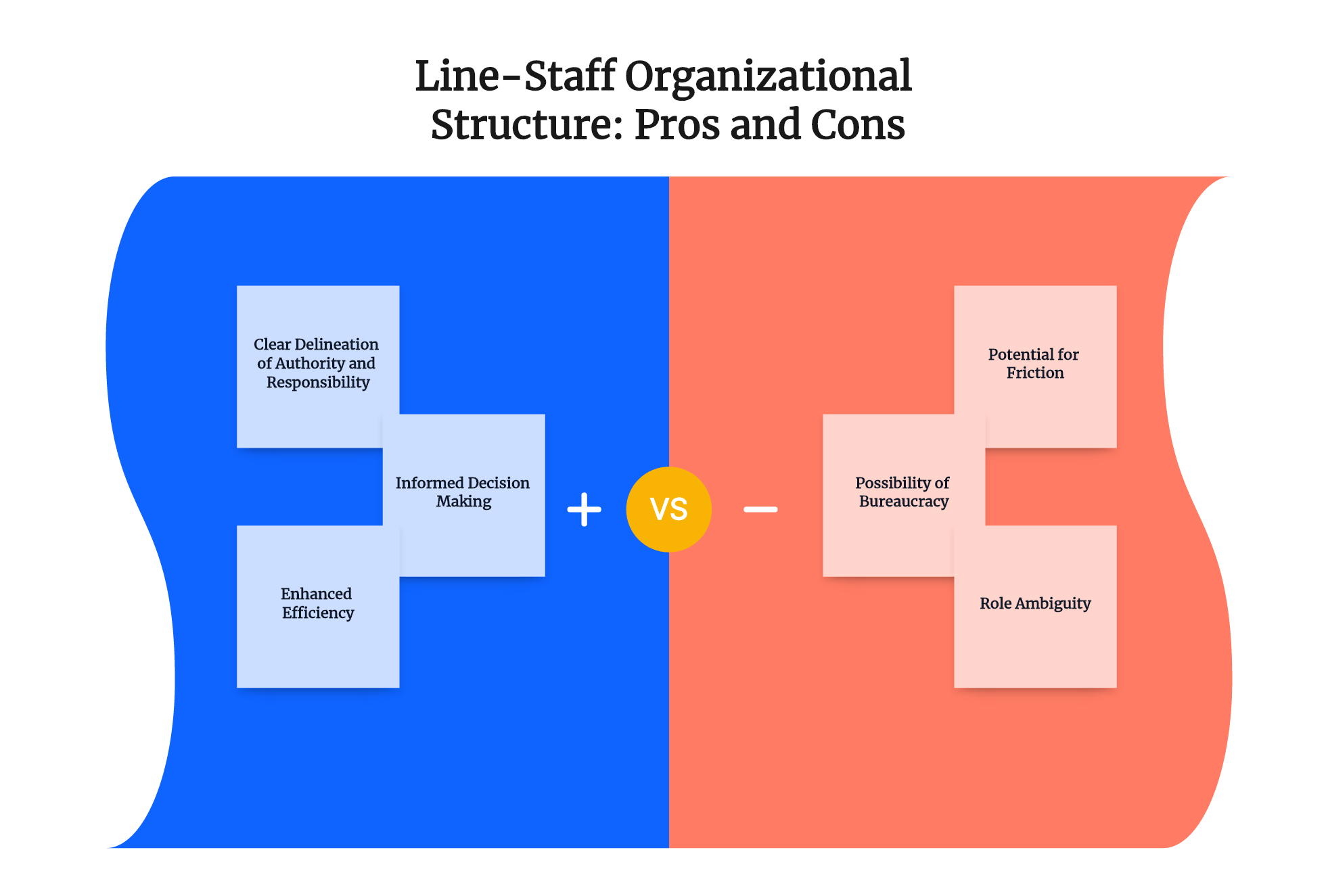
- Clear Delineation of Authority and Responsibility:One of the primary benefits of a line-staff structure is the clear definition of roles and responsibilities. With line positions directly contributing to an organization's primary goals and staff roles serving a supporting function, there is little scope for ambiguity or overlap. This clarity ensures smooth operations and minimizes conflicts over jurisdiction or tasks.
- Informed Decision Making:Line-staff structures inherently foster an environment that facilitates more informed decision making. Staff positions, with their specialized knowledge and expertise, provide valuable insights and suggestions to line positions. This interaction allows decisions to be made based on expert advice, thus enhancing their effectiveness.
- Enhanced Efficiency:By leveraging the specific skills and expertise of staff positions, a line-staff structure promotes operational efficiency. Staff roles support line positions by performing specialized tasks, enabling the latter to focus on their core responsibilities. This clear division of labor results in increased efficiency across the organization.
Cons of a Line-Staff Organizational Structure
Despite the numerous benefits it provides, a line-staff structure does have certain potential drawbacks. It’s crucial to recognize these cons to make an informed choice about the applicability of this structure in specific organizational contexts.
- Potential for Friction:One significant downside of a line-staff organizational structure is the potential for friction between line and staff personnel. Because staff positions don’t contribute directly to the achievement of an organization’s primary goals, line workers may be resistant to their advice. This friction can lead to decreased morale and efficiency if not properly managed.
- Possibility of Bureaucracy:In some instances, a line-staff structure can lead to an overly bureaucratic system. If too much emphasis is placed on maintaining strict delineations between line and staff roles, it may slow down decision-making processes or result in ineffective communication. This rigidity can stifle creativity and innovation.
- Role Ambiguity:Although the line-staff structure typically offers clear role definitions, it can sometimes result in ambiguity over who holds decision-making authority. For instance, staff personnel might be mistaken for having decision-making powers due to their advisory role to the line personnel.
Tips for Using the Line-Staff Organizational Structure
Adopting a line-staff organizational structure can bolster a business's performance, but the real challenge lies in effectively implementing it. This type of organizational structure is inherently complex and requires astute management to maximize its potential benefits. The following tips offer guidance on successfully implementing a line-staff structure.
Ensure Clear Role Definition
A crucial first step when implementing a line-staff structure is ensuring clear role definitions for both line and staff positions. All employees should have a thorough understanding of their responsibilities and the extent of their decision-making authority. They should also understand the responsibilities of their counterparts to avoid confusion and conflict.
Promote Open Communication
Effective communication forms the backbone of a successful line-staff structure. Line and staff personnel must engage in open, respectful dialogue to facilitate informed decision-making. Organizations should promote an open-door policy, where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas, concerns, and suggestions.
Encourage Collaboration
While line positions carry the responsibility of making decisions, it's important to remember that staff roles play a pivotal part in informing these decisions. Encouraging collaboration between the two ensures that decisions are well-rounded and grounded in expert advice. A collaborative environment fosters mutual respect and decreases the chances of friction or misunderstandings.
Provide Training and Development Opportunities
Offer regular training and development opportunities for both line and staff personnel. Staff employees should be provided with the latest industry knowledge to offer valuable advice. Similarly, line personnel should be trained in leadership and decision-making skills.
Acknowledge Contributions of Both Line and Staff Roles
Recognition plays a crucial role in enhancing motivation and productivity. While line positions might seem more critical due to their decision-making power, the contributions of staff positions are equally significant. It's essential that organizations acknowledge the contributions of staff personnel, highlighting their role in the organization's success.
Examples of Line-Staff Organizational Structure in Different Sectors
The line-staff organizational structure is widely utilized across multiple sectors, enabling businesses to optimize their decision-making processes and operational efficiency. By maintaining a careful balance between decision-making authority and specialized expertise, this structure is particularly favorable for organizations operating on a large scale or in dynamic markets. Let's explore some real-world examples of the line-staff organizational structure in action.
McDonald's
Fast-food giant McDonald's operates on a line-staff organizational structure. The line personnel include restaurant managers and crew members responsible for fulfilling the company's primary goal - serving quality food quickly to customers. On the other hand, departments like marketing, human resources, and finance serve as staff roles that provide expert advice and support to these line roles.
For instance, while a restaurant manager (line role) might make decisions regarding daily operations, a human resources professional (staff role) would guide decisions related to hiring or training staff. By efficiently utilizing the expertise of staff roles to support decision-making by line roles, McDonald's has established a highly effective operational structure.
General Electric (GE)
General Electric, one of the world's largest conglomerates, also employs a line-staff structure. At GE, the line positions consist of roles directly responsible for product creation and sales, such as factory managers or sales representatives. Staff roles include departments like legal, finance, or human resources, which offer specialized knowledge and support to line personnel.
This structure has proven highly effective for GE, ensuring efficient use of specialized skills without compromising the decision-making authority of line positions.
Tesla
The renowned electric vehicle manufacturer Tesla also exemplifies a successful application of the line-staff organizational structure. In this context, the line positions include roles like production managers or assembly line workers involved in creating electric vehicles - Tesla's primary business goal. Simultaneously, departments like finance, public relations, or legal operate as staff roles that provide expert advice and guidance to these line positions.
Tesla's line-staff structure supports a clear division of responsibilities and encourages collaboration between roles, facilitating effective and efficient operations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Line-Staff Organizational Structures
What is the difference between a line-staff organization and functional organization?
A functional organization is characterized by grouping employees based on their specialization or function they perform in the company. In contrast, a line-staff organization involves a clear chain of command supported by consultative staff positions.
Are there any alternatives to a line-staff organizational structure?
Yes, there are several alternatives like the Hierarchical structure, Functional structure, Matrix structure, and Network structure. To get a deeper understanding of these different organizational structures, check out this article: 8 Types of Organizational Structures for Businesses.