Venturing into the vast landscape of project management, one is bound to encounter a multitude of methodologies, each with its unique approach and benefits. Among these diverse methodologies, Scrum emerges as a particularly compelling choice. This agile framework, renowned for its ability to deliver substantial value swiftly throughout a project's lifecycle, has been widely adopted across industries. It offers an innovative approach to managing complex projects effectively. As we navigate through this comprehensive guide, we aim to provide a deeper understanding of what Scrum in project management truly means and how it can revolutionize your project execution strategies.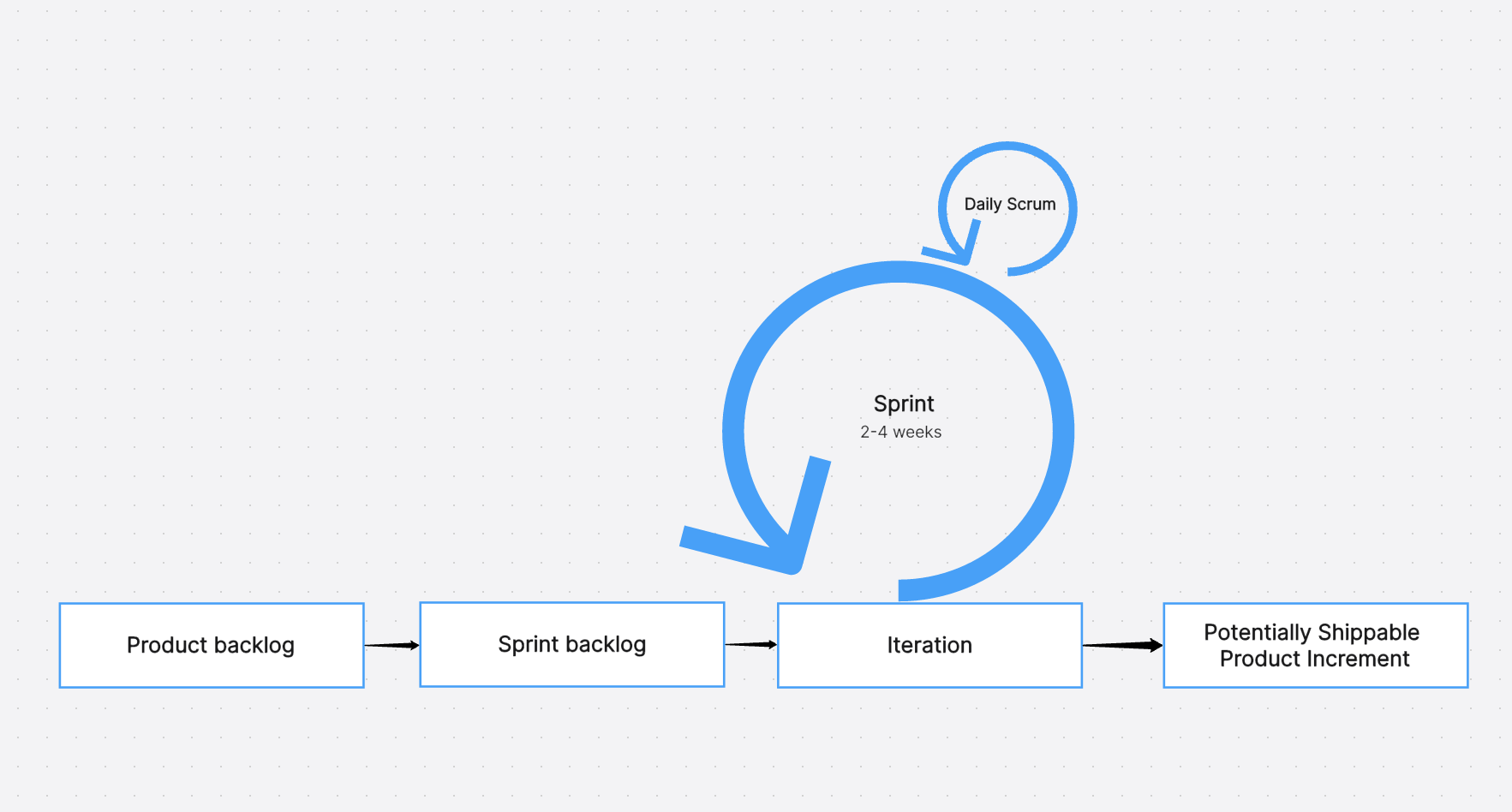
Part 1. What Is Scrum in Project Management?
Scrum is an iterative and incremental agile software development framework that has been specifically designed to manage product development. It places a strong emphasis on flexibility, fostering a culture of collaboration, and ensuring customer satisfaction. Originating from the principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto, Scrum promotes a self-organizing team structure. This structure encourages teams to either physically co-locate or maintain close online collaboration among all team members. A key aspect of this methodology is the practice of daily face-to-face communication among all team members, which fosters transparency and quick resolution of issues. This unique approach allows for rapid adjustments based on feedback and changing requirements, thereby ensuring that the end product aligns closely with customer needs and expectations.
Part 2. What Are the Roles of Scrum in Project Management?
Within the dynamic environment of Scrum, three critical roles form the backbone of any project:
The Product Owner: The visionary of the team, the Product Owner defines and communicates the product's vision. They are responsible for prioritizing tasks based on business value and customer needs, ensuring that everyone is aligned with the end goal.
The Scrum Master: Acting as a facilitator and coach, the Scrum Master ensures that everyone adheres to Scrum theories and practices. Their role involves removing obstacles that may hinder the team's progress and promoting an environment conducive to high productivity.
The Development Team: This group consists of cross-functional professionals who collaborate intensively to deliver potentially shippable increments at the end of each sprint. Their collective skills and efforts translate into tangible results that drive project success.
Part 3. What Are Scrum Principles in Project Management?
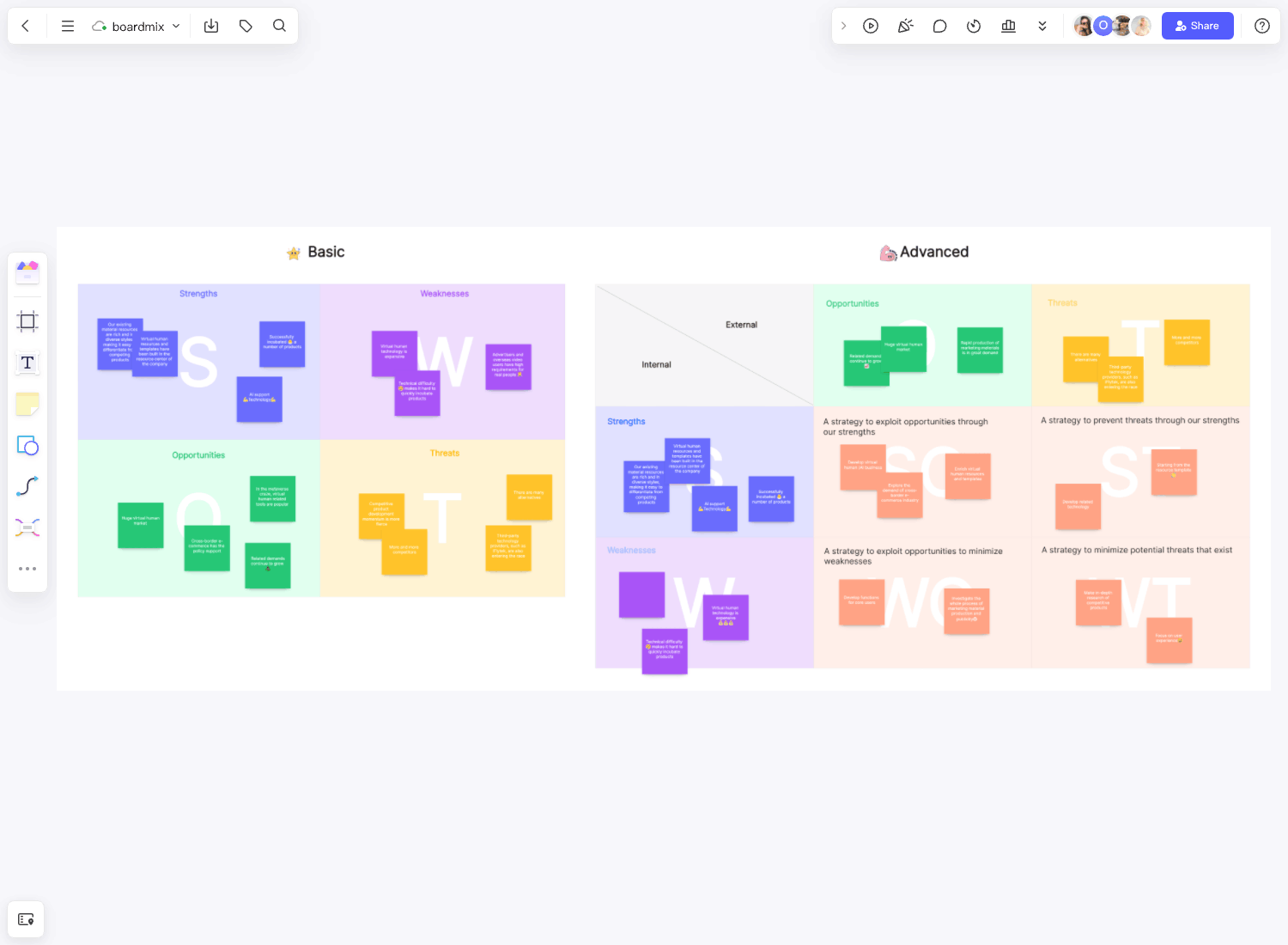
Delving deeper into the core of Scrum, we encounter five fundamental principles that guide its implementation. These principles form the bedrock of this agile methodology and are crucial to its success.
- Transparency: This principle ensures that all information about the project is visible to all team members. It fosters an open and honest environment where everyone has a clear understanding of the project status, tasks, and progress.
- Inspection: Regular checks on progress towards a goal are integral to Scrum. These inspections help identify any deviations from the plan early on and allow for timely corrective actions.
- Adaptation: If accepted standards or goals are not being met, adjustments are made promptly. This flexibility allows teams to adapt to changes or unforeseen challenges without derailing the entire project.
- Iterative Progress: Work in Scrum is divided into small parts or iterations known as sprints. Each sprint results in a potentially shippable increment, allowing for regular feedback and adjustments.
- Incremental Delivery: Delivering work in smaller pieces allows for quicker feedback and reduces the risk associated with large-scale changes or updates. It also ensures that value is delivered continuously throughout the project lifecycle.
Part 4. Techniques for Scrum Project Management
Scrum methodology incorporates a variety of effective techniques that facilitate smooth project execution. Here are some of the most popular ones:
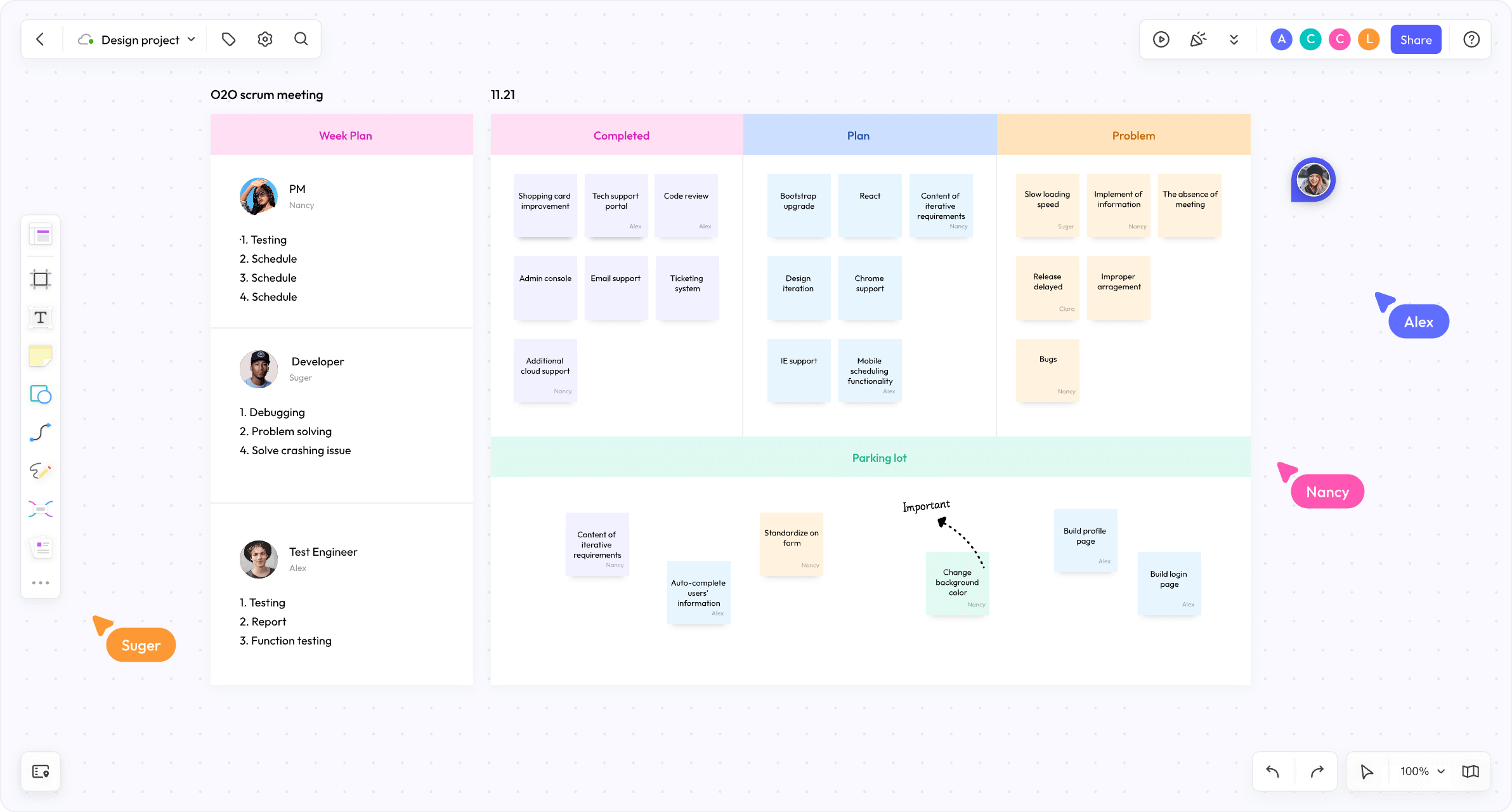
- Daily Stand-up Meetings: These are short, daily meetings where team members provide status updates and discuss any potential roadblocks. This fosters transparency and ensures everyone is aligned with the day's objectives.
- Sprint Planning Meetings: At the onset of each sprint, these meetings are held to allocate tasks for the upcoming period. Team members collaborate to define the sprint goal and decide on the user stories that will be tackled.
- Sprint Reviews: Conducted at the end of each sprint, Sprint Reviews involve inspecting the increment towards goals and demonstrating the work done. Stakeholders provide feedback which can influence future sprints.
- Retrospective Meetings: These meetings offer a platform for reflecting on past sprints - what went well, what didn't, and what could be improved in future sprints. It's an opportunity for continuous improvement within the team.
- Backlog Refinement (Grooming): This ongoing process involves updating user stories or adding new ones to ensure that the product backlog remains relevant and prioritized according to business value or customer needs.
Part 5. Pros and Cons of Scrum Project Management
Having explored the principles and techniques of Scrum, it's important to weigh its potential benefits against its drawbacks. This will provide a balanced view and help determine if it's the right fit for your project or organization.
Pros of Scrum
- Increased Productivity: By breaking down complex projects into manageable sprints, teams can focus on high-priority tasks first, leading to increased productivity.
- Improved Quality: Regular feedback loops and incremental delivery allow for constant improvements and adjustments, resulting in a higher quality end product.
- Reduced Time-to-Market: With work being delivered incrementally, products or features can be launched faster and more frequently.
However, like any methodology, Scrum is not without its challenges. Here are some potential cons to consider:
Cons of Scrum:
- Difficulty Predicting Project Timelines: Due to its iterative nature, predicting timelines in Scrum can be challenging as changes may occur during the project lifecycle.
- Potential Scope Creep: Without detailed specifications from the outset, there's a risk of scope creep - where the project's requirements start to increase beyond its original goals.
- Requires Commitment and Collaboration: For Scrum to work effectively, it requires a high level of commitment from all team members and close collaboration. This may not suit all organizations or team dynamics.
Part 6. What Is the Difference Between Scrum and Kanban?
Both Kanban and Scrum are Agile methodologies that prioritize delivering increments of work. However, they differ significantly in their approach to achieving this goal. Here's a more detailed comparison:
- Approach to Delivery: Kanban focuses on continuous delivery while ensuring that team members are not overloaded with tasks. It emphasizes flow and aims to reduce the time it takes for a task to move from the 'start' point to the 'finish' point.
- Work Cycles: On the other hand, Scrum operates in fixed-length iterations known as sprints, typically lasting two weeks or a month. Each sprint results in a potentially shippable increment of work.
- Roles: Scrum assigns specific roles such as Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team who have distinct responsibilities within the project. In contrast, Kanban does not prescribe any specific roles.
- Change Philosophy: While Scrum discourages changes within a sprint, Kanban is more flexible and allows for changes at any time as long as there's capacity within the system.
- Measurement of Progress: Scrum measures progress based on the amount of work completed in each sprint (velocity). In contrast, Kanban focuses on the cycle time or how long it takes for an individual task to be completed.
These differences highlight that while both methodologies aim for efficient project management, they offer different paths suitable for different team structures and project requirements.
Part 7. Boardmix Streamlines Scrum Project Management
As we wrap up our deep dive into the Scrum project management methodology, it's time to introduce a tool that can seamlessly integrate with your Scrum practices - Boardmix. This online whiteboard tool is designed with an array of features tailored to streamline your Scrum projects.
Boardmix comes equipped with intuitive templates specifically designed for planning sprints, conducting retrospective meetings, and more. These features are crafted to make your Scrum journey smoother and more efficient. Whether you're brainstorming ideas, mapping out tasks, or tracking progress, Boardmix provides a visual and interactive platform that can enhance collaboration and communication within your team.
We strongly recommend users leverage the capabilities of Boardmix to elevate their project management experience. By integrating this tool into your Scrum practices, you can effectively visualize your workflow, keep track of tasks and goals, and foster a more productive and collaborative environment for your team.