A comprehensive Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy is essential for successfully launching a new product or service. Defined as the blueprint for introducing products or services to the market, it encompasses crucial elements like target audience, channels, and messaging. Boardmix offers a comprehensive and free GTM Strategy Template, aiding businesses in structuring their approach effectively. Let's learn this proven framework equips enterprises with the tools to navigate competitive landscapes and maximize their market potential.
Define Go-to-Market Strategy
A Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy is a plan created by an organization outlining how it will sell its product or service to customers. The strategy typically includes information on the target market, unique selling propositions, pricing strategy, sales and distribution channels, and customer support.
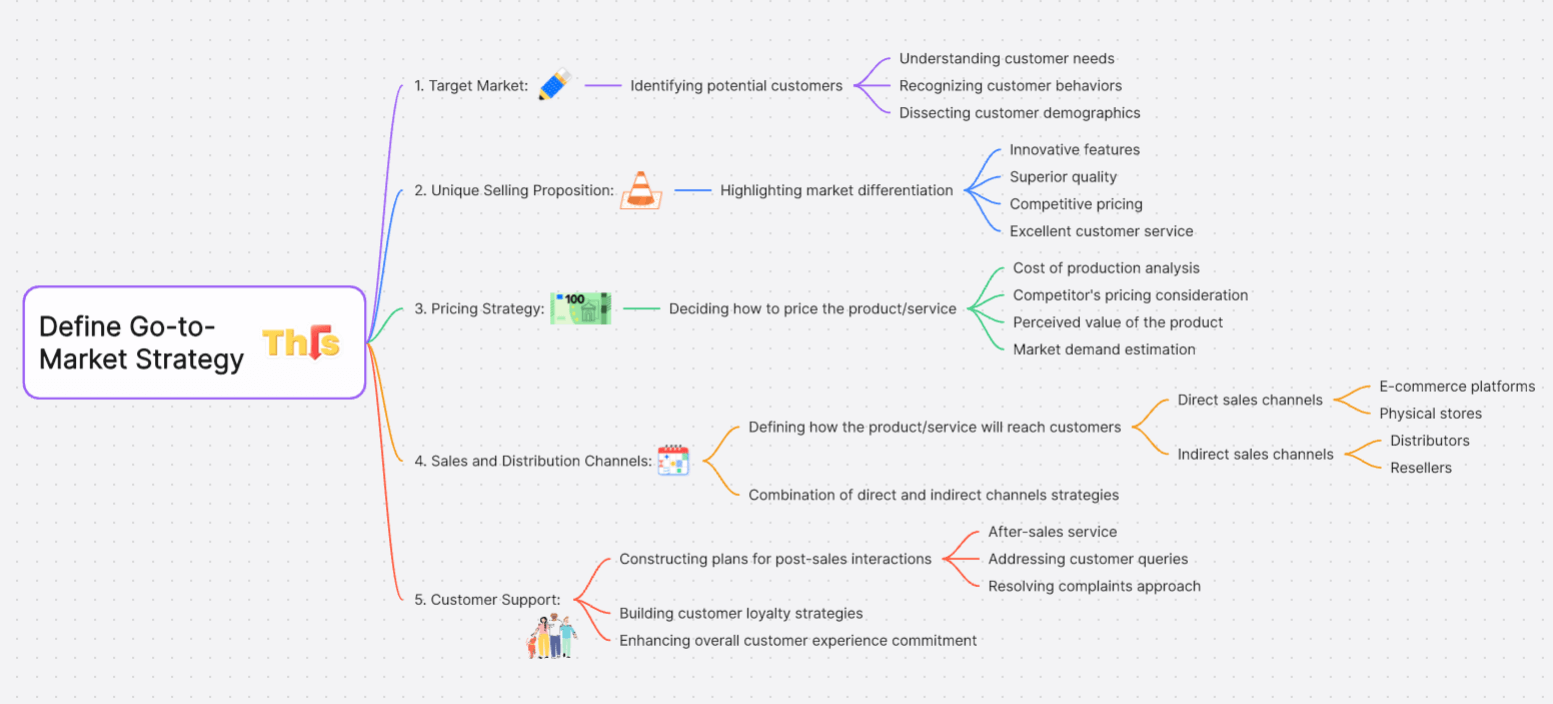
1. Target Market: This involves identifying who the potential customers are. It includes understanding customer needs, behaviors, and demographics.
2. Unique Selling Proposition: What makes the product or service stand out in the market? It could be the innovative features, superior quality, competitive pricing, or excellent customer service.
3. Pricing Strategy: This element focuses on how to price the product or service. Pricing can be based on factors like cost of production, competitor's pricing, perceived value of the product, and market demand.
4. Sales and Distribution Channels: This part of the GTM strategy defines how the product will reach the customer. It could be through direct sales (e-commerce, physical store), indirect sales (distributors, resellers), or a combination of both.
5. Customer Support: This includes plans for after-sales service, addressing customer queries, and resolving complaints. Good customer support can help build customer loyalty and enhance the overall customer experience.
The goal of a GTM strategy is to provide a clear roadmap for introducing a product or service to the market in a way that enables the organization to achieve its business objectives. It serves as an essential link between the product development stage and its actual implementation in the market.
What Are the 5 Go-to-Market Strategies
While there are several ways an organization can approach its Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy, here are five commonly adopted core strategies.
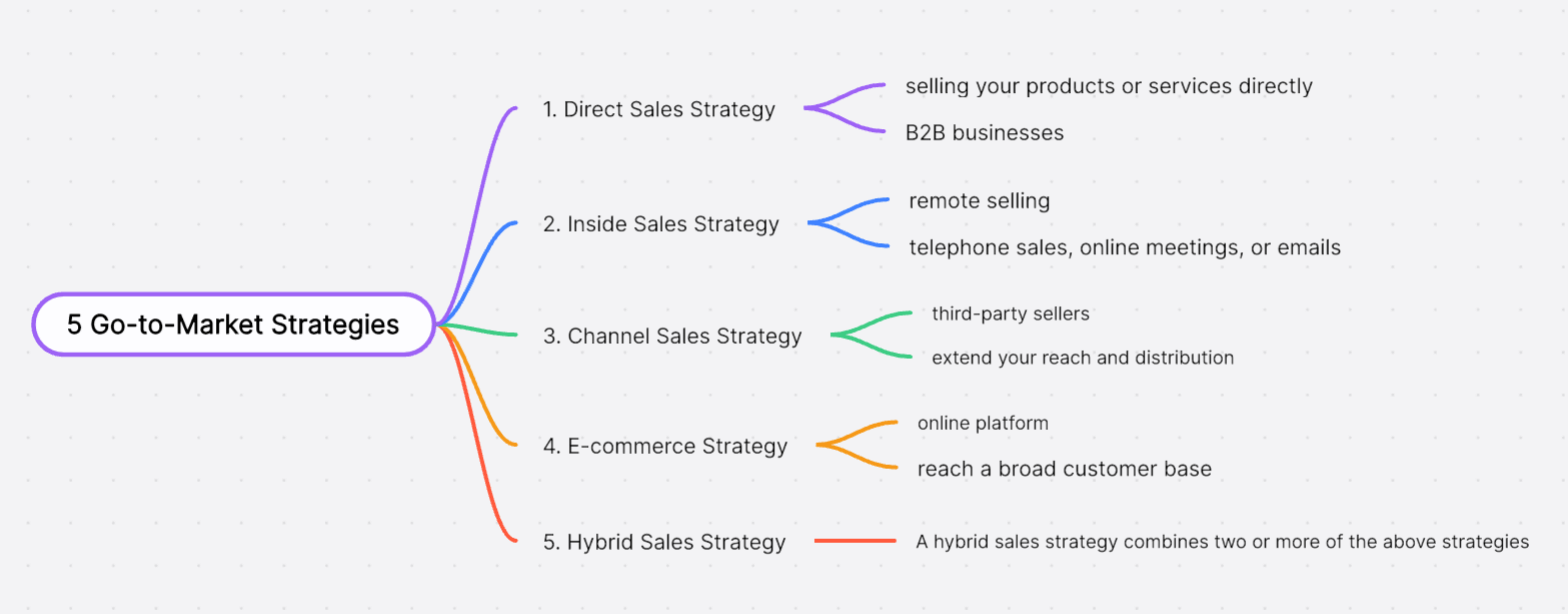
1. Direct Sales Strategy
A direct sales strategy involves selling your products or services directly to the customer without the use of intermediaries. This allows the company to maintain full control over the entire sales process. It's a particularly effective strategy for B2B businesses, where personal relationships and direct interaction often drive sales decisions.
2. Inside Sales Strategy
The inside sales strategy primarily revolves around remote selling. This could be through telephone sales, online meetings, or emails. This strategy allows for increased sales volume, and greater reach, and is more cost-effective compared to field sales. However, it requires robust training and management to ensure effectiveness.
3. Channel Sales Strategy
The channel sales strategy uses third-party sellers, such as resellers, distributors, affiliates, or partners, to market and sell the products or services. This strategy helps extend your reach and distribution without incurring the cost of hiring a large in-house sales team.
4. E-commerce Strategy
With the rise of digital technology and online shopping trends, the e-commerce GTM strategy has become increasingly popular. This involves selling products or services through an online platform. It's an effective way to reach a broad customer base, operate around the clock, and easily track customer behavior and preferences.
5. Hybrid Sales Strategy
A hybrid sales strategy combines two or more of the above strategies. For instance, a company could use a combination of direct sales for high-value clients and e-commerce for retail customers. This allows businesses to leverage the advantages of different strategies based on specific market segments or product lines.
All in all, the choice of a GTM strategy largely depends on your business model, target market, product or service type, and resources available. The ultimate goal should always be to maximize your reach while optimizing costs and delivering value to your customers.
Boardmix: Free Go-to-Market Strategy Template
Every successful Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy follows a structured process that can be broadly classified into five stages - Provocation, Discovery, Diagnostic, Design, and Recommendation. To simplify the process, we are offering a free template that outlines the critical components of a GTM strategy. The Go-to-Market template available on Boardmix helps you organize your thoughts, data, and plans systematically and professionally.
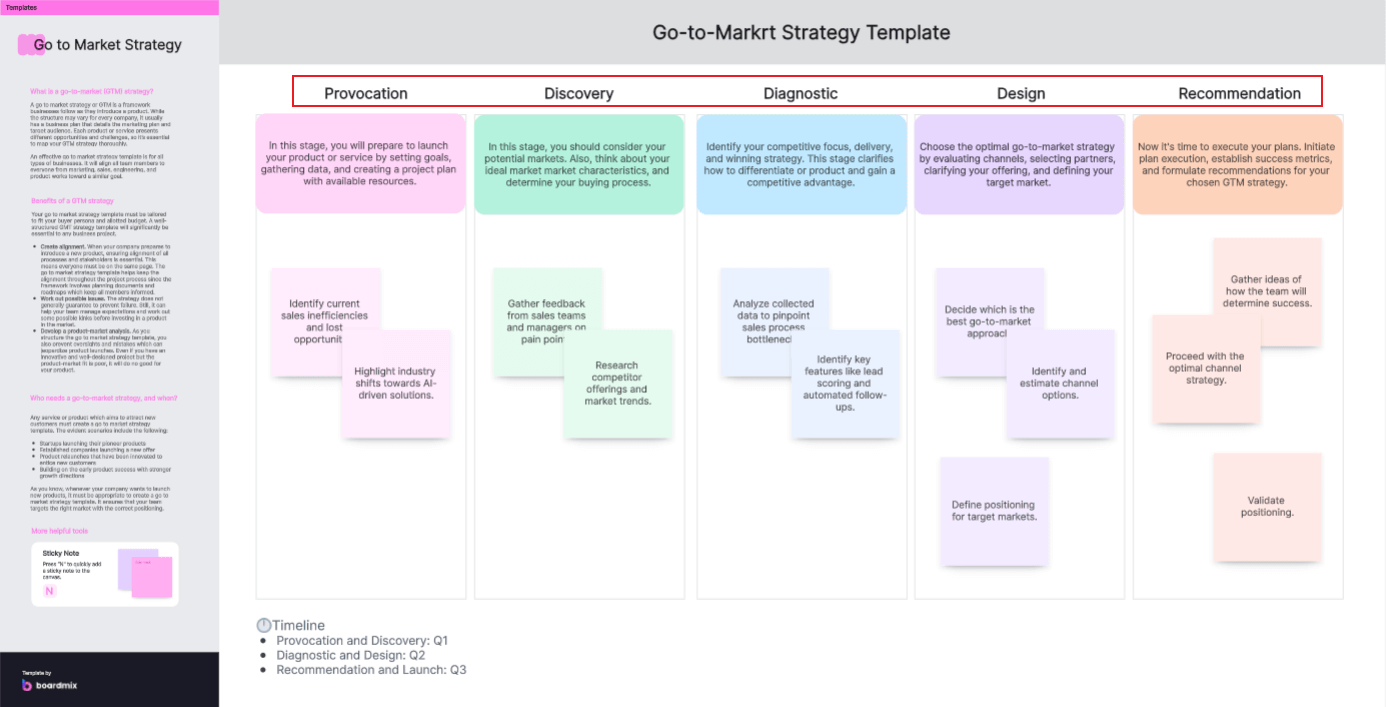
1. Provocation
At the provocation stage, identify an opportunity, need, or issue that triggers the development of a new GTM strategy. This is reflected in the Executive Summary section of our template. Here, clearly define the product or service, the target market, and the unique selling proposition that will drive your strategy.
2. Discovery
This stage involves gathering necessary data and information about the market and your potential customers. This is covered in the Market Analysis and Customer Persona sections of our template. Analyze market conditions and trends, identify customer segments, and develop detailed customer personas to get a comprehensive understanding of who you are selling to and what their needs are.
3. Diagnostic
During the diagnostic stage, determine the strengths and weaknesses of your current strategies and identify areas for improvement. The Unique Value Proposition section in our template can help you understand what differentiates your product from competitors. In addition, the Sales and Distribution Plan section can assist in diagnosing your current distribution channels and strategies.
4. Design
This is where you start developing the actual GTM strategy. Our template provides sections for Pricing and Positioning Strategy, as well as Marketing Plan. Here, detail your pricing model, how you plan to position your product in the market and elaborate on the marketing strategies you intend to employ.
5. Recommendation
Finally, present your GTM strategy along with anticipated results based on the information gathered and strategies developed in previous stages. In the Financial Projections section of our template, forecast revenues, costs, and profitability associated with implementing your GTM strategy.
The free GTM strategy template on Boardmix guides you through each stage of developing a robust GTM strategy that aligns with your business objectives. Download the template today and get started on planning a successful product or service launch.
Example Explained 1: Go-to-Market Strategy of McKinsey
Global management consulting firm McKinsey & Company has been a thought leader in the area of strategy development, including Go-to-Market (GTM) strategies. Let's examine how McKinsey & Company's Go-to-Market (GTM) Strategy could be structured using the five stages - Provocation, Discovery, Diagnostic, Design, and Recommendation.
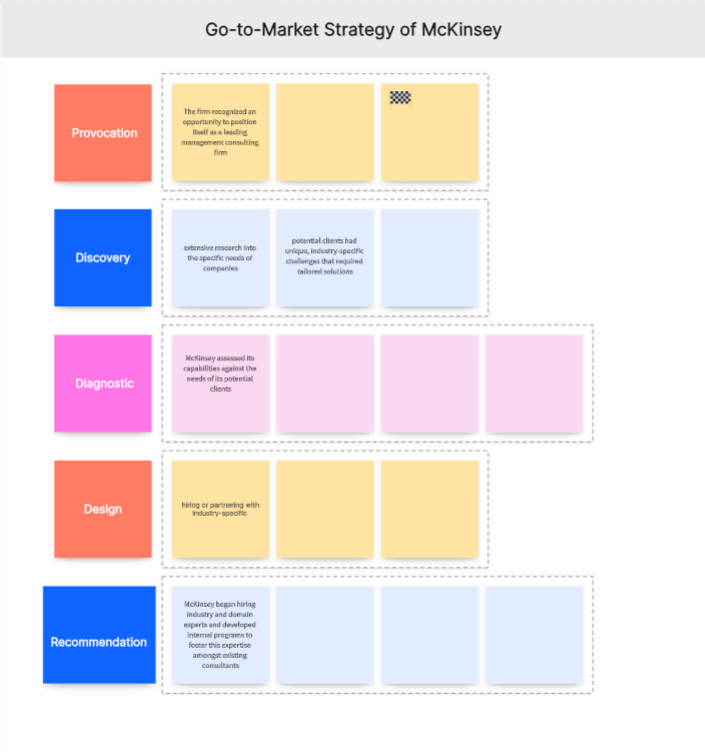
1. Provocation
The initial provocation for McKinsey's GTM strategy was the increasing demand for strategic advisory services as businesses grew more complex. The firm recognized an opportunity to position itself as a leading management consulting firm.
2. Discovery
In the discovery phase, McKinsey conducted extensive research into the specific needs of companies across various sectors and geographies. They discovered that their potential clients had unique, industry-specific challenges that required tailored solutions.
3. Diagnostic
During the diagnostic stage, McKinsey assessed its capabilities against the needs of its potential clients. They identified a gap in their offering: while they had industry-wide knowledge and advisory capabilities, they lacked deep, industry-specific expertise.
4. Design
In response to this insight, McKinsey designed a new GTM strategy that included hiring or partnering with industry-specific experts to deliver bespoke solutions to clients. This marked a significant shift from their previous approach of employing mostly generalist consultants.
5. Recommendation
The final stage was implementing this new GTM strategy. McKinsey began hiring industry and domain experts and developed internal programs to foster this expertise amongst existing consultants. This approach enhanced their credibility as a go-to strategic advisor for companies in various sectors.
By aligning its GTM strategy with market needs and leveraging its strengths, McKinsey successfully established itself as a leading management consulting firm that delivers impactful, industry-specific solutions for its clients.
Example Explained 2: Adobe's Go-to-Market Strategy
Adobe Systems Incorporated, a multinational computer software company, has a well-defined and effective Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy. Let's look at how Adobe's Go-to-Market (GTM) Strategy could be structured using the five stages - Provocation, Discovery, Diagnostic, Design, and Recommendation.
1. Provocation
Adobe recognized the shift in software consumption trends, with users moving away from physical software to digital and subscription-based models. This realization acted as a provocation for Adobe to rethink its GTM strategy.
2. Discovery
Adobe conducted thorough research to understand the changing needs of its consumers, especially creative professionals. The discovery phase revealed that customers preferred a more integrated and continuously updated suite of creative tools over standalone software.
3. Diagnostic
Adobe examined its existing product offerings and sales model. They discovered that although they had robust standalone software solutions, they lacked an integrated offering that delivered continual updates - a critical need for many of their customers.
4. Design
In response to their findings, Adobe designed a cloud-based subscription model known as Adobe Creative Cloud. This new GTM strategy integrated Adobe's key creative software into a single platform, offered regular updates, and shifted the revenue model from one-off purchases to recurring subscriptions.
5. Recommendation
The recommendation stage culminated with the launch of Adobe Creative Cloud. It addressed customer needs and wants uncovered in the discovery stage, resolved weaknesses identified in the diagnostic phase, and executed the design of its new GTM strategy.
This change in strategy was a tremendous success for Adobe and has since set the standard for software distribution within the industry. Adobe's GTM strategy hinges on understanding its customers, delivering value through cloud-based solutions, diversifying its offerings, and building a strong community. Its strategic moves showcase a customer-centric approach that has ensured Adobe's sustained success in its markets.
FAQs About Go-to-Market Strategy
What are the 4 fundamentals of strategy McKinsey?
While McKinsey has developed various frameworks and methodologies over the years, the following four fundamentals are often emphasized in strategic planning:
1. Direction: This involves setting a clear and ambitious direction for the company, defining its purpose, and determining where it wants to play in the market.
2. Discipline: Strategy requires discipline in execution. This means setting priorities, allocating resources efficiently, and maintaining focus on the chosen path.
3. Diagnostics: Understanding the current situation through rigorous analysis is crucial. This includes assessing the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis), as well as the competitive landscape.
4. Horizon Thinking: Effective strategy considers both the immediate and the long-term. It involves balancing short-term actions with long-term aspirations, often referred to as "horizon thinking," where companies plan across different time frames (Horizon 1 for short-term, Horizon 2 for medium-term, and Horizon 3 for long-term initiatives).
What are the 5 pillars of go-to-market strategy?
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, the following five pillars are commonly considered essential for a robust go-to-market strategy:
1. Target Customer Segmentation: Identifying and understanding the specific customer groups the company aims to serve.
2. Value Proposition: Clearly defining the unique value the company offers to its target customers and why they should choose the company's products or services over competitors.
3. Channel Strategy: Determining the most effective channels to reach and serve the target customers, which may include direct sales, online platforms, retail partnerships, etc.
4. Messaging and Positioning: Crafting compelling messages that resonate with the target audience and positioning the company and its offerings in the market.
5. Metrics and Measurement: Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the success of the go-to-market strategy and make data-driven decisions.
What are the 6 components of a go-to-market strategy?
A go-to-market strategy can be broken down into the following six components:
1. Market Analysis: Understanding the market landscape, including customer needs, competitive analysis, and market trends.
2. Product/Service Offering: Defining the features, benefits, and unique selling points of the product or service being offered.
3. Pricing Strategy: Setting the price points that reflect the value proposition and are competitive in the market.
4. Distribution Strategy: Deciding how the product or service will be made available to the target customers, including online, retail, or direct sales.
5. Promotion and Marketing: Planning how to promote the product or service through various marketing and advertising channels.
6. Sales Strategy: Developing the approach for the sales team, including sales targets, processes, and training to effectively engage with customers.
Conclusion
A well-defined Go-to-Market strategy is not just a luxury but a necessity for businesses striving to thrive in today's dynamic marketplaces. By leveraging the insights provided by Boardmix's free GTM Strategy Template and studying successful examples like McKinsey and Adobe, companies can steer their initiatives toward success. This framework serves as a guiding light, enabling organizations to align their resources effectively, engage their target audience, and seize growth opportunities. With the right strategy in place, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of the market and establish themselves as leaders in their respective domains.









