By utilizing the Business Canvas Model, businesses can stay agile, responsive, and strategically aligned. Embrace this model to unlock new opportunities and drive your business towards sustained growth and success.
What is the Business Canvas Model?
The Business Canvas Model is a strategic management tool that allows businesses to visualize, design, and innovate their business models. Developed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, this model provides a comprehensive yet straightforward framework for understanding the key components of a business. It comprises nine essential building blocks: customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. Each block represents a critical aspect of the business, offering a holistic view that helps in aligning operations and strategies effectively.
Why Use Business Canvas Model?
Using the Business Canvas Model offers several significant advantages for businesses of all sizes and stages:
1. Simplifies Complexity
The Business Canvas Model breaks down complex business planning into nine manageable components, making it easier to understand and analyze each part of the business. This simplification helps in identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats within the business model.
2. Promotes Flexibility and Adaptability
The Business Canvas Model is highly flexible, allowing for quick adjustments and iterations. This adaptability is crucial in today’s dynamic business environment, where agility and responsiveness are key to maintaining a competitive edge. Businesses can rapidly test different hypotheses, pivot strategies, and refine their models based on feedback and market changes.
3. Encourages Innovation
By visually mapping out the business model, the Business Canvas Model encourages creative thinking and innovation. It helps identify new opportunities for value creation, potential partnerships, and innovative revenue streams, driving business growth and differentiation.
4. Supports Strategic Alignment
The Business Canvas Model provides a holistic view of the business, ensuring that all elements are aligned with the overall strategy. This alignment helps in setting clear objectives, allocating resources efficiently, and maintaining a cohesive direction for the business.
5. Facilitates Investor Communication
For startups and businesses seeking funding, the Business Canvas Model is an effective tool for communicating the business plan to investors. Its clear and concise format provides a comprehensive overview of the business, highlighting its value proposition, market potential, and operational strategy, which can enhance investor confidence and support.
6. Provides a Comprehensive Evaluation Tool
The Business Canvas Model can be used as a diagnostic tool to evaluate existing business models. By examining each component, businesses can identify areas of improvement, streamline operations, and enhance overall efficiency.
Business Model Canvas Examples
1. Airbnb
Airbnb’s business model canvas highlights its value proposition of offering unique travel experiences and affordable accommodation options. Key resources include its platform, brand, and vast network of hosts. Revenue streams are generated from service fees charged to guests and hosts, while customer segments range from budget travelers to luxury seekers.
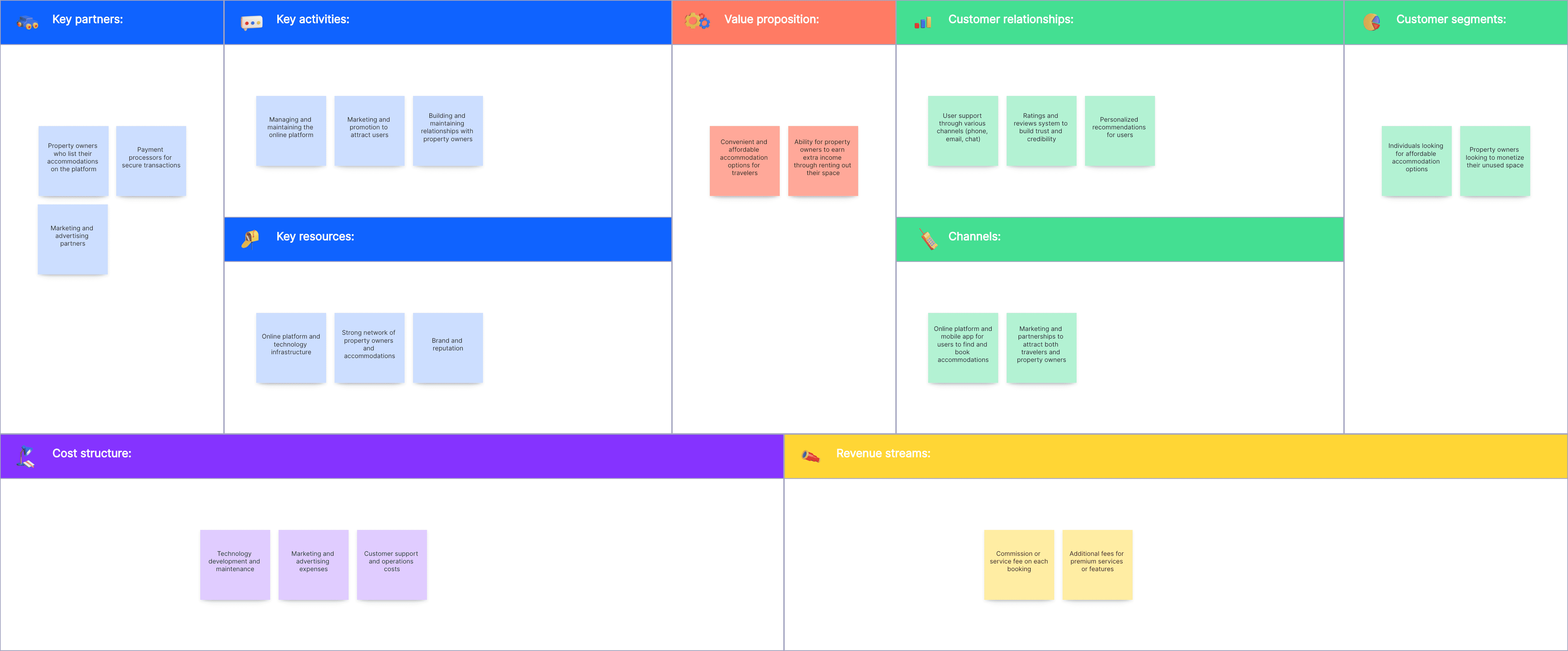
Customer Segments:
Travelers seeking affordable and unique accommodations
Hosts looking to monetize their extra space
Value Propositions:
Affordable, personalized travel experiences
Opportunity for hosts to earn extra income
Channels:
Website and mobile app
Social media
Customer Relationships:
Community-based interactions
Customer support through online help centers
Revenue Streams:
Service fees from guests and hosts
Key Resources:
Platform Infrastructure
Strong brand reputation
Host network
Key Activities:
Platform maintenance and development
Marketing and customer support
Key Partnerships:
Payment processors
Local governments for regulatory compliance
Cost Structure:
Technology development and maintenance
Customer support
Marketing and advertising
2. IKEA
IKEA’s canvas focuses on its value proposition of providing stylish, affordable furniture. Key activities include designing, manufacturing, and distributing products. The company’s customer segments include young adults, families, and small businesses. Revenue streams are primarily from product sales, with cost structure focused on production and logistics efficiency.
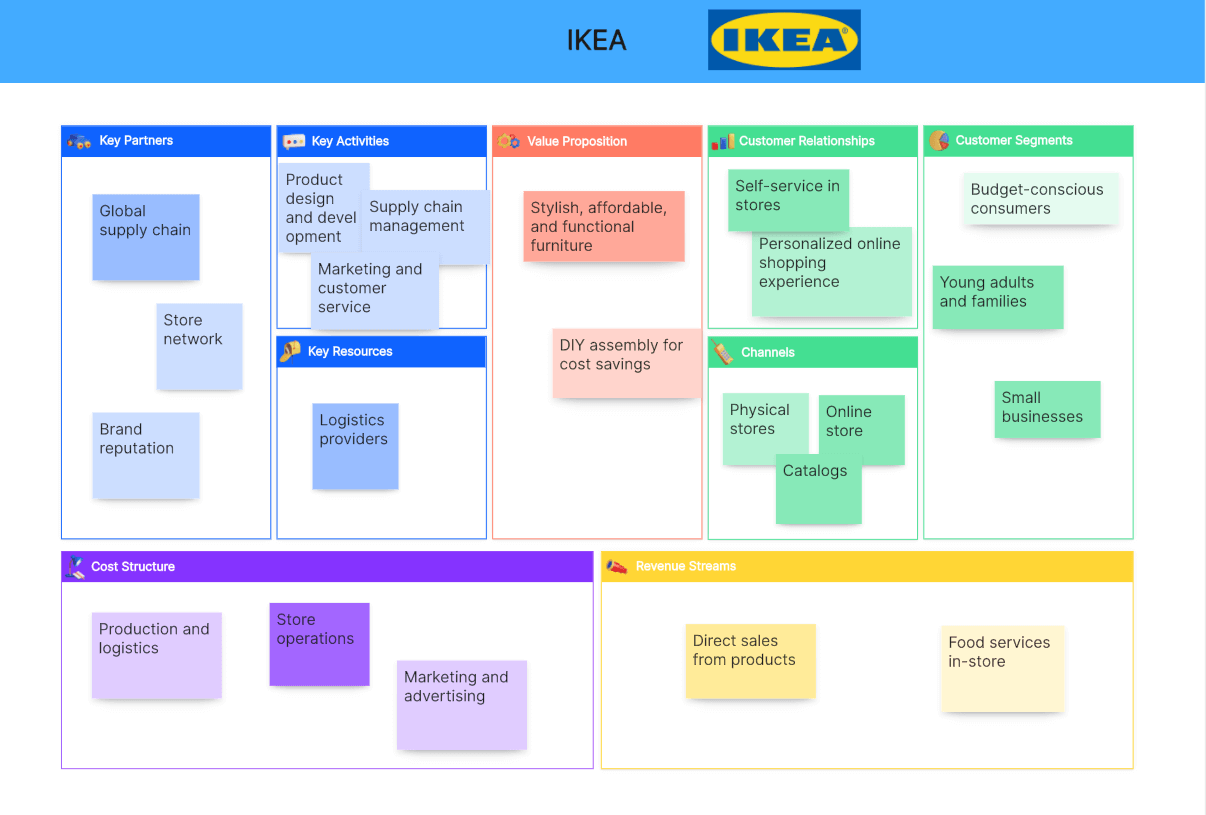
Customer Segments:
Budget-conscious consumers
Young adults and families
Small businesses
Value Propositions:
Stylish, affordable, and functional furniture
DIY assembly for cost savings
Channels:
Physical stores
Online store
Catalogs
Customer Relationships:
Self-service in stores
Personalized online shopping experience
Revenue Streams:
Direct sales from products
Food services in-store
Key Resources:
Global supply chain
Store network
Brand reputation
Key Activities:
Product design and development
Supply chain management
Marketing and customer service
Key Partnerships:
Suppliers and manufacturers
Logistics providers
Cost Structure:
Production and logistics
Store operations
Marketing and advertising
3. Netflix
Netflix’s model emphasizes its value proposition of unlimited streaming of diverse content. Key resources include its extensive content library and advanced algorithms for personalized recommendations. Customer segments are global, spanning various demographics. Revenue streams come from subscription fees, with key activities revolving around content acquisition and technology development.
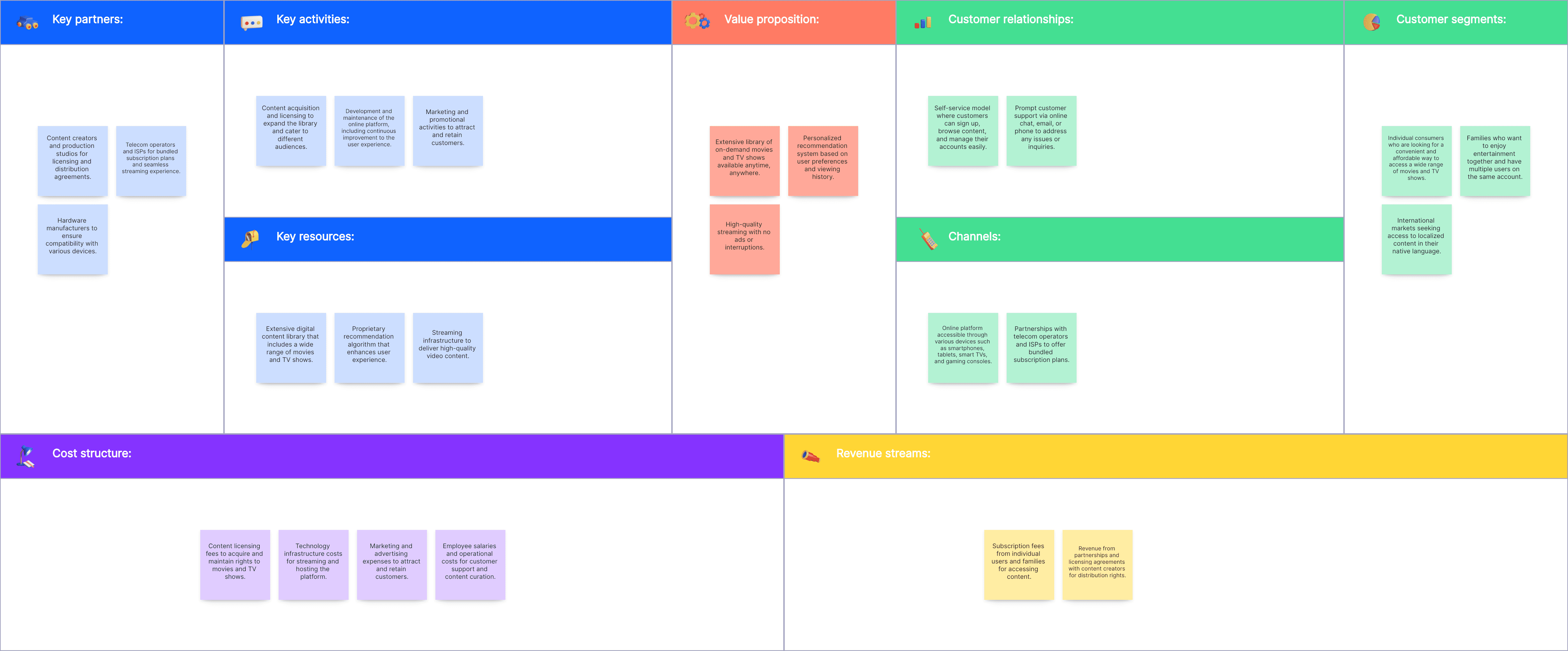
Customer Segments:
Global streaming audience
Various demographic groups (age, location, preferences)
Value Propositions:
Unlimited streaming of diverse content
Personalized recommendations
Ad-free viewing experience
Channels:
Online platform (website and app)
Smart TVs and streaming devices
Customer Relationships:
Subscription-based service
Customer support via the online help center
Revenue Streams:
Subscription fees
Key Resources:
Content Library
Streaming technology
Data and algorithms for recommendations
Key Activities:
Content acquisition and production
Platform maintenance and development
Marketing and customer service
Key Partnerships:
Content producers and studios
Internet service providers
Device manufacturers
Cost Structure:
Content acquisition and production
Technology infrastructure
Marketing and advertising
4. Amazon
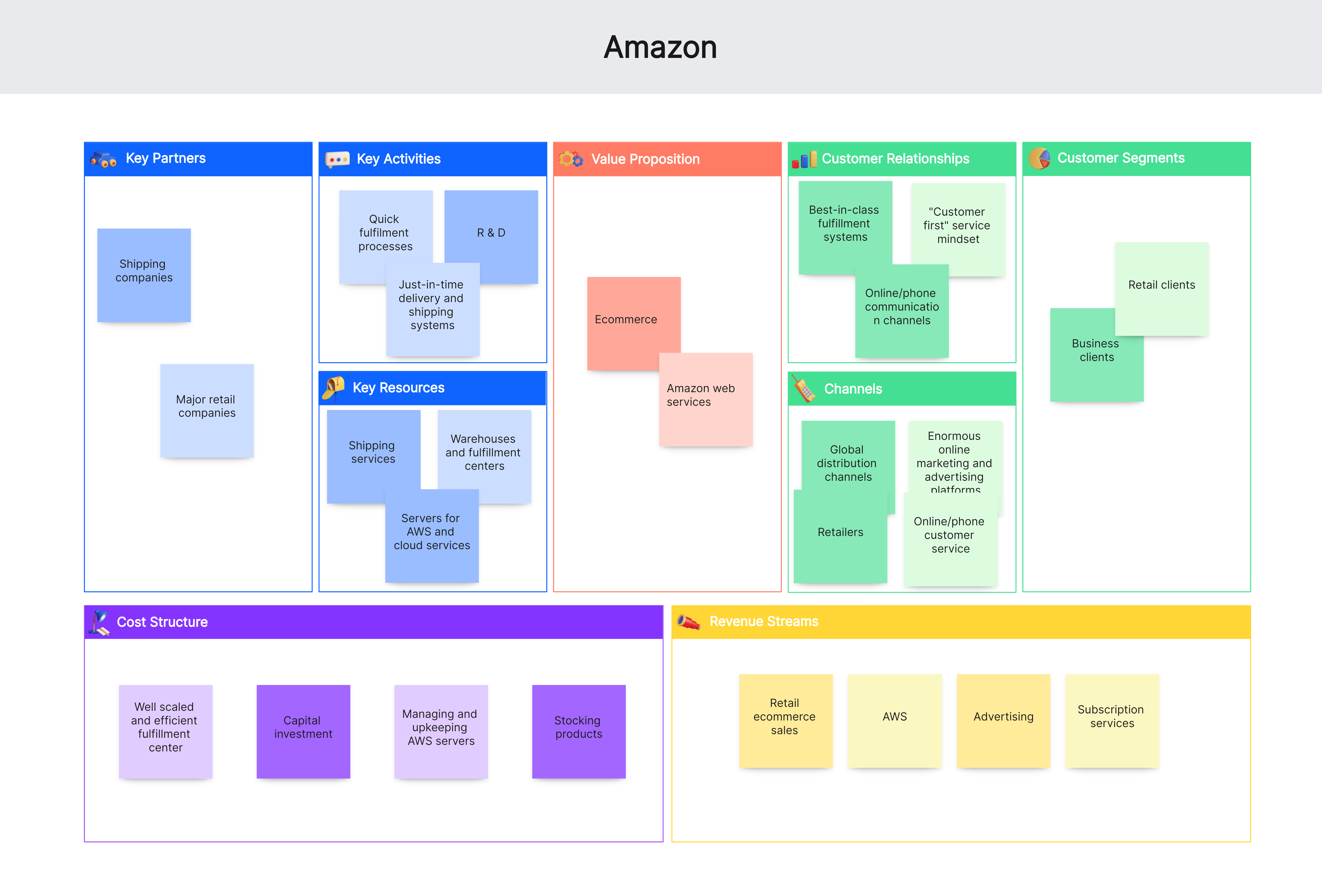
Customer Segments:
Individual consumers
Businesses and organizations
Sellers on the marketplace
Value Propositions:
Wide selection of products
Fast and reliable delivery
Customer-centric services (e.g., Prime membership)
Channels:
Online marketplace
Mobile app
Customer Relationships:
Personalized recommendations
Efficient customer service
Revenue Streams:
Product sales
Subscription fees (Prime)
Third-party seller fees
Key Resources:
Extensive distribution network
Technology infrastructure
Brand reputation
Key Activities:
Supply chain management
Platform development
Marketing and customer service
Key Partnerships:
Suppliers and manufacturers
Delivery services
Cost Structure:
Warehousing and logistics
Technology development
Marketing and advertising
5. Uber
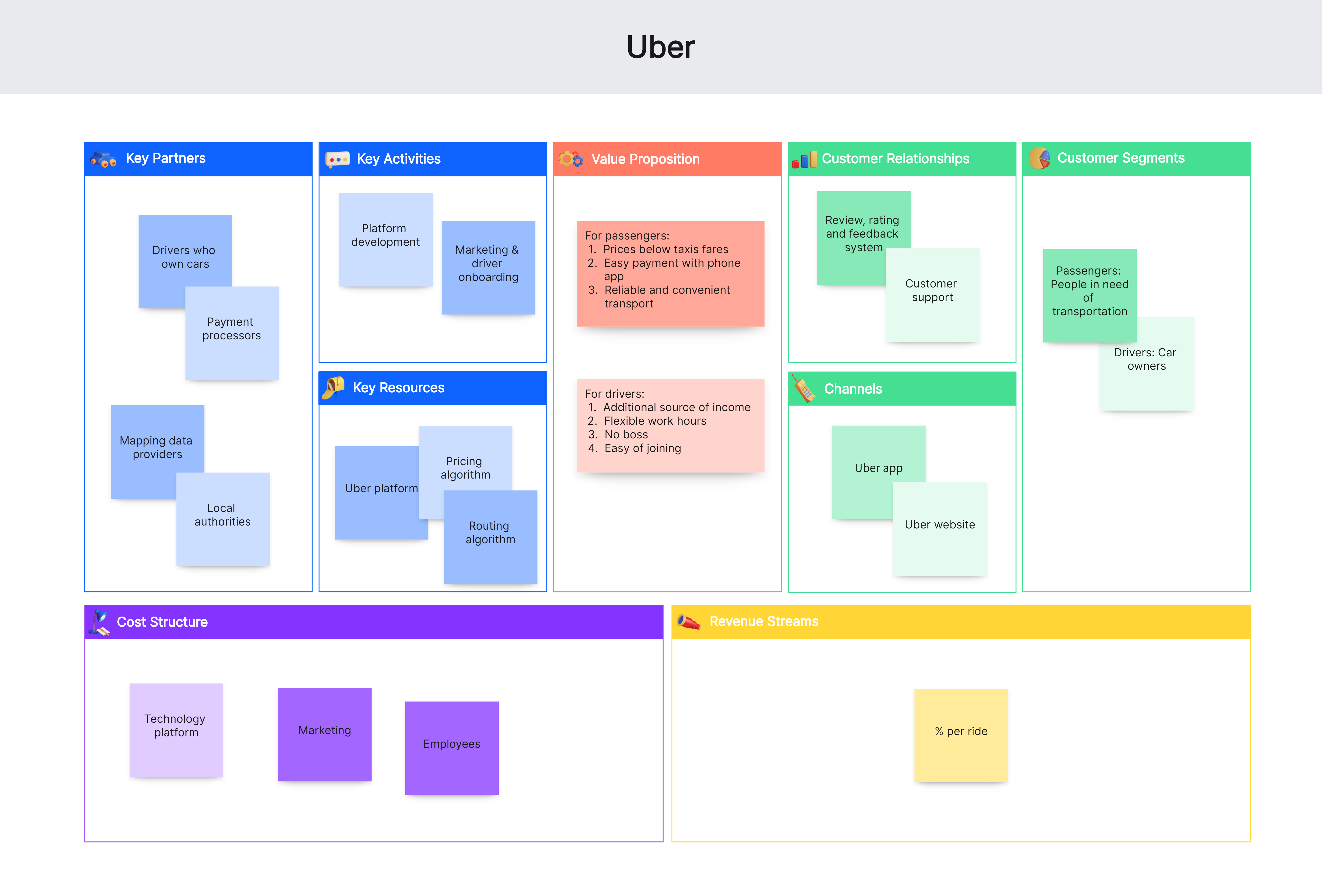
Customer Segments:
Riders seeking convenient transportation
Drivers looking for flexible earning opportunities
Value Propositions:
Convenient and reliable transportation
Income opportunities for drivers
Channels:
Mobile app
Customer Relationships:
Automated service with customer support
Revenue Streams:
Ride fares
Service fees from drivers
Key Resources:
Technology platform
Driver network
Brand reputation
Key Activities:
Platform maintenance and development
Marketing and customer service
Key Partnerships:
Payment processors
Automotive companies
Cost Structure:
Technology development
Marketing and promotions
Customer support
These examples illustrate the versatility and applicability of the Business Model Canvas across different industries, highlighting how businesses can structure and optimize their operations for success.
When Should You Use the Business Model Canvas?
The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a versatile tool that can be applied at various stages of a business’s lifecycle. Here are some key instances when using the BMC can be particularly beneficial:
1. Startups and New Business Ventures
Ideation and Planning: For entrepreneurs starting a new business, the BMC helps in crystallizing and visualizing the core components of their business idea. It ensures that all critical aspects are considered and aligned, providing a clear roadmap from concept to execution.
Pitching to Investors: The concise and comprehensive format of the BMC is ideal for presenting business ideas to potential investors. It provides a clear overview of the business model, highlighting the value proposition, market potential, and strategic plan, which can enhance investor confidence and support.
2. Existing Businesses
Strategic Review and Refinement: Established businesses can use the BMC to review and refine their current business models. By evaluating each component, companies can identify areas for improvement, streamline operations, and adapt to changing market conditions.
Innovation and New Projects: When launching new products, services, or business units, the BMC helps in planning and integrating these initiatives into the overall business strategy. It ensures that new projects are aligned with the company’s goals and resources.
3. Continuous Improvement
Performance Evaluation: The BMC is an effective tool for ongoing performance evaluation and optimization. By regularly revisiting the canvas, businesses can track progress, measure success, and make data-driven decisions to enhance performance.
Employee Engagement and Training: Using the BMC can help engage employees and foster a deeper understanding of the business model. It can be used in training sessions to educate new hires and ensure that all team members are aligned with the company’s strategic objectives.
4. Strategic Planning and Goal Setting
Long-Term Planning: The BMC aids in long-term strategic planning by providing a clear and holistic view of the business. It helps in setting realistic goals, allocating resources efficiently, and aligning short-term actions with long-term objectives.
Crisis Management: In times of crisis, such as financial distress or operational disruptions, the BMC can serve as a guide for identifying critical areas to address and developing contingency plans. It helps in maintaining focus and coherence during challenging times.
How to Make a Business Canvas Model?
Creating a Business Canvas Model involves several steps that help in structuring and visualizing your business model effectively. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define Customer Segments
Identify and describe the different groups of people or organizations your business aims to reach and serve. Consider demographics, preferences, and needs. Ask questions like: Who are our most important customers? What are their characteristics and needs?
2. Clarify Value Propositions
Determine what unique value your business offers to each customer segment. Identify the problems you are solving or the needs you are fulfilling. Ask: What value do we deliver to the customer? Which customer problems are we helping to solve?
3. Establish Channels
Outline how your business will communicate with and reach your customer segments to deliver the value proposition. Include both direct and indirect channels. Ask: Through which channels do our customer segments want to be reached? How are we reaching them now?
4. Develop Customer Relationships
Describe the type of relationship you will establish with each customer segment. Consider how you will acquire, retain, and grow your customer base. Ask: What type of relationship does each customer segment expect? How costly are these relationships?
5. Identify Revenue Streams
Determine how your business will earn revenue from each customer segment. Consider pricing mechanisms and revenue models. Ask: For what value are our customers willing to pay? How are they currently paying?
6. List Key Resources:
Identify the most important assets required to offer and deliver your value propositions, reach your markets, maintain relationships, and earn revenue. Ask: What key resources do our value propositions require?
7. Outline Key Activities
Describe the most important activities your business must perform to operate successfully. Include activities related to production, problem-solving, and networking. Ask: What key activities do our value propositions require?
8. Form Key Partnerships
Identify the network of suppliers and partners that will help your business achieve its objectives. Consider alliances, joint ventures, and buyer-supplier relationships. Ask: Who are our key partners? Which key resources do we acquire from partners?
9. Determine Cost Structure
Outline the costs associated with operating your business model. Identify both fixed and variable costs. Ask: What are the most important costs inherent in our business model? Which key resources and activities are most expensive?
In summary, the Business Canvas Model is a versatile and powerful tool that simplifies business planning, enhances communication, promotes flexibility and innovation, supports strategic alignment, and facilitates effective investor communication. By leveraging this model, businesses can gain a clearer understanding of their operations, make informed decisions, and drive sustainable growth. Using an online platform like Boardmix, you can create, share, and continuously refine your Business Canvas Model, ensuring that it accurately reflects your business strategy and operations.








