Value Chain Analysis Examples for Beginners
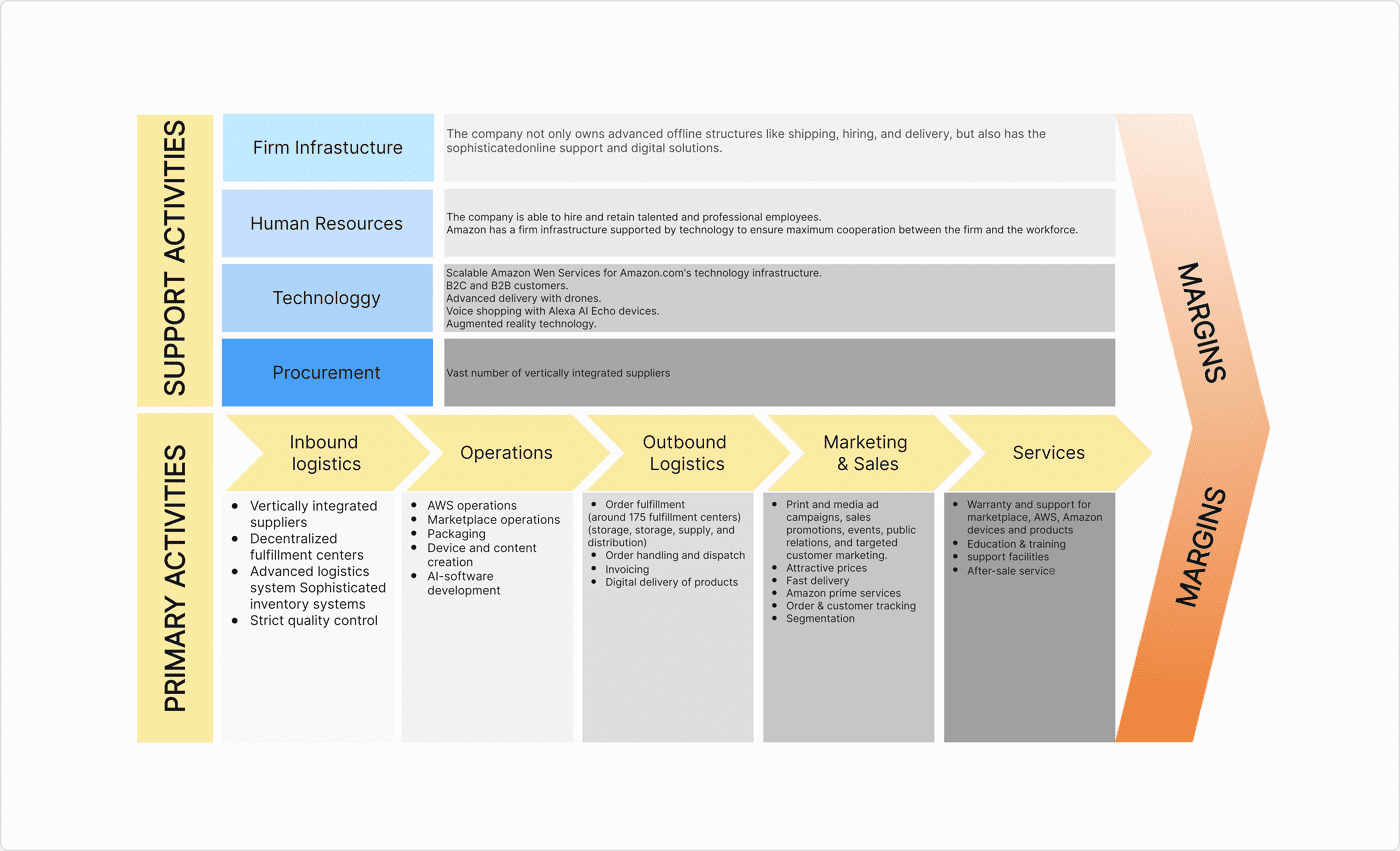
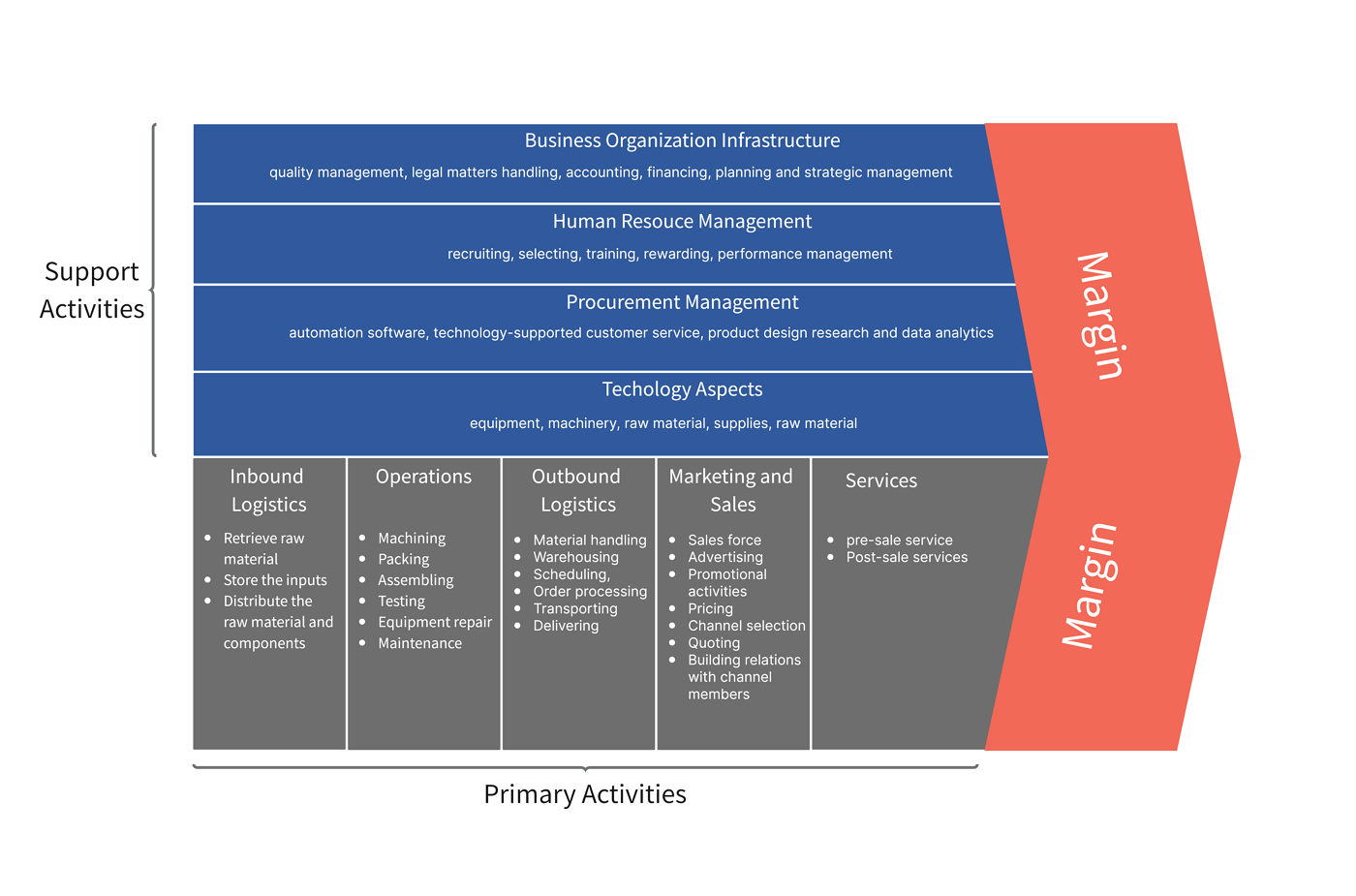
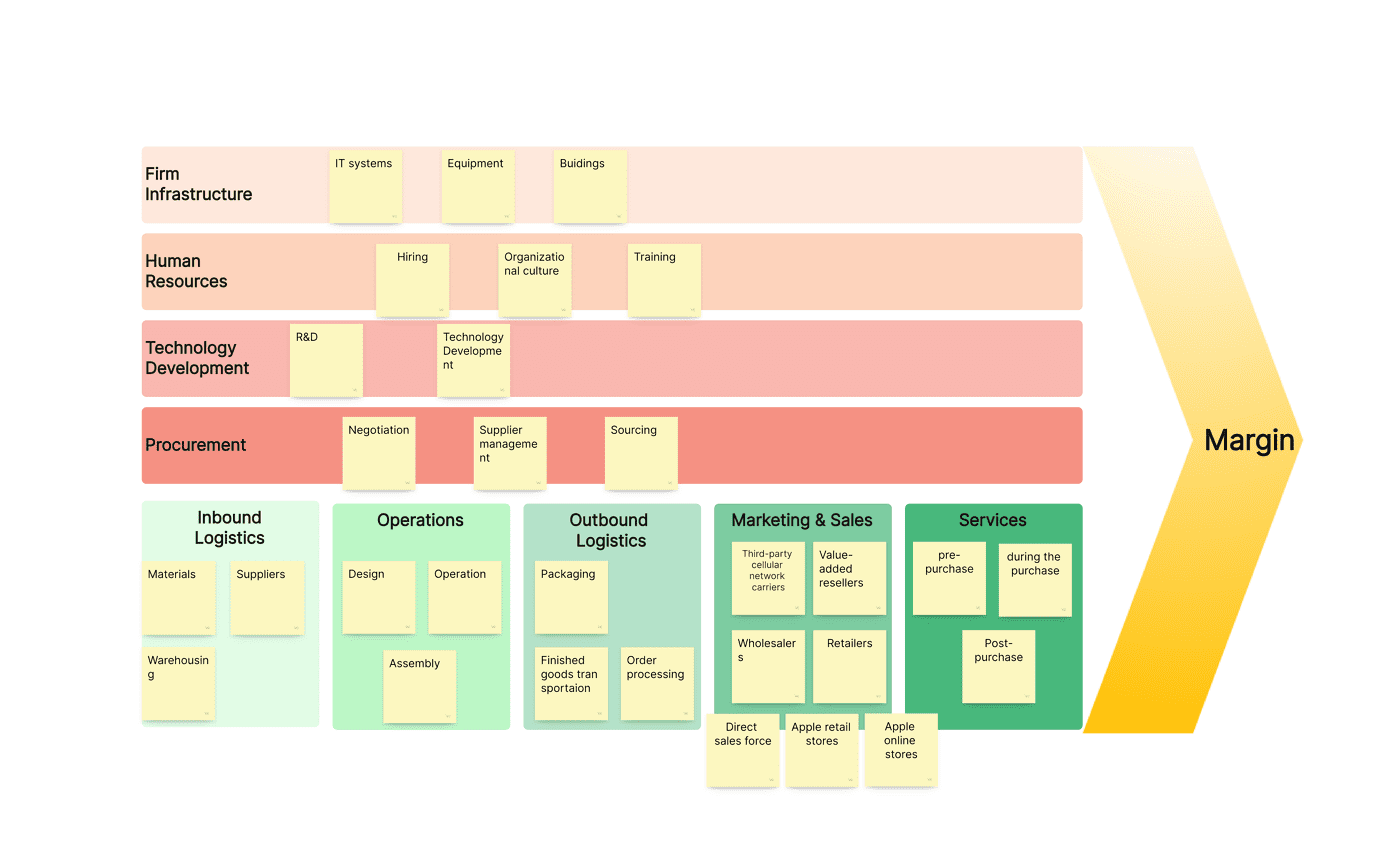
Primary Activities
These are the key functions of the value chain that all businesses need to deliver their goods or services.
Inbound Logistics
Inbound logistics refers to the management of sourcing, transportation, and storage of materials. An example of this is Amazon. The company is one of the largest businesses in the world and they have developed a powerful system to enable a global supply chain that is efficient and allows for the company to store goods for delivery across the world.
Operations Example
The second stage of a value chain analysis example will be the operations state. This focuses on transforming raw materials into the finished products that the business sells to customers. Toyota is a great example of this, as their operations procedure enables them to efficiently transform their materials into high-quality products, minimize waste, and maintain consistently high standards.

Outbound Logistics Example
The Outbound Logistics focus within a value chain example refers to the logistics of getting a product from the company to the customer swiftly, and without damage. FedEx has developed an extensive outbound logistics network that includes sorting, transportation, and delivery services. This was all created with the help of tracking technology that allows them to monitor packages, and their network of physical distribution centers and hubs.
Marketing and Sales Example
The marketing and sales component of a value chain analysis example will identify all of the actions a business takes to generate demand for their product or service, increase customer awareness of their brand, and overall create opportunities for customers to purchase from them. Historically, Apple was very consistent when it came to creating unique and innovative advertisements linked to each of their products, which created a strong brand identity in general but also connected customers to the latest that they had to offer. As a result, they are one of the leaders in technology in terms of sales.
Service Example
The fifth element of a value chain analysis is service. Regardless of the success of a product or service, good customer service is a necessary tenet for longevity and customer loyalty. This includes elements of support like 24/7 phone or email connection, returns and refunds where appropriate, and additional care such as free shipping. An example of a company with excellent service is Zappos, which strives to support its customers before, during, and after their purchases as much as possible.
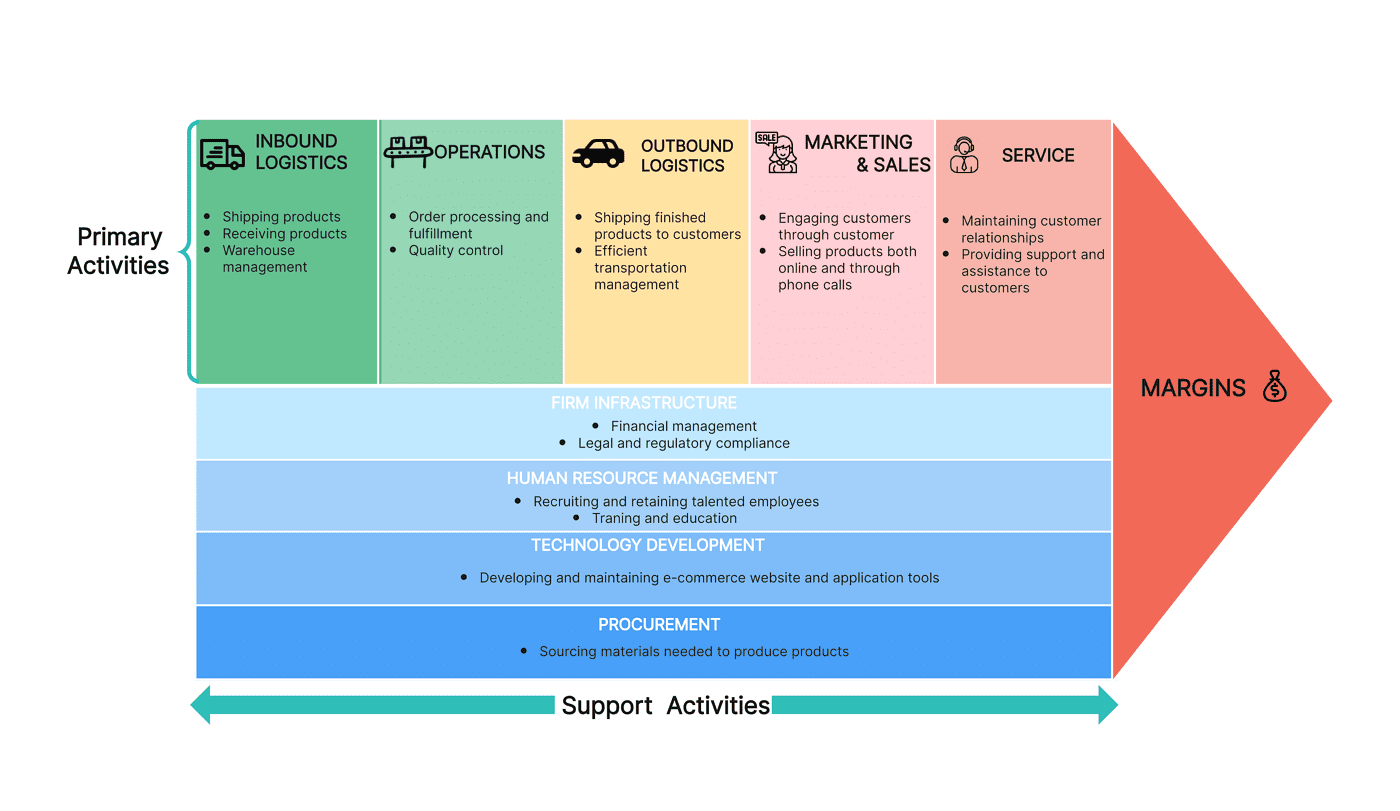
Support Activities
Support (or secondary) activities are also valuable aspects of the value chain, but not as directly. Instead, they support the primary activities to ensure they function as intended.
Procurement Example
Procurement activities within a value chain analysis example pertain to sourcing goods that are cheap, efficiently accessible, and high-quality. An excellent example of this is the Walmart chain, which is large enough to be able to negotiate effectively to receive goods at low prices for customers.
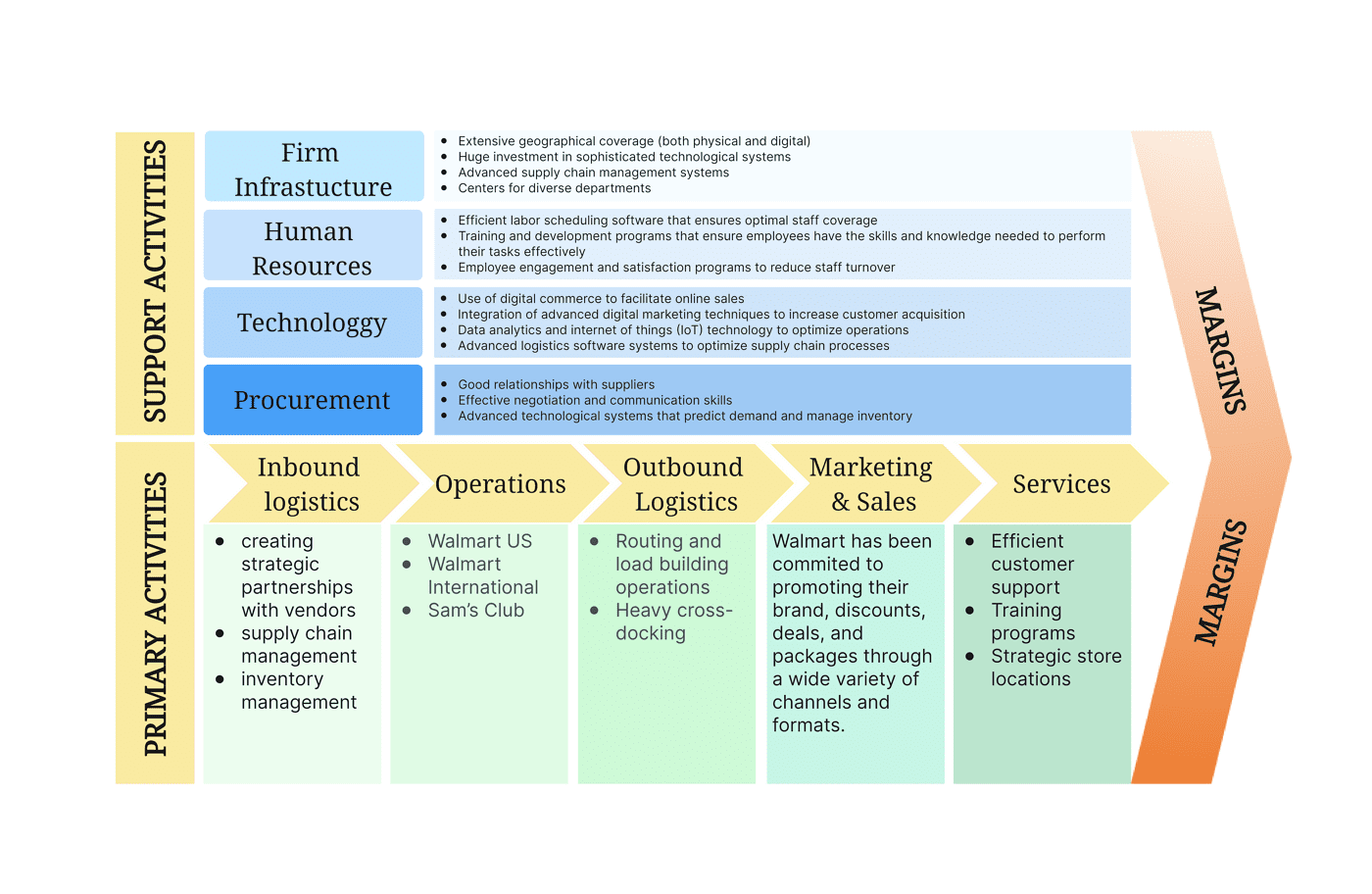
Technology Development Example
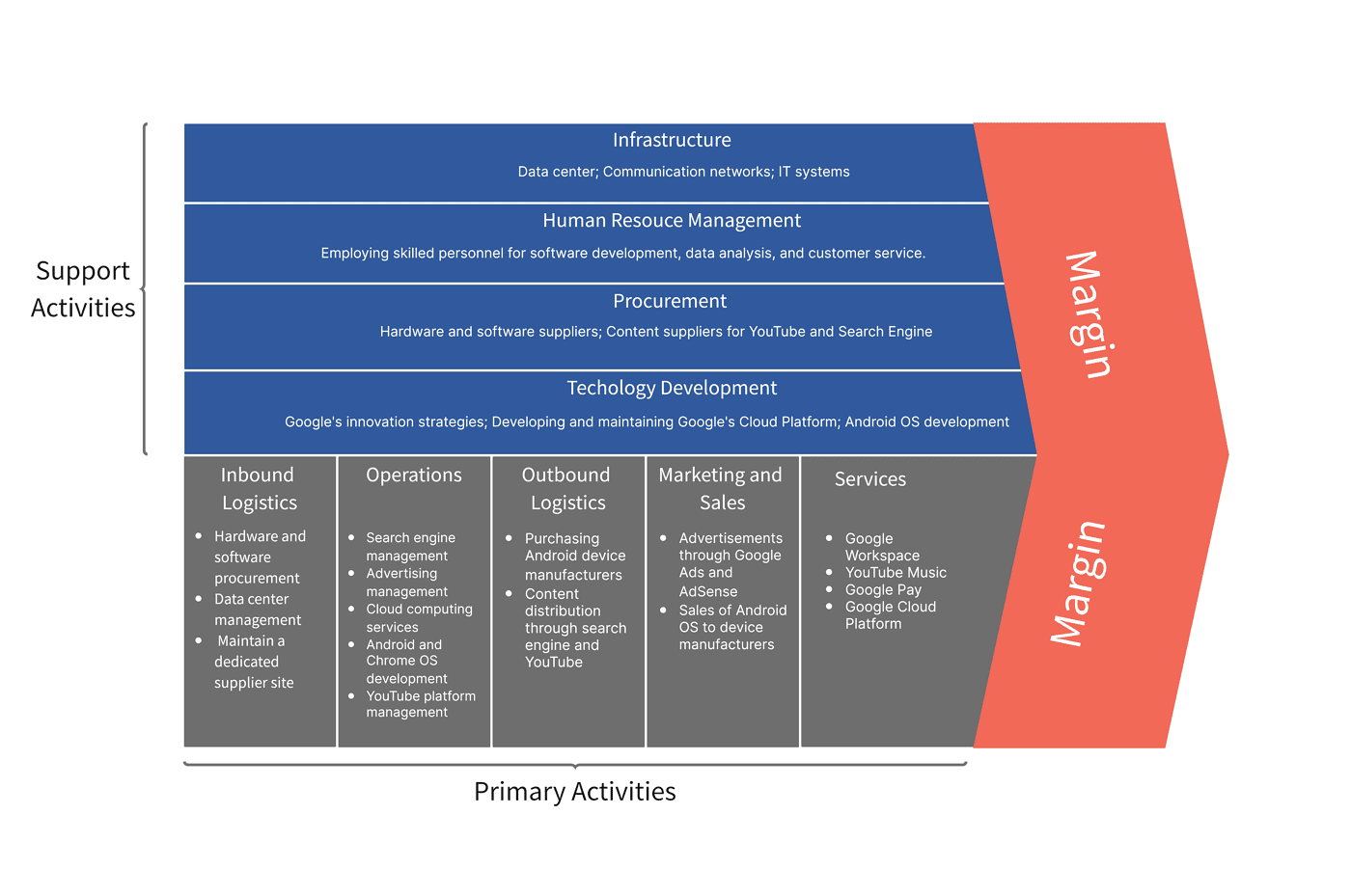
Technology and developing technology are what allow businesses to grow and develop, especially in competitive industries. Google is the perfect example of this value chain analysis factor, as a core aspect of their work is dedicated to invention and innovation, resulting in some of the most used technological tools in the world, such as Google Maps and the Google Search engine.
Human Resource Management Example
All businesses require human resource management, no matter how larger or small. This aspect of the value chain pertains to caring for staff through training, employee benefits such as flexible working or perks, which in turn generate greater results for the company. A great example of this is Starbucks, which is known for its efforts to create positive work environments and great working opportunities for staff.
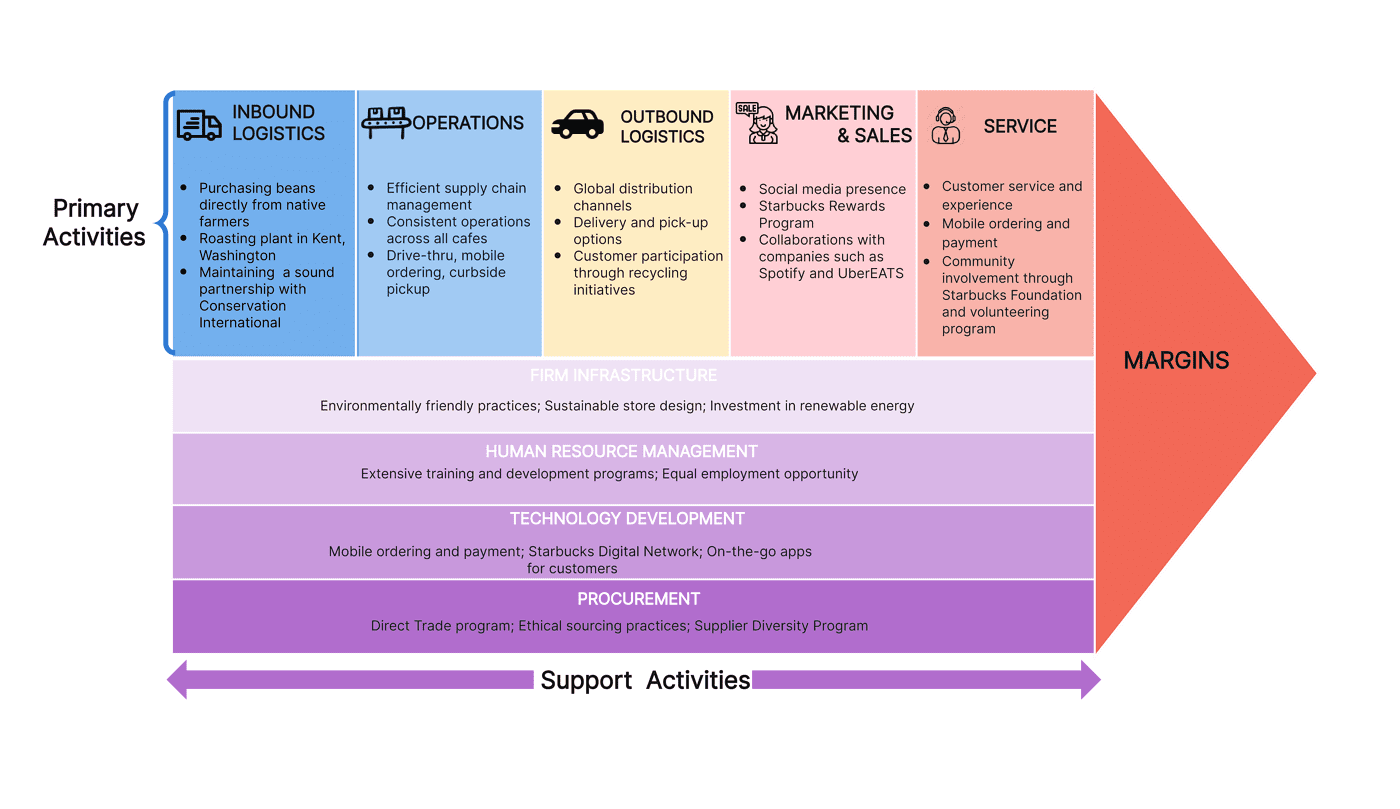
Firm Infrastructure Example
To have successful value chain operations, companies need to invest in solid infrastructure to support this. A solid example of this can be found in Microsoft, which has developed powerful hubs for its staff and data. In turn, this allows employees access to the equipment they need to develop Microsoft services and cloud technology, without worrying about its foundations.
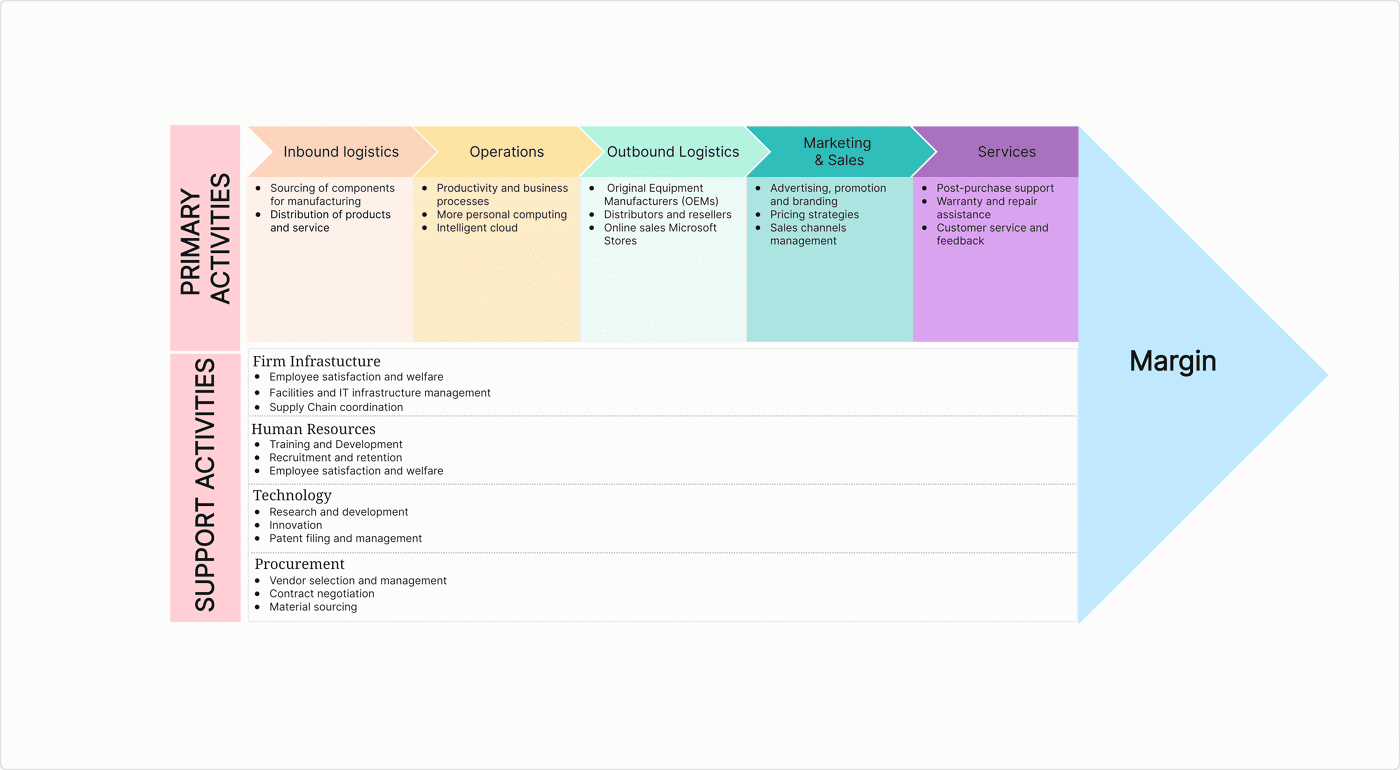
In-depth Analysis of Value Chain Examples
To understand how analysis of value chains can be utilized, it may be useful to further examine each example to understand how it impacts the rest of the value chain, and how it may be improved:
Inbound Logistics Example
Amazon has spent years building their sophisticated supply chain, which allows them to minimize lead times (get products to customers as quickly as possible, sometimes the same day as they were ordered), while still keeping prices competitive. Amazon is able to do this while keeping stock of their inventory, and generally keeping this filled as needed. Despite its success, Amazon could still potentially improve by exploring further partnerships with local suppliers. This would help to keep delivery costs low everywhere, and maintain swift delivery times in countries other than main Amazon hubs such as the United States.

Operations Example
Toyota strives to reduce waste and deliver consistently high outputs with their manufacturing system, reducing unnecessary excess at all steps. Although great, this system can continuously be improved as new technologies develop, and they should continue to focus on automation to continue to streamline this process.

Outbound Logistics Example
FedEx's capacity to deliver goods efficiently and without major issues means that customers are happy, and the company can keep up with high demand. Although their system is currently successful, the company could pursue more eco-friendly delivery systems, as a way to garner further public support and approval without impacting the quality of outputs.

Marketing and Sales Example
Apple has developed its own successful brand of marketing that is appealing and identifiable to customers and potential Apple customers. While they are already successful (as proven through top sales), they operate on a level of exclusivity in regard to where and how they advertise. The company could potentially expand its advertising options, making itself more accessible to a wider audience.

Service Example
Zappos has become the frontrunner for their excellent customer service that is consistently of a high standard, resulting in customer loyalty. The company could expand upon this by utilizing data analytics further, gaining more insight into their customer's preferences to generate proactive customer service, rather than just reactive support.

Benefits of using Value Chain Analysis
There are many benefits to using a value chain analysis to understand the strengths and weaknesses of a business's production to deliver to consumers. It offers a rounded view of the organization’s workings, allowing companies to examine processes as a whole, and make informed decisions regarding aspects such as resource allocation. It also identifies opportunities for cost-saving actions, where processes can become more efficient and reduce waste or increase outputs. In turn, this can increase their competitive edge over opposing brands and companies, helping them to stand out in the market for better access to consumers.
-
Enhanced Understanding: It provides a detailed view of your business operations, helping you understand how each activity contributes to the overall value creation.
-
Competitive Advantage: By identifying and optimizing the most valuable activities, companies can gain a competitive edge over rivals.
-
Cost Optimization: Value Chain Analysis helps in identifying areas of inefficiency or waste, enabling businesses to reduce costs and improve profitability.
-
Improved Decision Making: With a clear understanding of the value chain, businesses can make more informed decisions about where to invest resources for maximum impact.
-
Strategic Planning: It aids in strategic planning by identifying opportunities for innovation, diversification, and collaboration within the value chain.
-
Customer Satisfaction: By focusing on activities that add the most value, companies can enhance product quality or customer service, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
-
Supply Chain Management: It can help improve supply chain management by identifying bottlenecks or weak links in the chain that may affect product delivery or quality.
Limitations of using Value Chain Analysis
Using a value chain analysis can be beneficial for any business, but it should not be the only tool utilized to understand trends and data. It has its own pitfalls, namely that it is time-consuming and offers a relatively limited scope. It offers solid insights into internal activities within the businesses, which are important, however, it gives minimal weight to external factors that may also influence the success of a company - in reality, and these can have a far more significant impact on all steps of the value chain.
-
Complexity: The process of conducting a Value Chain Analysis can be complex and time-consuming. It requires a deep understanding of all business operations, which may not be feasible for large or diversified businesses.
-
Subjectivity: The assessment of what constitutes 'value' can be subjective and may vary among stakeholders. This can lead to conflicts or misinterpretations during the analysis.
-
Static Analysis: Value Chain Analysis often provides a snapshot of the business at a particular point in time, ignoring the dynamic nature of business environments. Changes in technology, market trends, or competitive landscapes may quickly render the analysis outdated.
-
Focus on Internal Activities: While it's great for examining internal processes, Value Chain Analysis often overlooks external factors such as market conditions, competitor actions, or regulatory changes that can significantly impact the value chain.
-
Cost Focus: Sometimes, there is an overemphasis on cost reduction rather than value creation. This could potentially lead to compromised product quality or customer satisfaction.
Value Chain Analysis Template
Boardmix emerges as a innovative platform that offers a ready-made template that streamlines the initiation of feedback sessions, creating an environment conducive to growth and progress within organizations. Its transformative capabilities position it as a one-stop solution, revolutionizing the way feedback is conducted and utilized.
Explore the transformative capabilities of Boardmix and discover how it stands as a real-time collaboration platform to facilitate cohesive and constructive feedback processes. Visit Boardmix to access an array of innovative solutions designed to meet the needs of modern organizations
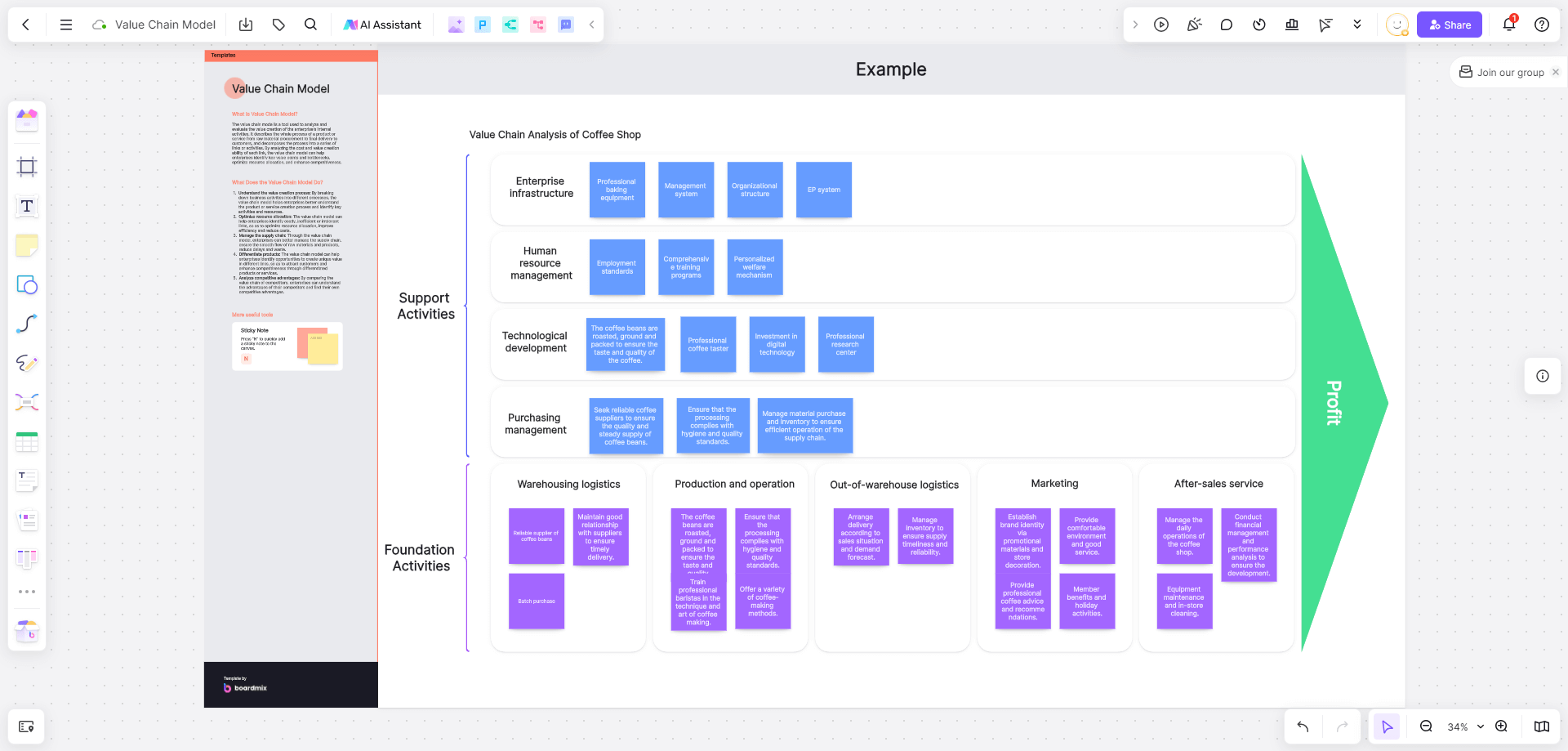
Step to Create Value Chain in Boardmix
1. Identify Primary Activities: Start by listing all the primary activities in your business. These are the main activities involved in creating, selling, and delivering your product or service. They typically include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing & sales, and service.
2. Identify Support Activities: Next, list down the support activities that help enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your primary activities. These typically include procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure.
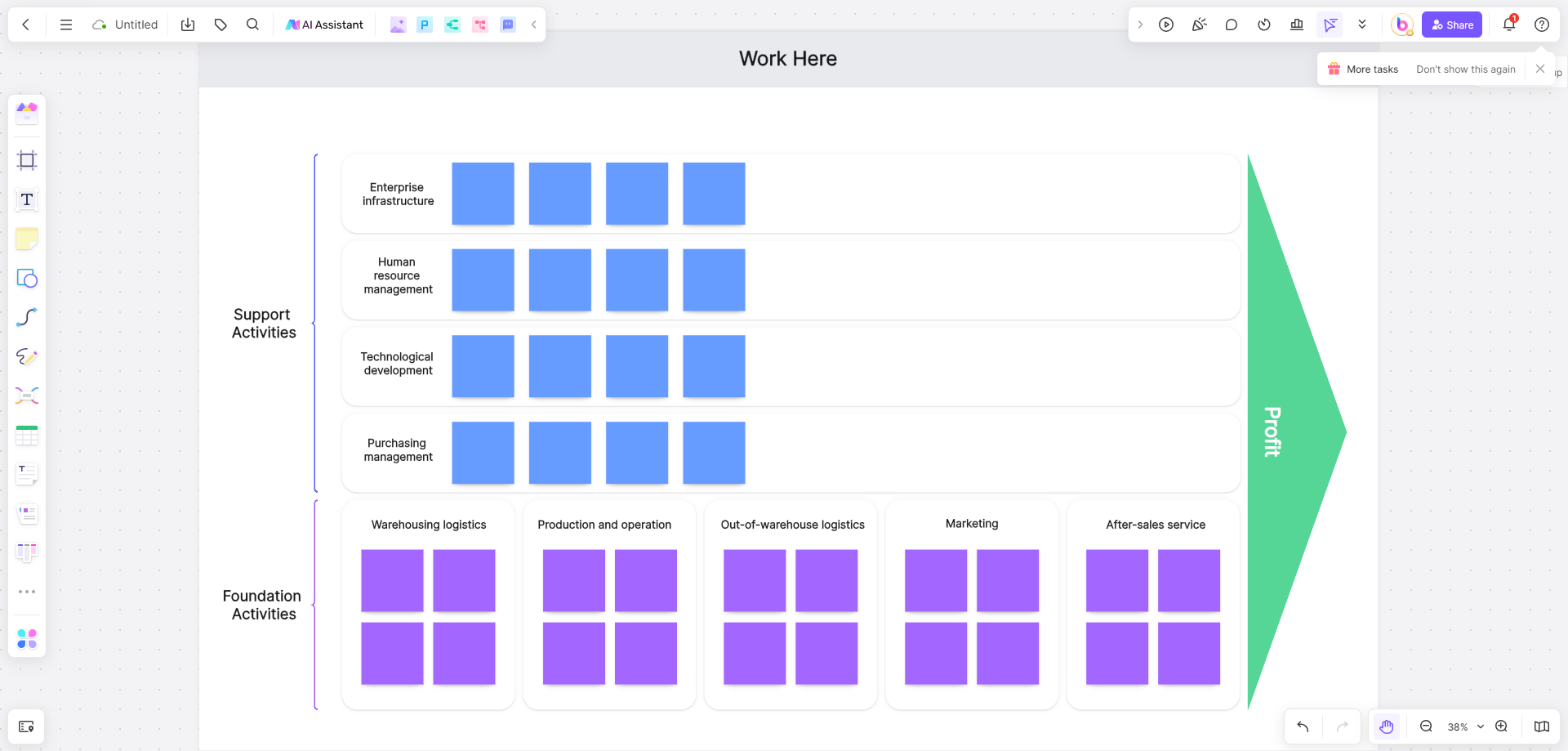
3. Create a Diagram: In Boardmix, create a new diagram and start adding boxes for each of these activities. Arrange them in a sequence that reflects your value chain - primary activities usually go in the center with support activities around them.
4. Add Details: For each activity box, add details about what it involves, how it adds value to your product or service, and any costs associated with it.
5. Analyze Costs and Value: Evaluate each activity to identify where you're spending the most and where you're creating the most value. This can help you identify areas for improvement.
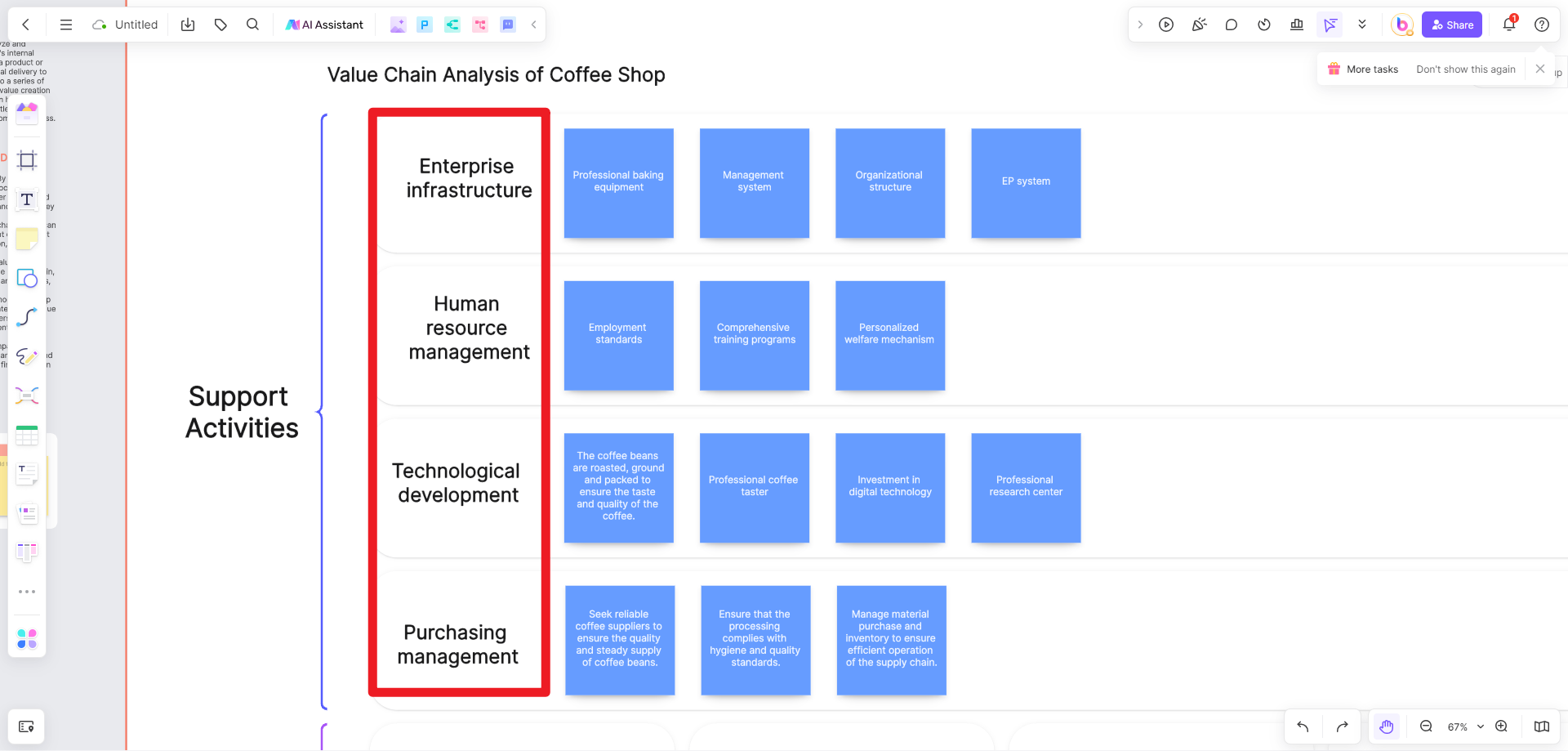
6. Draw Connections: Use arrows or lines to show connections between different activities. This can help illustrate how different parts of your business interact with each other.
7. Review and Refine: Once you've mapped out your entire value chain, review it to ensure accuracy and completeness. Make any necessary adjustments or refinements.
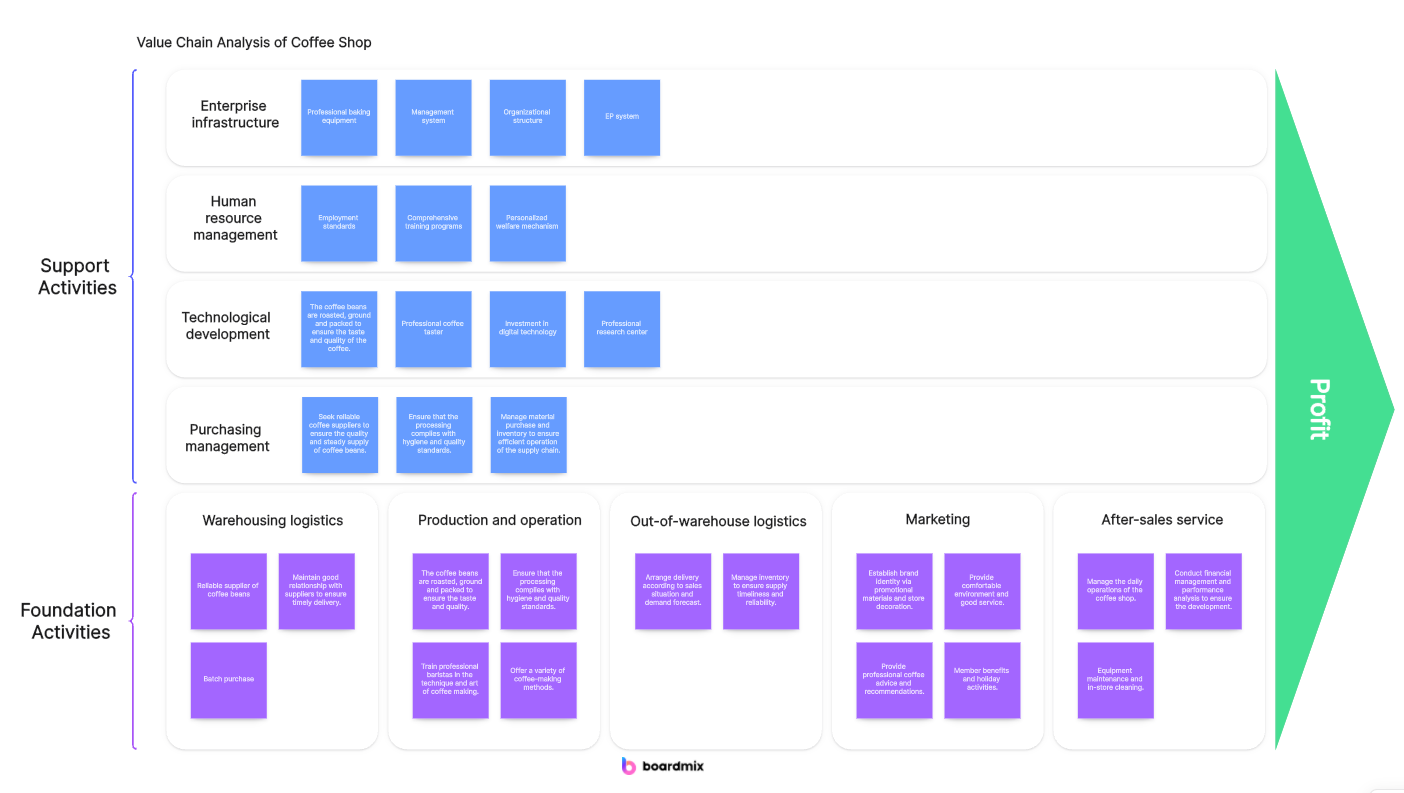
Remember, creating a Value Chain is an iterative process that may require multiple revisions as you gain a deeper understanding of your business operations. It's also important to update it regularly to reflect any changes in your business environment or strategy.









