Go-to-Market strategy, short for GTM strategy, is an integral part of any business plan. It provides a framework for defining target markets, delivering value propositions, and structuring sales and marketing efforts. Ultimately, an effective GTM strategy can drive growth and success in the marketplace. A well-defined Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy can provide a competitive advantage. But what is a GTM strategy, and why is it so crucial? In this article, we will dive into the world of Go-to-Market Strategy and help you build it instantly with the help of Boardmix.
What is Go-to-Market Strategy
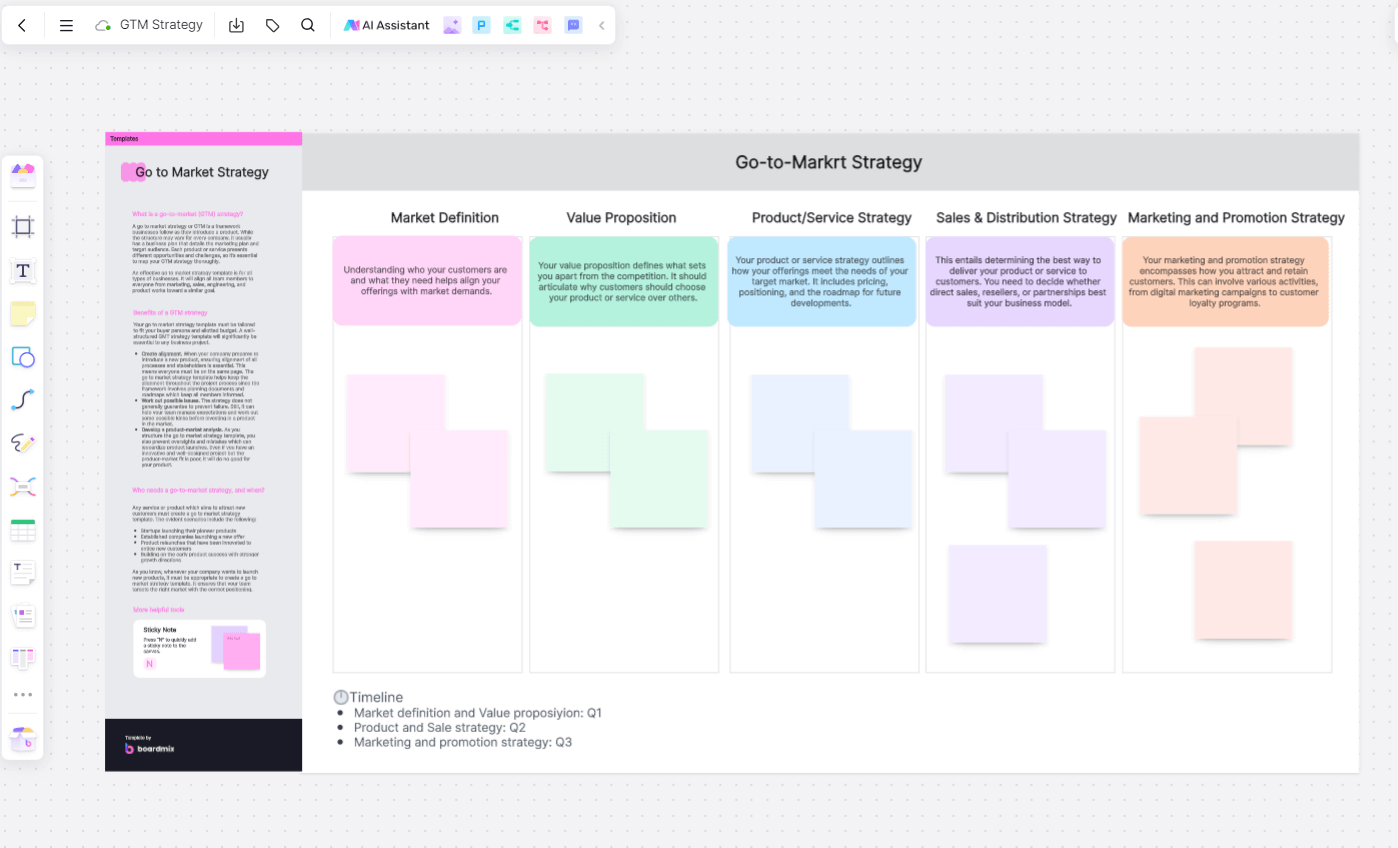
A Go-to-Market strategy is the action plan through which a company delivers its unique value proposition to customers. It outlines the steps a company must take to succeed in reaching its market and compete effectively. A robust GTM strategy typically consists of several core components:
1. Market Definition
First, it's essential to define your target market clearly. Understanding who your customers are and what they need helps align your offerings with market demands.
2. Value Proposition
Your value proposition defines what sets you apart from the competition. It should articulate why customers should choose your product or service over others.
3. Product/Service Strategy
Your product or service strategy outlines how your offerings meet the needs of your target market. It includes pricing, positioning, and the roadmap for future developments.
4. Sales & Distribution Strategy
This entails determining the best way to deliver your product or service to customers. You need to decide whether direct sales, resellers, or partnerships best suit your business model.
5. Marketing and Promotion Strategy
Your marketing and promotion strategy encompasses how you attract and retain customers. This can involve various activities, from digital marketing campaigns to customer loyalty programs.
A GTM strategy provides clear direction and focus, ensuring all parts of the organization are aligned toward achieving common goals. It provides a roadmap for penetrating new markets, boosting sales, and increasing competitive advantage.
How to Build a Go-to-Market Strategy
Creating a comprehensive Go-to-Market strategy requires a thoughtful approach. Fortunately, Boardmix provides an intuitive platform where you can outline, organize, and collaborate on your GTM strategy. Below is a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Set Up Your GTM Project
After logging into your Boardmix account, navigate to the "New Project" tab and start a new project for your GTM strategy. Give it an identifiable name that reflects the business idea or product you plan to launch.
Step 2: Create Boards for Key GTM Components
In your project, create separate boards for each key component of your GTM strategy. To start quickly, you can use the Go-to-Market Strategy template in the diagram library for free.
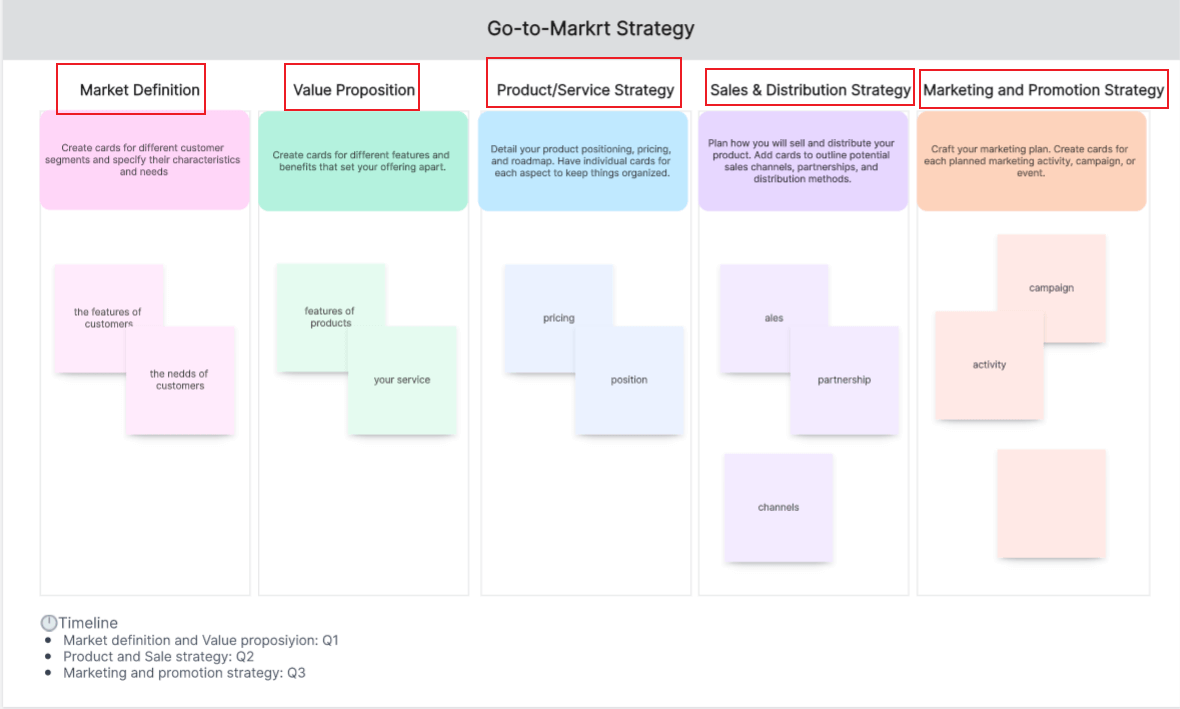
- Market Definition: Identify your target customers and their needs. Create cards for different customer segments and specify their characteristics and needs.
- Value Proposition: Highlight what makes your product or service unique. Create cards for different features and benefits that set your offering apart.
- Product/Service Strategy: Detail your product positioning, pricing, and roadmap. Have individual cards for each aspect to keep things organized.
- Sales & Distribution Strategy: Plan how you will sell and distribute your product. Add cards to outline potential sales channels, partnerships, and distribution methods.
- Marketing & Promotion Strategy: Craft your marketing plan. Create cards for each planned marketing activity, campaign, or event.
Step 3: Add Details to Each Card
For each card you create, add further details in the description or comment section. These details might include timelines, responsibilities, metrics for success, and any other relevant information.
Step 4: Invite Your Team to Collaborate
If you're working with a team, use Boardmix's collaboration features. Invite your team members to view, comment on, or edit your GTM project by clicking on the "Invite" button and entering their email addresses.
Step 5: Review and Refine
Continually review and refine your GTM strategy as you get feedback from your team and gain more insights. Use Boardmix's easy editing features to make any updates or adjustments.
Go-to-Market Strategy Examples for Startups
Startups often operate in unique business environments characterized by fast growth, high risk, and frequent change. Having a well-defined Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy can be a game-changer in such conditions. Here are examples of effective GTM strategies implemented by successful startups. Below are the Go-to-Market strategies for start-up companies, focusing on their market definition, value proposition, product/service strategy, sales and distribution strategy, and marketing and promotion strategy.
Go-to-Market Strategy Example 1: Dropbox - Freemium Model
Dropbox, a cloud-based storage solution, implemented a freemium GTM strategy. They offered a basic version of their service for free while charging for premium features. This approach helped them rapidly increase their user base and convert a percentage into paying customers.
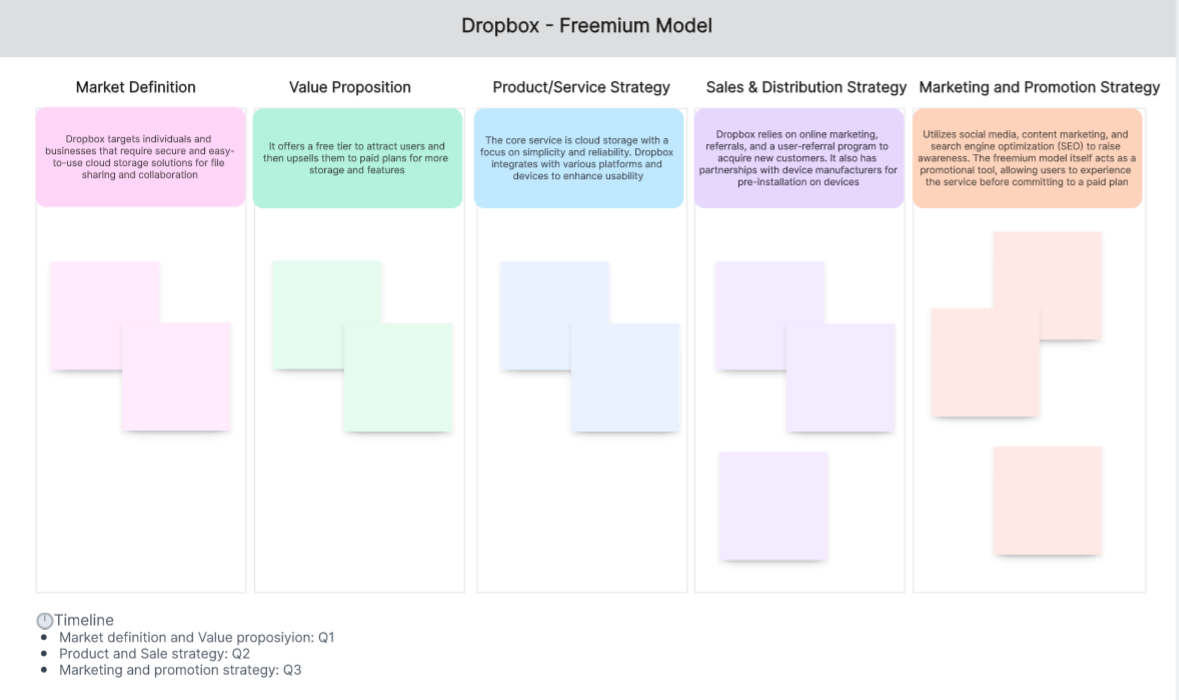
Market Definition: Dropbox targets individuals and businesses that require secure and easy-to-use cloud storage solutions for file sharing and collaboration.
Value Proposition: It offers a free tier to attract users and then upsells them to paid plans for more storage and features.
Product/Service Strategy: The core service is cloud storage with a focus on simplicity and reliability. Dropbox integrates with various platforms and devices to enhance usability.
Sales & Distribution Strategy: Dropbox relies on online marketing, referrals, and a user-referral program to acquire new customers. It also has partnerships with device manufacturers for pre-installation on devices.
Marketing & Promotion Strategy: Utilizes social media, content marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO) to raise awareness. The freemium model itself acts as a promotional tool, allowing users to experience the service before committing to a paid plan.
Go-to-Market Strategy Example 2: Slack - Bottom-Up Adoption
The communication platform Slack initially targeted small teams within larger organizations for its service. This bottom-up approach allowed individuals and small groups to start using Slack and spread its usage organically within the organization.
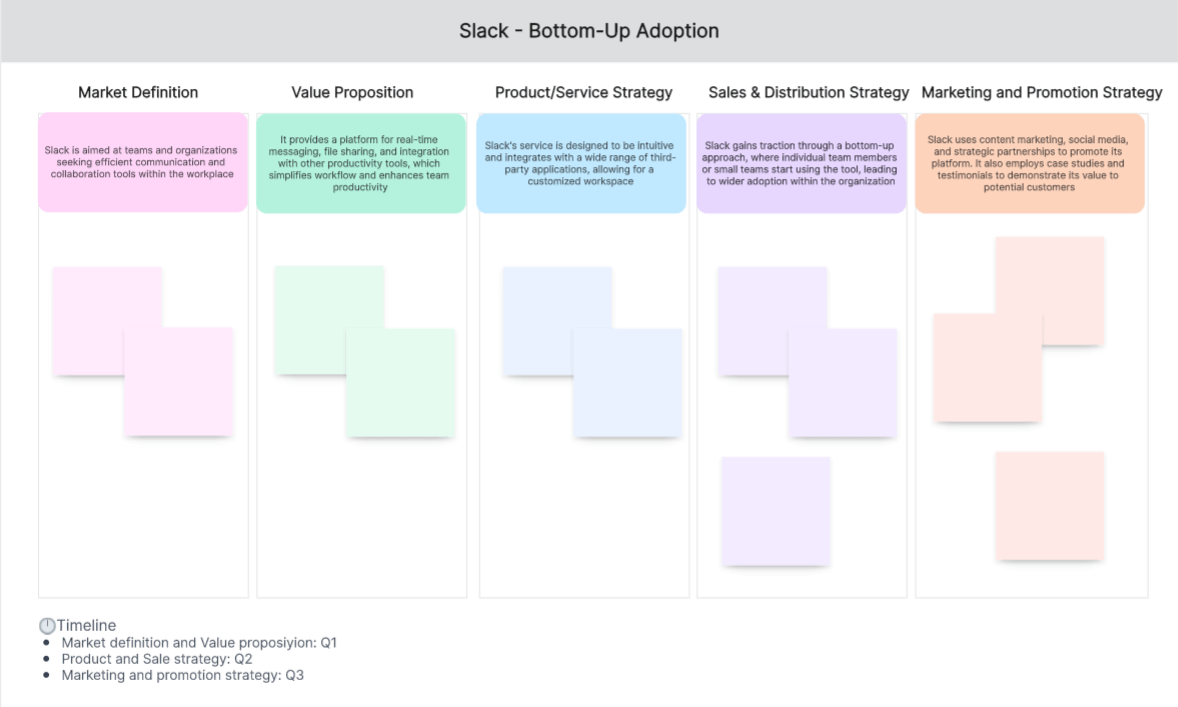
Market Definition: Slack is aimed at teams and organizations seeking efficient communication and collaboration tools within the workplace.
Value Proposition: It provides a platform for real-time messaging, file sharing, and integration with other productivity tools, which simplifies workflow and enhances team productivity.
Product/Service Strategy: Slack's service is designed to be intuitive and integrates with a wide range of third-party applications, allowing for a customized workspace.
Sales & Distribution Strategy: Slack gains traction through a bottom-up approach, where individual team members or small teams start using the tool, leading to wider adoption within the organization.
Marketing & Promotion Strategy: Slack uses content marketing, social media, and strategic partnerships to promote its platform. It also employs case studies and testimonials to demonstrate its value to potential customers.
Go-to-Market Strategy Example 3: Uber - City by City Expansion
Ride-hailing service Uber adopted a city-by-city GTM strategy. They launched their service in one city at a time, customized their approach to local regulations and market characteristics, established a solid user base, and then moved on to the next city.
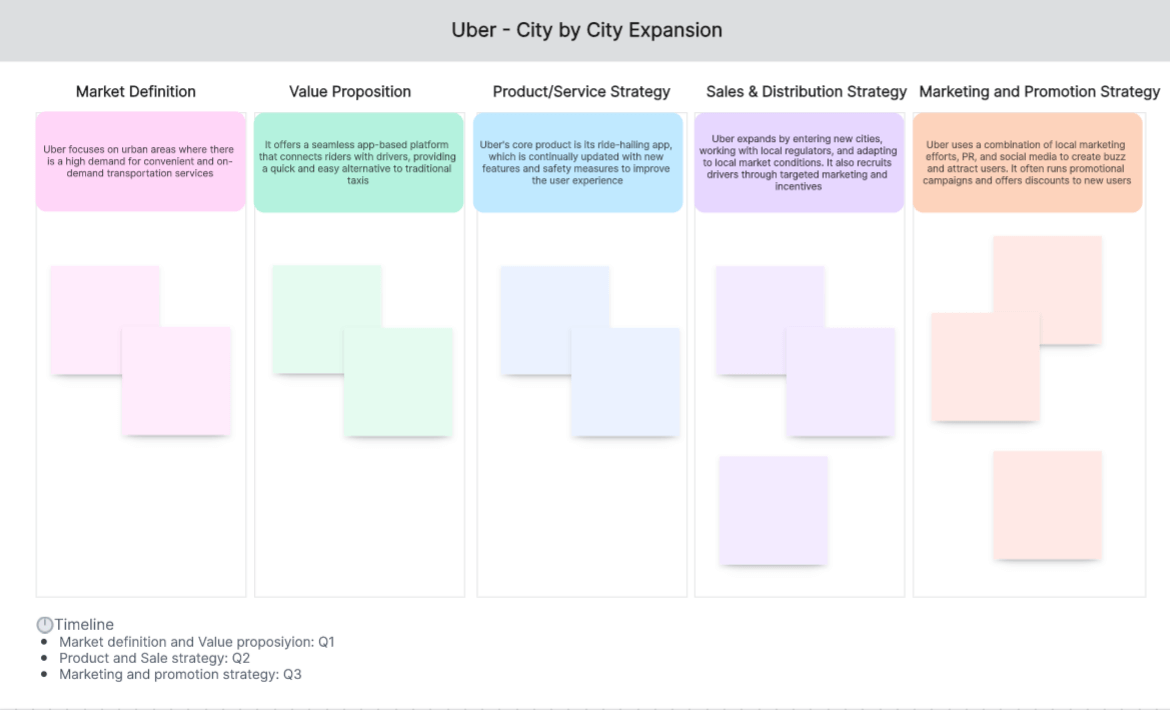
Market Definition: Uber focuses on urban areas where there is a high demand for convenient and on-demand transportation services.
Value Proposition: It offers a seamless app-based platform that connects riders with drivers, providing a quick and easy alternative to traditional taxis.
Product/Service Strategy: Uber's core product is its ride-hailing app, which is continually updated with new features and safety measures to improve the user experience.
Sales & Distribution Strategy: Uber expands by entering new cities, working with local regulators, and adapting to local market conditions. It also recruits drivers through targeted marketing and incentives.
Marketing & Promotion Strategy: Uber uses a combination of local marketing efforts, PR, and social media to create buzz and attract users. It often runs promotional campaigns and offers discounts to new users.
Go-to-Market Strategy Example 4: Product Hunt - Community Building
Product Hunt, a website that lets users share and discover new products, focused on building an engaged community of early adopters from the start. Their GTM strategy hinged on creating an enthusiastic community that would actively participate in product discovery and promotion.
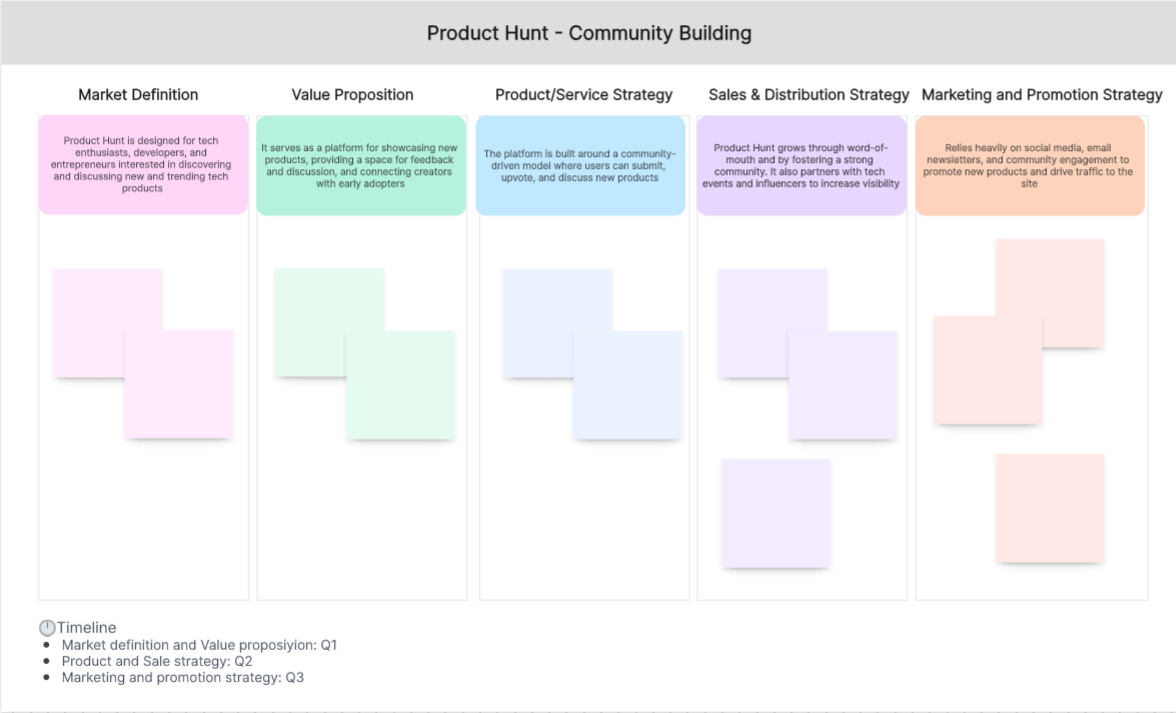
Market Definition: Product Hunt is designed for tech enthusiasts, developers, and entrepreneurs interested in discovering and discussing new and trending tech products.
Value Proposition: It serves as a platform for showcasing new products, providing a space for feedback and discussion, and connecting creators with early adopters.
Product/Service Strategy: The platform is built around a community-driven model where users can submit, upvote, and discuss new products.
Sales & Distribution Strategy: Product Hunt grows through word-of-mouth and by fostering a strong community. It also partners with tech events and influencers to increase visibility.
Marketing & Promotion Strategy: Relies heavily on social media, email newsletters, and community engagement to promote new products and drive traffic to the site.
Go-to-Market Strategy Example 5: Airbnb - Event Piggybacking
In its early days, Airbnb targeted attendees of large events who struggled to find available hotel accommodations. They piggybacked off events like tech conferences or music festivals to reach potential users when demand for their service would be particularly high.
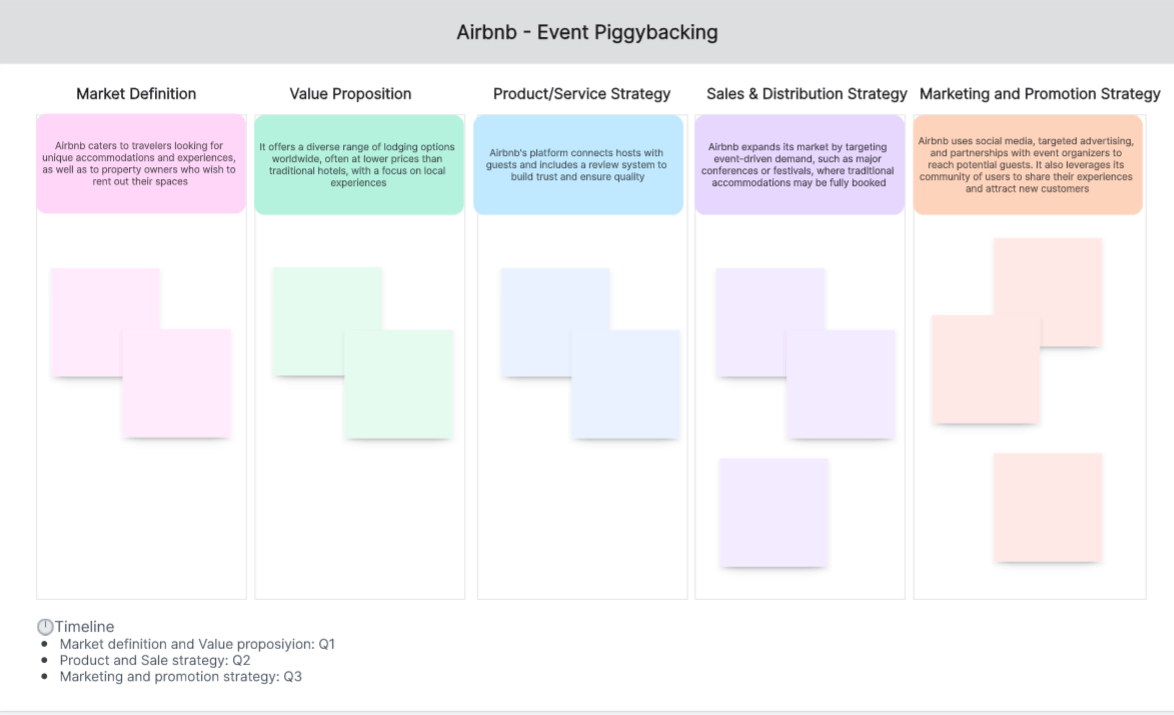
Market Definition: Airbnb caters to travelers looking for unique accommodations and experiences, as well as to property owners who wish to rent out their spaces.
Value Proposition: It offers a diverse range of lodging options worldwide, often at lower prices than traditional hotels, with a focus on local experiences.
Product/Service Strategy: Airbnb's platform connects hosts with guests and includes a review system to build trust and ensure quality.
Sales & Distribution Strategy: Airbnb expands its market by targeting event-driven demand, such as major conferences or festivals, where traditional accommodations may be fully booked.
Marketing & Promotion Strategy: Airbnb uses social media, targeted advertising, and partnerships with event organizers to reach potential guests. It also leverages its community of users to share their experiences and attract new customers.
These examples showcase the versatility and creativity startups can apply when developing their GTM strategies. Depending on their unique product offerings, target customers, market conditions, and resources, startups can craft a GTM strategy that not only guides their market entry but also fuels growth and success.
Tips for Building Go-to-Market Sales Strategy
Creating a Go-to-Market sales strategy is essential for any organization aiming to launch a new product or service, enter new markets, or reposition itself in existing markets. Here are some useful tips to build an effective GTM sales strategy.
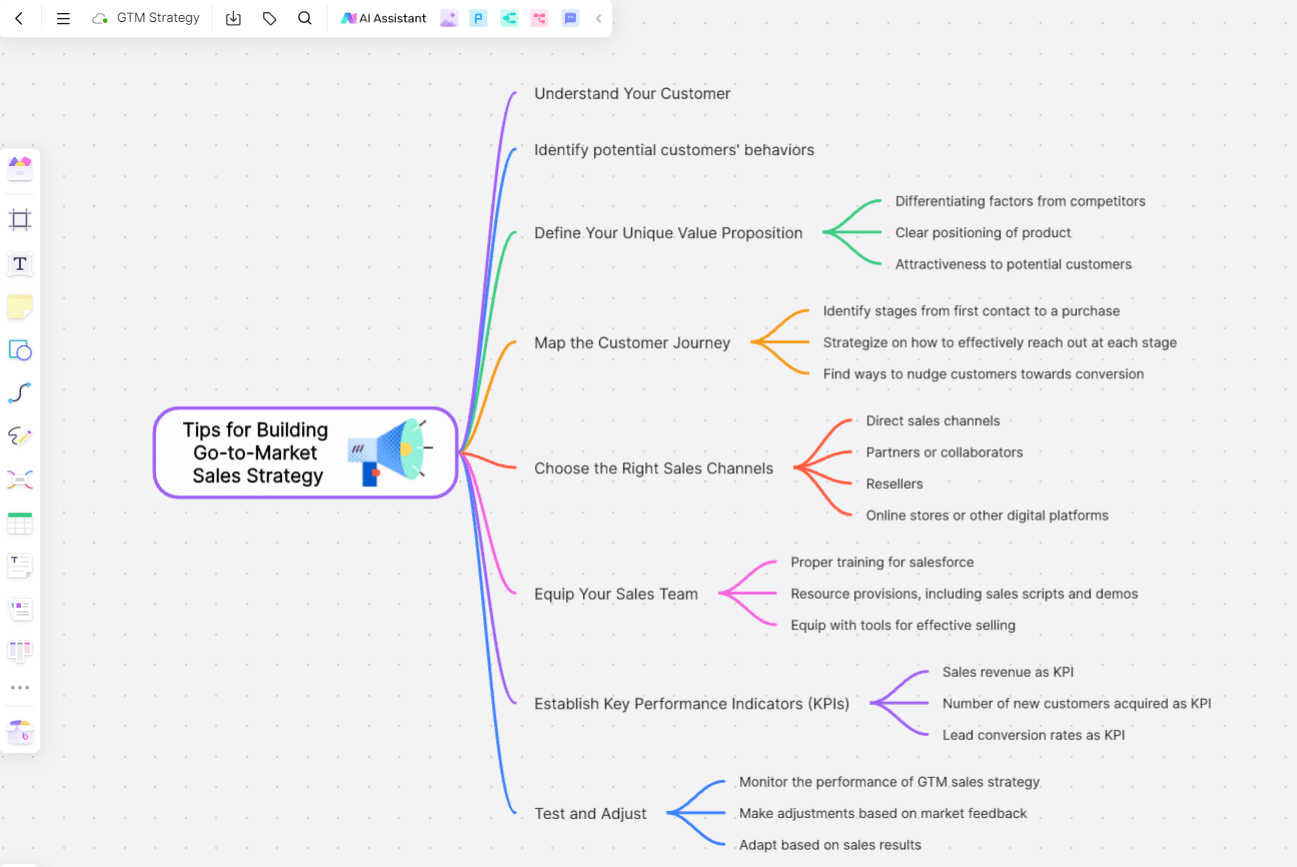
1. Understand Your Customer
The first step is to identify and understand your target customers. Conducting market research can help you gain valuable insights about your potential customers’ behaviors, needs, and preferences.
2. Define Your Unique Value Proposition
What differentiates your offering from competitors in the market? Having a clear value proposition can help position your product or service attractively in the minds of prospective customers.
3. Map the Customer Journey
Outline the stages your customer goes through from the first contact to making a purchase. Understanding this path will allow you to effectively reach out to them at each stage and move them toward conversion.
4. Choose the Right Sales Channels
Determine the best channels to reach your target customers. This might include direct sales, partners, resellers, online stores, or a combination of these.
5. Equip Your Sales Team
Ensure your sales team is prepared and equipped to effectively sell your offering. This could involve training, resources, sales scripts, demos, and more.
6. Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs help measure the effectiveness of your GTM sales strategy. These could include sales revenue, number of new customers acquired, lead conversion rate, etc.
7. Test and Adjust
Once your GTM sales strategy is in place, monitor its performance and be ready to make adjustments as necessary based on market feedback and sales results.
Remember, an effective GTM sales strategy should be dynamic and flexible to adapt with changing market conditions and customer needs. By following these tips, you'll be well on your way to developing a GTM sales strategy that helps drive sales and grow your business. Boardmix offers an effective way of creating a structured GTM strategy that aligns with your organization's goals. By utilizing its customizable features, you can create a robust GTM strategy that propels your business forward.









