Business Process Mapping is essential for organizations aiming to optimize their workflows and enhance operational efficiency. These visual maps help decision-makers spot potential issues, improve decision-making, and ensure processes are followed accurately.
In this article, we'll explore what is business process mapping and 5 powerful Business Process Mapping examples that showcase how different types of flowcharts and diagrams can enhance business operations across various industries.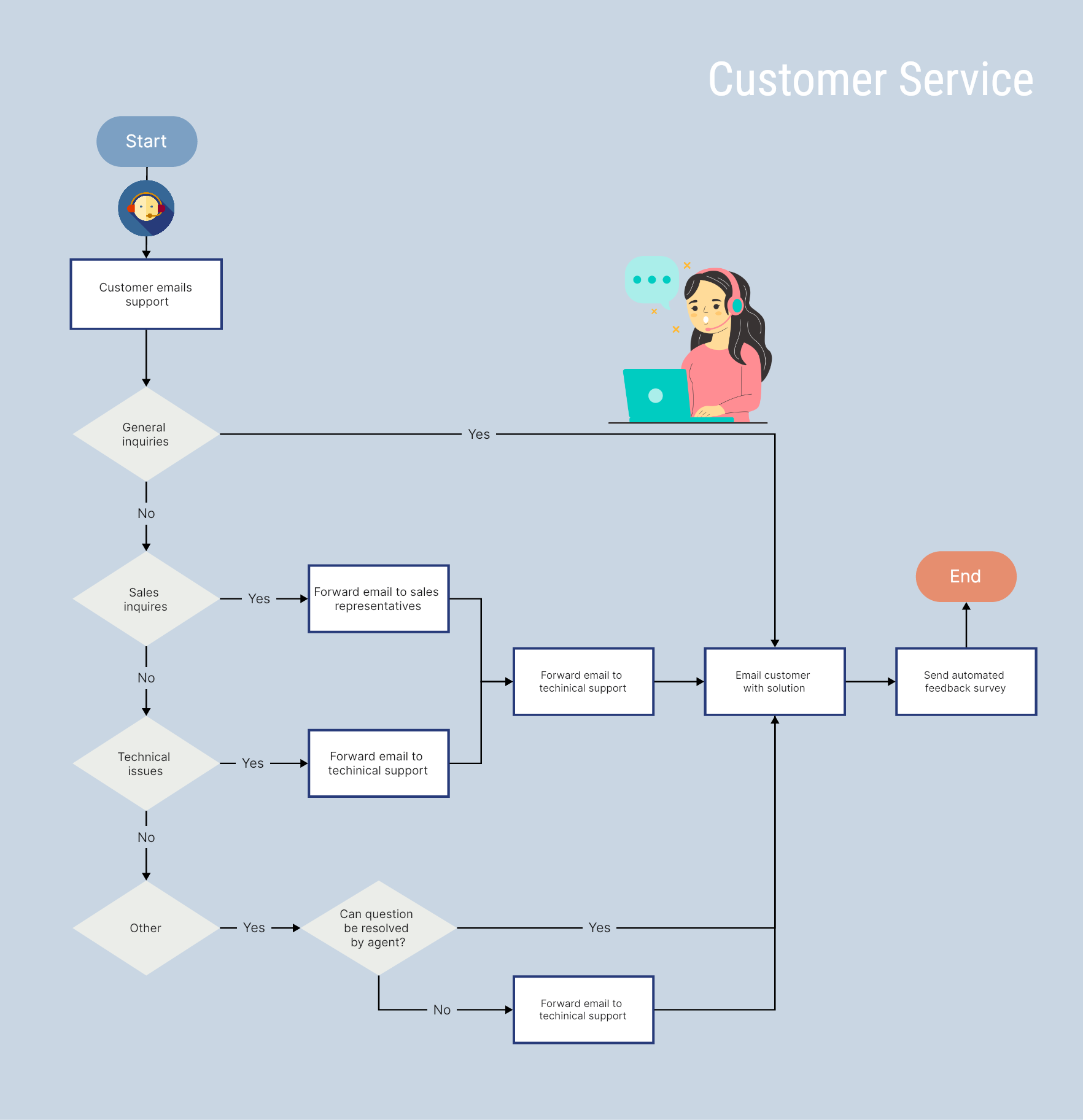
What is Business Process Mapping?
Business Process Mapping (BPM) is a graphical technique used to describe and analyze business processes within an organization. By creating process diagrams or flowcharts, BPM visually represents each step, task, role, decision point, and the relationships between them. This helps organizations better understand their workflows, identify inefficiencies, and make improvements to optimize operations.
What Should Business Process Mapping Include?
- Process Goals: It’s essential to define the objectives and expected outcomes of the process, such as improving efficiency, reducing costs, or enhancing customer satisfaction. Clearly stated goals ensure everyone understands the purpose of the process and the value it adds.
- Key Steps: A detailed breakdown of every task and activity in the process helps create clarity around what needs to be done, when, and by whom. This makes each stage of the process transparent and easier to follow.
- Decision Points: These are critical nodes in the process where choices must be made, influencing the direction of the workflow. Examples include approval decisions, quality checks, or customer feedback evaluations.
- Participants and Roles: Clearly defining which departments or individuals are involved in each step ensures accountability. Understanding who is responsible for what helps prevent confusion and errors.
- Inputs and Outputs: BPM should outline the inputs (e.g., customer orders, raw materials) at the start of the process and the outputs (e.g., delivered products, completed services) at the end. This creates a clear understanding of what is required to initiate and complete the process.
- Tools and Resources: Any tools, technologies, or resources necessary to execute the process should be mapped out. This includes software systems, equipment, and any additional resources that support the workflow.
- Time and Sequence: A process map should reflect the sequence of events and the time required for each step. This helps identify inefficiencies, redundancies, or delays, which can be optimized for better performance.
- Potential Risks and Bottlenecks: Business Process Mapping also highlights any risks or bottlenecks that might slow down the process. By identifying these challenges early on, organizations can take proactive steps to mitigate them and improve workflow efficiency.
When to Use Business Process Mapping?
- Process Optimization: When organizations want to enhance or streamline existing processes, BPM provides a clear overview of which steps are redundant, time-consuming, or inefficient. This allows for targeted improvements.
- Employee Training: During onboarding or training sessions, process maps help new or current employees quickly understand business workflows and their specific responsibilities. Visual aids make complex processes easier to digest.
- Process Standardization: For organizations with multiple teams or departments, Business Process Mapping ensures that all parts of the company follow the same procedures, reducing misunderstandings and errors. It aligns everyone on the same page.
- Problem Diagnosis: When an organization encounters inefficiencies or bottlenecks in its workflow, BPM helps pinpoint exactly where the issues lie. It provides a systematic way to analyze and diagnose problems, making it easier to find effective solutions.
- Project Management: In project planning and execution, BPM is invaluable for helping teams visualize each task, its dependencies, and key milestones. This ensures that everyone is aligned and that the project stays on track.
- Compliance and Auditing: For companies ensuring they meet industry standards or regulatory requirements, Business Process Mapping helps document and analyze existing processes. It provides a structured approach to ensure processes are compliant with laws and regulations.
- Business Process Mapping helps increase efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance team collaboration by providing a clear, visual representation of workflows. By using BPM, companies can optimize operations, foster consistency, and make informed decisions that drive success.
5 Excellent Business Process Mapping Examples: Real-World Applications
An effective Business Process Mapping example should offer clarity, encourage collaboration, and provide actionable insights for process improvement. Below are several examples of how Business Process Mapping is applied in different business contexts, demonstrating its importance and versatility.
- Business Process Flowchart
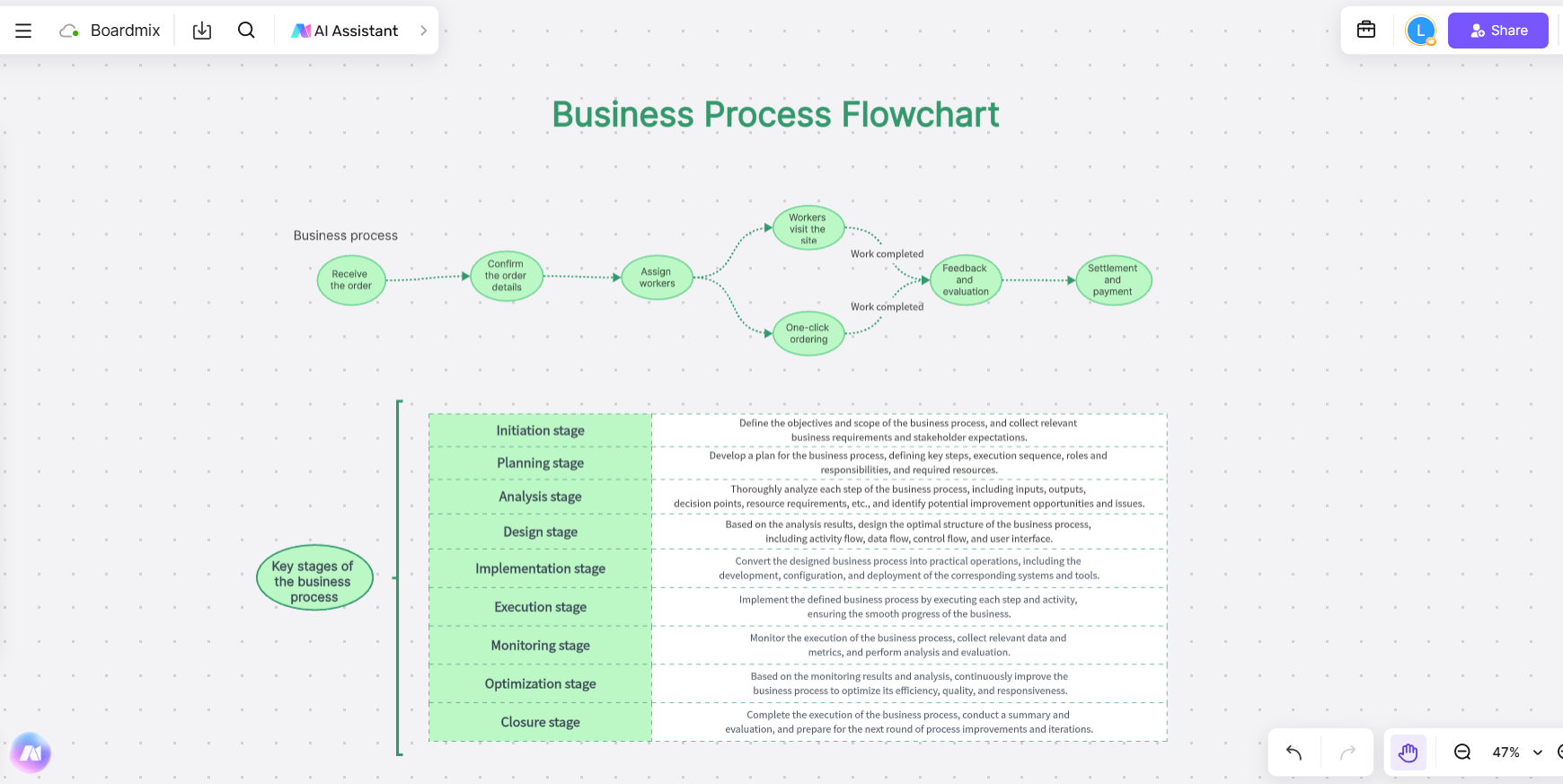
A Business Process Flowchart is a visual tool used to map out a business process step-by-step, improving efficiency and communication between teams. This type of Business Process Mapping example is particularly effective for training new employees, allowing them to understand company workflows and responsibilities quickly. By documenting standard operating procedures, a Business Process Flowchart serves as a reference and ensures consistency.
Key Features of This Business Process Mapping Example:
- Clear steps and roles: Each task and decision point is mapped with associated responsibilities, helping teams identify bottlenecks or unnecessary steps.
- Decision points: The flowchart highlights where decisions impact the process, such as approvals or quality checks, helping decision-makers make informed choices.
- Optimization opportunities: The map reveals areas for improvement, such as eliminating redundant steps, which can lower costs and enhance overall efficiency.
- Modular Business Process Flowchart
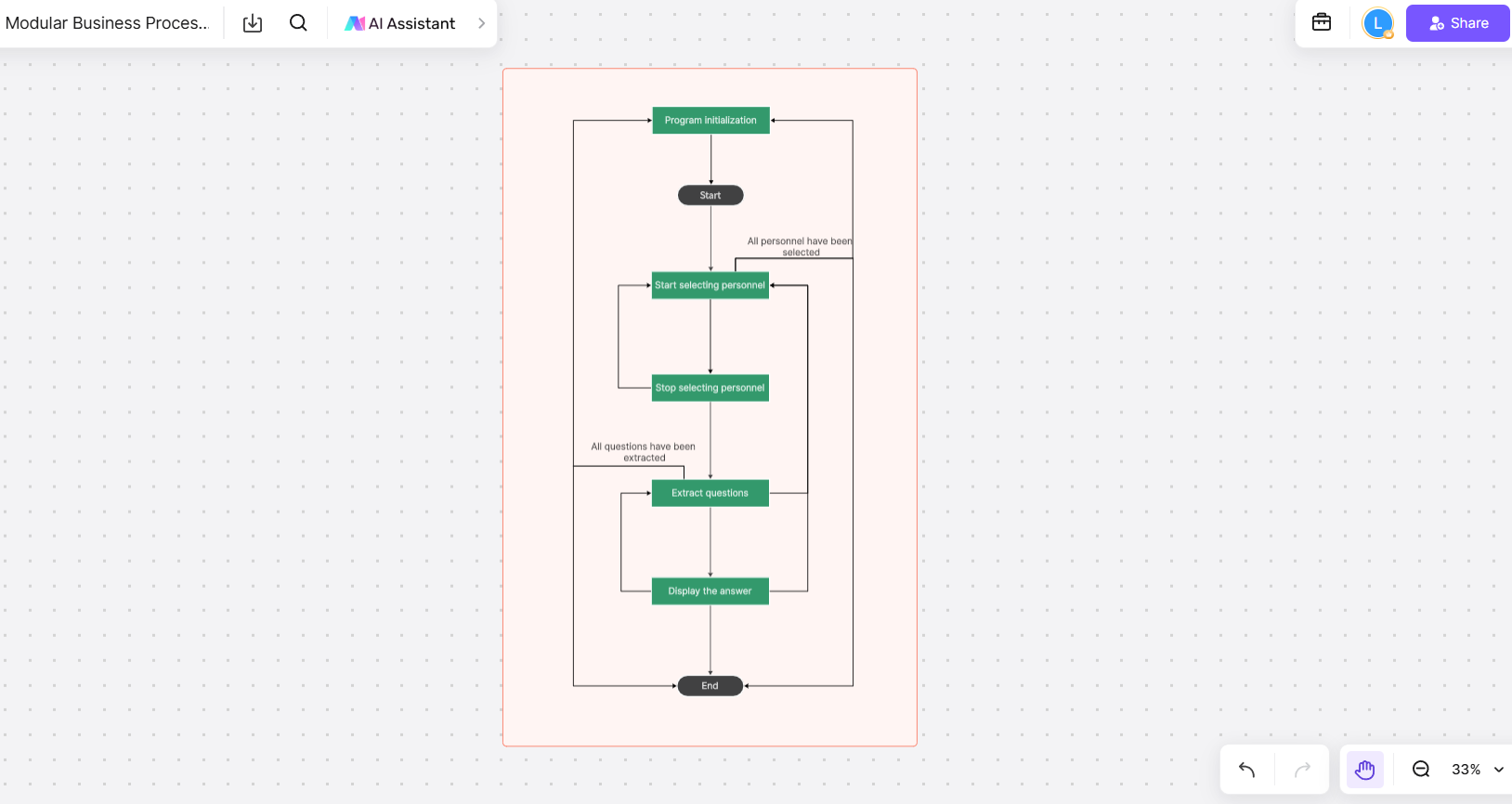
A Modular Business Process Flowchart represents the interactions between different modules or components within a system. This business process mapping example is especially useful during the system design phase, helping stakeholders understand the system structure and data flow.
Key Features of This Business Process Mapping Example:
- Modular components: Each module’s process flow and interactions with other modules are clearly illustrated, providing a detailed view of the system’s functionality.
- Issue identification: When problems arise, this map helps pinpoint the problematic module and provides a direction for optimization.
- System design application: This business process mapping example is vital in software development, supporting improved system architecture and development efficiency.
- Advertising Monitoring Business Process
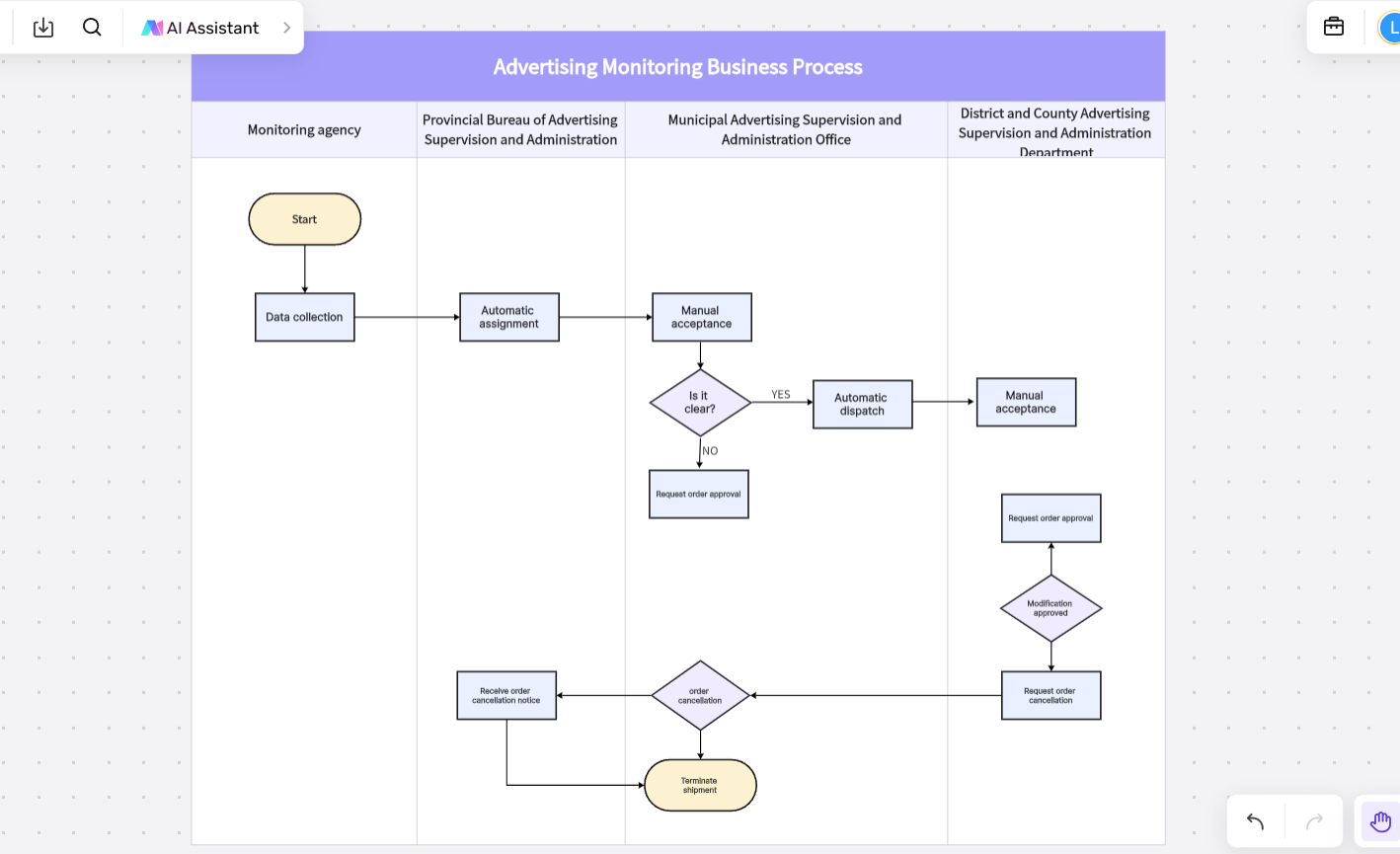
In digital marketing, the Advertising Monitoring Business Process is crucial for tracking ad campaign effectiveness. This Business Process Mapping example helps advertisers monitor key metrics like impressions, clicks, and conversions, allowing them to evaluate ad performance and optimize strategies.
Key Features of This Business Process Mapping Example:
- Data tracking: Captures critical metrics such as ad impressions, clicks, and conversions to measure campaign performance.
- Performance evaluation: The business process mapping example shows how ads perform across various channels and target audiences, offering insights for decision-making.
- Optimized ROI: By analyzing the data, this process allows marketers to adjust their strategies, improving the return on investment.
- Vehicle Management Business Process
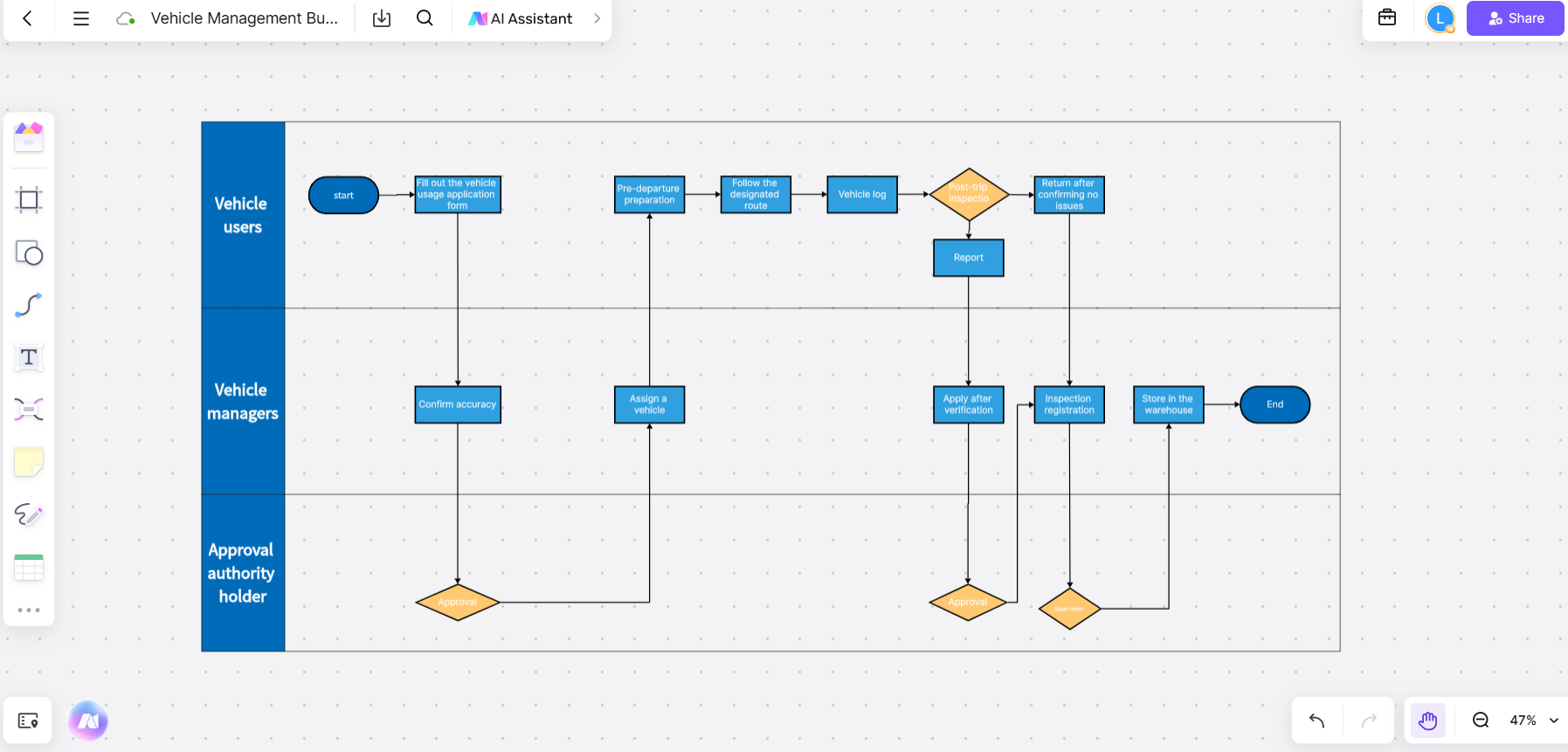
The Vehicle Management Business Process maps out the management activities related to an organization's fleet, such as procurement, maintenance, and disposal. This Business Process Mapping example helps ensure vehicles are used efficiently, maintained properly, and operated safely, ultimately reducing costs and improving fleet performance.
Key Features of This Business Process Mapping Example:
- Comprehensive tracking: Tracks vehicle usage, maintenance schedules, and other relevant data to ensure optimal vehicle operation.
- Cost control: Helps businesses identify and reduce unnecessary expenses related to vehicle maintenance and operation.
- Risk management: Ensures that vehicles are well-maintained and comply with safety regulations, mitigating the risk of accidents.
- Product Business Process Flowchart
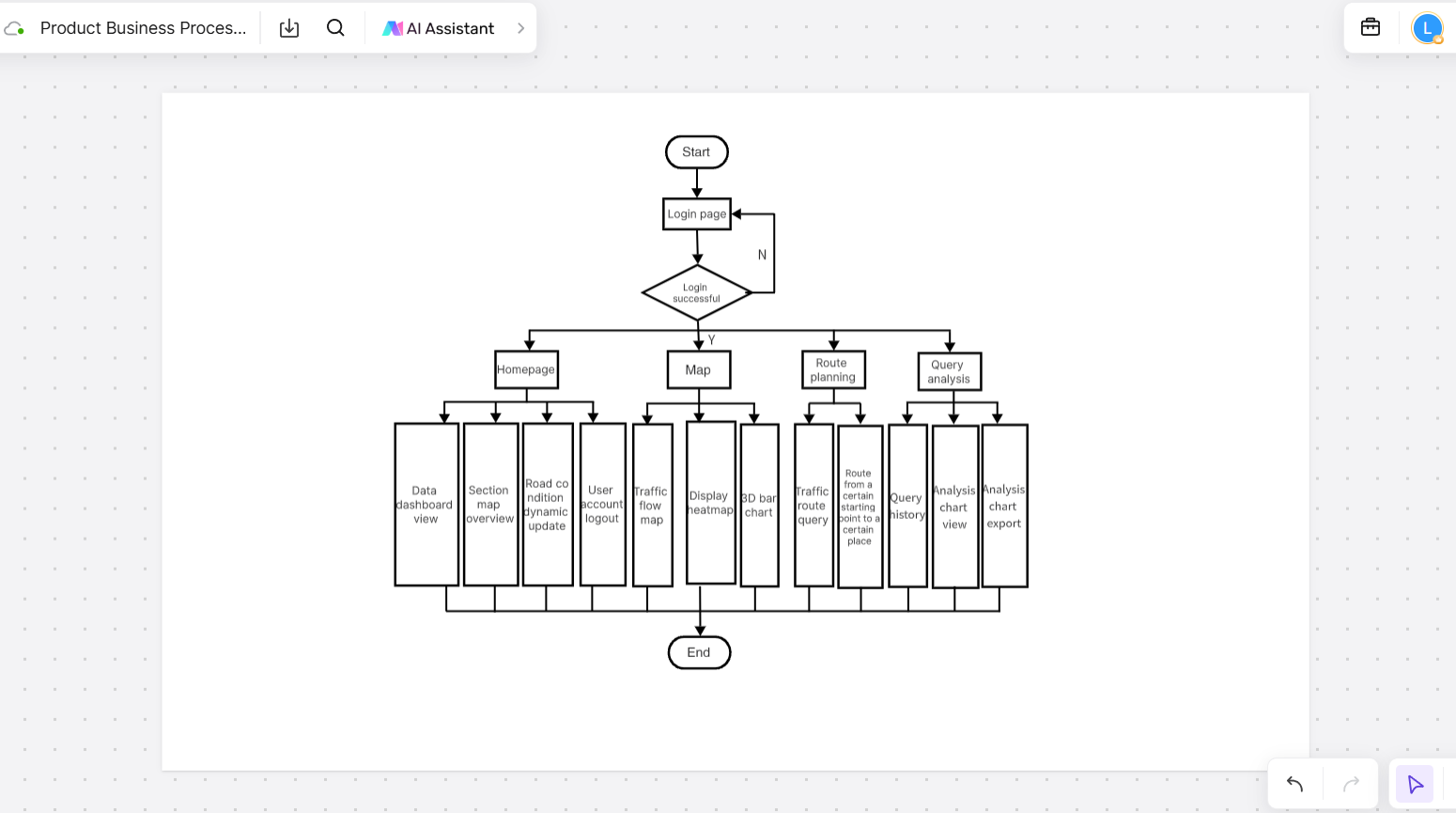
The Product Business Process Flowchart illustrates the steps involved in the development, delivery, and maintenance of a product. This Business Process Mapping example helps product teams, managers, and stakeholders understand how the product operates from concept to delivery.
Key Features of This Product Business Process Flowchart:
- Clear product flow: The flowchart demonstrates the entire product lifecycle, from design to production and delivery.
- Bottleneck identification: Teams can spot inefficiencies or delays in the product development process and take steps to resolve them.
- Continuous improvement: By analyzing the process, teams can identify areas for improvement and streamline operations to enhance product quality and user experience.
Whether you are optimizing a business process, tracking ad performance, managing a fleet of vehicles, or developing a product, Business Process Mapping plays a vital role in enhancing clarity, improving communication, and identifying opportunities for optimization. These business process mapping example illustrate how mapping can be used across different domains, enabling businesses to streamline operations, reduce inefficiencies, and make better, data-driven decisions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, using Business Process Mapping can significantly improve a business’s workflow by providing a visual representation of processes, helping identify inefficiencies, and offering clear guidance for optimization.
From training new employees with a Business Process Flowchart to managing complex systems with a Modular Business Process Flowchart, each example serves a unique purpose.
In this case, we recommend exploring business process mapping examples from Boardmix, a powerful tool that simplifies the process of creating and customizing business process maps for teams of all sizes. Start your mapping journey on Boardmix today!









