In the bustling corporate world, the art of managing stakeholders is not only a necessity, but a science that can streamline decision-making, enhance corporate transparency, and foster sustainable growth. As the backbone of organizational success, effective stakeholder management aligns the objectives of different parties with business strategies. This comprehensive guide will delve into the realm of stakeholder management and shed light on its multiple facets, techniques, and applications.
What is Stakeholder Management?
Stakeholder management, in essence, is an analytical approach employed by organizations to manage, influence and understand stakeholders. It serves as an insightful tool to determine the expectations and potential influence of various parties associated with the company. To simplify further, it is a tactical way to ensure that all interested parties are heard, their concerns addressed, and interests aligned with the business trajectory.
Rooted in strategic planning and communication, stakeholder management navigates relationships with entities that either affect or are affected by an organization's actions. It spans shareholders, employees, customers, suppliers, government entities, and more. This umbrella term encompasses activities such as stakeholder identification, prioritization, analysis, planning, and engagement.
Benefits of Stakeholder Management
Implementing effective stakeholder management within a business environment can have substantial pay-offs, often beyond what many organizations anticipate.
- Enhanced Communication:First and foremost, it serves to open up avenues for dialogue between the company and its stakeholders. This line of communication creates a symbiotic relationship wherein the organization learns from the insights, experience, and perspectives of its stakeholders, and in return, the stakeholders stay informed about the decisions and progress of the company. It fosters an environment of trust, leading to better collaboration and conflict resolution.
- Informed Decision-making:Engaging with stakeholders equips businesses with a holistic view of their operations from multiple perspectives. As a result, companies can make more informed decisions that are likely to receive broad support. This boosts the likelihood of successful implementation of initiatives and projects.
- Improved Reputation:Effective stakeholder management also significantly enhances a company's reputation. By ensuring transparency and active engagement with stakeholders, businesses can present themselves as credible entities that value stakeholder input, thereby strengthening their brand image.
- Risk Management:Another significant benefit is in risk management. By understanding stakeholder expectations and potential roadblocks they may present, organizations can proactively strategize to mitigate risks. It allows companies to anticipate and respond more swiftly to potential problems, thereby preventing escalation and damage.
- Increased Stakeholder Buy-in:Lastly, strong stakeholder management ensures that all parties feel valued and invested in the organization's mission and goals. When stakeholders feel they are heard and their inputs are incorporated into decision-making processes, they are more likely to support the organization, leading to increased buy-in and commitment.
Thus, stakeholder management goes beyond maintaining positive relationships; it creates a virtuous cycle where all parties feel engaged and invested, ultimately driving the organization towards its objectives with a united front.
Stakeholder Management Process
The stakeholder management process is a well-defined roadmap guiding businesses to engage with stakeholders effectively. It includes the following stages:
Stakeholder Identification
At the core of any successful stakeholder management process is accurate and thorough stakeholder identification. This initial stage revolves around recognizing everyone who can potentially influence or be affected by the organization's decisions or activities.
Understanding Stakeholders
Stakeholders, in a broader sense, encompass a wide array of entities. They can be individuals, teams, organizations or even entire communities that have an interest or concern in the outcomes of a company's actions. They might be directly involved with the organization or indirectly linked.
Internal Stakeholders
These include employees, management, and board members within the organization. They are an integral part of the company, directly contributing to its functioning and outcomes. Their concerns, suggestions, and involvement can significantly influence company decisions.
External Stakeholders
On the other hand, external stakeholders might not be directly involved in daily operations but still possess a vested interest in the company's decisions. This category includes clients or customers, suppliers, investors, government agencies, community groups, and more. Their input can also wield considerable influence over strategic decisions.
Creating a Stakeholder List
The stakeholder identification process involves creating a comprehensive list of all these potential stakeholders. The goal is to leave no stone unturned – all possible entities that have some stakes in the organization need to be noted down. This is the base upon which the subsequent stages of stakeholder management will build.
Creating a Stakeholder Mind Map
Creating a mind map can be a highly effective tool for stakeholder identification. A mind map visually organizes information, making it easier to comprehend and track stakeholders. The organization is at the center of the map, and various branches stemming from it represent different stakeholder categories and sub-categories.
Stakeholder Prioritization
Once identified, the stakeholders need to be prioritized. As resources and time are often limited, not all stakeholders can be attended to equally. Prioritization helps allocate attention where it's needed the most. Factors to consider include their level of influence, urgency of their needs, and their potential impact on the company's operations. By evaluating and ranking these factors, companies can categorize their stakeholders into groups like high priority, medium priority, and low priority.
Stakeholder Analysis & Mapping
Stakeholder analysis and mapping are critical steps that delve into the understanding of stakeholders' perspectives, influence, interests, and potential impact on the organization. This stage paves the way for tailored engagement strategies and fosters positive relationships.
Stakeholder Analysis
A stakeholder analysis explores each stakeholder's needs, expectations, and potential influence. Companies can adopt several methods to gather this information, like surveys, interviews, focus groups, or public data. The collected data serves as the base to comprehend the following elements:
- Stakes: What interest or claim does the stakeholder have in the organization's decisions or projects?
- Influence: Does the stakeholder have the power to impact the organization's decisions? If so, to what extent?
- Attitudes: What is the stakeholder's attitude towards the organization's projects or decisions - positive, neutral, or negative?
- Communication Preferences: How does the stakeholder prefer to receive information - via meetings, emails, newsletters, etc.?
Stakeholder Mapping
After the analysis comes the process of stakeholder mapping - visually displaying the importance of stakeholders based on their influence and interest. Some commonly used tools are RACI Matrix, Power/Interest Grid, and Influence/Impact Matrix.
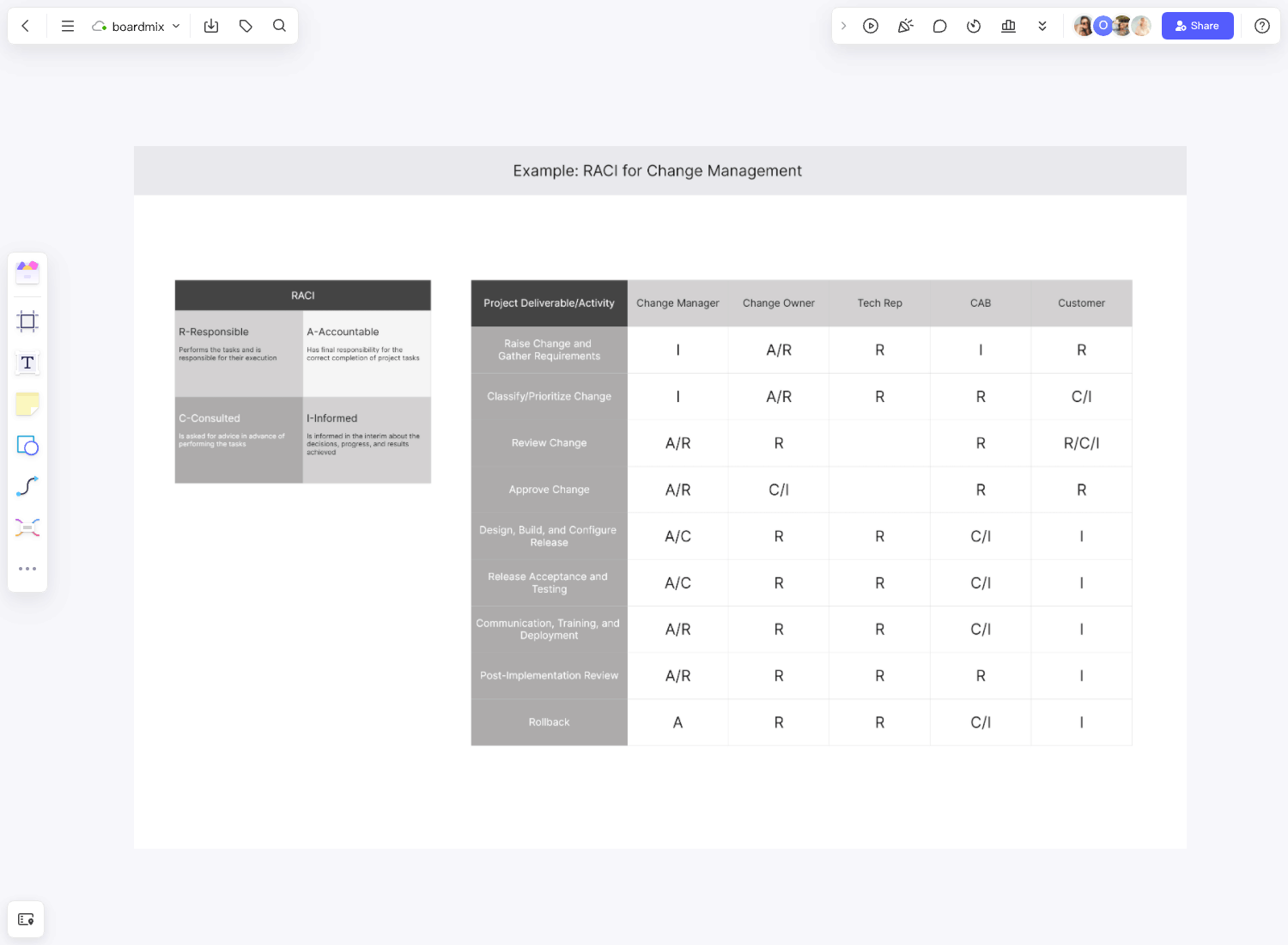
RACI Matrix
The RACI matrix stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed. It helps assign roles and responsibilities to stakeholders based on their involvement in a project or decision-making process. A simplified example could look like this:
This matrix provides a clear picture of who should be informed about progress (I), who needs to give advice (C), who is completing the tasks (R), and who has the final decision (A) for each project or decision.
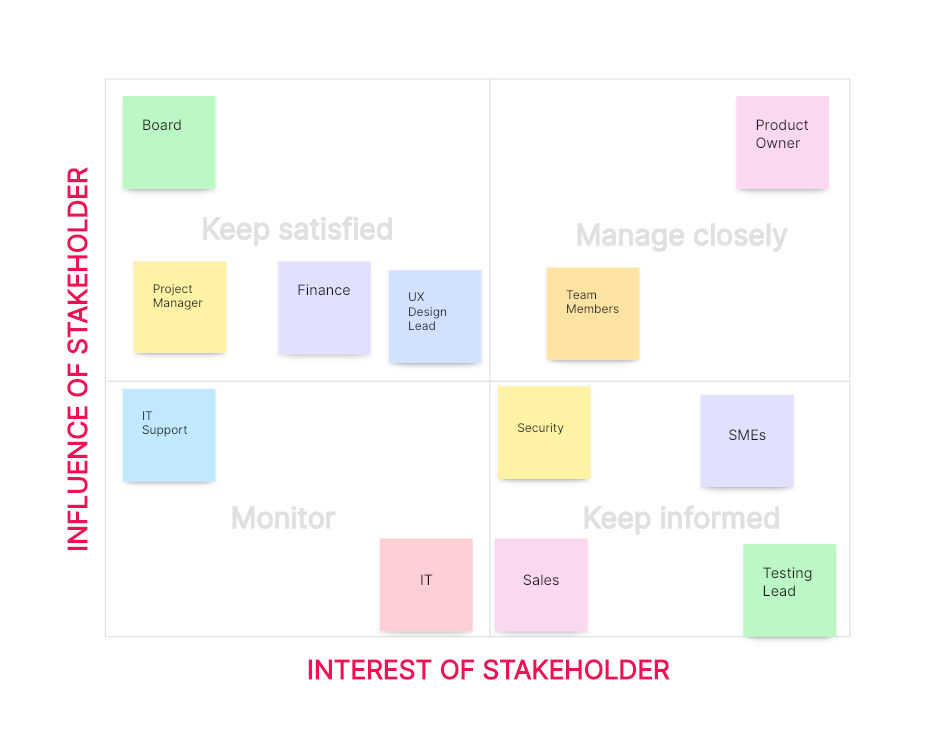
Power/Interest Grid
The Power/Interest Grid, also known as the Salience Model, categorizes stakeholders based on their power (ability to influence) and interest (level of concern) regarding an organization’s actions. An example is as follows:
Stakeholders in the 'High Power, High Interest' quadrant like Product Owner are the most influential and require maximum attention.
Influence/Impact Grid
The Influence/Impact grid identifies stakeholders based on their capacity to influence a project versus their potential to be impacted by it.
Stakeholders with 'High Influence, High Impact' are both heavily affected by the organization's decisions and wield significant sway over them.
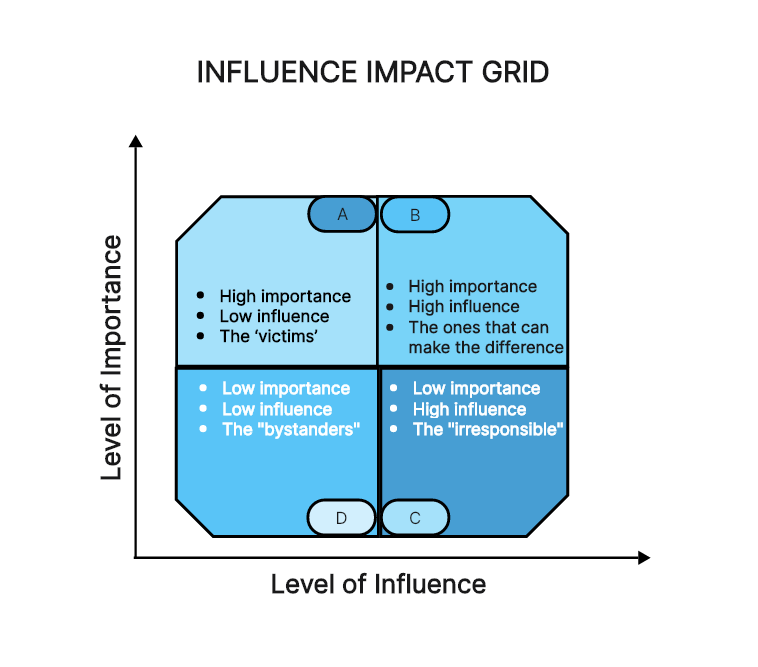
By conducting thorough stakeholder analysis and effective mapping, organizations can align their stakeholder engagement strategies with the stakeholders' needs and expectations, fostering meaningful relationships.
Stakeholder Planning
Stakeholder planning is the strategic blueprint that outlines how an organization will engage with its various stakeholders. The aim is to address their needs, meet their expectations, mitigate conflicts, and secure their support for the company's projects. This process usually involves several steps:
- Set Objectives:Determine what you hope to achieve from each stakeholder relationship. Are you seeking their input, approval, or simply keeping them informed?
- Develop Engagement Strategies:Decide how to engage with different stakeholders. For instance, for high-priority stakeholders like major investors, regular face-to-face meetings might be essential. However, for lower-priority stakeholders like suppliers, periodic emails could suffice.
- Create Communication Plans:Develop comprehensive communication plans specifying the frequency, mode, and content of your communication with each stakeholder group. For example, employees may need weekly project updates, while customers may prefer quarterly newsletters.
- Define Key Messages:Identify what you want to communicate to each stakeholder group. Ensure these messages align with your objectives.
- Allocate Responsibilities:Assign who in the organization will be responsible for managing each stakeholder relationship. This could be project managers, team leads, or the communications department.
- Plan for Contingencies:Prepare for potential risks or changes in stakeholder dynamics. This includes identifying possible challenges and having backup plans in place.
Stakeholder Engagement
After planning comes stakeholder engagement - the execution phase of the stakeholder management process. Here are the main elements of effective stakeholder engagement:
- Open Communication:Engage with your stakeholders as planned, keeping lines of communication open and ensuring transparency. This could range from conducting town hall meetings for employees to sending out regular newsletters for customers.
- Active Listening:Pay attention to the feedback and concerns voiced by your stakeholders. Actively responding to their input helps build trust and positive relationships.
- Addressing Stakeholder Needs:Keep working on addressing your stakeholders' needs and meeting their expectations as identified during the analysis phase.
- Managing Conflicts:Conflicts can arise in any relationship. Prompt and respectful handling of disputes can prevent small issues from ballooning into major problems.
- Stakeholder Inclusion:Include stakeholders in relevant decision-making processes when appropriate. This helps them feel valued and invested in your organization's success.
Tips & Techniques for Effective Stakeholder Management
Mastering stakeholder management involves more than just understanding its steps; it also requires an array of soft skills and a proactive approach. Here are some proven tips and techniques for successful stakeholder management:
Build Trust through Transparency
Transparency builds trust in any relationship, and the same goes for stakeholders. Honest and open communication about your plans, projects, and decisions, including both successes and failures, fosters trust among stakeholders. This means not just delivering good news but also addressing issues and concerns promptly.
Prioritize Stakeholder Relationships
Not all stakeholders are created equal; some may have more interest or influence than others. Use tools like the Power/Interest Grid to categorize and prioritize your stakeholders. Devote more time and resources to those with high interest and high power.
Adopt a Proactive Approach
Don’t wait for problems to arise before engaging with your stakeholders. Regular interaction helps you stay ahead of potential issues. Use platforms that are convenient for your stakeholders and conducive to open dialogue.
Utilize Empathy and Active Listening
Understanding your stakeholders’ perspectives can lead to stronger, more productive relationships. Listen attentively to their needs, suggestions, and concerns. Responding thoughtfully shows you value their input and can pave the way for collaboration.
Establish Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Clarity in roles and responsibilities can minimize confusion and misunderstandings. Tools like RACI matrix help outline who’s responsible for what within the organization.
Manage Expectations
Avoid promising more than you can deliver. It's better to under-promise and over-deliver than vice versa. Keeping expectations realistic helps maintain a positive rapport with stakeholders.
Regular Reviews and Adjustments
Stakeholder management isn’t a one-off task but an ongoing process. Regularly review your strategies, plans, and relationships, making necessary adjustments to address changes in stakeholder dynamics.
To boost the effectiveness of your stakeholder management, consider utilizing dedicated tools like Boardmix, a leading stakeholder map maker. It helps streamline the process, ensuring efficient identification, analysis, planning and engagement.
Take Your Stakeholder Management to the Next Level
Supercharging stakeholder management can have profound impacts on organizational success. By maintaining positive stakeholder relations and aligning stakeholders’ needs with organizational goals, companies can achieve heightened collaboration, minimized conflicts, and increased credibility in the market. Leverage the information presented here to revolutionize your stakeholder management process and steer your organization towards unprecedented heights.
Remember, engaging stakeholders is not just a process—it’s an art that could be the secret to your business success.