What are Porter’s five forces?
Michael Porter’s Five Forces Model, also known as Porter competitiveness model, was proposed by Michael Porter in the early 1980s. It holds that there are five forces that determine the scale and degree of competition in an industry. Together, these five forces influence the attractiveness of the industry. The five factors are bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, entry barriers, threat of substitutes, and competition among existing competitors.
Bargaining power of suppliers
The reasons for the high bargaining power of suppliers are as follows:
- The supplier has a large number of downstream customers, while enterprises have a lower proportion of purchases.
- The supplier’s products have certain characteristics, making the conversion cost too high. Therefore, the buyer is highly dependent on the supplier.
- There is no substitute in the supplier’s product.
Bargaining power of buyers
The influencing factors of buyers’ bargaining power are as follows:
- The products purchased by buyers account for a large proportion of the overall product sales of enterprises, which virtually increases the power of bargaining in business negotiations. The big customer who plays a decisive role is like the God.
- Sellers belong to industries made up of a large number of relatively small companies. Small scale means little bargaining power.
- Buyers have the ability to achieve backward integration, while sellers cannot achieve forward integration.
Entry barriers
When an enterprise enters a new industry, it will certainly bring new production capacity and new industrial resources. However, the market has been carved up by existing enterprises in the industry. If a new enterprise wants to obtain a place, it will inevitably have fierce competition with existing enterprises in terms of market share and raw material supply. The final result may be a decline in profitability or even an existential crisis for existing companies in the industry.
The entry barriers are decided by 2 factors:
- The response of incumbents to new entrants. The expected reaction of the existing enterprises to the entrants, mainly the possibility of taking retaliatory actions, depends on the financial situation of the relevant manufacturers, the record of retaliation, the scale of fixed assets, the growth rate of the industry, etc.
- The size of barriers and expected earnings of new enterprises entering new fields. The entry barriers mainly include economies of scale (the effect of economies of scale is to force new enterprises to enter the industry at a large scale, and at great risk of being isolated and boycotted), product differentiation, capital requirements, resale costs, sales channel development, government actions and policies, cost disadvantages independent of scale, natural resources, geographical environment and more. Some of these obstacles are difficult to break through with the help of copying or imitation.
Threat of substitutes
What are substitutes? Substitutes have similar performance as existing products or services and can meet the same needs of customers. The threat of substitutes is that the price and profitability of existing products will be limited.
Competition among existing competitors
Generally, there are 4 situations in which the competition between enterprises in the industry intensifies:
- The entry barriers of the industry are relatively low, and the competition is evenly matched. There are more competitors and a wide range of participants. As there are too many companies in the same industry, enterprises in the industry cannot implement marketing strategies against competitors.
- The market is saturated, the growth of demand is basically stagnant, the competition between enterprises is low in technology content. The means of competition are also relatively simple, which can only reduce the price of products or increase the marketing budget, advertising and other ways to promote sales.
- There is almost no difference between the products or services provided by competitors, and the brand loyalty shown by customers is actually a kind of habitual purchasing behavior. Changing product choice has little impact on customers, and the cost of changing brand choice is extremely low.
- Under the great pressure of competition, sometimes the decision-makers of enterprises have to take the "gambling" way to participate in the market competition. A right strategic decision can bring huge benefits to the enterprise, but a wrong strategic decision may make the enterprise never turn over. The business decisions of enterprises face great risks under the pressure of the market.
Why using Porter’s five forces model?
Porter’s Five Forces model helps companies to make informed decisions on entering a specific market, as well as penetrating or launching a product into the market. Specially, it helps companies to conduct a comprehensive industry analysis, evaluate investment options, assess market attractiveness and the competitive environment, as well as anticipate industry changes. In this way, companies can easily understand the internal and external factors that influence their profitability.
Therefore, Porter’s Five Forces model is a valuable tool for businesses to assess the competitive landscape, make informed strategic decisions, and gain a competitive edge in their industry. It provides a structured approach to understanding industry dynamics, evaluating market attractiveness, and formulating effective strategies to achieve long-term success.
How to use Porter’s five forces model?
To effectively use the model, start by looking at each of the five forces in turn, and think about how they apply in your industry. To this end, you should be familiar with the five forces, understand the factors and dynamics that influence each force, and gather relevant information.
Next, evaluate the impact and strength of each force on your industry. You may write down the forces that are at play in your industry, and summarize the size and scale of each.
Finally, analyze the results of your assessment to identify key insights and trends. Based on the analysis, develop strategies to address the findings of each force.
Due to the dynamic nature of industry, remember to regularly monitor the five forces and reassess your industry analysis. Always adapt your strategies accordingly to maintain a competitive advantage. What’s more, it may be more effective to use Porter’s Five Forces in conjunction with a SWOT analysis, since the former is a macro tool while the latter is a micro-analytical tool. Also, note that although the model provides a structured framework, the depth and extent of analysis may vary depending on the specific industry and business context.
10 Porter’s Five Forces Examples for Beginners
The Airline Industry
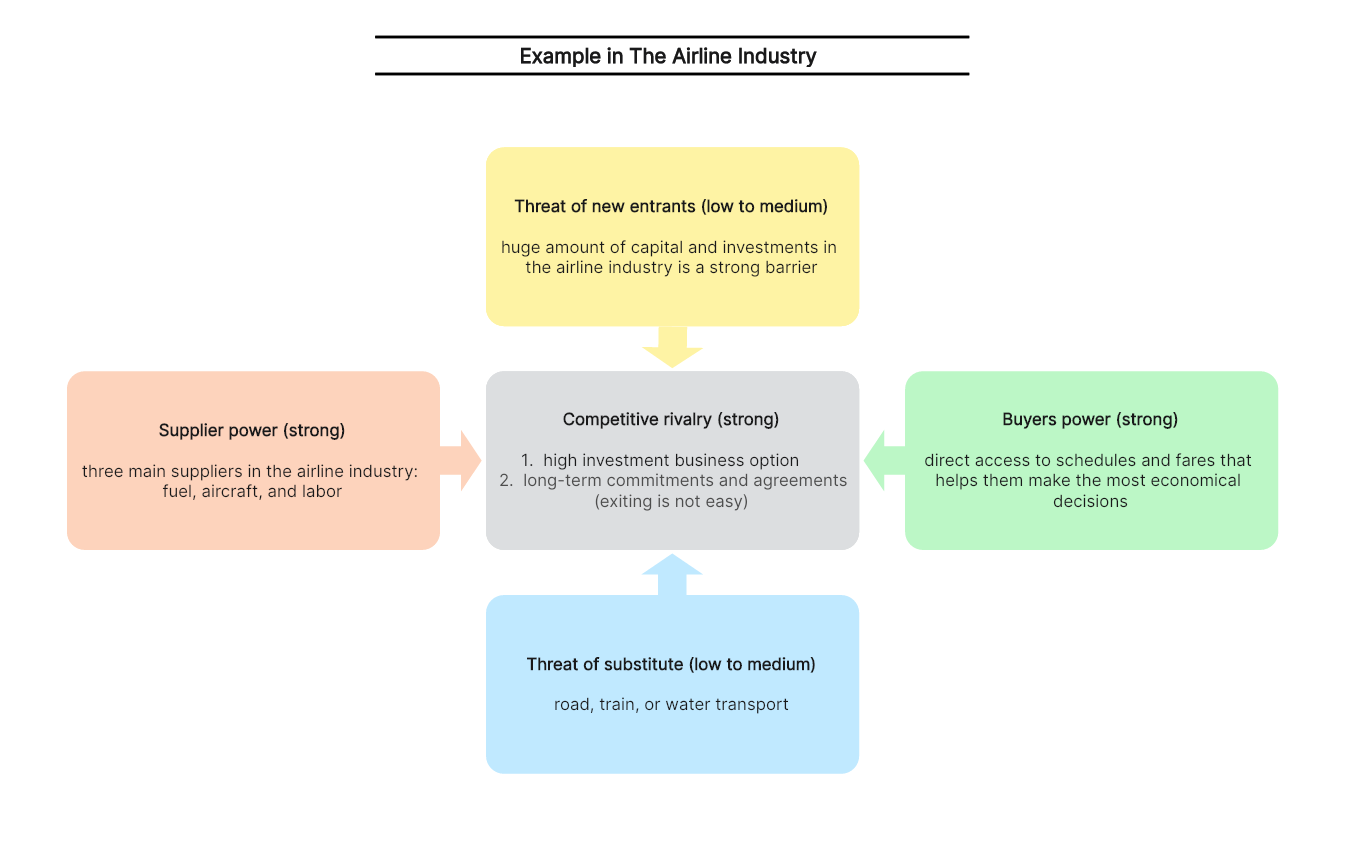
Here we analyze Porter’s five forces in the airline industry to understand the different dynamics of the airline industry.
- Competition in the industry (strong force)
The airline industry competitors analysis shows that the rivalry in the airline industry is extremely strong due to the following reasons. Firstly, since it is a high investment business option, the number of competitors is not increasing phenomenally. Also, exiting is not easy because of long-term commitments and agreements.
- The threat of new entrants (low to medium force)
The huge amount of capital and investments in the airline industry is a strong barrier. The brand image, brand loyalty, and market share of airline industry can mitigate this risk effectively. Also, exclusive access to raw materials and suppliers is another factor contributing to airline industry ‘ competitive edge.
- The bargaining power of suppliers (strong force)
There are three main suppliers in the airline industry, including fuel, aircraft, and labor. Firstly, the oil price is fixed based on global fluctuations. The second factor is aircraft companies. The bargaining power of these suppliers is very strong, for there are two big suppliers, i.e., Airbus and Boeing. Finally, the labor always challenges companies with union politics and demands.
- The bargaining power of customers (strong force)
The online ticketing and distribution system allow customers to have direct access to schedules and fares that helps them keep the most economical decisions. The entry of low-cost carriers has also increased the bargaining power of customers in Porter’s five forces in the airline industry.
- Threat of substitute products or services (medium force)
There are many alternatives for passengers to replace air travel. They can travel by road, train or water transport. However, air travel is still the best option when time is a factor. So it is considered a low to medium force. This factor has greater impact on regional travel, where short distance makes road and train travel more economical, while in international travel, this factor has a very minimal effect.
Reference: https://www.edrawmax.com/article/airline-industry-porters-five-forces-analysis.html
The Fast Food Industry
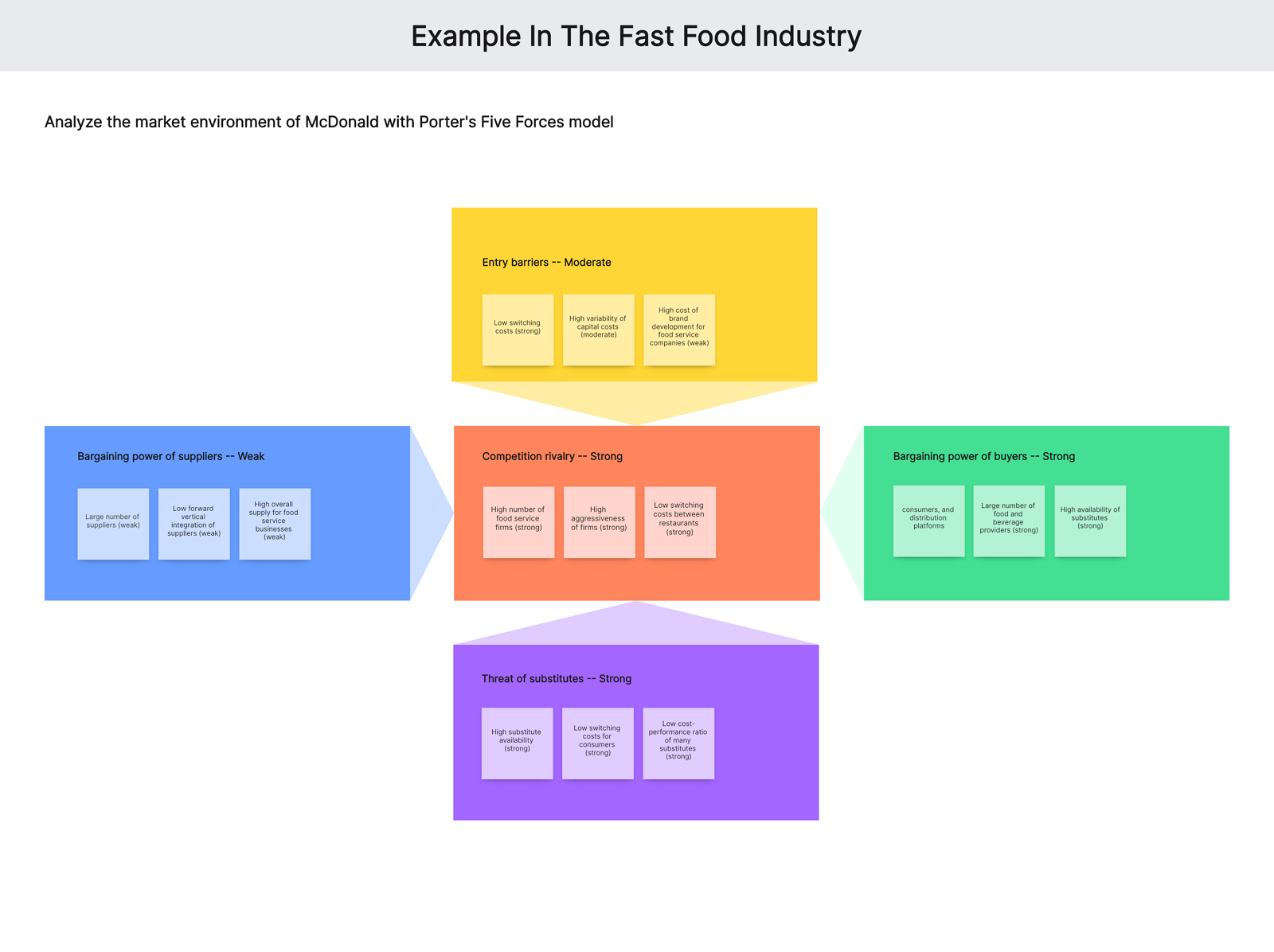
Here we analyze Porter’s five forces in the fast food industry, taking McDonald’s Corporation as an example.
Competition in the industry (strong force)
In McDonald’s case, the strong force of competitive rivalry is based on the following external factors:
- High number of food service firms – strong force
- High aggressiveness of firms – strong force
- Low switching costs between restaurants – strong force
The bargaining power of customers (strong force)
This element of the Five Forces analysis deals with the leverage of consumers, and how their decisions impact food service businesses. In McDonald’s case, the following are the external factors that contribute to the strong bargaining power of buyers:
- Low switching costs – strong force
- Large number of food and beverage providers – strong force
- High availability of substitutes – strong force
The bargaining power of suppliers (strong force)
This element of the Five Forces analysis model shows the impact of suppliers on firms and the fast-food restaurant industry environment. In McDonald’s case, the weak bargaining power of suppliers is based on the following external factors:
- Large number of suppliers – weak force
- Low forward vertical integration of suppliers – weak force
- High overall supply for food service businesses – weak force
Threat of New Entrants or New Entry (moderate force)
This element of the Five Forces analysis refers to the effects of new players on restaurant businesses. In McDonald’s case, the moderate threat of new entry is based on the following external factors:
- Low switching costs – strong force
- High variability of capital costs – moderate force
- High cost of brand development for food service companies – weak force
Threat of substitution (strong force)
This element of deals with the potential effects of substitutes on the growth of the restaurant chain business. The following external factors make the threat of substitution a strong force against McDonald’s:
- High substitute availability – strong force
- Low switching costs for consumers – strong force
- Low cost-performance ratio of many substitutes – strong force
Reference: https://panmore.com/mcdonalds-five-forces-analysis-porters-model
The Smartphone Industry
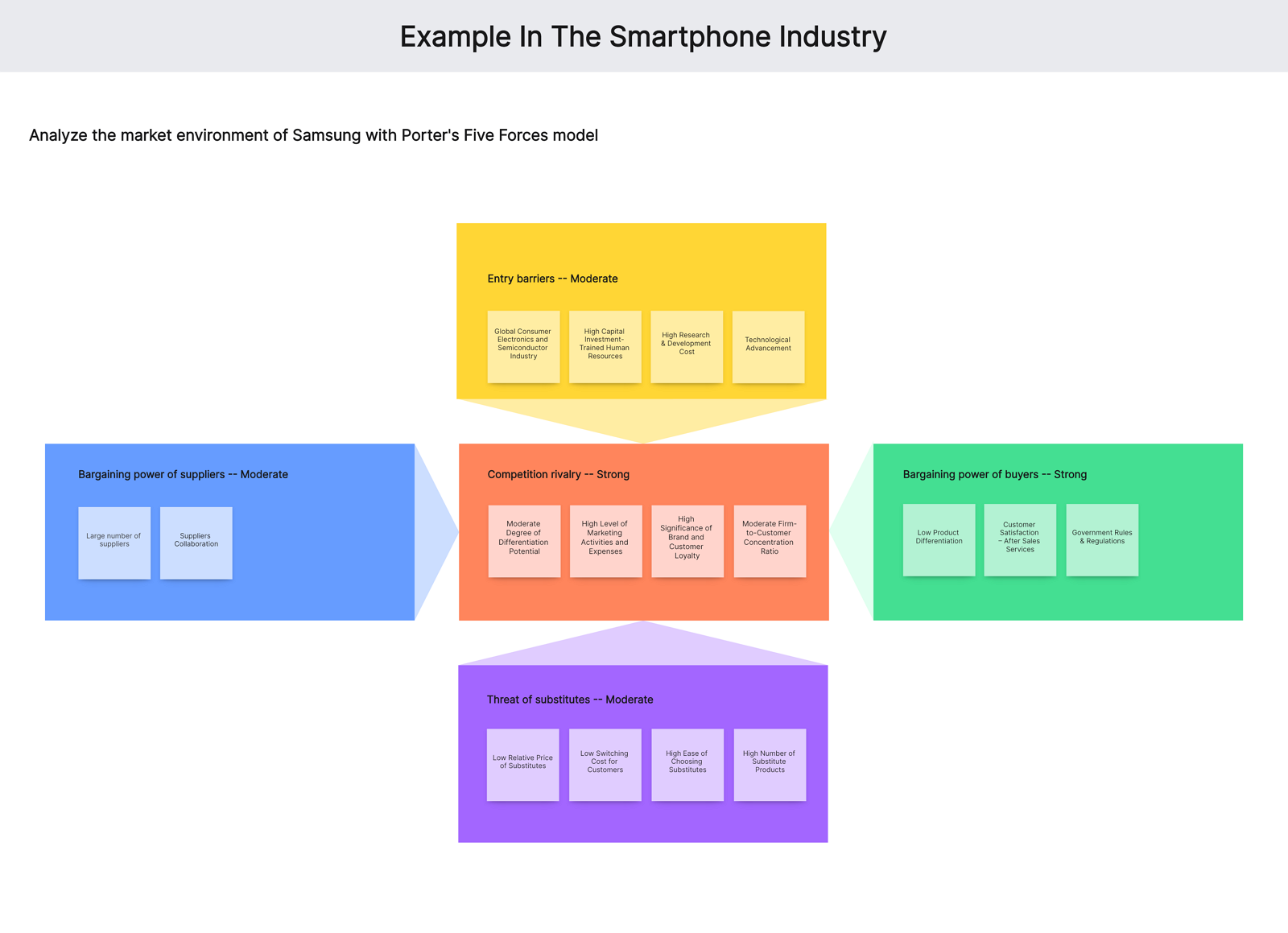
Here we analyze Porter’s five forces in the smartphone industry to understand the different dynamics of the Smartphone industry.
Competition in the industry
- Moderate Degree of Differentiation Potential: The products of Samsung have some unique selling points but this does not mean that consumers are left with no choices. Some of their differentiating qualities are passable and can be considered a mere marketing gimmick.
- High Level of Marketing Activities and Expenses: Most consumer electronics companies spend billions of dollars each year to increase or retain brand awareness and push their products to their target consumers.
- High Significance of Brand and Customer Loyalty: Brand reputation and customer loyalty are also of great significance. Take note that one of the competitive advantages of Apple is its legion of steadfast customers and its established reputation as a premium and dependable brand.
- Moderate Firm-to-Customer Concentration Ratio: The size of the global target market for consumer electronic products is about 3 to 5 billion people. The number of consumer electronics companies is thousands. While it seems low, less than a hundred incumbents and newer entrants collectively hold a greater portion of the entire market share.
The threat of new entrants
- Global Consumer Electronics and Semiconductor Industry: High revenue and growth potential in the Consumer Electronics market. Besides, the segment Telephony is the market’s largest segment.
- High Capital Investment-Trained Human Resources: The new entrant will be requiring high capital investment. As due to the specialized nature of the product only limited human resource can handle such high-end products.
- Technological Advancement: Due to the changing trend in consumer electronic, semiconductor and engineering industry towards technological advancement, only high technological advance companies or groups can enter such a market.
The bargaining power of suppliers
- Large Number of Suppliers: There is low level of differentiation and there are many suppliers in the industry. Majority of the manufacturing operations are outsourced to under developed countries, so suppliers have less influence.
- Suppliers Collaboration: Samsung Electronics has an enormous supply chain around the globe. The company has close ties and collaboration with the suppliers and practices Green Management with its suppliers
The bargaining power of customers
- Low Product Differentiation: Switching does not bring a significant change in the product that customer needs due to low product differentiation.
- Customer Satisfaction – After Sales Services: Samsung always received high customer satisfaction around the world.
- Government Rules & Regulations: Changing government rules and regulations are formulated in the favor of customers which added in the buying bargain power.
Threat of substitute products or services
- Brand Loyalty: The substitute for Samsung products are the competitors within the industry as customer can easily switch from one brand to another with low switching cost, usually because of lower prices but poor quality, so any substitution can only be replaced at the cost of brand loyalty.
References: https://www.konsyse.com/articles/porters-five-forces-analysis-of-samsung/
https://www.portersfiveforces.org/samsung-porters-five-forces/
The Retail Industry
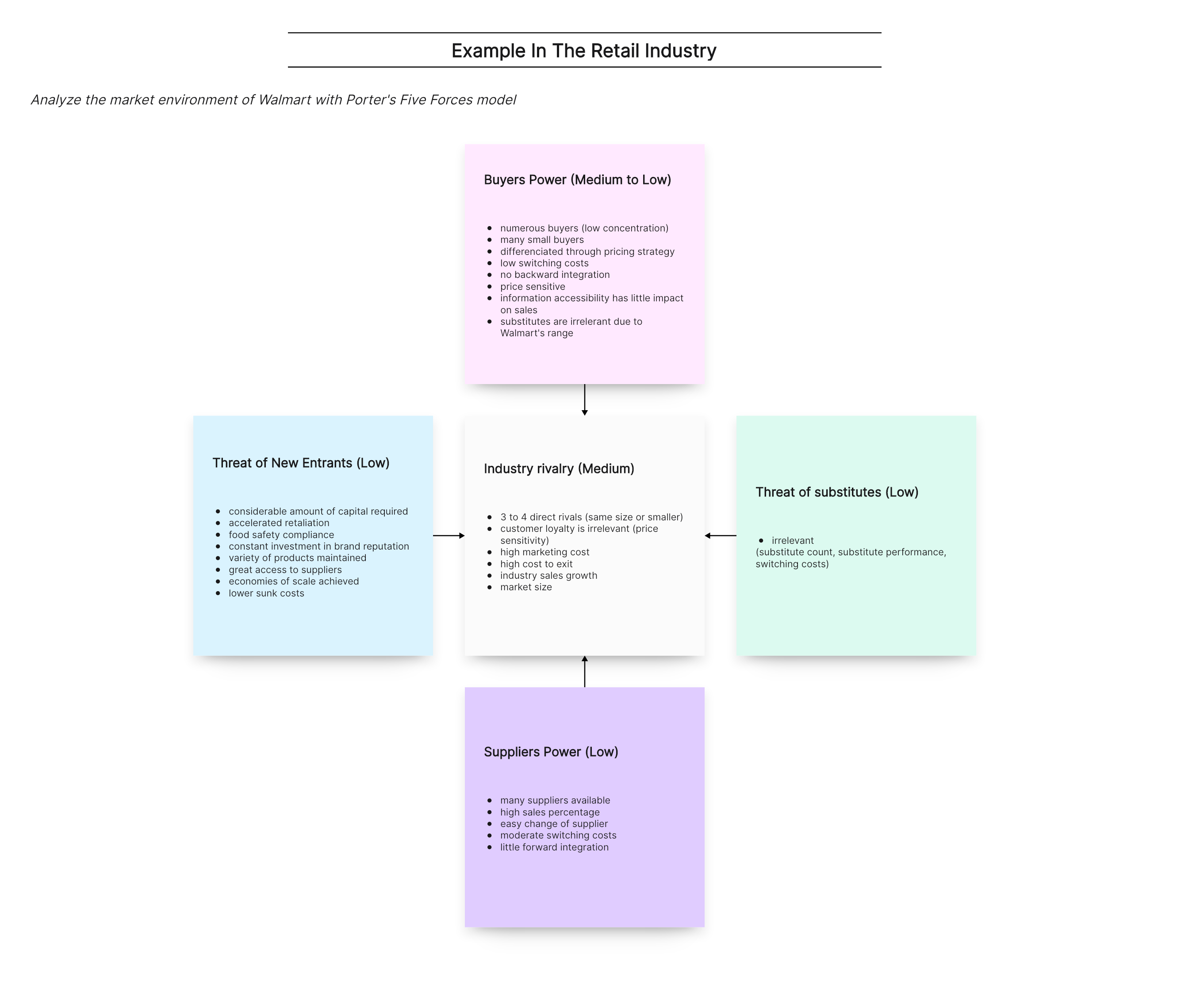
The following shows an example of Porter’s five forces analysis based on Walmart Inc.
- Competitive rivalry
The competitive advantage economies of scale and price strategy bring to Walmart can hardly be found elsewhere. There are, however, a few rivals the company must keep a vigilant eye on, including Costco, Target, Kroger, and Amazon. Still, their distribution channels and pricing strategies are yet to outperform Walmart’s.
- Threat of New Entrants
Walmart invests a lot in sales, marketing, distribution, and product development, posing a financial threat to new comers. Walmart sustains a great relationship with suppliers and sells to many customers, so economies of scale indeed work in its favor. Because of its well-designed distribution systems and range, there are also low sunk costs.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
Walmart deals with many small buyers daily, which disseminates the purchasing power of those buyers. It offers exclusive low-price approach and convenience. Retail industries are always differentiated through pricing strategy. Besides, switching costs are low. However, Walmart’s product variety, low prices, and locations are usually superior than other stores.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
With its large purchasing volumes and broad customer reach, Walmart is a buyer of high power. That’s why its suppliers ensure they cater to its needs as best as possible. Besides, Walmart has long employed a Supplier Diversity Program as part of its Corporate Social Responsibility outlook, further mitigating its dependency on a single distributor.
- Threat of Substitutes
Since almost all product variations are easily found on the store shelves of Walmart, there’s no real threat of substitutes to consider.
Reference:https://www.studysmarter.co.uk/explanations/business-studies/business-case-studies/porters-five-forces-walmart/
The Film Industry
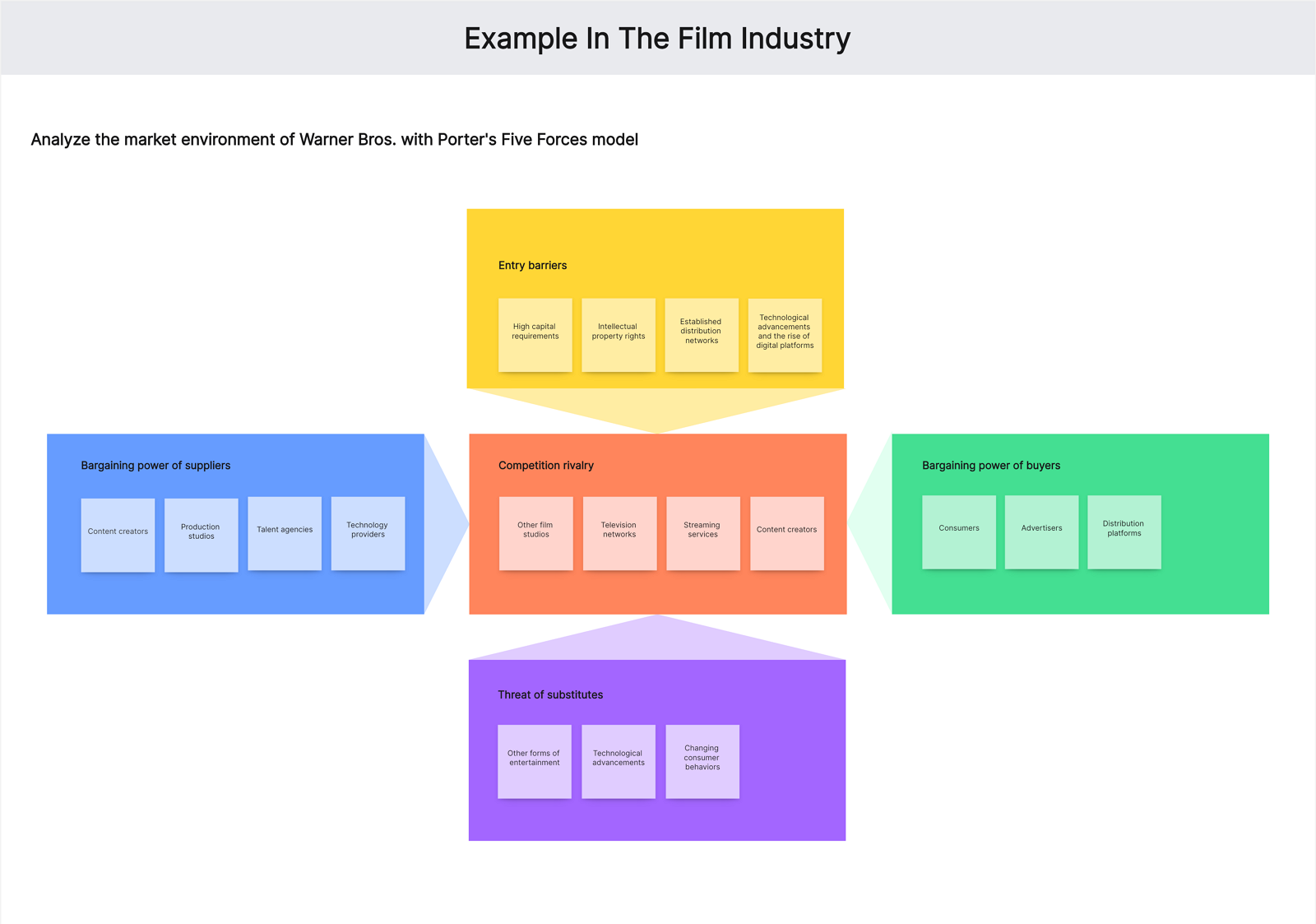
Here’s an example of applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis to Warner Bros.
- Threat of new entrants
This element has to consider factors like high capital requirements, intellectual property rights, and established distribution networks. Besides, technological advancements and the rise of digital platforms have lowered some barriers for new competitors to enter the market.
- Bargaining power of suppliers
Suppliers in the entertainment industry include content creators, production studios, talent agencies, and technology providers. The bargaining power of suppliers can vary depending on their popularity, exclusivity, and the demand for their content.
- Bargaining power of buyers
Buyers in the entertainment industry consist of consumers, advertisers, and distribution platforms. The bargaining power of buyers is influenced by factors such as audience preferences, advertising budgets, and the availability of alternative content.
- Threat of substitute products or services
Substitutes include other forms of entertainment, such as video games, live events, books, and other media formats. Technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors can lead to shifts in consumer spending and time allocation.
- Intensity of competitive rivalry
Competitors include other film studios, television networks, streaming services, and content creators. Competitive rivalry is driven by factors such as content quality, originality, marketing efforts, distribution reach, and audience engagement.
Reference: https://research-methodology.net/warner-bros-porters-five-forces-analysis/
The Pharmaceutical Industry

Here’s an example of applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis to Indian pharmaceutical industry.
- Threat of new entrants
On the one hand, strict government regulations prevent entry of new players. On the other hand, it is difficult for pharmaceutical companies to survive because of high gestation period.
- The power of buyers
In India, generic drugs offer a cost effective alternative to drug innovators and significant savings to customers. In addition, biosimilars offer significant cost saving for insurance companies for people in India.
- The power of suppliers
The difficulty to manufacture APIs such as steriods, sex hormones and peptides give bargaining power to suppliers. However, generic APIs do not have much of that power.
- Threat of substitutes
While the threat from substitute products is low, Homeopathy (a pseudo-scientific system of alternative medicine) and Ayurvedic (the ancient Indian medical system) medicines can provide competition.
- Rivalry among competitors
Growth opportunities are expected to grow in next few years with many drugs going off patent in the US and other countries, thus increasing competition. Besides, India pharma companies will face competition from other big pharma companies.
Reference:https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329238103_Indian_Pharmaceutical_Industry_The_Changing_Dynamics
The Automobile Industry
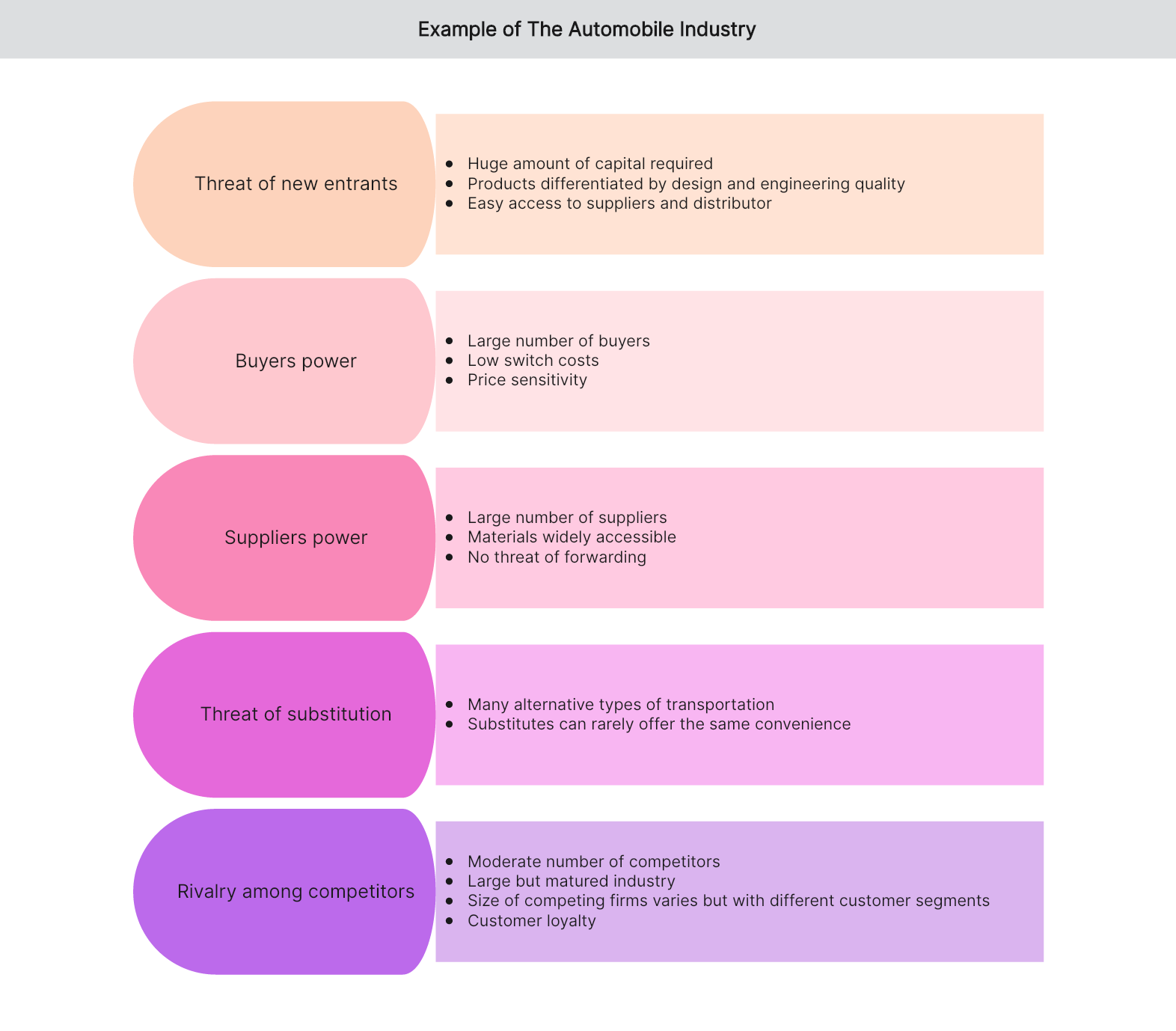
Here’s an example of applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis to Indian pharmaceutical industry.
Threat of new entrants
- To enter this industry requires huge amount of capital investment.
- Products are mainly differentiated by design and engineering quality.
- New entrants could easily access suppliers and distributors, reducing the barriers of entrance.
Power of buyers
- There are large number of buyers.
- It cost little for buyers to switch to another brand of vehicle or to start using another type of transportation.
- Buyers are price sensitive and their decision is often based on how much a vehicle costs.
Power of suppliers
- There are large number of suppliers.
- Materials are widely accessible in this industry.
- Suppliers do not pose any threat of forwarding.
Threat of substitution
- There are many alternative types of transportation, such as bicycles, motorcycles, trains, buses, or planes.
- Substitutes are not always as convenient as vehicles.
Competitive rivalry
- There are moderate number of competitors.
- The automobile industry is very large but matured.
- The size of competing firms varies but they usually compete for different consumer segments.
- Customers in this field are always loyal to their brands.
Reference:https://www.slideteam.net/porters-five-forces-analysis-of-the-automotive-industry-world-motor-vehicle-production-analysis.html
The Hotel Industry
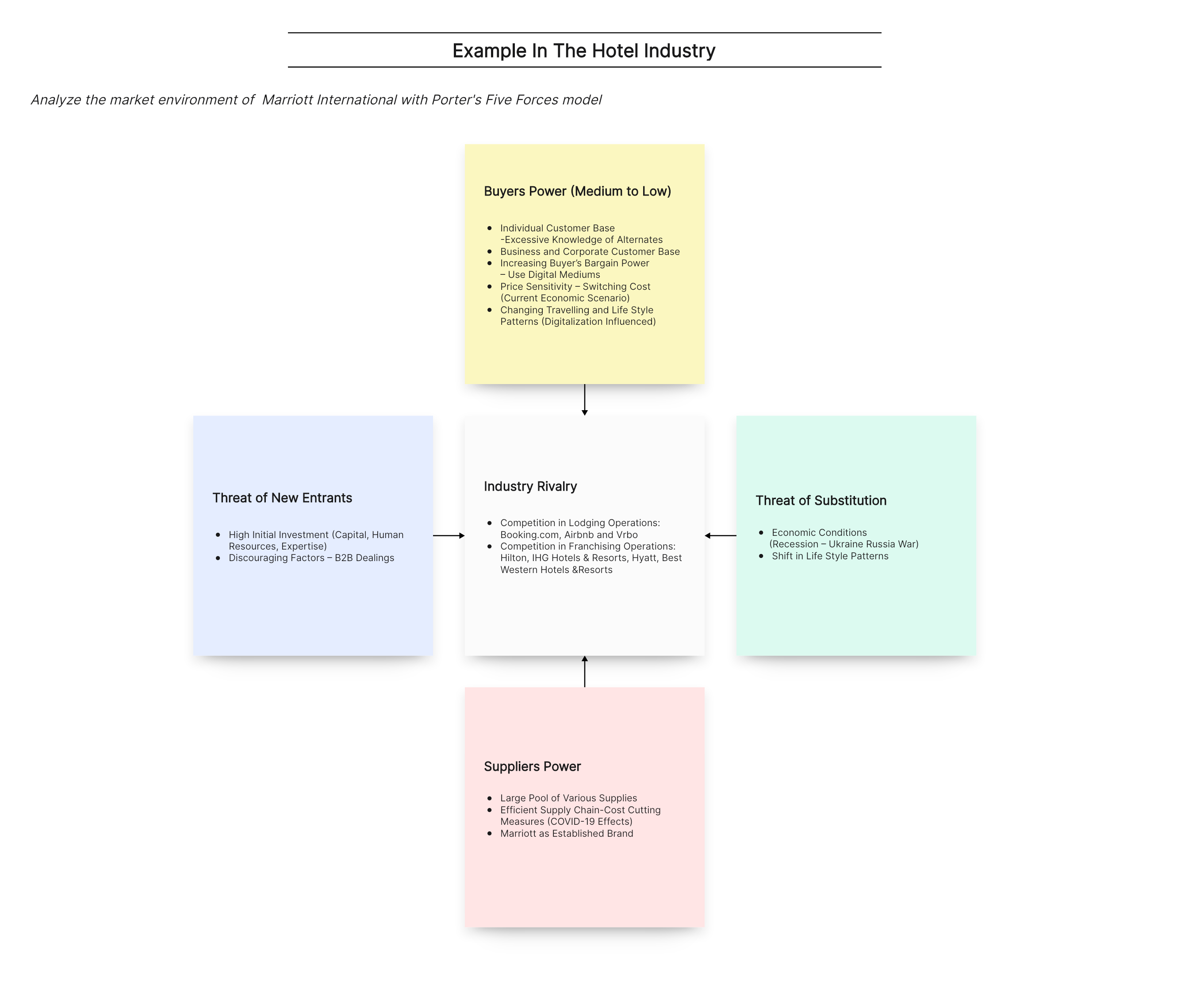
Below we can see an example of Porter’s five forces analysis based on Marriott International.
Threat of new entrants
- High Initial Investment (Capital, Human Resources, Expertise): Launching an extensive arrangement does not only need huge capital but also trained human resource and expertise to manage and plan all this, which is challenging for a new entrant.
- Discouraging Factors–B2B Dealings & Sudden Business Impacted: Marriott International serves 2 types of customers including individuals and corporate business clients (via large contracts). The past COVID 19 also exert a sudden discouraging impact on new entrants.
Power of buyers
- Individual Customer Base–Excessive Knowledge of Alternates: The bargain power for individual customers is increasing due to digitalization, life style shifts and changing business model, easy and fast travel booking, etc.
- Business and Corporate Customer Base: This customer base has less options or tied with the hotels via large contracts with a long term relationship.
- Increasing Buyer’s Bargain Power–Use Digital Mediums: Increasing Use of digital mediums and developing digital mediums expertise also increasing buyer’s bargain power.
- Changing Travelling and Life Style Patterns (Digitalization Influenced): Selection between a physical meeting or digital meeting is available also gives more power in the customer’s hand.
Power of suppliers
- There are large number of suppliers.
- Efficient Supply Chain–Cost Cutting Measures (COVID-19 Effects): Due to COVID-19 lockdown, various cost cutting measures were adopted with the efficient supply chain management to reduce the operational cost to maximum. This further reduces the supplier’s bargain power.
- Marriott as Established Brand: Marriott International is an established brand keep attracting suppliers to remain a Marriott supplier, also bulking buying from a trusted customer are the factors decreasing supplier bargain power.
Threat of substitution
- Economic Conditions (Recession–Ukraine Russia War): Currently global recession and increasing war trends may further impact the hotel industry which can be avoided by major business model changes.
- Shift in Life Style Patterns: Any new trending and excessively changing life style patterns can substantially offer substitution services and products for leisure to travel and stay possibilities.
Competitive rivalry
- Competition in Lodging Operations: Marriott International is facing tough competition from different international travelling companies with online booking services and online platforms. This increase the competition from service to pricing, brand recognition, safety and many other important areas.
- Competition in Franchising Operations: Brand affiliation is common in US for attracting the guests and franchisees. In franchising business Marriott International is facing tough competition from Hilton, IHG Hotels & Resorts, Hyatt, Best Western Hotels & Resorts (Marriott International, Annual Report, 2021).
Reference: https://www.portersfiveforces.org/marriott-porters-five-forces/
The Banking Industry
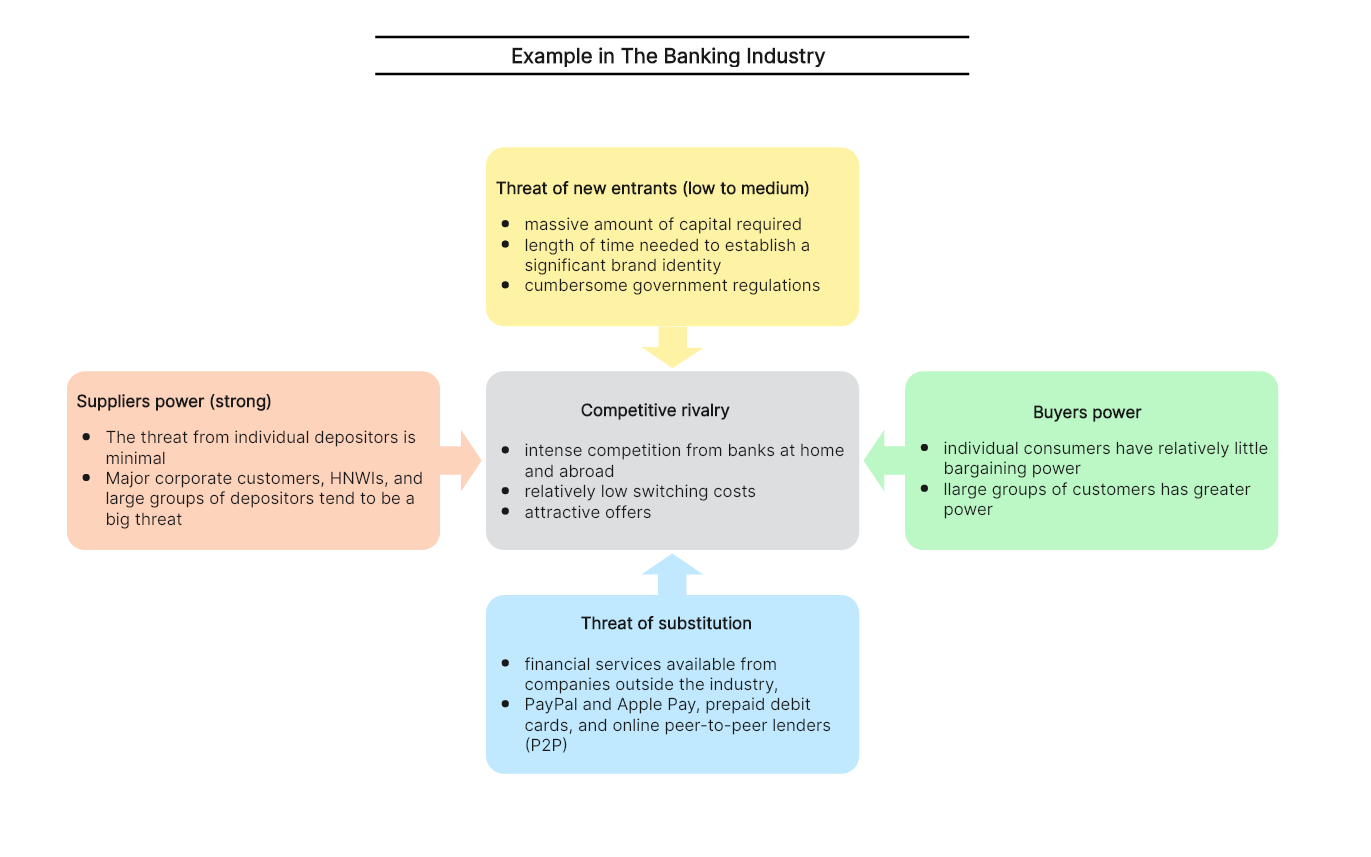
Here’s an example of applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis in the banking industry.
Threat of new entrants
- There are massive amount of capital required to enter the banking industry.
- There is length of time needed to establish a significant brand identity.
- There are cumbersome government regulations to follow.
Power of buyers
In terms for the bargaining power of customers, things vary because individual consumers have relatively little bargaining power while large groups of customers have greater power.
Power of suppliers
- The threat from individual depositors is minimal.
- Major corporate customers, HNWIs, and large groups of depositors tend to be a big threat.
Threat of substitution
The threats mainly come from financial services available from companies outside the industry, including PayPal and Apple Pay, prepaid debit cards, and online peer-to-peer lenders (P2P).
Competitive rivalry
- There are intense competition from banks at home and abroad.
- The switching costs from one bank to another is relatively low.
- Many banks tend to provide attractive offers to their customers, which may increase the competitive level.
Reference: https://www.porteranalysis.com/porter-five-forces-analysis-of-banking-industry/
The E-commerce Industry
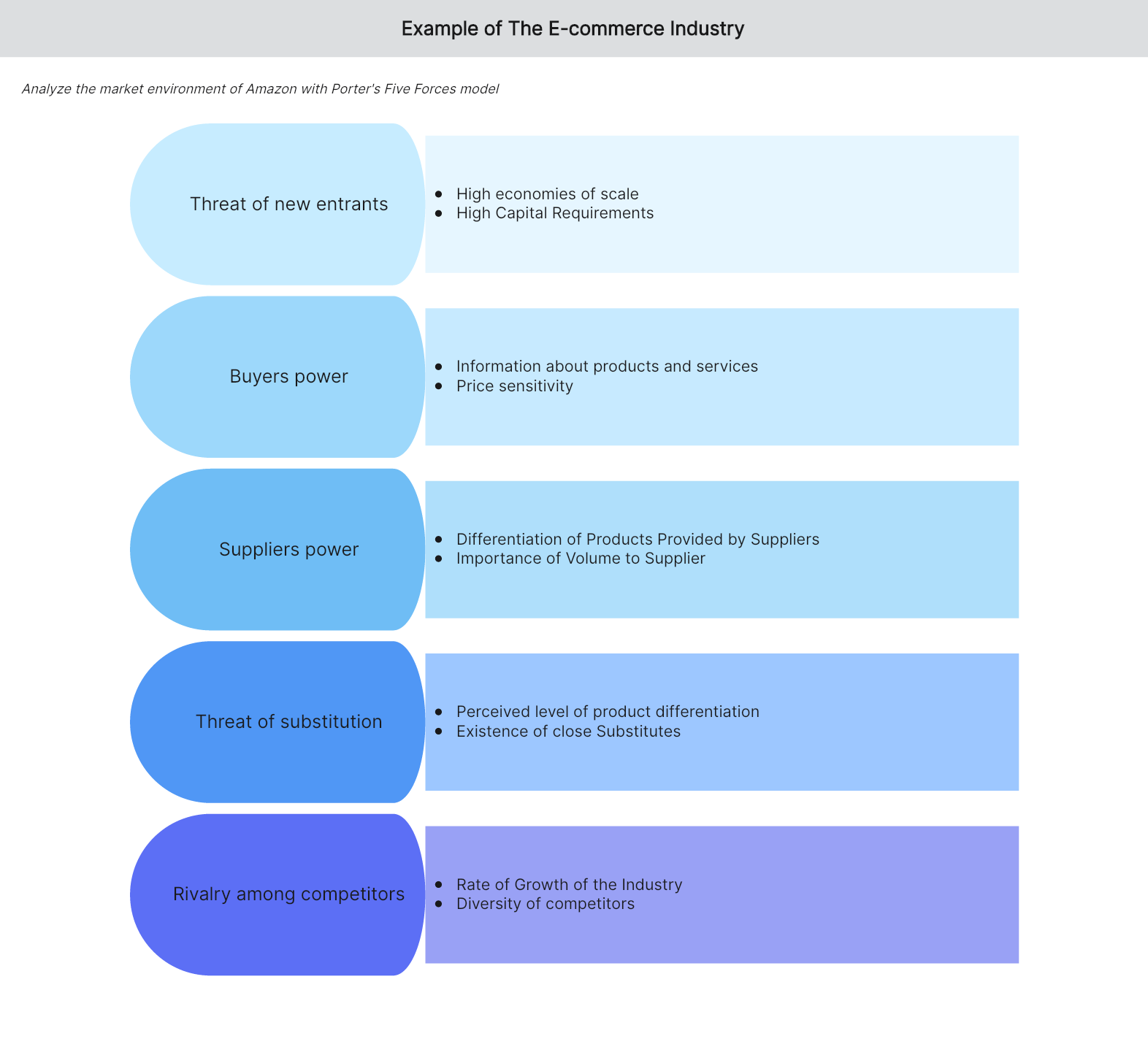
The last example presented below is a Porter’s Five Forces analysis of Amazon.
Threat of new entrants
- Economies of Scale: Amazon enjoys high economies of scale, strengthening the giant retail business. New entrants can quickly adapt to Amazon’s business model but cannot enjoy economies of scale at the same level as Amazon, which is a barrier to the new entrants.
- Capital Requirements: Amazon is an established brand image that has invested heavily in many fields in the industry, which poses a financial challenge to the new entrants.
Power of buyers
- Information About Products and Services: Customers can access first-hand information regarding the type of products offered by different online retailers, making it easy for them to find alternatives.
- Customer’s Price Sensitivity: Informed buyers are susceptible to prices. When a new entrant has a way of providing the same products at a lower cost, customers are likely to shift from Amazon.
Power of suppliers
- Differentiation of Products Provided by Suppliers: Certain suppliers with differentiated products and services may enjoy monopoly power in the market. But this differentiation can moderately affect Amazon since it already has a significant market share in the industry.
- Importance of Volume to Supplier: Since Amazon can purchase a large volume of products from its suppliers, no supplier would wish to lose a bulk buyer like Amazon, which moderately limits suppliers’ bargaining power.
Threat of substitution
- Perceived Level of Product Differentiation: Some suppliers are focused on differentiating their products, creating a level of uniqueness for their products. When such suppliers are not a part of Amazon’s supply chain, customers will get that product from another retailer.
- Existence of close Substitutes: Despite being a giant retailer, Amazon sells the same products as other retailers, and customers can easily change from Amazon to other e-commerce or physical retailers.
Competitive rivalry
- Rate of Growth of the Industry: In recent years, many players have risen, with some physical retailers like Walmart offering selling online. Given the aggressiveness of retail businesses, it poses a solid challenge to Amazon in maintaining and increasing the profit margin and market share.
- Diversity of competitors: In the e-commerce retail industry, different organizations have strategically positioned themselves differently--some operating both physically and online like Walmart; others provide a wide range of products and services like Amazon.
Reference: https://www.pdfagile.com/blog/amazon-porters-five-forces-analysis









