In today's fast-paced business landscape, having a clear and concise business model is essential for success. With innovative Business Model Canvas feature, entrepreneurs can now streamline their business planning process, visualize key components, and drive strategic decision-making with ease.
1. What is the Business Model Canvas
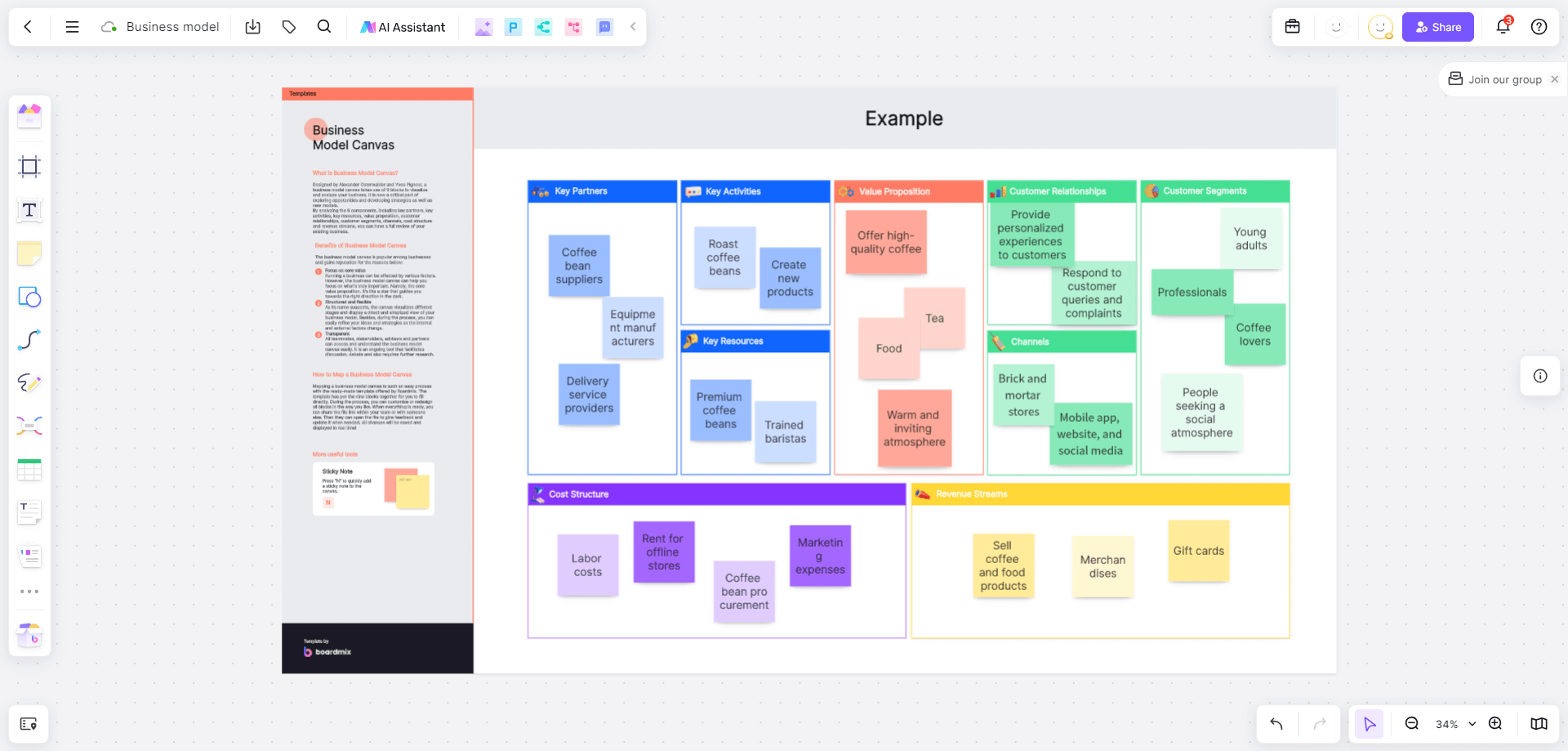
The Business Model Canvas is a visual chart that displays an organization's business model. It is a tool and method for organizing business models, helping to describe, assess, and change business models in a concise, visual, one-page format. The Business Model Canvas can help managers generate ideas, reduce risks, accurately target users, solve problems effectively, review existing businesses properly, and discover new business opportunities.
2. Components of the Business Model Canvas
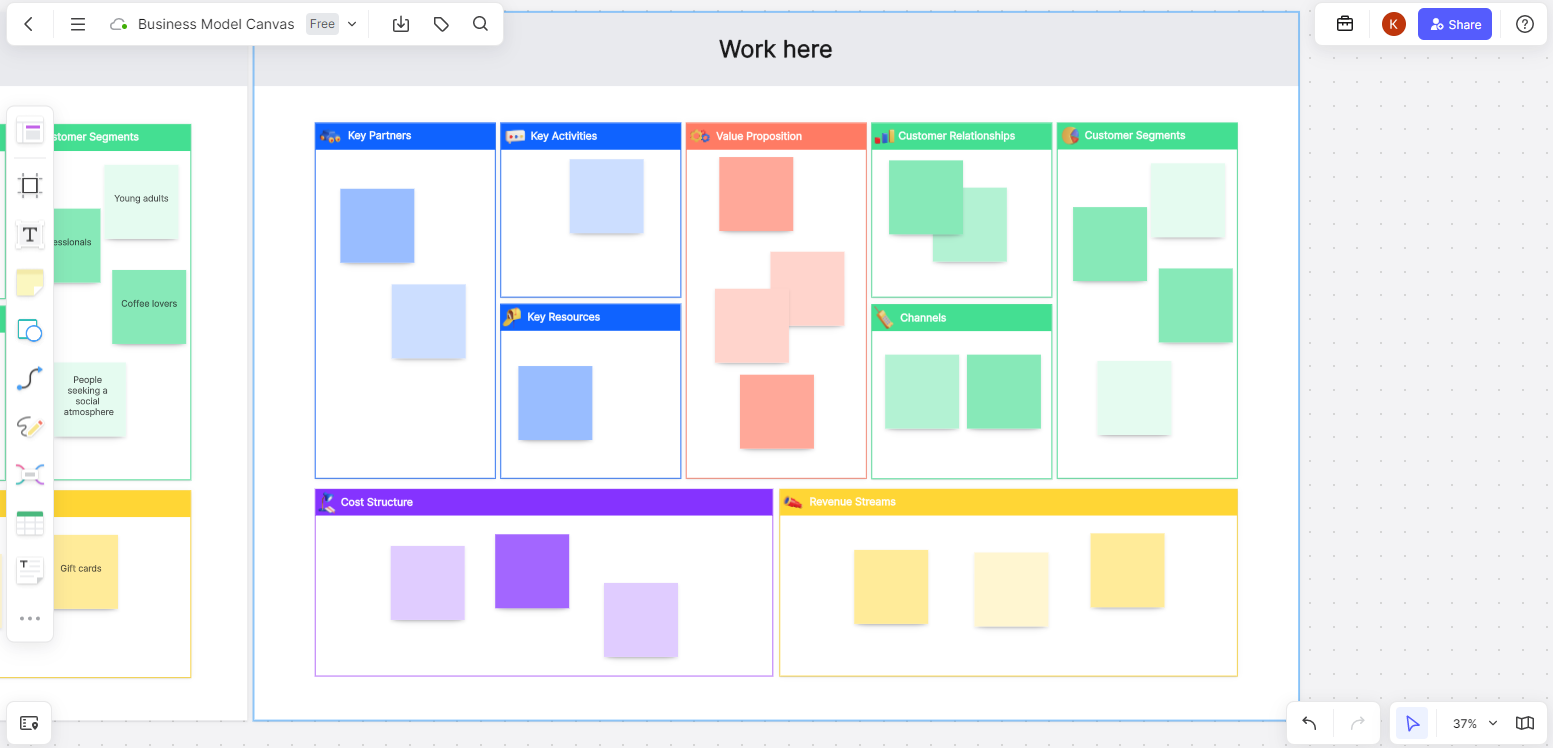
The Business Model Canvas uses visualization to help team members reach a consensus, facilitating discussions in a unified language. It consists of nine interconnected and mutually influential modules. We will use Boardmix online whiteboard to demonstrate this:
(1) Customer Segments
Businesses divide customers into several segments, each with common needs, behaviors, and other attributes. A business model can define one or multiple customer segments.
Key questions: Who are we creating value for? Who are our most important customers?
(2) Value Propositions
This section describes the series of products or services that create value for specific customer segments. Value propositions can be quantitative (e.g., price, speed of service) or qualitative (e.g., design, customer experience).
Key questions: What value are we delivering to the customer? What problems are we helping our customers solve? What needs are we satisfying? What products or services are we offering to each customer segment?
(3) Channels
This section describes how the company communicates with and reaches its customer segments to deliver its value proposition. Channels are customer touchpoints that play an important role in the customer experience, encompassing communication, distribution, and sales.
Key questions: Through which channels do our customer segments want to be reached? How are we reaching them now? How are our channels integrated? Which channels are most effective? Which channels are most cost-efficient? How are we integrating our channels with customer routines?
(4) Customer Relationships
This section describes the types of relationships a company establishes with specific customer segments. Businesses should clarify the desired types of relationships with each customer segment, which can coexist within the enterprise and its customer segments.
Key questions: What type of relationship does each of our customer segments expect us to establish and maintain? Which relationships have we established? How costly are these relationships? How are they integrated with the rest of our business model?
(5) Revenue Streams
This section describes the cash a company generates from each customer segment (costs must be subtracted from revenues to create earnings). A business model can involve multiple revenue streams, including one-time payments and recurring revenue.
Key questions: What value are our customers really willing to pay for? What do they currently pay for? How do they prefer to pay? How much does each revenue stream contribute to overall revenues?
(6) Key Resources
This section describes the most important assets required to make a business model work. These resources can be physical, financial, intellectual, or human and can be owned, leased, or acquired from partners.
Key questions: What key resources do our value propositions require? What key resources do our distribution channels require? What key resources do our customer relationships require? What key resources do our revenue streams require?
(7) Key Activities
This section describes the most important activities a company must undertake to make its business model work. These activities are necessary for creating and delivering value, reaching markets, maintaining customer relationships, and earning revenues. Different business models require different key activities.
Key questions: What key activities do our value propositions require? What key activities do our distribution channels require? What key activities do our customer relationships require? What key activities do our revenue streams require?
(8) Key Partnerships
This section describes the network of suppliers and partners that make the business model work. Partnerships can optimize business models, reduce risk, or acquire resources.
Key questions: Who are our key partners? Who are our key suppliers? Which key resources are we acquiring from partners? Which key activities do partners perform?
(9) Cost Structure
This section describes all costs incurred to operate a business model. Every business model component incurs costs.
Key questions: What are the most important costs inherent in our business model? Which key resources are most expensive? Which key activities are most expensive?
3. Business Model Canvas of Mobike
Next, we'll use Mobike as an example and create its Business Model Canvas using Boardmix online whiteboard.
Starting with customer segments: Mobike’s target customers are those who use public transportation but need to walk the last mile. Based on this customer group, our value proposition is to provide cheap and convenient short-distance transportation.
Through the solution of QR code payment and a flexible bike rental service, we connect with customers in densely populated urban areas. Due to the low cost and convenient usage, we can establish a stable relationship with customers without needing maintenance.
For revenue, Mobike earns from bike usage and also benefits from the deposit customers pay. The cost structure mainly involves bike procurement, maintenance, and business expansion expenses.
This is the detailed Business Model Canvas for Mobike created using Boardmix. By summarizing each module, we have a complete and detailed business model canvas for Mobike.
The drawing tool used in this article is Boardmix online whiteboard, and the Mobike business model canvas analysis diagram also comes from its extensive community resources. In addition, Boardmix offers a wide range of useful chart templates, all free to use with a single click, such as SWOT analysis templates, flowchart templates, brainstorming templates, work plan templates, and more. Just add or remove elements from the basic template to suit your needs, making it very convenient and practical. Try it out now!








