What Fishbone Analysis is and why it is Useful
Fishbone analysis, also known as Ishikawa or cause-and-effect analysis, is a visual method used to identify and analyze the root causes of a problem or an effect. It is named after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa, a Japanese quality control expert. The technique gets its name from the shape of the diagram, which resembles the skeleton of a fish, with the "head" representing the problem or effect and the "bones" branching off to indicate potential causes.
The primary purpose of fishbone analysis is to provide a structured approach to problem-solving and root cause identification. Here's why it is useful:
Systematic Approach: Fishbone analysis provides a systematic and organized way to explore the various factors that may contribute to a problem. It ensures that all possible causes are considered and evaluated.
Visual Representation: The visual nature of the fishbone diagram makes complex relationships and interdependencies easy to understand. It helps teams see the bigger picture and how different factors may be interconnected.
Team Collaboration: Fishbone analysis is often conducted in a collaborative setting, involving individuals from different departments or with various expertise. This collaboration fosters a shared understanding of the problem and encourages diverse perspectives.
Identification of Root Causes: By breaking down the problem into categories (commonly referred to as the 6Ms Manpower, Method, Machine, Material, Measurement, and Mother Nature), fishbone analysis aids in identifying the root causes rather than just addressing symptoms.
Prevention of Recurrence: Understanding and addressing the root causes of a problem can help prevent its recurrence. Fishbone analysis supports the development of effective solutions that target the source of the issue.
Decision Making: The insights gained from fishbone analysis empower teams to make informed decisions about the most appropriate actions to address the problem. It helps prioritize solutions based on their potential impact on root causes.
Continuous Improvement: Fishbone analysis is a key component of continuous improvement methodologies, such as Six Sigma and Total Quality Management. It fosters a culture of ongoing assessment and enhancement.
In short, fishbone analysis is a valuable tool for problem-solving and root cause analysis due to its systematic approach, visual representation, collaborative nature, and its effectiveness in identifying and addressing the underlying causes of an issue. It is widely used across various industries to improve processes, enhance quality, and drive continuous improvement initiatives.
Steps: Fishbone Analysis Process
The fishbone analysis process is a systematic and collaborative method designed to identify and analyze the root causes of a problem. This structured approach, also known as Ishikawa or cause-and-effect analysis, involves several key steps that guide teams through the process of understanding, visualizing, and addressing complex issues.
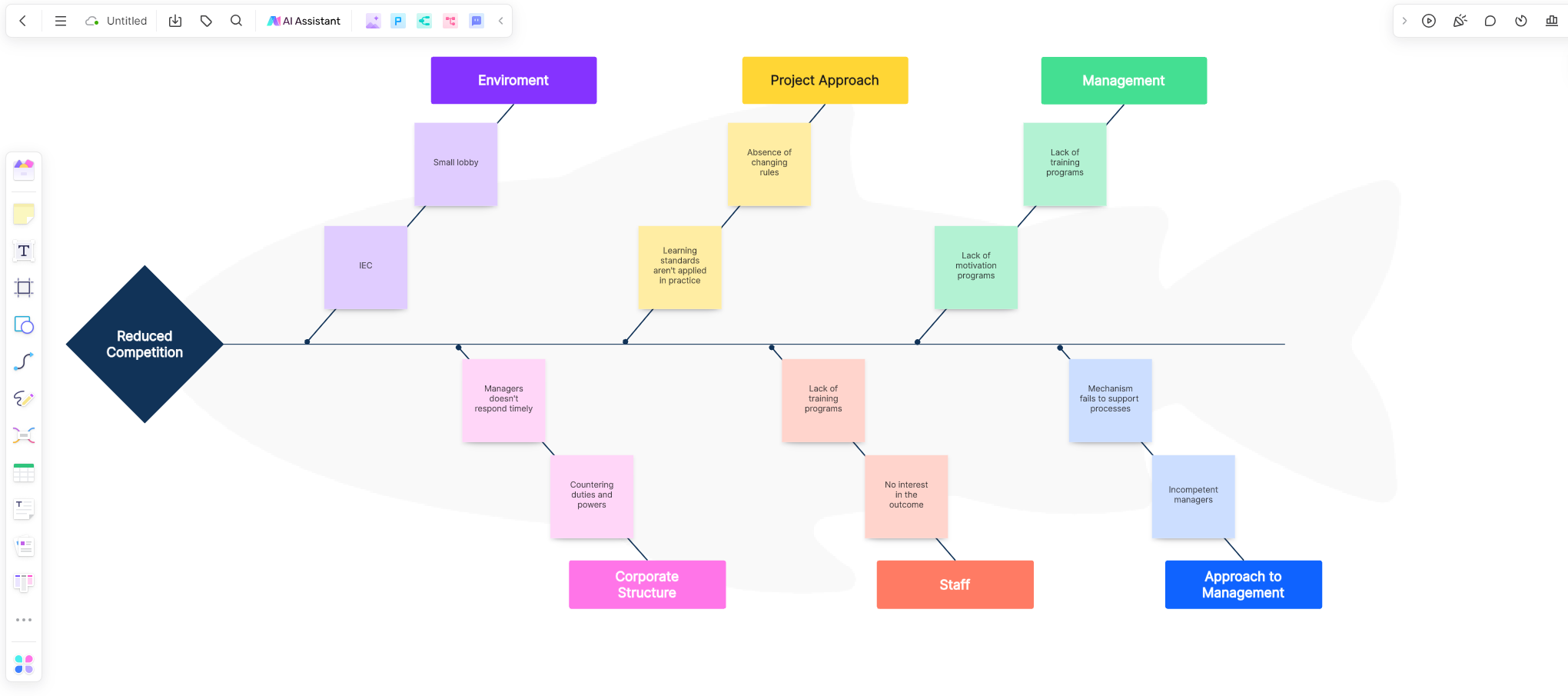
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in the fishbone analysis process is to clearly define the problem or effect that needs to be addressed. This step sets the stage for the entire analysis, ensuring that the team is focused on a specific issue and its associated challenges.
Step 2: Create the Fishbone Diagram
Once the problem is defined, the next step is to create the fishbone diagram. Draw a horizontal arrow pointing to the right, representing the problem. This arrow serves as the "spine" of the fishbone. Branch off from the spine with diagonal lines, creating the "bones" of the fishbone. Label each bone with one of the common categories of causes, often referred to as the 6Ms: Manpower, Method, Machine, Material, Measurement, and Mother Nature.
Step 3: Brainstorm Potential Causes
With the fishbone diagram in place, the team engages in a collaborative brainstorming session to identify potential causes within each category. This step encourages diverse perspectives and insights from team members with different expertise. As ideas are generated, they are added as branches or sub-bones extending from the main categories.
Step 4: Analyze and Categorize Causes
After the brainstorming session, the team reviews and analyzes the potential causes. Similar or related causes are grouped together, helping to identify patterns and connections. This process of categorization contributes to a more thorough understanding of the complex interactions contributing to the problem.
Step 5: Identify Root Causes
The analysis continues by probing deeper into the identified causes to determine the root causes—the fundamental factors that directly contribute to the problem. This step involves asking "why" multiple times to trace each cause back to its origin. The goal is to reach the underlying issues rather than addressing surface-level symptoms.
Step 6: Prioritize and Develop Solutions
Once the root causes are identified, the team prioritizes them based on their impact and feasibility for intervention. This step sets the foundation for developing effective solutions targeted at the core issues. It is essential to focus on preventive measures to avoid the recurrence of the problem.
Step 7: Implement and Monitor Solutions
The final step involves implementing the chosen solutions and monitoring their effectiveness. Continuous improvement is a key aspect of the fishbone analysis process, as it allows teams to refine their approach based on real-world outcomes and feedback.
The fishbone analysis process is a dynamic and iterative method that guides teams through a structured exploration of problems. By defining the problem, creating a fishbone diagram, brainstorming potential causes, analyzing and categorizing those causes, identifying root causes, and developing and implementing solutions, teams can gain valuable insights and foster a culture of continuous improvement within their organizations.
Application: Fishbone Analysis Sample
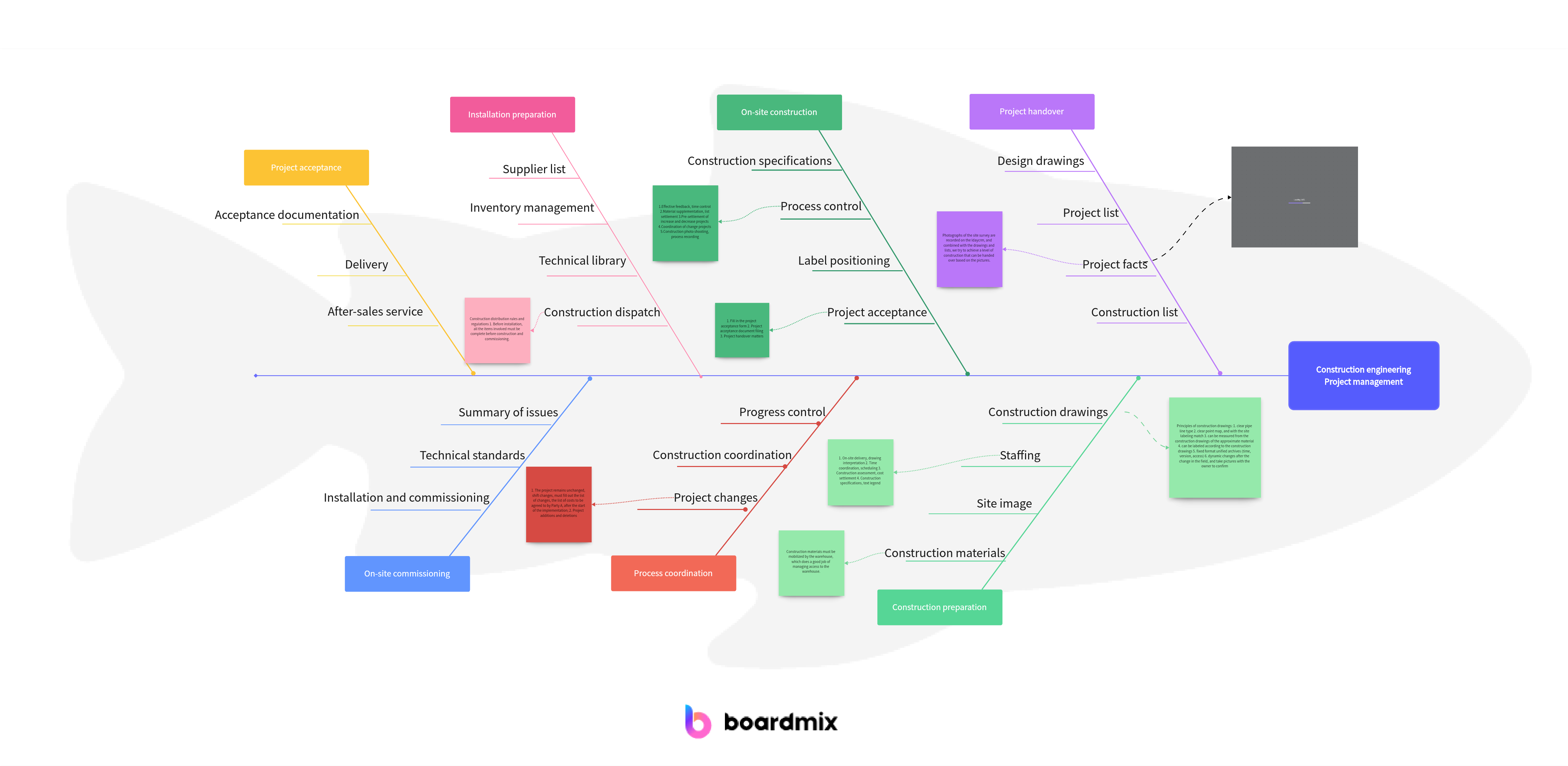
Let's delve into a practical example to illustrate the step-by-step process of conducting a fishbone analysis sample. Imagine a manufacturing company experiencing a consistent increase in product defects. The team decides to use fishbone analysis sample to identify and address the root causes of this quality issue.
Step 1: Define the Problem
The problem is clearly defined as an increase in product defects in the manufacturing process. The team aims to understand the factors contributing to this issue and work towards its resolution.
Step 2: Create the Fishbone Diagram
A horizontal arrow pointing to the right represents the problem—increased product defects. The main categories or "bones" branching off from the spine include Manpower, Method, Machine, Material, Measurement, and Mother Nature. Each category is crucial in understanding the potential causes related to the defects.
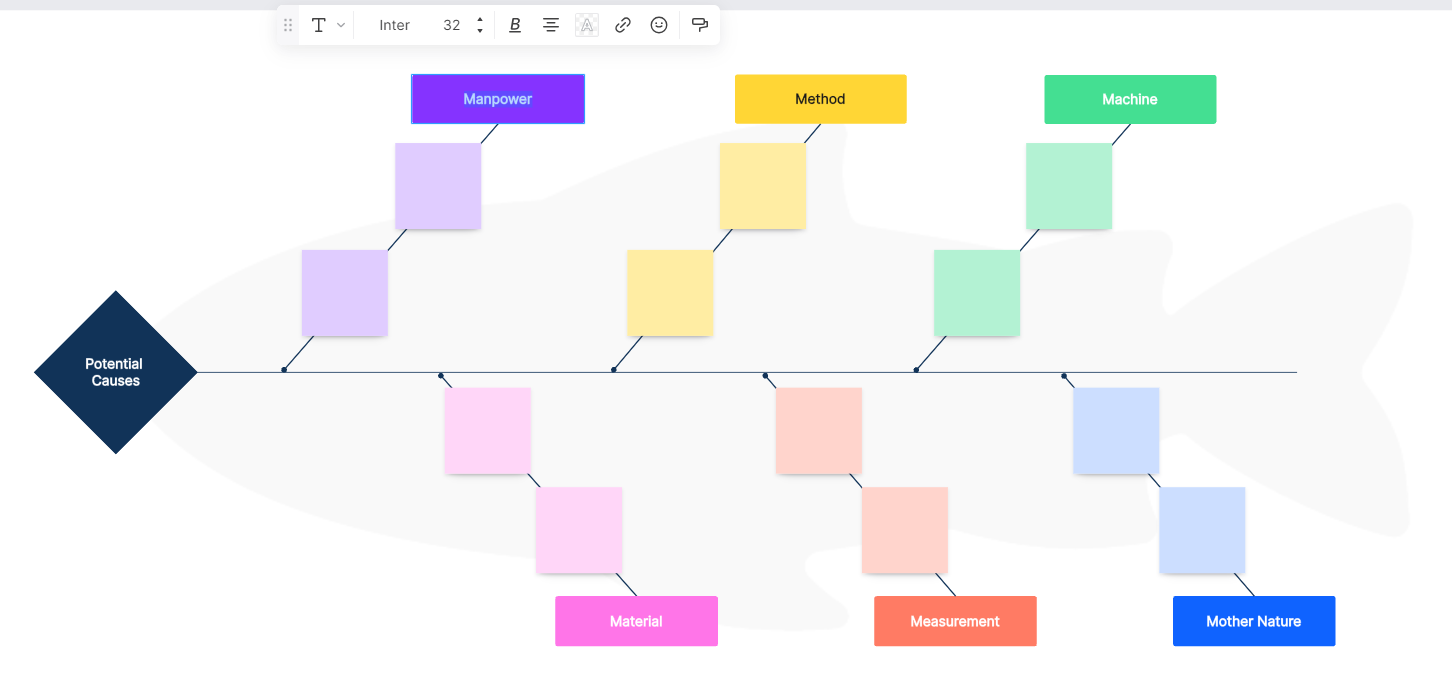
Step 3: Brainstorm Potential Causes
In a collaborative session, the team brainstorms potential causes within each category. For instance:
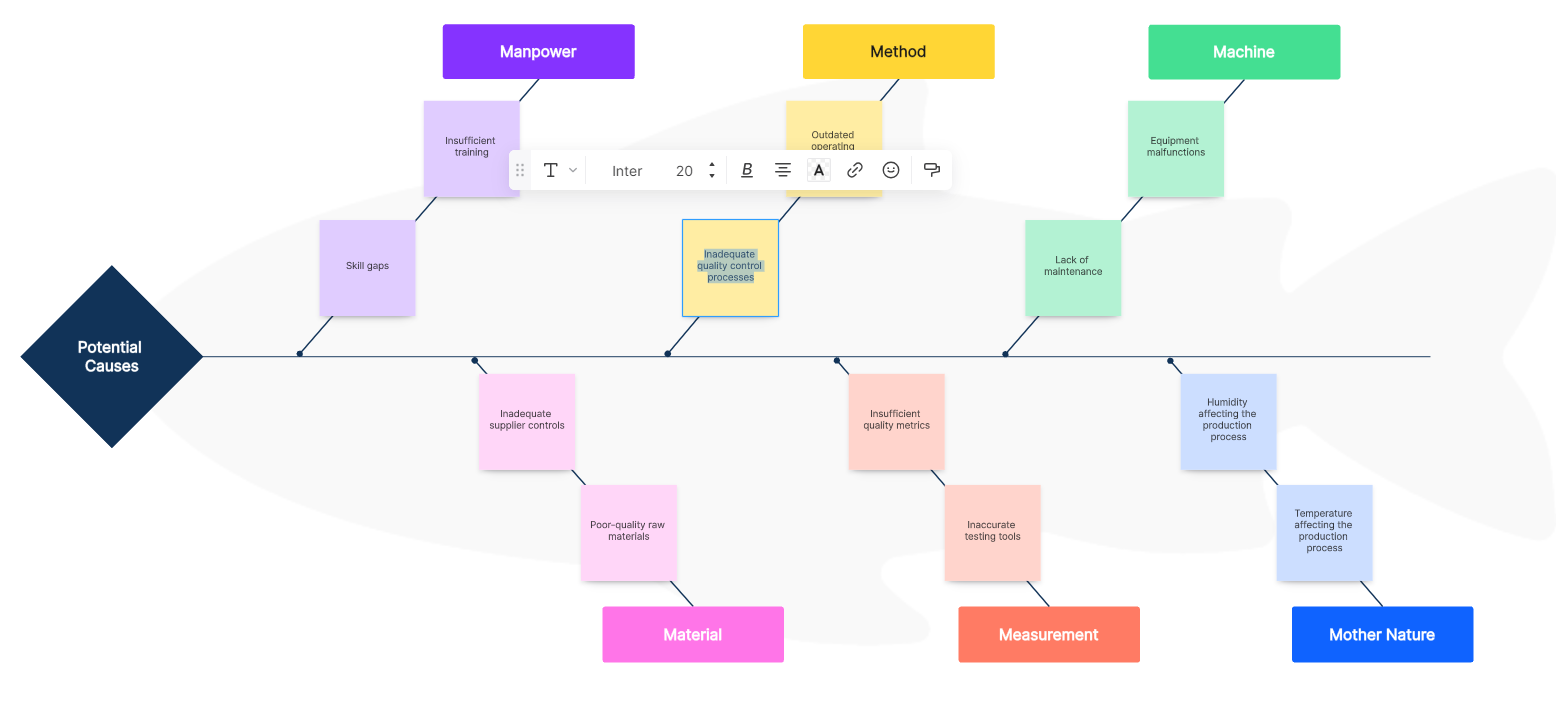
1. Under "Manpower," they identify issues like insufficient training or skill gaps.
2."Method" considerations might include outdated operating procedures or inadequate quality control processes.
3. In the "Machine" category, potential causes could involve equipment malfunctions or lack of maintenance.
4."Material" considerations might include poor-quality raw materials or inadequate supplier controls.
5."Measurement" issues might involve inaccurate testing tools or insufficient quality metrics.
6."Mother Nature" could encompass external factors like temperature or humidity affecting the production process.
Step 4: Analyze and Categorize Causes
After the brainstorming session, the team reviews and categorizes the potential causes. They discover that several issues relate to inadequate training (Manpower), outdated procedures (Method), and equipment malfunctions (Machine). These are grouped together to identify patterns and connections.
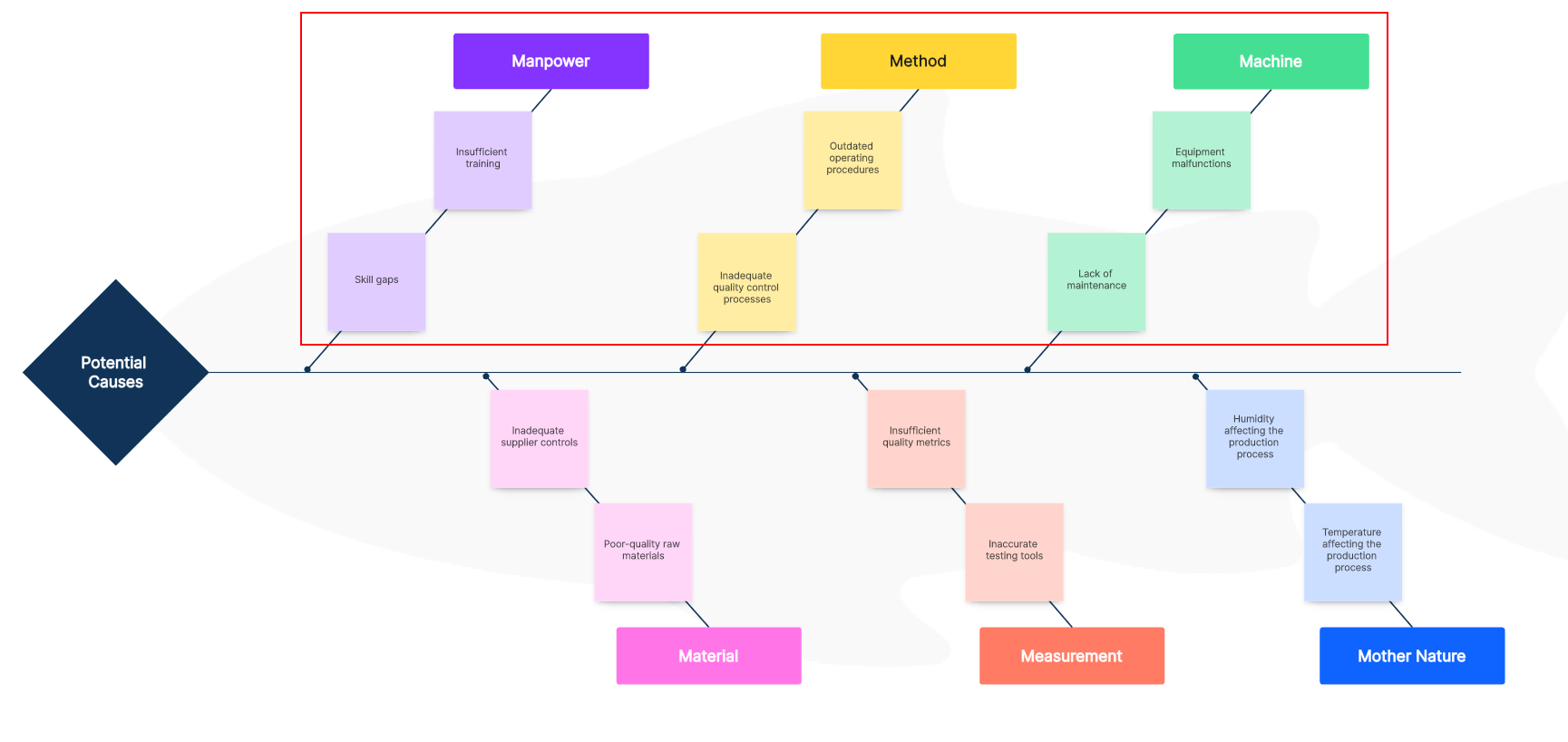
Step 5: Identify Root Causes
To identify root causes, the team probes deeper into the categorized issues. They ask "why" multiple times. For instance, if inadequate training is identified as a cause, the team might ask why the training is insufficient, leading them to discover issues with the training program or materials.
Step 6: Prioritize and Develop Solutions
With the root causes identified, the team prioritizes them based on impact and feasibility. In our example, they might decide to implement a comprehensive training program for the workforce, update operating procedures, and schedule regular maintenance for equipment.
Step 7: Implement and Monitor Solutions
The chosen solutions are implemented, and the team monitors their effectiveness. They observe a decrease in product defects over time, validating the success of their intervention. Continuous monitoring ensures sustained improvement and allows the team to adapt their strategies if needed.
In this example, the fishbone analysis process guides the team from defining the problem to implementing effective solutions. The structured approach not only addresses the immediate issue of increased product defects but also sets the stage for ongoing quality improvement within the manufacturing process.
Tips for Conducting a Successful Fishbone Analysis
Conducting a successful fishbone analysis requires careful planning, effective collaboration, and a commitment to uncovering the root causes of a problem. Here are some tips to ensure a fruitful fishbone analysis:
1. Clearly Define the Problem
Begin by clearly defining the problem or issue you aim to address. A well-defined problem statement sets the stage for focused and effective analysis.
2. Assemble a Diverse Team
Form a cross-functional team with members from different departments or areas of expertise. Diverse perspectives contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of potential causes.
3. Use a Whiteboard or Fishbone Software
Utilize a whiteboard or specialized fishbone diagram software to visually represent the causes and effects. This enhances clarity and facilitates collaboration during the analysis.
4. Encourage Open and Honest Communication
Foster an open and honest environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their insights and perspectives. Encourage everyone to contribute ideas without fear of judgment.
5. Brainstorm Extensively
Conduct a thorough brainstorming session to identify potential causes within each category. Emphasize quantity over quality during the initial brainstorming phase, and later refine the list.
6. Categorize Causes Effectively
Carefully analyze and categorize the identified causes. Group similar or related causes together to identify patterns and connections, making it easier to pinpoint root causes.
7. Ask "Why" Multiple Times
When identifying root causes, use the "5 Whys" technique. Ask "why" multiple times to trace each cause back to its origin and uncover the underlying issues contributing to the problem.
8. Prioritize Root Causes
Prioritize the root causes based on their impact on the problem and feasibility for intervention. This helps in focusing efforts on the most critical issues.
9. Develop Actionable Solutions
Once the root causes are identified, develop actionable and targeted solutions. Ensure that the solutions address the core issues to prevent the recurrence of the problem.
10. Implement and Monitor
Implement the chosen solutions and closely monitor their effectiveness. Regularly review progress and adjust strategies as needed. Continuous improvement is a key aspect of the fishbone analysis process.
11. Document the Process
Document the entire fishbone analysis proc, including the identified causes, root causes, and implemented solutions. This documentation serves as a valuable reference for future analyses and improvements.
12. Seek Feedback and Learn
Encourage feedback from team members and stakeholders throughout the process. Learn from the analysis and use insights gained to refine future problem-solving approaches.
By following these tips, teams can conduct a successful fishbone analysis that not only identifies the root causes of a problem but also lays the groundwork for continuous improvement and enhanced problem-solving capabilities.
Conclusion
The Fishbone Analysis Process, with its structured steps, empowers teams to methodically investigate and address issues. In the practical application of Fishbone Analysis through the provided sample, in this case, we explored the nuances of dissecting a specific problem—offering a tangible example of how this method can be applied to various scenarios. Boardmix becomes the digital space where teams can collectively engage in the analysis, fostering collaboration and innovation. Boardmix's user-friendly interface and collaborative features align seamlessly with this process, facilitating real-time collaboration and enhancing the efficiency of problem resolution. Take action today, leverage the collaborative power of Boardmix, and elevate your approach to problem resolution.