What is Agile project management? And what set it apart from the traditional project management? Explaining the differences between agile project management and traditional project management concepts alone can be boring and tedious, so let's use a cooking analogy to make it easier to understand.
Traditional project management is like traditional cooking. You need to know exactly what you're going to make right from the start, and you must prepare all the ingredients and seasonings in advance. This is akin to starting a project where you need to plan everything ahead, including the budget, timeline, personnel, and resources. You follow the plan step by step, much like following a recipe where each step must be executed perfectly. Any mistake can ruin the whole dish. This method is stable and orderly but lacks flexibility. If issues arise or client needs change, adjustments become cumbersome.
Agile project management, on the other hand, is like modern quick cooking. You can adjust your recipe based on the ingredients and time you have. In managing a project, you don't need to plan everything upfront. Instead, you adjust your plan based on project progress and client feedback. It's like realizing you're out of a certain spice mid-cooking and substituting it with another, or tasting the dish and tweaking the flavor as you go. Agile management is flexible and quickly adapts to changes but requires higher management skills and team collaboration.
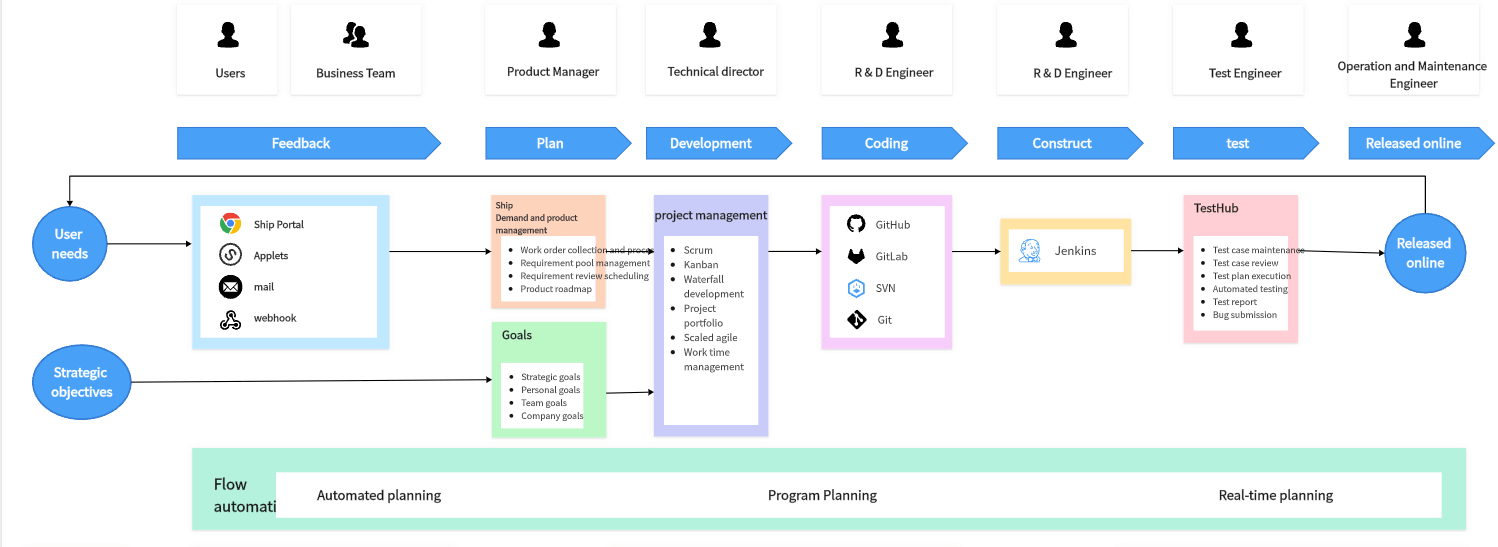
Agile Project Management vs. Traditional Project Management: Key Differences When Using Them
After learning these two concepts through the cooking analogy, let's further explore the methodological and differences between these two project management styles:
- Planning and Flexibility: Traditional project management (e.g., waterfall) involves detailed planning of all steps at the project's outset, followed by strict adherence to the plan. It designs all project details in one go and then executes them step-by-step. Agile project management, however, offers greater flexibility, allowing adjustments and changes during the project to meet evolving requirements.
- Feedback and Adjustment: In traditional project management, feedback typically occurs at the end or at the end of each phase, with limited opportunities for adjustment. Agile project management emphasizes continuous feedback and timely adjustments throughout the project. Agile methods involve short iteration cycles, with feedback and adjustments after each cycle.
- Delivery: Traditional project management tends to deliver all results at the end of the project. Agile project management delivers usable parts of the product after each iteration, enabling clients to see progress sooner and provide feedback.
- Project Roles: In traditional project management, the project manager usually makes decisions and maintains control. In agile project management, the project team has greater self-management, and decision-making is more decentralized.
- Risk Management: Agile management's flexibility and continuous feedback mechanism allow for earlier risk identification and mitigation, differing significantly from traditional waterfall management.
What is Traditional Project Management
Traditional project management encompasses various methods, including:
- Waterfall Model: Also known as waterfall management, it's the earliest and most well-known traditional method. Projects are divided into phases that proceed sequentially, with each phase's output serving as the next phase's input. These phases typically include requirements analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
- PRINCE2: Widely used in the UK, PRINCE2 emphasizes strict control and management from start to finish.
- PMBOK: The Project Management Body of Knowledge, published by the Project Management Institute (PMI), provides a standardized approach. It describes five process groups (initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closing) and ten knowledge areas.
- Critical Path Method (CPM): This technique focuses on identifying project activities' logical relationships and the critical path to manage key activities and ensure timely project completion.
- PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique): Used for assessing projects with uncertain schedules, PERT charts display all tasks and their dependencies, aiding in better project planning and control.
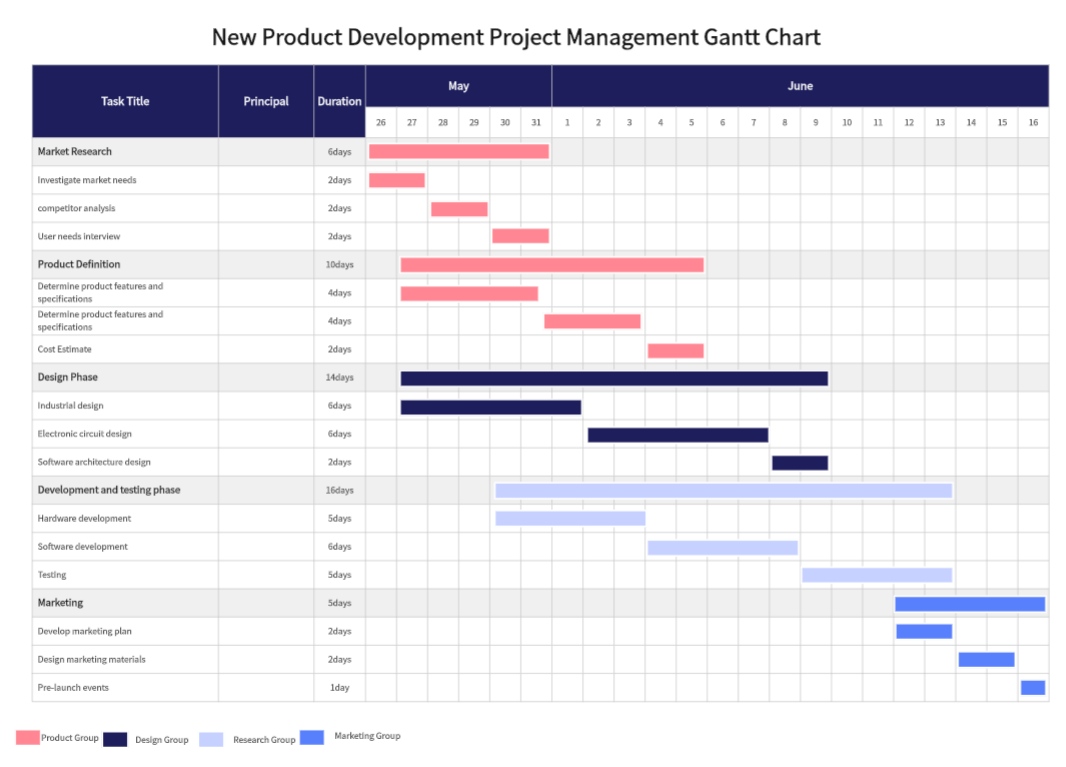
Pros and Cons of Traditional Project Management
Let’s take the waterfall model as an example, project development is divided into six stages: requirements analysis, project design, implementation/coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
These stages follow a fixed order, and each must be completed before the next begins. Once a project moves to the next stage, it cannot revert to a previous stage.
This method is like a waterfall, where water flows from top to bottom without reversing. The advantage is clear processes, easy to understand and manage. The disadvantage is inflexibility and difficulty adapting to changing needs. Mid-project issues or changing requirements often necessitate starting over.
In contrast, agile methods are more flexible, allowing adjustments during the project without needing to wait until the end or restart. This is why many projects, especially software development, prefer agile project management.
What is Agile Project Management
Like traditional project management, agile project management is subdivided into various methods, including:
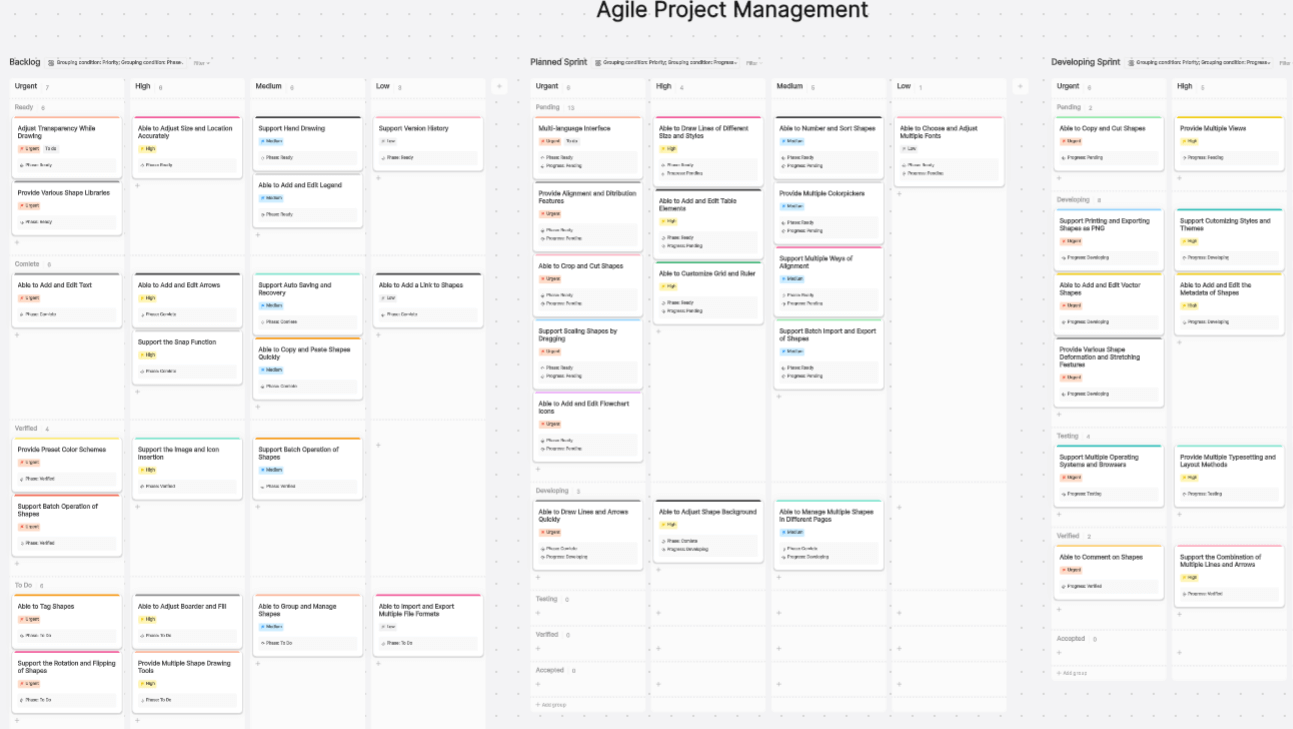
- Scrum: One of the most popular agile methods, especially in software development. Scrum emphasizes team collaboration and completing deliverable work in short periods (typically 2-4 weeks). Key roles include Scrum Master (a coach role helping the team understand and practice Scrum), Product Owner (responsible for defining and optimizing product requirements), and the development team.
- Kanban: Originating from Toyota's production system, Kanban emphasizes visualizing processes and limiting work in progress. Its core idea is to achieve smooth workflow by limiting the number of ongoing tasks, thus increasing efficiency.
- Extreme Programming (XP): This agile method focuses on maintaining high quality and efficiency throughout the project lifecycle. Key practices include continuous integration, test-driven development, and continuous refactoring.
- Lean: Also derived from Toyota's production system, Lean emphasizes eliminating waste, continuous improvement, and quick delivery of customer value. In software development, it involves early and continuous delivery, building a quality culture, and using Kanban for management.

- Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe): A framework for implementing agile methods in large organizations, combining elements of Scrum, Kanban, and Lean to handle large-scale, complex projects.
What you need to know when using scrum in agile project management
For beginners, Scrum is the most commonly used agile project management method. Scrum is a framework for developing, delivering, and sustaining complex products. Initially used in software development, it has expanded to other fields, including research, sales, marketing, and advanced technology.
A Scrum team is typically designed for a team of ten, delivering work iteratively and incrementally. Each iteration, or sprint, lasts no more than a month, usually two weeks. The team focuses on a single goal each sprint, holding daily stand-up meetings (Daily Scrum) to review progress and adjust plans. At the end of each sprint, the team conducts a sprint review with stakeholders to inspect the results and adjust plans, followed by a sprint retrospective to continuously improve.
Basic Elements of Scrum
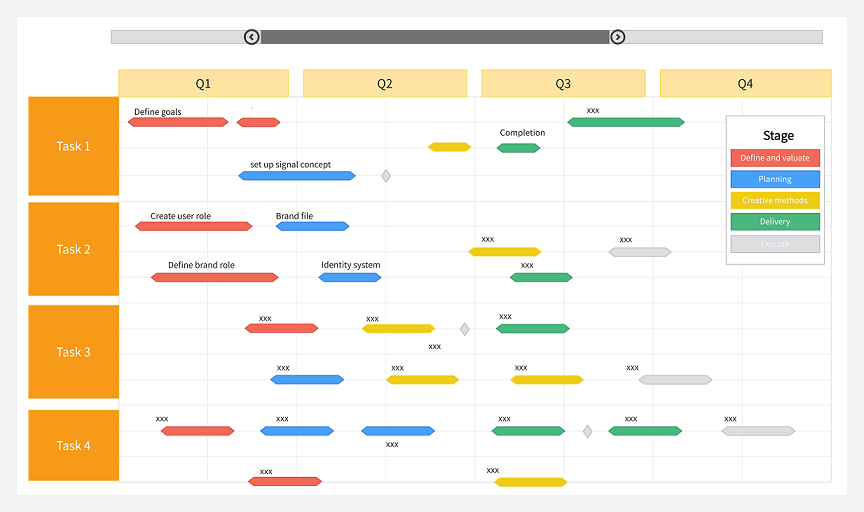
Scrum consists of three roles, five events, and three artifacts:
- Roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team.
- Events: Sprint (iteration), Daily Scrum, Sprint Planning, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
- Artifacts: Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
Among these elements, Daily Scrum and Sprint Retrospectives are crucial in Scrum practice.
Scrum Daily Stand-ups
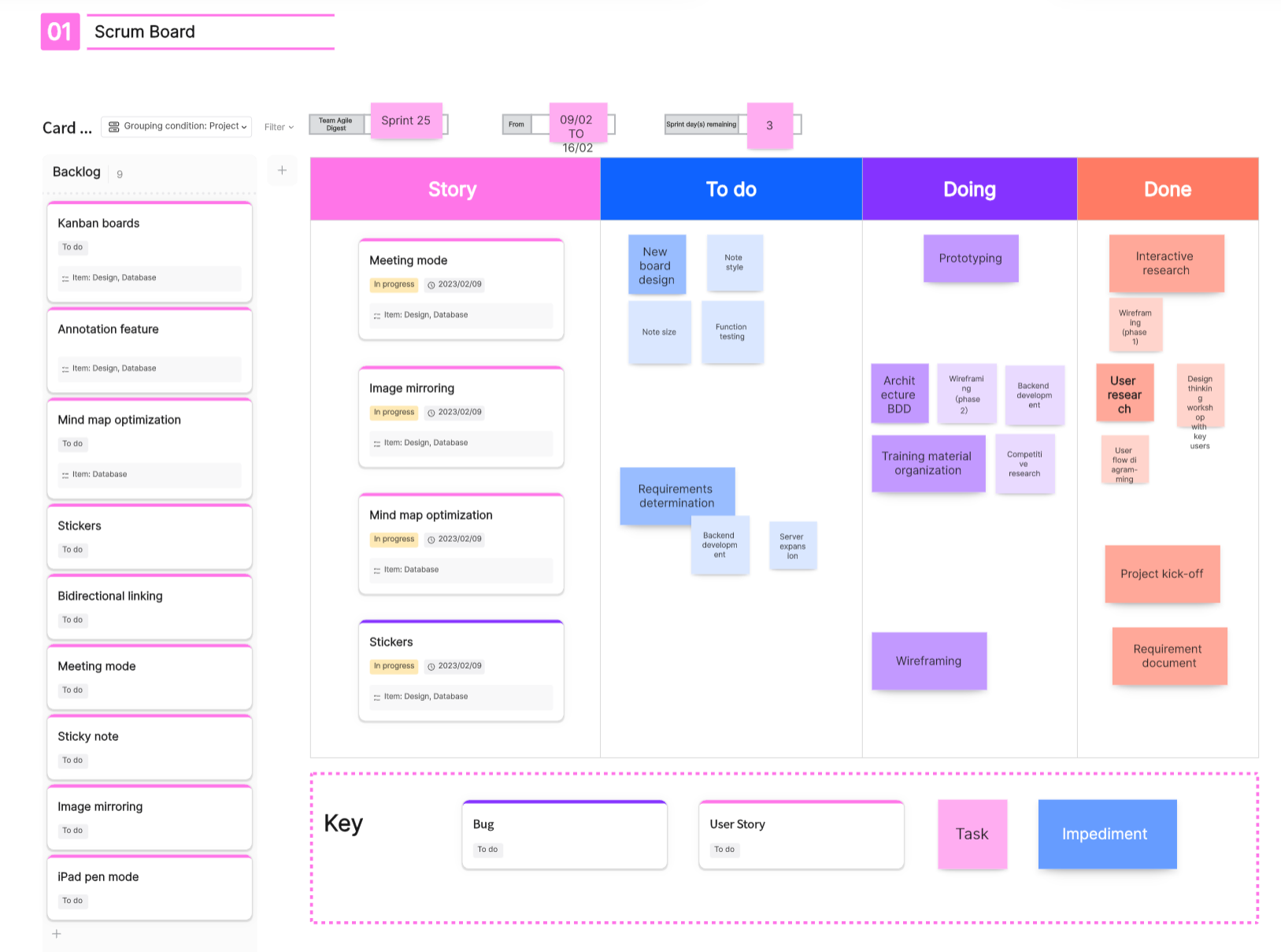
Daily stand-ups occur at a fixed time each day (usually morning), where team members briefly state what they did yesterday, what they plan to do today, and any issues needing resolution. This keeps everyone informed about project progress and helps quickly identify and solve problems. Documentation, tables, or online whiteboards can record each stand-up's content for follow-up, archiving, and review.
Scrum Sprint Retrospective
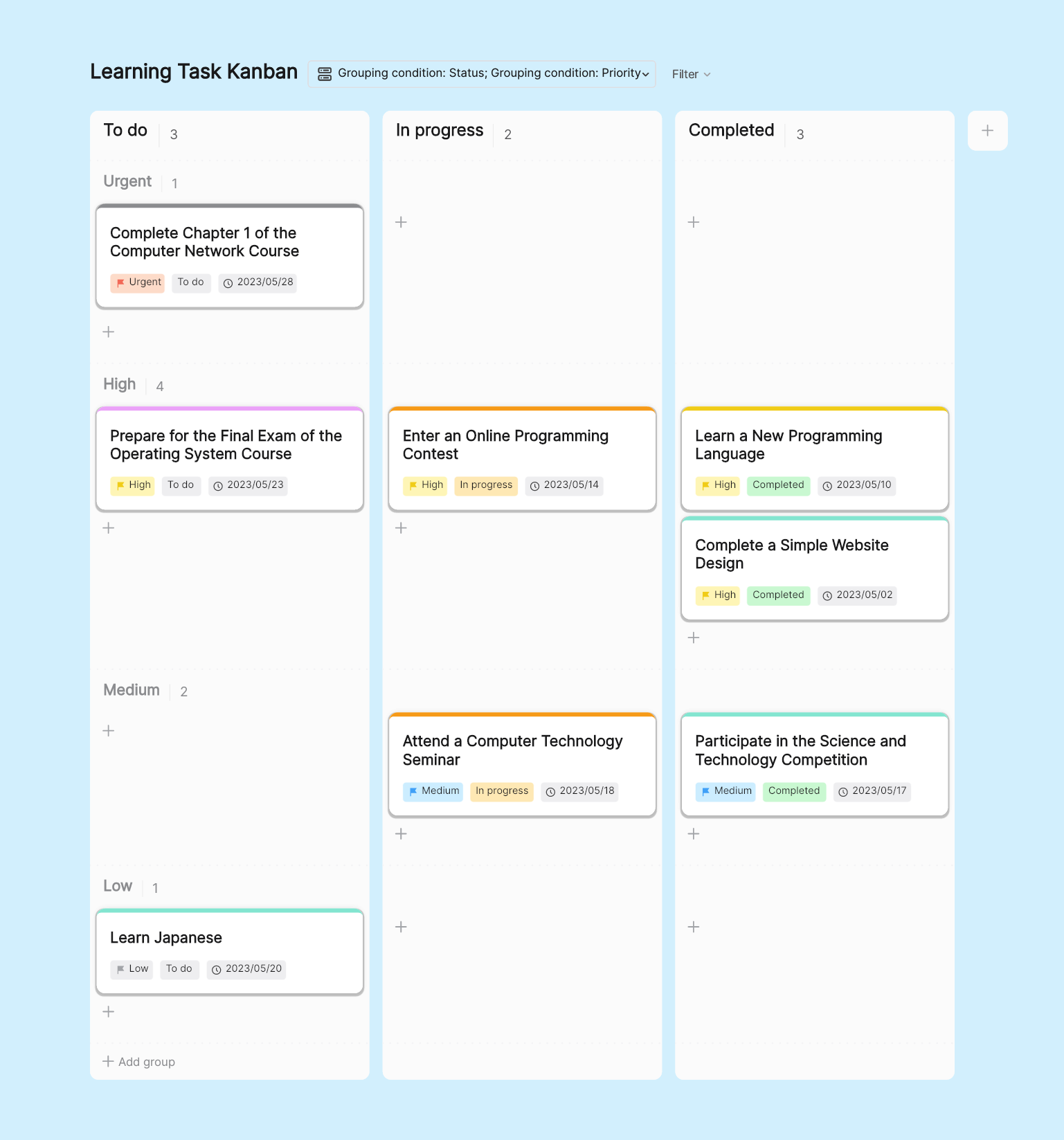
Sprint retrospectives are held at the end of each sprint. The team gathers to review the past sprint, discussing what went well and what needs improvement. This helps the team continuously improve their work methods and efficiency. Tools like boardmix can facilitate Scrum practice, offering templates for daily stand-ups, sprint retrospectives, user stories, and more, simplifying the process.
Scrum Team Roles
- Scrum Master: Facilitates the Scrum process, removing obstacles affecting the team's sprint goals. The Scrum Master is not the team leader (as the team is self-organized) but ensures the Scrum process is followed.
- Product Owner: Represents user interests, ensuring the team works on the right business tasks. The Product Owner writes user stories, prioritizes them, and adds them to the product backlog.
- Development Team: Responsible for delivering the product, usually comprising 5-9 cross-functional members with all necessary skills for product delivery.
Scrum is a powerful agile project management tool, beneficial for both beginners and experienced users. Additionally, tools like Boardmix, with templates for Scrum practices, can help you better understand and apply Scrum, making project management easier and more efficient.
Get Free Project Management Templates from Boardmix
Boardmix is an online digital whiteboard, which is perfect for project management. There are various ready-made project management templates on Boardmix, including Project management Kanban, Project Timeline, Daily Scrum meeting, Daily Work Report, Daily to-do list, and so on. All of them are free to use. Here is the step-by-step guide on using free project management templates on Boardmix.
Step 1: Log in to Your Boardmix Account
To begin, you'll need to access your Boardmix account. Go to the Boardmix website and enter your login credentials. If you don't have an account yet, you can sign up for a new one for free.
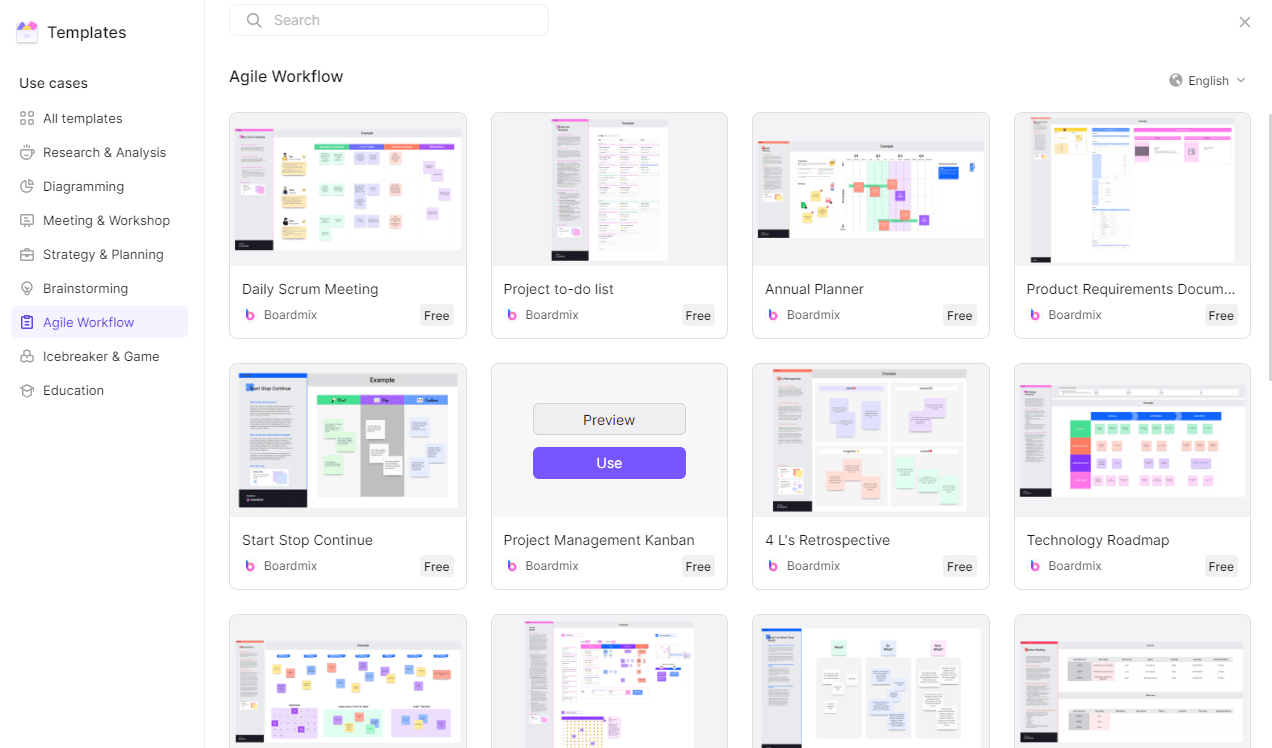
Step 2: Search and Choose Project Management Template
Once you're logged in, head over to the Template library. You can find this in the main dashboard. Type in some related keywords like “project”, “daily”, and search for the suitable template and click to use it for free.
Step 3: Customize and Edit Your Own Project
Now that you've chosen the template, it's time to customize it according to your needs. You can decorate your template with shapes, lines, drawing pens, icons, and other tools. The flexibility of Boardmix allows you to add or remove sections as needed. Simply click on a component to edit it.
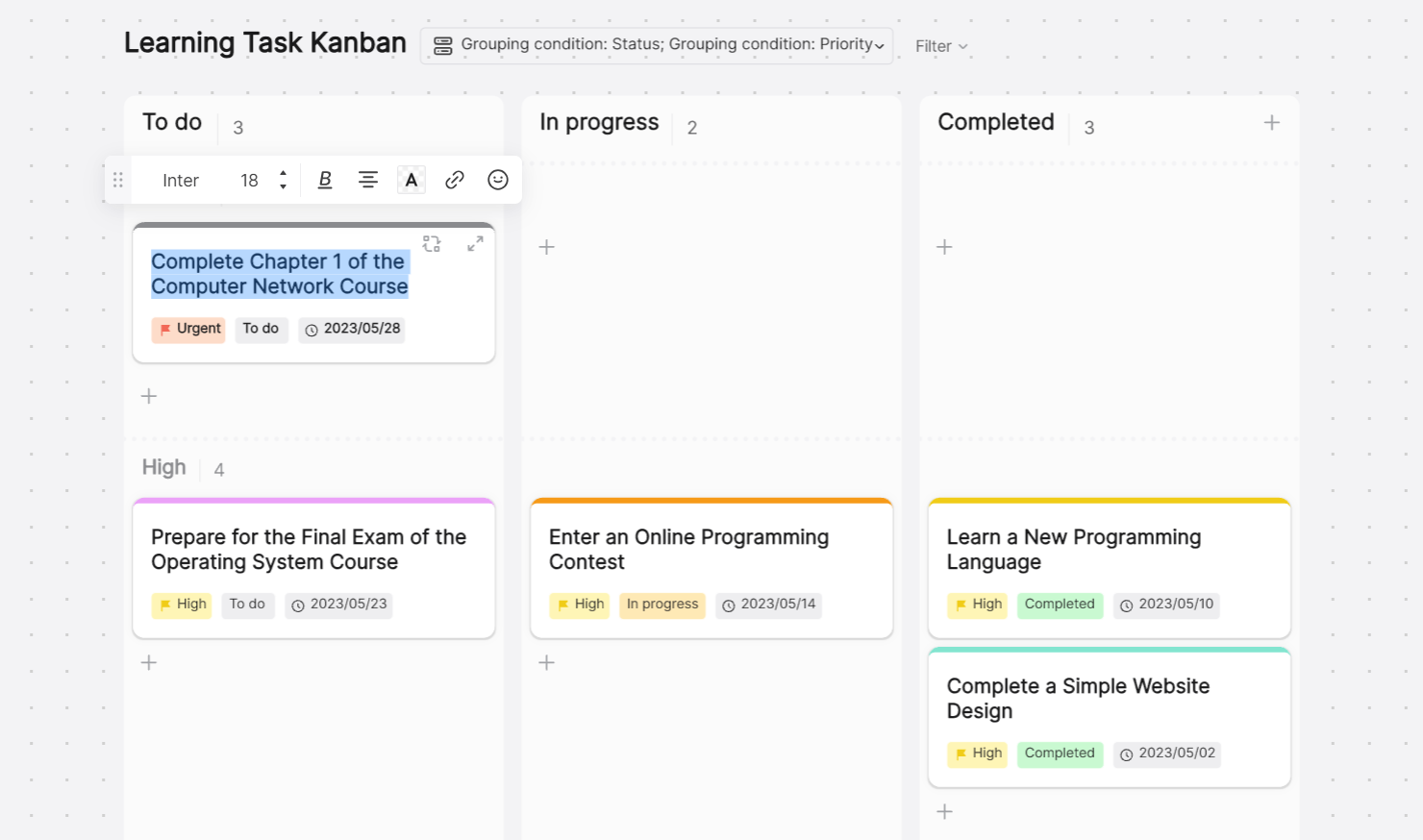
Step 4: Save Your Work, Share and Collaborate
When customizing your project plan, Boardmix autosaves your progress. Next, share your activity plan to collaborate with your team. Click on the "Share" button on the top right corner of the screen, copy the sharing link, and send it to anyone whom you want to collaborate with.
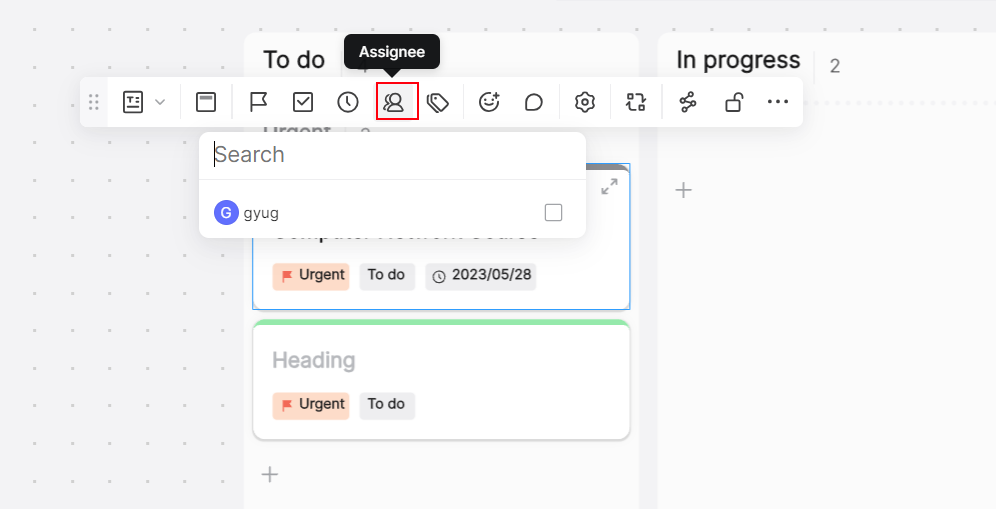
People can join this file to edit and collaborate on this file in real time by clicking this sharing link. We encourage your team to leave comments, suggest edits, or ask questions online so you can adjust it in time.
When comparing the differences between agile project management and traditional project management, you will find that the former is an extremely effective project management tool, and Boardmix is an excellent online tool that integrates the Kanban function. Whether you are an individual user or a team user, as long as you master the method of using Kanban in Boardmix, you can greatly improve your project management efficiency. Get stared today and manage your project online for free!








