In an era where collaboration is king and teamwork is the name of the game, the team-based organizational structure emerges as a game-changing trend in the business world. Although no one-size-fits-all organizational structure exists, the team-based model seems to fit snugly into a broad spectrum of businesses that aim to encourage collaboration, foster innovation, and enhance productivity.
What is a Team-Based Organizational Structure?
A team-based organizational structure, at its heart, is about collaboration and integration. This particular type of system veers away from the more traditional, top-down hierarchy commonly seen in businesses. It revolves around the concept of grouping employees into teams or groups, typically around projects or products, each with a specific purpose and goal.
In a team-based organizational structure, teams are usually cross-functional, pooling together employees with varying skills and expertise to address all aspects of the project. This encourages a holistic approach to problem-solving where different perspectives, knowledge areas, and skill sets unite to drive growth and innovation.
More than just an operational blueprint, this structure signifies a significant shift in company culture. It values every member's contribution regardless of rank or title. In the process, it champions diversity and fosters an inclusive work environment that encourages everyone to participate in decision-making processes. As such, employees in these structures often report higher job satisfaction and commitment.
The formation of teams can be permanent, temporary, or even dynamic in nature. Permanent teams are ongoing and may revolve around specific business functions or products. Temporary teams, on the other hand, exist for a limited time period, primarily focusing on accomplishing specific projects or tasks. Dynamic teams consist of members who fluidly move in and out based on the expertise needed at any given time.
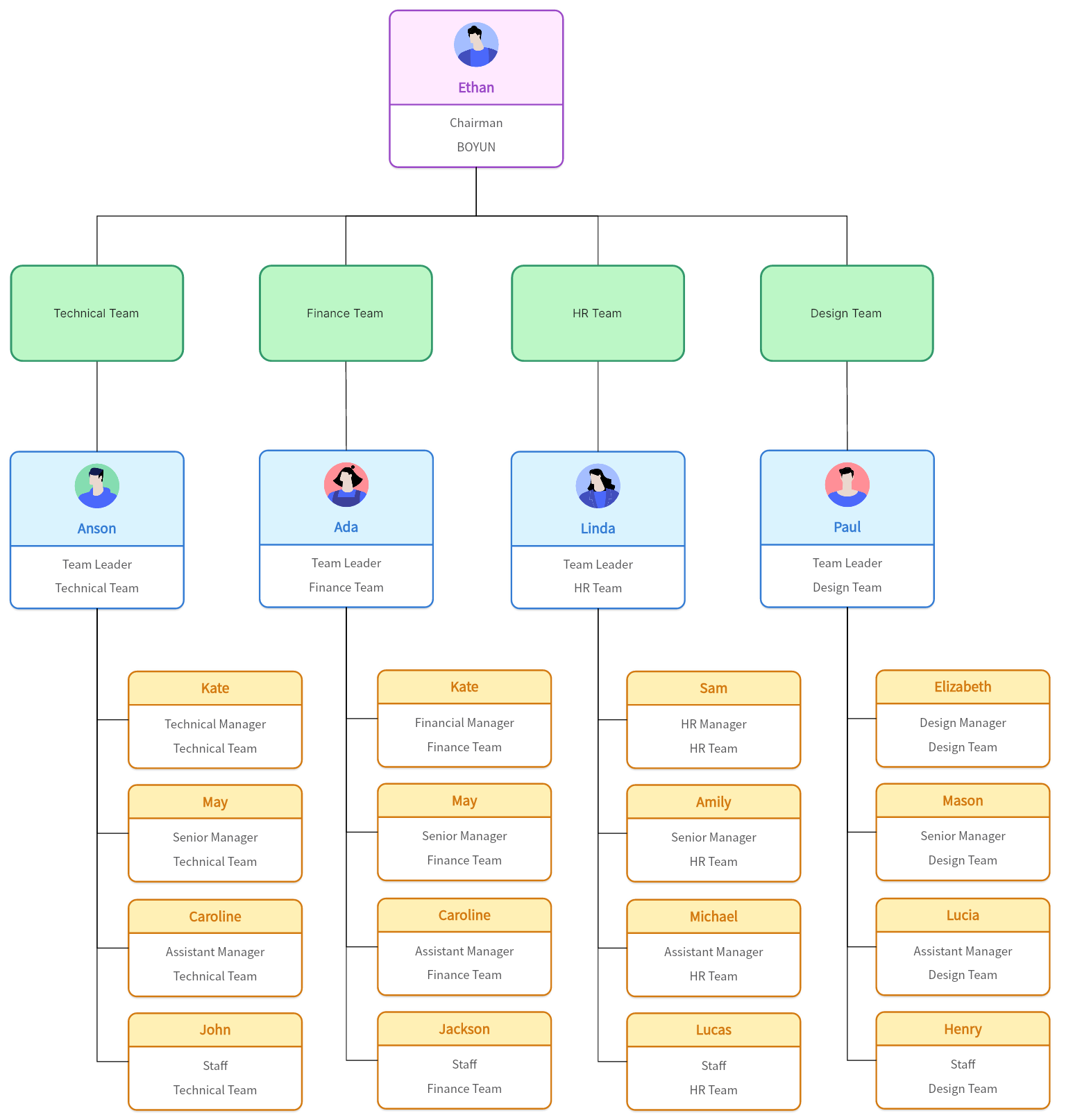
How Does a Team-Based Organizational Structure Work?
The functionality of a team-based organizational structure is deeply rooted in collaboration and equality. Rather than maintaining a vertical hierarchy with distinct levels of power, authority is spread more evenly amongst the team members.
In this setup, leaders take on more of a facilitator's role than an authoritative one. The objective is to ensure that every member's skills and insights are harnessed optimally and decisions are made collectively.
The collaborative ethos of the team-based model promotes active participation from all members, encouraging them to contribute ideas, express concerns, and work together towards common goals. Each team is generally autonomous, taking ownership of their specific projects or tasks. The breakdown of tasks is based on each member's skills, knowledge, and expertise rather than their titles or hierarchical position.
By breaking down silos between departments or roles, team-based structures create a work environment that promotes learning from each other. They also encourage faster decision-making as bureaucratic red tape is reduced with the removal of numerous hierarchical levels.
Moreover, this kind of organizational structure often implements feedback loops that allow for quick course correction whenever necessary. Regular meetings and discussions are held to check progress, discuss challenges faced by the team, brainstorm solutions, and refine strategies if needed.
Advantages of Team-Based Organizational Structures
Team-based organizational structures come with a wealth of benefits that can help organizations unlock the full potential of their workforce. These structures are particularly noted for fostering a dynamic and engaging work environment that encourages cooperation, mutual respect, and shared responsibility. Below, we dive into some of the most significant advantages:
- Improved Communication: Team-based structures naturally promote robust communication by encouraging team members to work closely together. In this type of organizational structure, regular team meetings and open dialogues become the norm, paving the way for clear, concise, and effective communication. This can significantly improve understanding and alignment within the team, which in turn, leads to fewer misunderstandings and faster problem-solving.
- Increased Flexibility: Unlike rigid hierarchical structures, team-based ones offer much-needed flexibility. These structures have an inherent ability to adapt quickly to changing market conditions or business dynamics, due to the distributed authority and the lack of bureaucratic red tape. Furthermore, as teams are usually built around projects or products rather than rigid department lines, it's easier to scale up or down, restructure, or even pivot entirely in response to business needs.
- Higher Productivity: By grouping diverse skills and perspectives together, team-based structures often witness a boost in productivity levels. The collaboration fosters an environment where tasks are divided according to each member's strengths, thereby maximizing efficiency. Moreover, the collective responsibility and camaraderie often result in high morale and motivation levels within teams, further fueling productivity.
- Enhanced Innovation: The essence of innovation lies in combining different perspectives, experiences, and skills – which is exactly what team-based structures do. By bringing together cross-functional individuals, these structures cultivate a rich breeding ground for innovative ideas and fresh thinking. This promotes creative problem-solving and encourages teams to explore out-of-the-box solutions for business challenges.
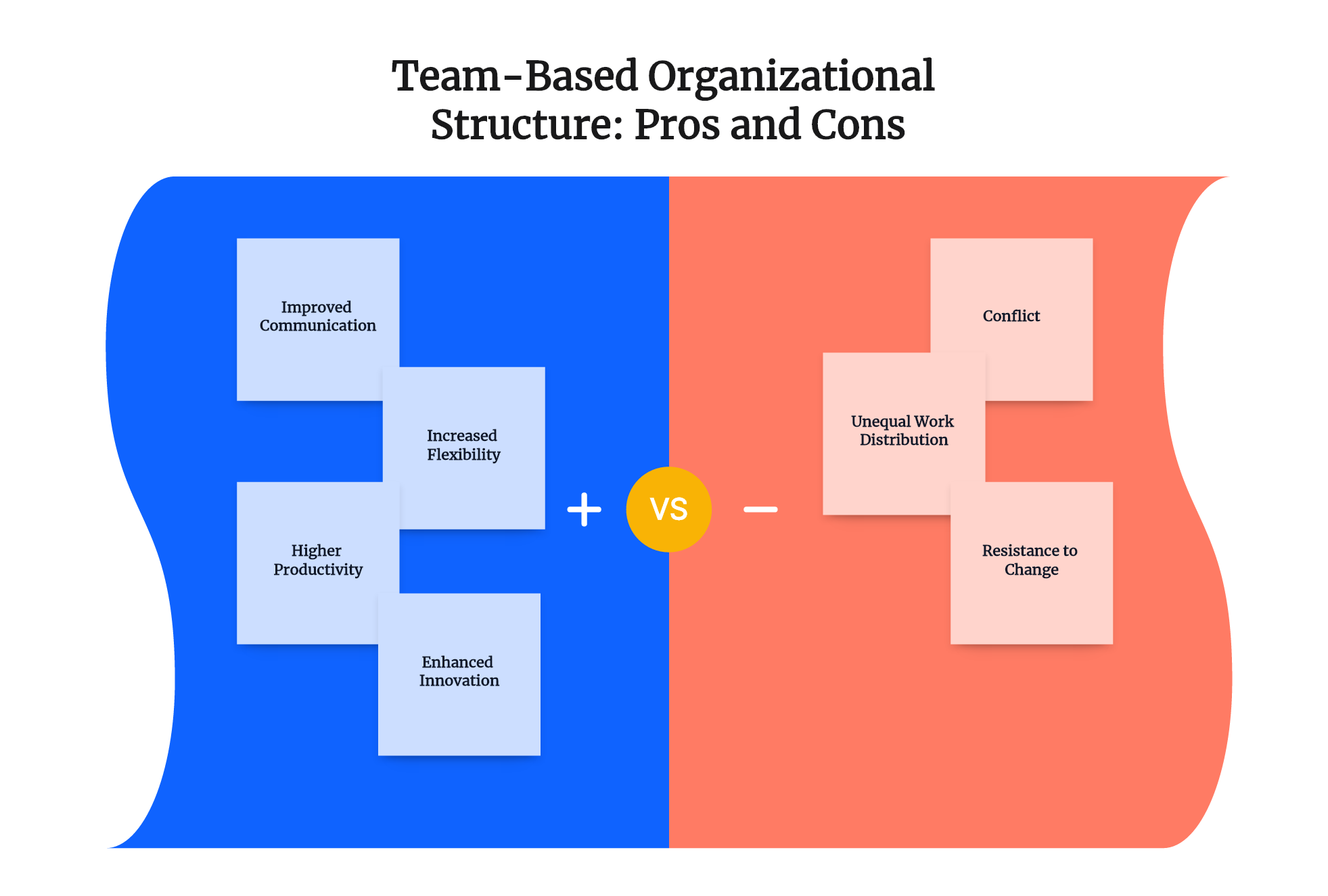
Disadvantages of Team-Based Organizational Structures
While team-based organizational structures offer substantial advantages, they are not without their potential drawbacks. Like any organizational model, this structure too has its own set of challenges that organizations should be aware of when considering its adoption. Let's delve deeper into these disadvantages:
- Conflict: Group dynamics can be complex and unpredictable. Differences in opinions, working styles, or personal values can lead to disagreements or conflicts within the team. Without proper conflict resolution strategies in place, these disputes can escalate, creating a tense work environment that hampers productivity and impedes team cohesion. Furthermore, in a team where everyone has a say, decision-making processes could potentially be drawn out due to differing viewpoints.
- Unequal Work Distribution: While the aim of team-based structures is to divide tasks based on individual strengths, there can be instances where workload distribution becomes unbalanced. Some team members may end up shouldering more responsibility than others, leading to feelings of resentment and decreased morale. On the flip side, some members might not be sufficiently challenged or utilized, causing them to disengage.
- Resistance to Change: Change is often met with resistance, and transitioning from a traditional hierarchical structure to a team-based one is no exception. Employees accustomed to clear-cut job roles and well-defined hierarchies might find the shift challenging. Moreover, those who were comfortable with their status and power in the old system might resist relinquishing their authority in a more democratic setting.
Tips for Using the Team-Based Organizational Structure
Adopting a team-based organizational structure necessitates thoughtful strategizing and implementation. To effectively navigate the transition and leverage the full potential of this model, consider the following practical tips:
- Clearly Define Team Roles and Responsibilities: With the dissolution of traditional hierarchy in a team-based structure, it's crucial to clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each team member. While a certain degree of fluidity is encouraged to facilitate adaptability, team members should have a clear understanding of what's expected of them. This promotes accountability and keeps everyone on the same page, reducing the risk of confusion or misunderstandings.
- Establish Performance Metrics Based on Team Results: Traditional performance metrics often focus on individual achievements. However, in a team-based structure, it's more relevant to assess team performance. Establishing clear, measurable, and objective performance indicators based on collective results encourages teamwork and aligns everyone towards a common goal. It's important to ensure that these metrics are fair, transparent, and understood by all team members.
- Encourage Open and Transparent Communication: In a collaborative environment, open and transparent communication is key. Fostering a culture that encourages team members to share their ideas, feedback, concerns, and insights without fear of retribution builds trust and improves team dynamics. Regular meetings, brainstorming sessions, or simply an open-door policy can promote free-flowing communication.
- Provide Resources for Team Development and Bonding: The strength of a team lies in its unity and mutual respect among members. To build strong, high-performing teams, invest in team development and bonding activities. This could include workshops, training sessions, team-building exercises, or social events. Providing such opportunities not only helps improve team skills but also fosters camaraderie and strengthens interpersonal relationships.
Examples of Team-Based Organizational Structure
The team-based organizational structure has proven to be effective across various sectors, enhancing collaboration, productivity, and innovation. Numerous high-profile companies across diverse industries have adopted this approach, tailoring it to their unique operational requirements and strategic objectives. Let's take a look at how some well-known companies implement a team-based structure:
Spotify: One of the most cited examples of a company adopting a team-based structure is Spotify. The global music streaming service is known for its unique model that comprises squads, tribes, chapters, and guilds. A 'squad' is essentially a small, cross-functional team that works autonomously on specific aspects of the product, while 'tribes' are collections of squads that work on related features. 'Chapters' are Spotify's take on line management, and 'guilds' are informal networks for sharing knowledge. This structure fosters agility, encourages cross-pollination of ideas, and keeps the company responsive to changing user needs.
Google: Google is another company that has successfully implemented a team-based structure. Known as the '20% time' rule, Google allows its engineers to spend 20% of their time working on projects that interest them outside their regular job duties. This practice not only breaks down silos and promotes collaboration but also encourages innovation. It has even led to the development of some of Google's most popular services like Gmail and AdSense.
Amazon: Amazon uses a variant of the team-based structure known as 'two-pizza teams'. The concept is simple: every internal team should be small enough that it could be fed with two pizzas. This keeps teams manageable and promotes efficient communication and decision-making. With this model, Amazon has managed to scale massively while maintaining the agility and innovative spirit of a startup.
Other Types of Organizational Structures
In addition to the team-based organizational structure, several other structures are prevalent across different sectors and industries. Let's delve into the distinctive features and attributes of each one, comparing them with the team-based structure.
Hierarchical Structure:This traditional organizational structure is characterized by a top-down approach, where authority and decision-making power are concentrated at the top levels. It typically consists of clearly defined ranks and roles, with each layer reporting to the layer above. While this structure offers clear roles and responsibilities, it lacks the flexibility and collaboration inherent in a team-based structure. The hierarchical structure can often lead to silos, slowing down decision-making processes.
Functional Structure:In a functional organizational structure, employees are grouped based on their specialties or roles, such as finance, marketing, human resources, etc. While this structure allows for in-depth focus and skill development within each function, it can lead to communication barriers between different departments. Conversely, in a team-based structure, cross-functional teams work collaboratively, breaking down departmental silos.
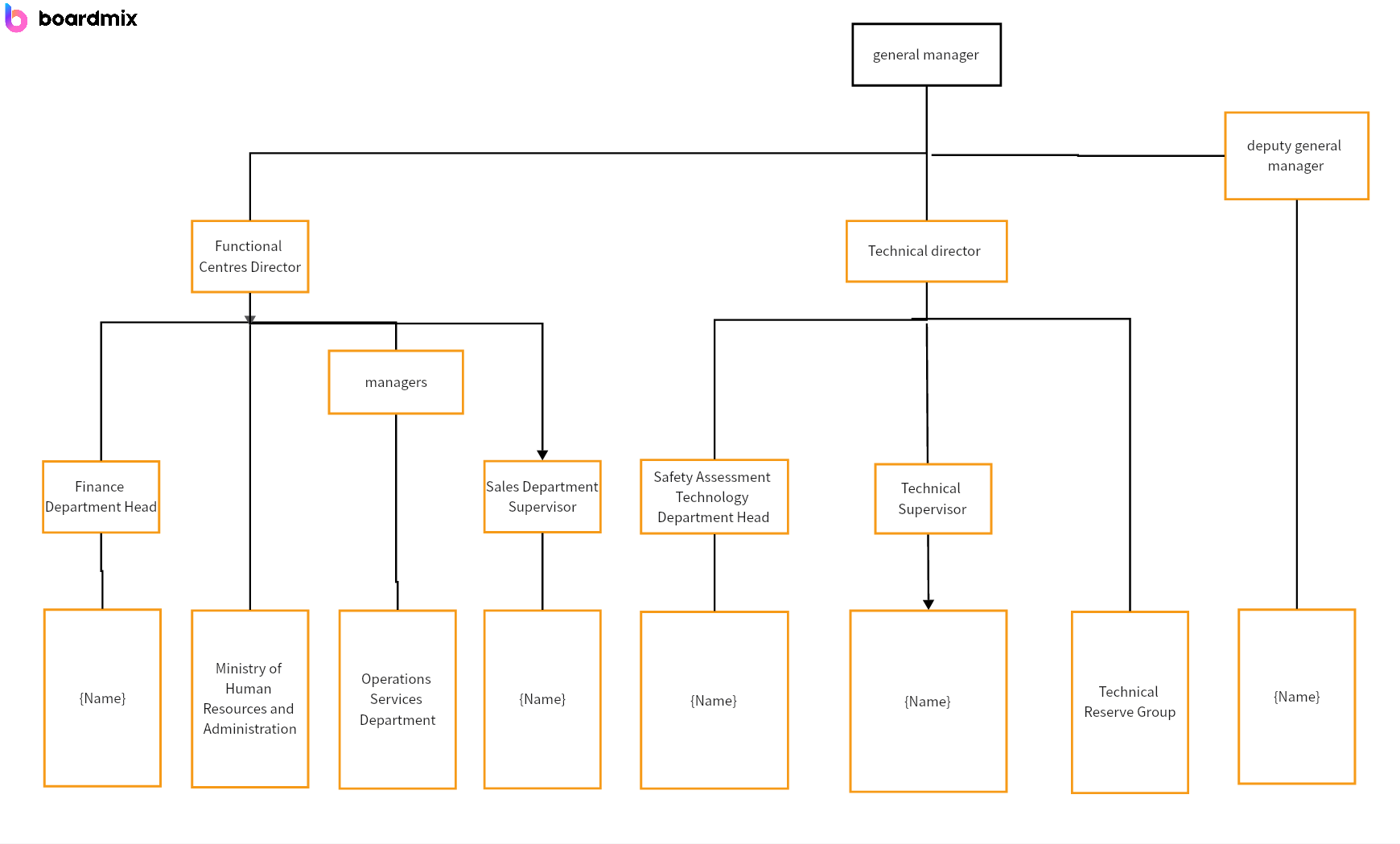
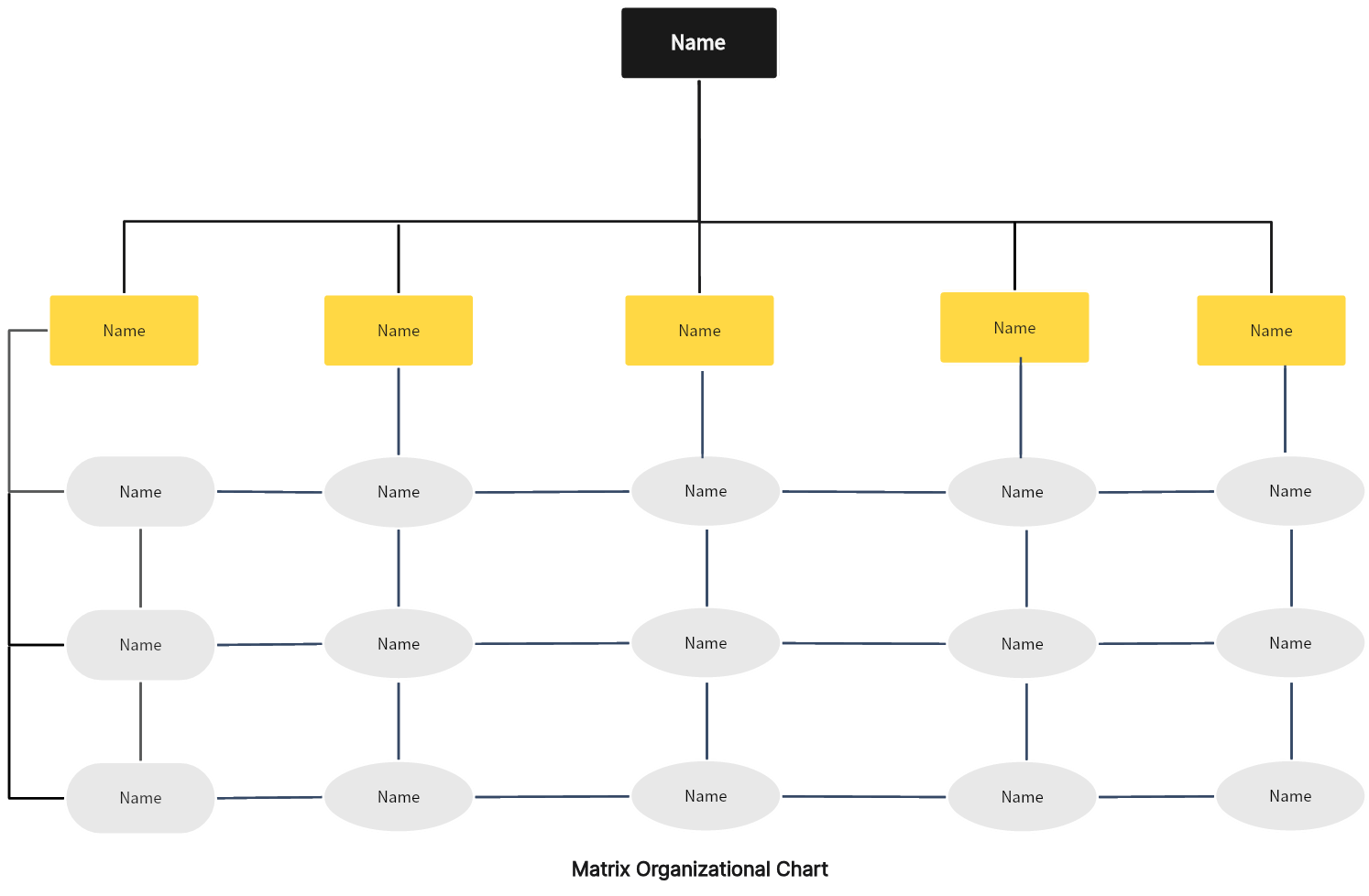
Matrix Structure:This structure is essentially a blend of the functional and project-based structures. Employees have dual reporting relationships - typically to both a functional manager and a project or product manager. Although it facilitates resource sharing and integrates diverse skills, the matrix structure can result in role confusion and conflicting loyalties. The team-based structure provides more clarity in roles and fosters unity towards a common objective.
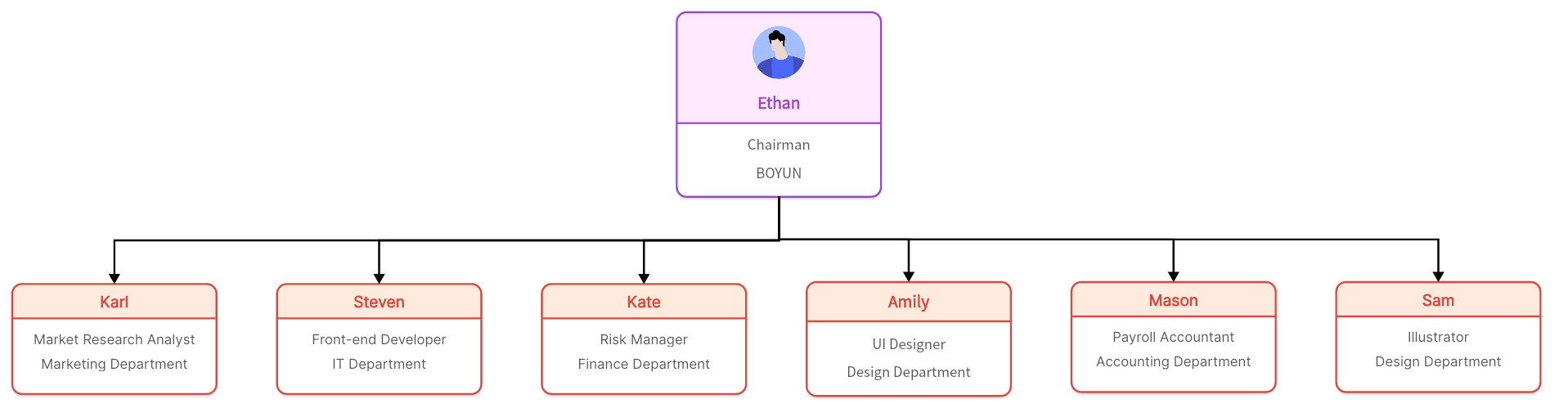
Flat Structure:Also known as a horizontal structure, this model eliminates or greatly reduces middle management, promoting a more direct line of communication between executives and frontline employees. While it encourages autonomy and faster decision-making, it may lead to blurred roles and responsibilities. The team-based structure addresses this issue by defining clear roles within each team while still promoting autonomy.
For a more in-depth understanding of various organizational structures including Divisional Structure, Network Structure, etc., we recommend reading this comprehensive article: 8 Types of Organizational Structures for Businesses. It provides valuable insights into different types of organizational structures and can help you make an informed choice for your organization.