Amazon, a multinational conglomerate specializing in e-commerce, cloud computing, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence, plays a significant role in the global market. It's a force to be reckoned with, achieving record-breaking revenue figures yearly. This remarkable achievement can be credited to their sophisticated value chain. This comprehensive analysis will scrutinize the primary and support activities of Amazon’s Value Chain, including its logistics, marketing strategies, and overall infrastructure.
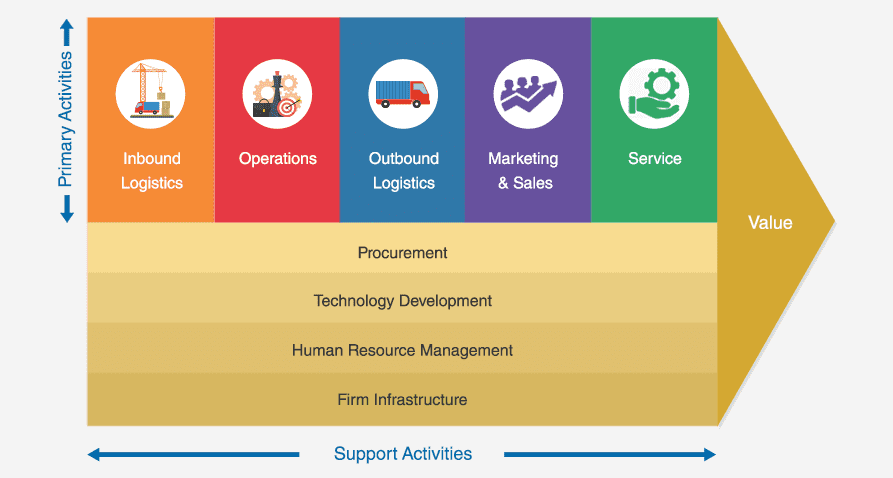
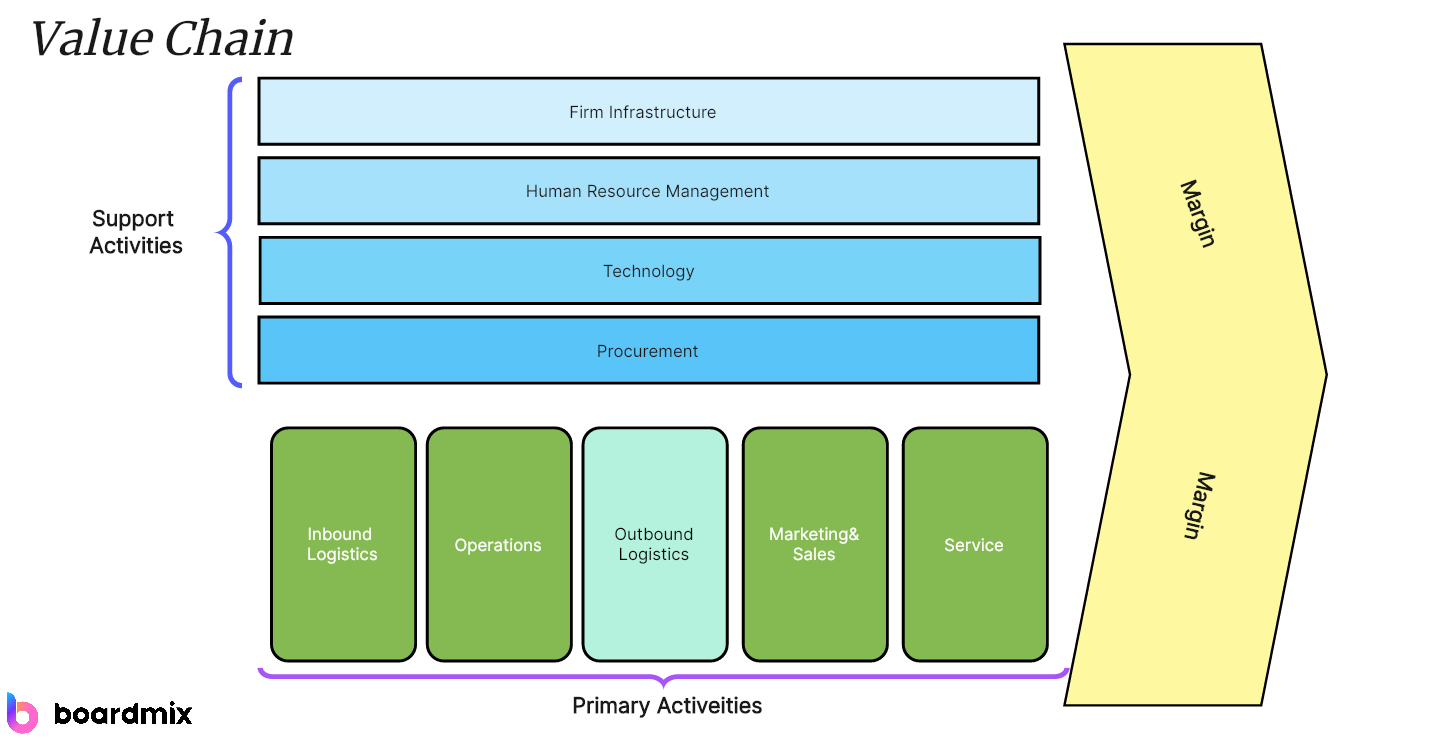
Primary Activities of Amazon’s Value Chain
Inbound Logistics
Amazon's impressive inbound logistics are a fundamental component of its value chain. The vast network of fulfillment centers located strategically across the globe forms the backbone of their inventory management system. These centers are equipped with state-of-the-art technologies to ensure an efficient receipt, storage, and dispatch of goods from a diverse range of suppliers.
Amazon's robust supplier relationships play a pivotal role in its inbound logistics operations. They have forged partnerships with suppliers worldwide, ensuring a continuous influx of products into their fulfillment centers. This broad supplier base not only enhances Amazon's product offerings but also buffers it against potential supply disruptions.
Key to Amazon's inbound logistics success is its investment in advanced inventory management systems. Utilizing AI and ML technologies, Amazon maintains optimal inventory levels, minimizing storage costs while ensuring that popular products are readily available for shipment. This system is capable of predicting demand patterns, and adjusting inventory levels accordingly.
Moreover, Amazon utilizes innovative methods like drop-shipping for certain products. In this process, products are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer, bypassing the need for storage in Amazon's warehouses, reducing storage costs and delivery times.
During peak periods such as Black Friday or Cyber Monday, Amazon's inbound logistics system showcases its robustness. Their operations can swiftly scale up to accommodate the surge in product inflow, managing increased volumes without compromising efficiency.
Operations
Amazon's operations represent the very heart of its value chain. These operations consist of order processing, inventory management, delivery management, customer service, and a host of other activities that directly contribute to customer satisfaction and experience.
A standout feature of Amazon's operational processes is its warehouse management. Amazon operates over 175 fulfillment centers around the world, accounting for more than 150 million square feet of space. They have harnessed the power of robotics and artificial intelligence, deploying over 200,000 robots in these centers. This advanced technology significantly streamlines warehousing operations, improving efficiency and reducing processing times.
A key operational strategy of Amazon is its Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory system. Through this, Amazon holds only the necessary inventory at any given time, reducing storage costs and ensuring faster turnaround times. This is coupled with predictive analytics and demand forecasting algorithms which enhance inventory turnover rates by aligning inventory with customer demand patterns.
On the customer service front, Amazon’s operations excel through their 'customer-obsessed' approach. The company has made significant strides in enhancing user experience by simplifying the ordering process and providing swift problem resolution. They have robust customer service systems in place which can handle hundreds of thousands of queries daily across various platforms, reflecting their operational efficiency.
Amazon's operational strategy also takes into account environmental sustainability. The company is continually striving to minimize waste through eco-friendly packaging and has committed to reaching net-zero carbon by 2040.
Outbound Logistics
The outbound logistics process at Amazon is as meticulously designed and managed as their inbound logistics. With a customer base exceeding 300 million active users, the efficiency and reliability of their outbound logistics significantly influence customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Central to Amazon's outbound logistics is its extensive distribution network. This includes over 175 fulfillment centers and numerous delivery stations globally, facilitating swift order fulfillment and shipping. In addition to these physical resources, Amazon utilizes sophisticated logistics software to manage the movement of goods from the warehouses to the customers.
Furthermore, Amazon offers a variety of shipping options to cater to different customer needs. These range from Amazon Prime's same-day or two-day delivery to standard shipping that takes a few days. Amazon Prime Air, a future delivery system designed to safely transport packages to customers in 30 minutes or less using unmanned aerial vehicles, is another testament to their commitment to revolutionizing their logistics.
In its pursuit of logistical excellence, Amazon has even ventured into creating its own shipping and delivery network - Amazon Logistics. This arm provides last-mile delivery, allowing Amazon to maintain control over the delivery process. By 2022, Amazon Logistics is expected to deliver 88% of Amazon's packages in the US.
Enhancing this robust logistical structure are technological tools like artificial intelligence and machine learning. These tools aid in demand forecasting, ensuring that the right product quantities are available at the correct locations, thus speeding up delivery times.
Marketing & Sales
Amazon's approach to marketing and sales is deeply rooted in data analytics and personalization. They leverage customer data to tailor marketing messages and product recommendations, creating a customized shopping experience that not only drives sales but also fosters customer loyalty.
A central pillar of Amazon's marketing strategy is its use of artificial intelligence. Amazon's recommendation engine, for example, utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze customers' browsing and purchasing behavior. This allows them to provide personalized product suggestions that improve the relevance of their marketing messages and increase conversion rates. According to a report by McKinsey, Amazon's recommendation engine drives 35% of its total sales.
Sales at Amazon are predominantly driven by their user-friendly online platform. Their one-click purchasing system, patented in 1999, simplifies the checkout process and has significantly increased transaction speed and conversion rates.
Further enhancing their sales strategy is Amazon Prime, a subscription service that offers numerous benefits including expedited shipping, access to exclusive deals, and a host of digital services. By 2020, Amazon Prime had amassed over 200 million subscribers worldwide, highlighting its effectiveness as a sales and retention tool.
Amazon's digital marketing efforts are complemented by traditional methods such as TV advertising. In 2019, Amazon spent nearly $4.5 billion on TV advertising alone, indicating its commitment to broadening brand reach and awareness.
Services
Amazon’s diversified portfolio of services significantly enhances its value proposition, making it much more than just an e-commerce platform.
A cornerstone of Amazon's services is Amazon Web Services (AWS), a cloud computing platform that offers a variety of services including computing power, database storage, and content delivery. Since its launch in 2006, AWS has grown exponentially, with millions of customers worldwide and accounting for nearly 12% of Amazon’s total revenue in 2020.
Further expanding its service range, Amazon introduced Amazon Prime, a paid subscription service that offers members numerous benefits. These include free expedited shipping on eligible purchases, access to streaming music and video, and more. Amazon Prime had over 200 million subscribers worldwide as of 2021, indicating the service's immense popularity.
On the digital content front, Amazon has made significant strides with Kindle eBooks, Amazon Music, and Prime Video. Kindle has revolutionized digital reading with its extensive library of eBooks, while Amazon Music and Prime Video compete directly with the likes of Spotify and Netflix.
Additionally, Amazon extends its footprint to the online food delivery service through Amazon Fresh. Offering a wide variety of groceries and household items, Amazon Fresh provides both delivery and pick-up services to customers, offering flexibility and convenience.
In the physical retail space, Amazon owns and operates several types of stores, including Amazon Go, Amazon Books, and Amazon 4-star stores, each offering a unique shopping experience.
Support Activities of Amazon’s Value Chain
Amazon’s value chain is not just defined by its primary activities. It's the amalgamation of the company's supporting activities that further strengthen the value chain, enabling the company to maintain its competitive edge.
Infrastructure
Amazon's corporate infrastructure plays a crucial role in shaping its value chain. As one of the world's largest internet retailers, Amazon has built a resilient infrastructure that enables the smooth operation of its vast online marketplace. This includes state-of-the-art data centers, software development facilities, and administrative systems. Amazon's corporate policies, procedures, and management controls are also part of this infrastructure, contributing to its efficient and effective operations.
Human Resource Management
People are at the core of Amazon's operations. The company invests heavily in recruiting, training, and retaining talent. They promote a performance-driven culture that rewards innovation and customer-centricity. With over a million employees globally, Amazon’s HR strategies play a critical role in driving its success.
Technology Development
Amazon's commitment to technology development is central to its business strategy. The company has pioneered numerous technological advancements such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Alexa voice service, and robotics in their fulfillment centers. Continuous investment in technology has kept Amazon at the forefront of innovation, differentiating its offerings and enhancing the overall customer experience.
Procurement
Amazon's procurement strategy is a key component of its value chain. With a broad array of products available on its platform, effective sourcing is vital. The company partners with thousands of suppliers worldwide, ensuring the consistent availability of products. These relationships also allow Amazon to offer competitive prices to its customers.
Amazon Value Chain Analysis Example
To further illustrate Amazon's value chain, consider this simplified diagram:
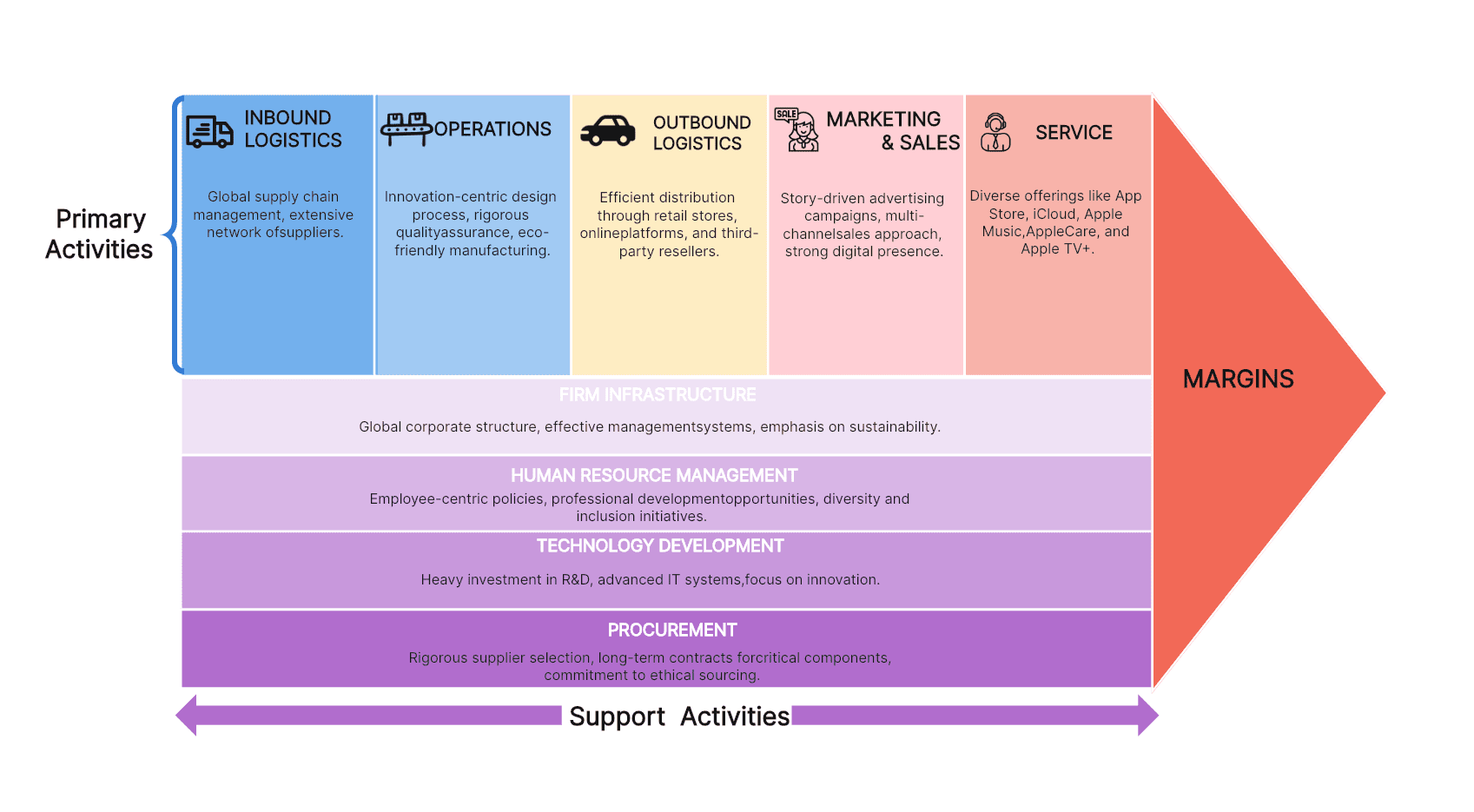
It succinctly captures the primary and support activities contributing to Amazon’s success.
Key Takeaways
Understanding the operations of an industry giant like Amazon can offer valuable insights for businesses striving for growth. The effective management of both primary and supporting activities within the value chain creates a sustainable competitive advantage in the digital marketplace.
For more in-depth value chain analysis like this, our Boardmix whiteboard solution offers pre-built templates for quick and easy use. Click here to access these resources.