In a rapidly changing business environment, maintaining a competitive edge requires more than just a solid strategy. This is where the McKinsey 7-S Model comes in, providing a comprehensive framework for achieving organizational alignment and effectiveness. In this article, we will explore the McKinsey 7-S Model in detail. We'll define each of the seven key elements, provide real-world examples to illustrate its application and offer a practical template for using this model to assess and improve your organization. Let's delve deep into what this model is and how it can facilitate better business performance.
What is Mckinsey 7-s Model?
The McKinsey 7-S Model is a strategic planning tool designed to help organizations understand how they can achieve their objectives. Developed by Tom Peters and Robert Waterman during their tenure at McKinsey & Company, the model underlines seven fundamental factors that are interrelated and crucial for any organization's ability to achieve its objectives.
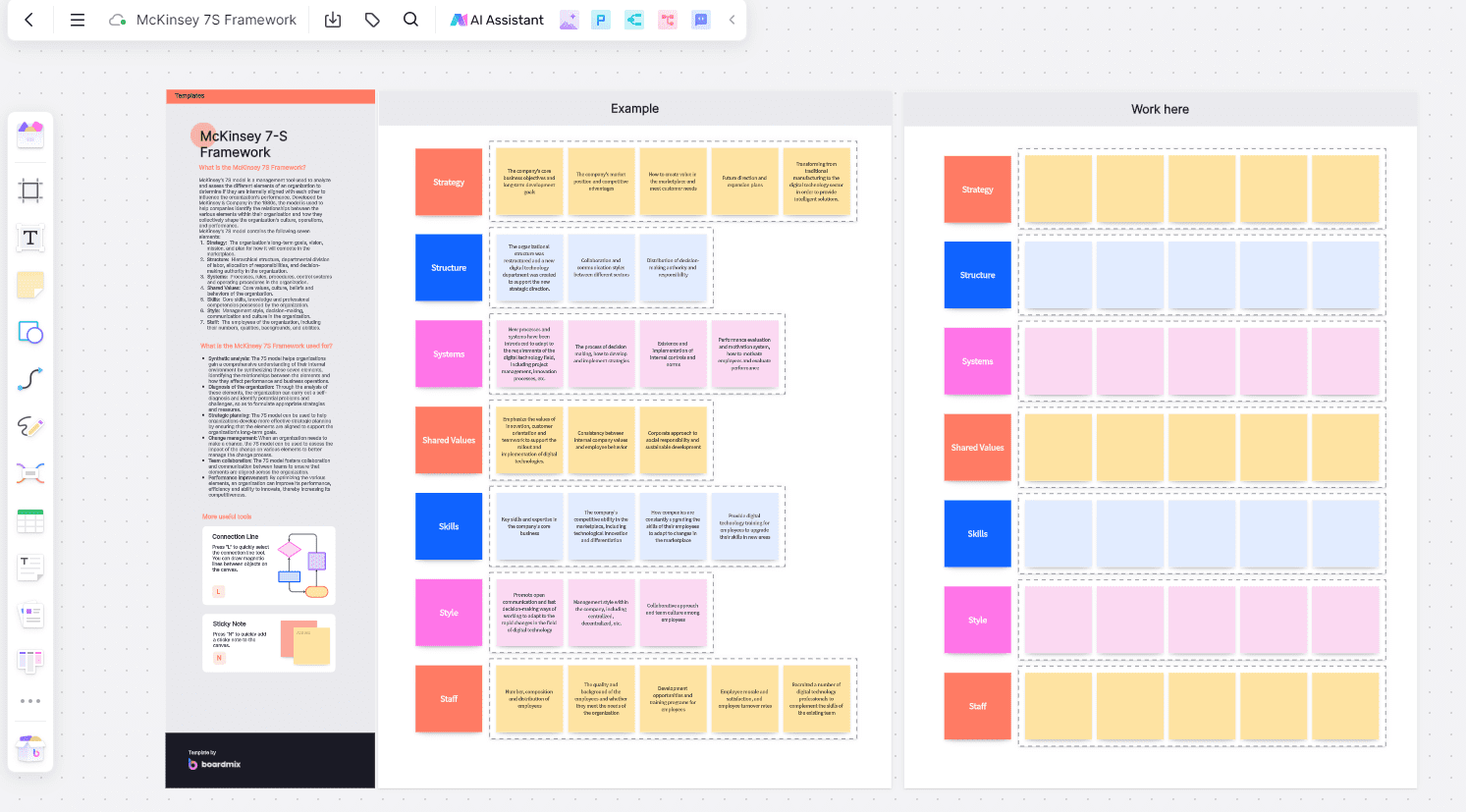
The model comprises seven elements, divided into 'hard' and 'soft' elements, including Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Skills, Style, and Staff. The 'hard' elements are relatively easy to identify and directly influenced by management. On the other hand, the 'soft' elements, while harder to describe, are equally significant and often influenced by the corporate culture.
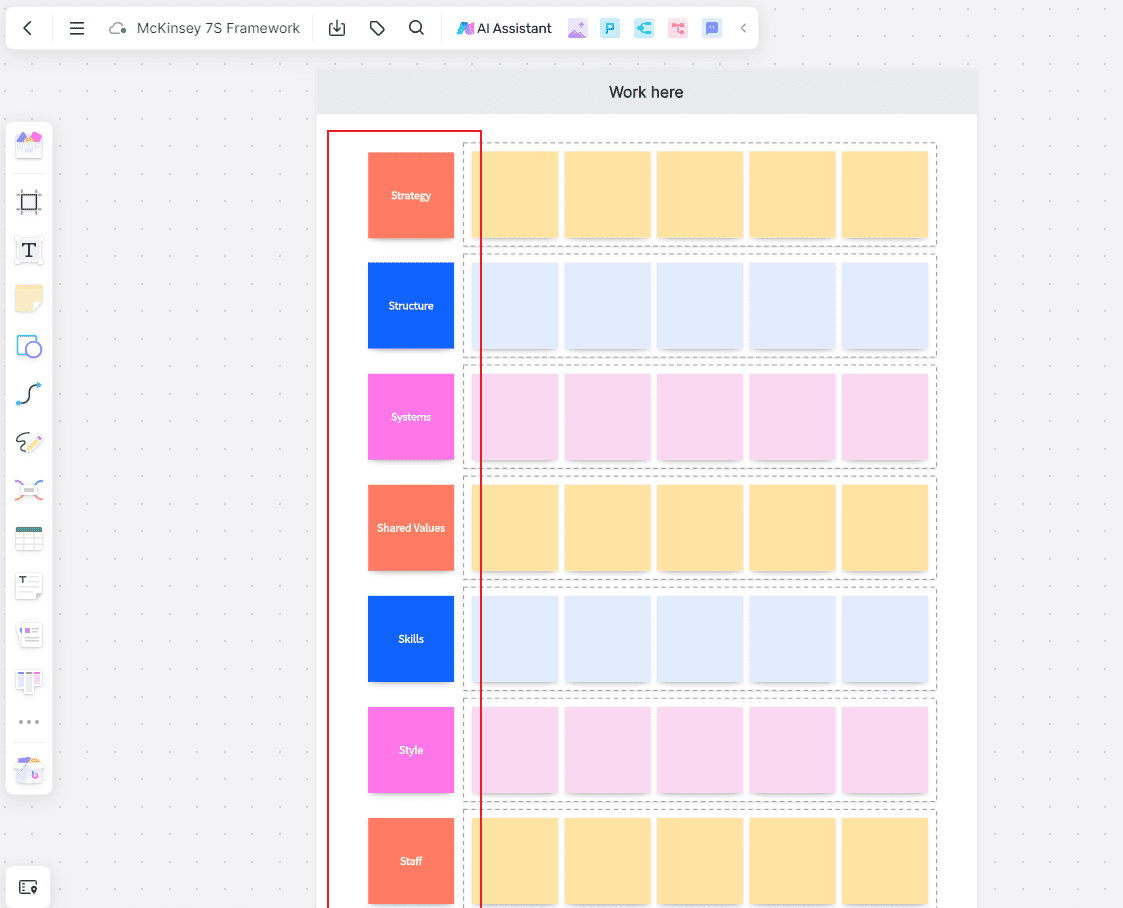
Mckinsey 7-s Model Elements
Firstly, hard elements mainly include:
Strategy: Strategy refers to the plan of action an organization devises to achieve its long-term goals. This involves assessing the organization's position, making strategic decisions, and executing these decisions to gain a competitive edge.
Structure: The Structure is how an organization is hierarchically arranged--including how roles and responsibilities are distributed among staff members.
Systems: Systems consist of all processes and procedures that underlie an organization's operations. This can include information systems, financial systems, recruitment procedures, and evaluation mechanisms that govern day-to-day operations.
Soft Elements refer to more intangible, harder to define, and generally influenced by corporate culture, including:
Shared Values: Shared Values are the core of the McKinsey 7-S model. These are the guiding principles or beliefs that are intrinsic to an organization and help shape its culture and identity. These values guide employee behavior and shape company decisions across the board.
Style: The leadership approach and management styles practiced within the organization. It reflects how leaders interact with employees and stakeholders.
Staff: The human resources within the organization, encompassing employee numbers, development, motivation, reward systems, expertise, and demographics.
Skills: Skills reflect the capabilities that exist within the organization. The unique capabilities and competencies that the organization possesses or needs to develop among its employees.
These elements are interdependent, with changes in one affecting the others. The model is often represented visually as a set of interconnected nodes, emphasizing the need for alignment across all seven elements.
Mckinsey 7-s Model Pros and Cons
The McKinsey 7-S Model is a powerful framework for analyzing and improving organizational alignment, but like any analytical tool, it has its strengths and weaknesses. Below are the pros and cons of the McKinsey 7-S Model.
Pros of the McKinsey 7-S Model
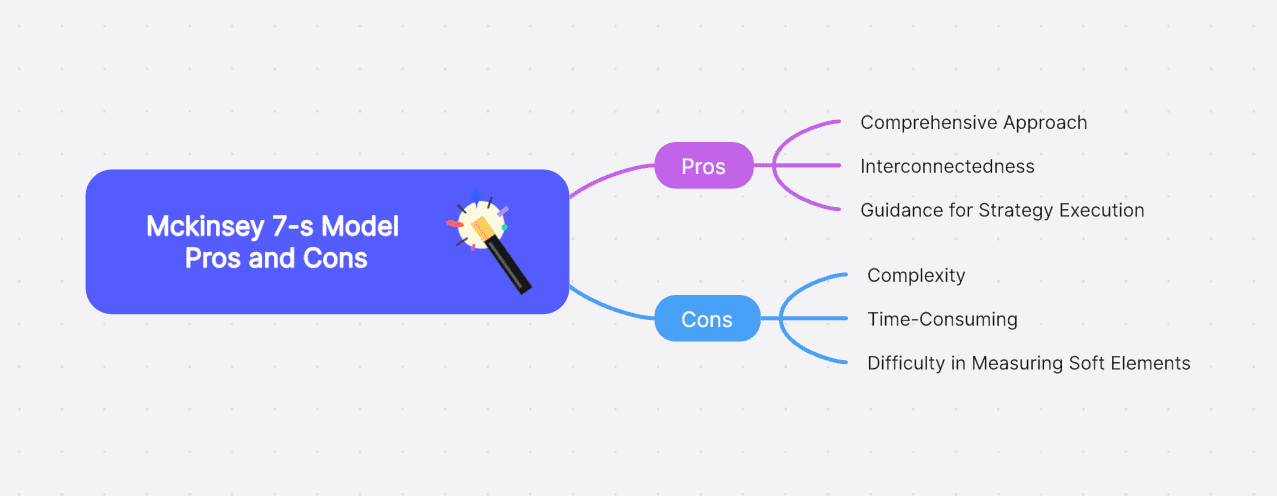
Comprehensive Approach: The model offers a comprehensive view of an organization by considering seven critical aspects: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Skills, Style, and Staff. It helps identify the organization's strengths and weaknesses across these facets.
Interconnectedness: The McKinsey 7-S Model emphasizes that all seven elements are interdependent. A change in one element can have a ripple effect on others, thereby promoting a holistic view when considering strategic decisions or changes.
Guidance for Strategy Execution: The model can guide strategy execution by highlighting the need for alignment between strategy and other organizational elements. It encourages organizations to consider how changes in structure or systems impact strategic objectives.
Cons of the McKinsey 7-S Model
Complexity: The interconnectedness of the seven elements can lead to complexity. It might be challenging to understand or manage the impact of changes in one aspect on others.
Time-Consuming: Analyzing all seven elements in-depth can be time-consuming. Organizations must be ready to invest considerable time and effort to benefit from this model fully.
Difficulty in Measuring Soft Elements: While the inclusion of soft elements adds depth to the analysis, these are often subjective and can be difficult to measure or compare effectively.
Overall, the McKinsey 7-S Model is a valuable framework for understanding and improving organizational alignment. Its comprehensive and interconnected approach can drive significant benefits, but its complexity and abstract elements require careful consideration and a committed effort to implement effectively.
Mckinsey 7-s Model with Example
The following cases provide a clearer understanding of the practical application of the McKinsey 7-s model.
1. Google Inc
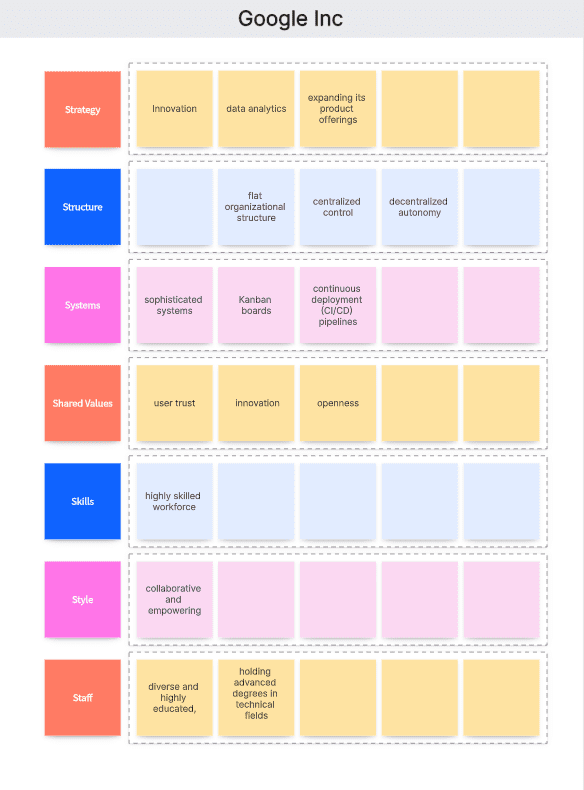
Strategy: Google's strategy has been focused on innovation, data analytics, and expanding its product offerings while maintaining a strong presence in search and advertising. They have also ventured into adjacent markets like cloud services, hardware, and AI.
Structure: Google has a flat organizational structure that encourages innovation and quick decision-making. It allows for both centralized control and decentralized autonomy, especially after the creation of its parent company, Alphabet Inc., which operates as a conglomerate.
Systems: Google has developed sophisticated systems for everything from its search algorithm to its advertising platform. Such as the use of Kanban boards and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Shared Values: Google's ten shared values and its current principles, like “it’s best to do one thing well”, emphasize user trust, innovation, and openness. These values guide the company's culture and decision-making.
Skills: Google has a highly skilled workforce, with a strong emphasis on hiring top talent in technology and engineering.
Style: Google's leadership style is collaborative and empowering, with a focus on giving employees the freedom to pursue innovative ideas, as seen with their "20% time" policy, where employees can spend 20% of their time on projects outside their regular work.
Staff: Google's staff is diverse and highly educated, with many employees holding advanced degrees in technical fields.
2. Amazon
Amazon has continued to expand globally, entering new markets and launching localized versions of its services.
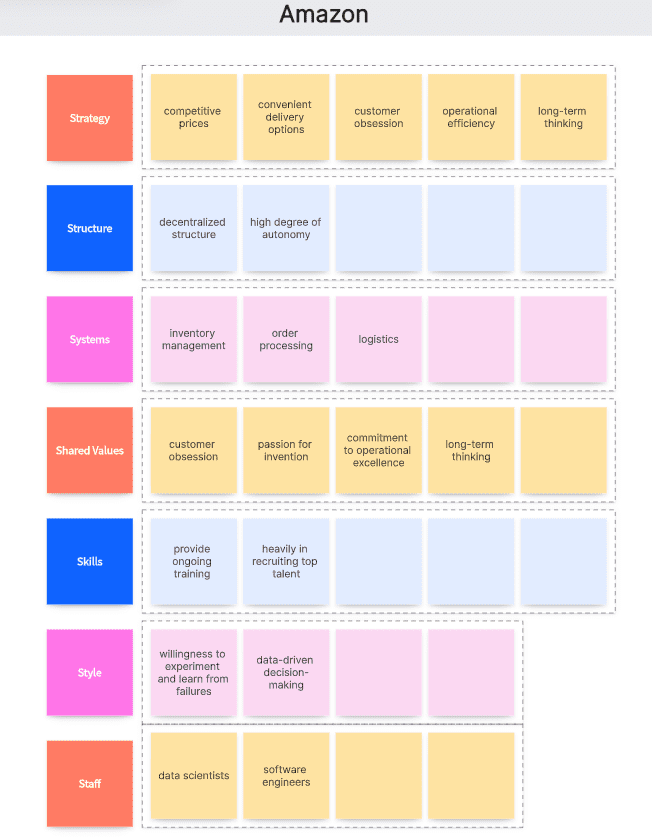
Strategy: Amazon's strategy has been to become the everything store, offering a vast selection of products at competitive prices with convenient delivery options. Their strategy also focuses on customer obsession, operational efficiency, and long-term thinking.
Structure: Amazon has a decentralized structure, with individual teams operating with a high degree of autonomy. The company is organized around its core businesses, with a strong emphasis on technology and logistics.
Systems: Amazon has developed advanced systems for inventory management, order processing, and logistics (such as their fulfillment centers and delivery network).
Shared Values: Amazon is guided by four principles: customer obsession rather than competitor focus, passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence, and long-term thinking. These values guide decision-making and behavior across the organization and are a key part of Amazon's culture.
Skills: Amazon has built a skilled workforce in technology, logistics, and retail. They invest heavily in recruiting top talent and provide ongoing training and development to ensure employees can adapt to the company's evolving needs.
Style: Amazon's leadership style is characterized by its emphasis on data-driven decision-making, a bias for action, and a willingness to experiment and learn from failures.
Staff: Amazon's staff is diverse and includes a wide range of roles, from software engineers and data scientists to warehouse associates and delivery drivers.
3. Starbucks
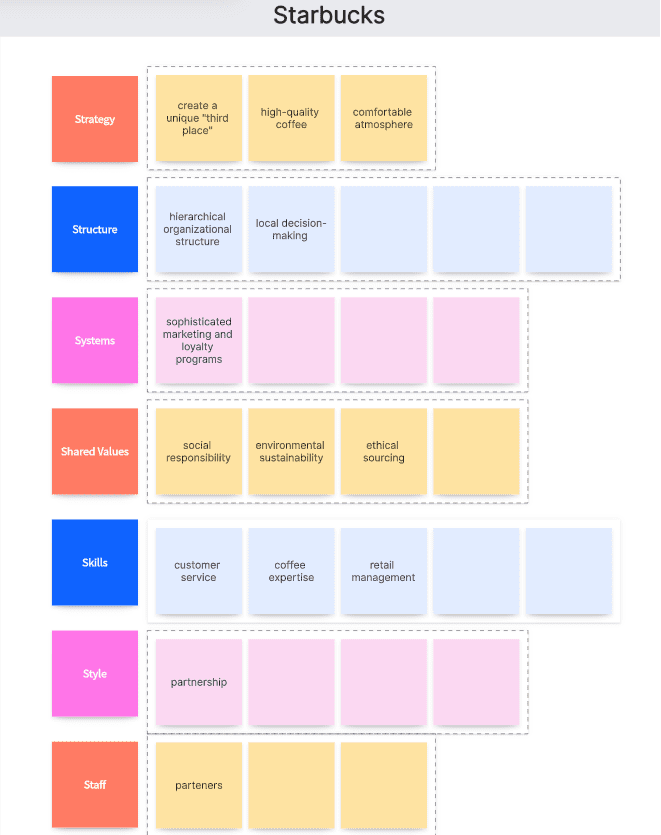
Strategy: Starbucks' strategy has been to create a unique "third place" between home and work where people can enjoy high-quality coffee and a comfortable atmosphere.
Structure: Starbucks has a hierarchical organizational structure with regional divisions and a strong central leadership. This structure allows for local decision-making while maintaining global consistency in brand standards and operations.
Systems: Starbucks uses sophisticated marketing and loyalty programs to engage customers and collect data for targeted promotions.
Shared Values: Starbucks has a strong set of shared values that emphasize social responsibility, environmental sustainability, and ethical sourcing.
Skills: Starbucks has focused on developing skills in customer service, coffee expertise, and retail management.
Style: The leadership style at Starbucks is collaborative and values-driven. Starbucks’s culture is built around the concept of "partnership," where employees are considered partners in the business.
Staff: Starbucks' staff, often referred to as "partners," are a key part of the company's success.
Mckinsey 7-s Model for Organizational Effectiveness
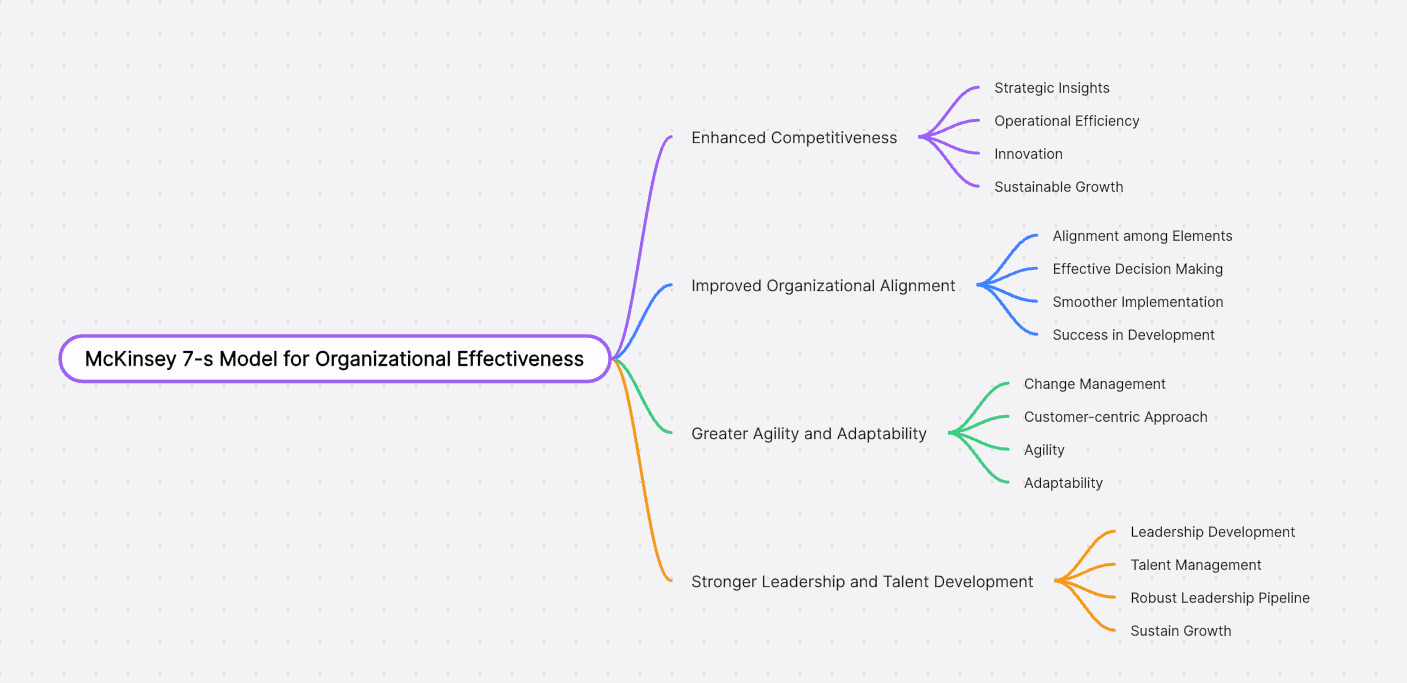
Enhanced Competitiveness
By adopting McKinsey 7-s model companies can develop a competitive edge. Strategic insights, operational efficiency, and innovation drive corporate development, allowing companies to outperform competitors and achieve sustainable growth.
Improved Organizational Alignment
McKinsey's frameworks, like the 7-S model, help organizations achieve better alignment among different elements. This alignment leads to more effective decision-making and smoother implementation of strategic initiatives, contributing to successful corporate development.
Greater Agility and Adaptability
McKinsey's focus on change management and customer-centricity fosters a culture of agility and adaptability. This approach enables companies to respond effectively to changing market conditions, emerging trends, and customer demands, supporting future corporate development.
Stronger Leadership and Talent Development
The emphasis on leadership development and talent management contributes to a robust leadership pipeline. This ensures that companies have suitable people to drive corporate development and sustain growth over time.
Mckinsey 7-s Model Template & Tool
An effective McKinsey 7S model will help you analyze your company and identify any performance gaps. To ensure you are getting the right information, you need to include all the important information. The Boardmix McKinsey Model Template is a one-stop tool to get you started with this management model. It will help you map out what you need to do to achieve your business strategy. Simply sign up and start filling it out with appropriate information!
Visual Collaboration
Boardmix provides a flexible canvas for teams to create and share diagrams, charts, and frameworks. This is particularly useful for illustrating complex concepts like McKinsey's 7-S model, where visualizing the relationships between different elements is important. Teams can collaboratively map out these frameworks, adding notes and connecting ideas.
Template Libraries
Boardmix often includes pre-made templates or allows users to create and share their templates. This feature can be used to create McKinsey-based templates, such as the 7-S model, business model canvases, or strategic planning templates. Teams can use these templates to quickly set up their brainstorming sessions or strategic planning meetings.
Real-time Collaboration
One of Boardmix's strengths is its capacity for real-time collaboration. This allows team members from different locations to work together on the same board simultaneously. When discussing McKinsey's 7-S models, such as strategy formulation or organizational structure, real-time collaboration can enhance communication and facilitate consensus-building among stakeholders.
Customizable and Adaptable
Boardmix allows users to customize templates to suit their specific needs. This flexibility is crucial when using frameworks like the 7-S model, which may require adaptation to reflect the unique aspects of a particular organization. Users can adjust the structure, add elements, and create links to reflect their organizational context accurately.
Sharing
Once a McKinsey-based template is filled out, Boardmix allows for easy documentation and sharing. Teams can export their work as PDFs or images for presentations or further analysis. This capability is valuable when presenting strategic plans to executives or board members, as it provides a clear visual representation of the concepts discussed.
Overall, Boardmix serves as a versatile tool for customizing and collaborating on McKinsey templates, enhancing communication and facilitating strategic planning within organizations. It can play a significant role in bringing McKinsey's frameworks to life, enabling teams to work together effectively and align their goals with broader corporate objectives.









