One effective method for gathering and implementing feedback is through the Start Stop Continue exercise, also known as the stop start and continue exercise or stop continue start feedback. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to conduct a Start Stop Continue exercise, complete with detailed examples to illustrate its practical applications.
What is the Start Stop Continue Model?
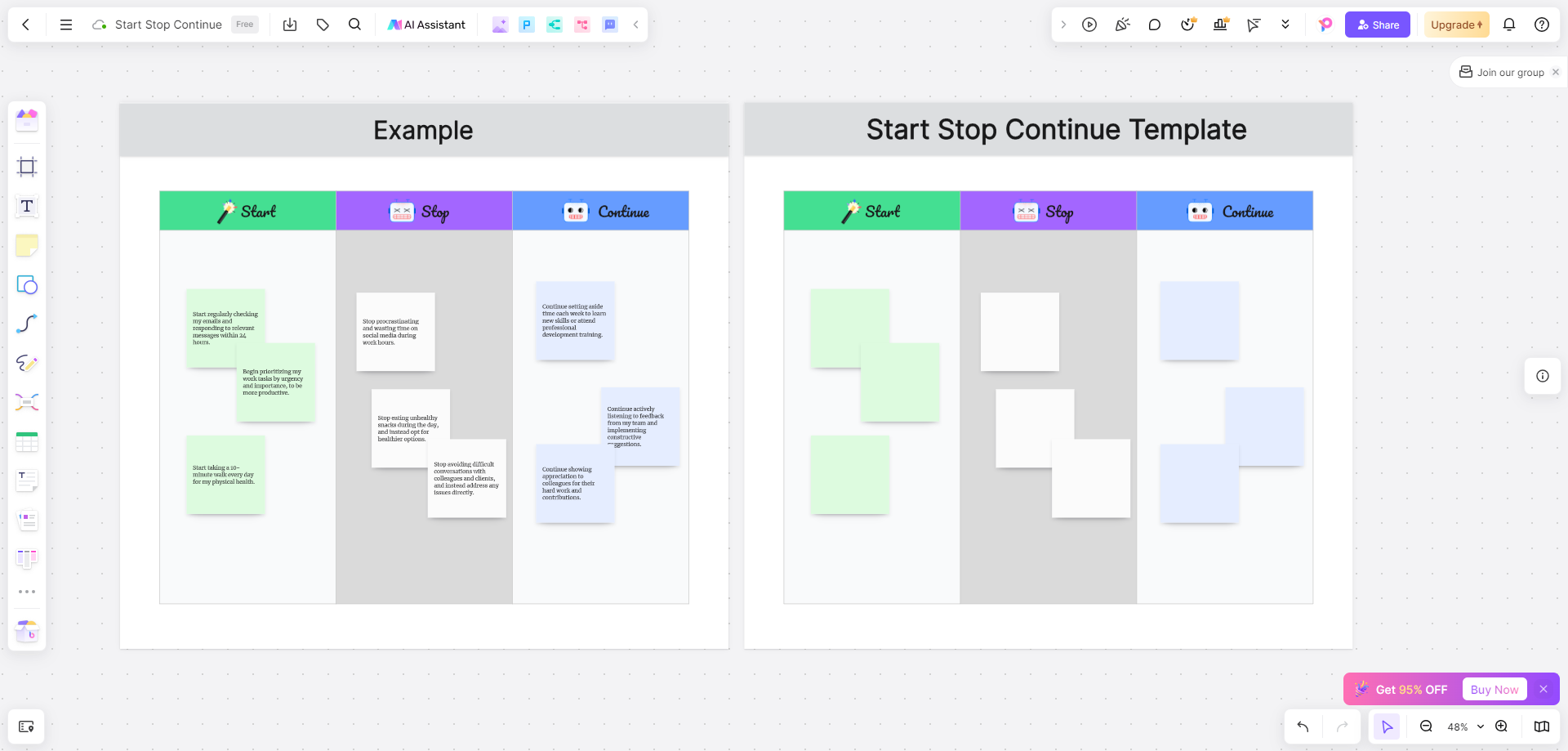
The Start Stop Continue model is a straightforward, yet powerful tool used to solicit feedback and foster continuous improvement. The model encourages individuals or teams to reflect on their actions and categorize them into three areas:
Start: New actions or behaviors that should be initiated.
Stop: Existing actions or behaviors that should be discontinued.
Continue: Current actions or behaviors that are effective and should be maintained.
Historical Context
The Start Stop Continue model has its roots in Agile and Lean methodologies, which emphasize iterative processes and constant enhancement. Originally developed as a simple retrospective tool, it has since been adopted across various industries and contexts due to its versatility and effectiveness.
Key Benefits
Encouraging Constructive Feedback: Provides a structured way for individuals to give and receive feedback.
Promoting Transparency and Open Communication: Fosters an environment where everyone’s voice can be heard.
Facilitating Continuous Improvement and Innovation: Helps identify areas for improvement and innovation.
Simplicity and Adaptability: Easy to understand and implement across different settings.
Components of the Start Stop Continue Exercise
Start
The Start component encourages the introduction of new actions or behaviors that can improve processes or outcomes. The steps involved include:
Brainstorming: Generate new ideas and strategies.
Feasibility: Assess the practicality and resource requirements of these new actions.
Implementation: Plan and execute the integration of the new actions into existing workflows.
Stop
The Stop component focuses on identifying actions or behaviors that are ineffective, counterproductive, or harmful. The steps involved include:
Identification: Recognize actions that are not contributing positively or are causing issues.
Impact Analysis: Evaluate the negative effects these actions have on productivity, morale, or other areas.
Decision Making: Reach a consensus on which actions should be ceased.
Continue
The Continue component highlights existing actions or behaviors that are effective and should be maintained. The steps involved include:
Recognition: Identify successful practices that are currently in place.
Reinforcement: Encourage and support the continuation of these effective actions.
Optimization: Explore ways to further enhance these practices.
How to Conduct a Start Stop Continue Exercise with Boardmix
Getting Started with Boardmix
Boardmix is an excellent tool for conducting a Start Stop Continue exercise due to its user-friendly interface and collaborative features. Here’s how to get started:
Account Setup: Create or log into your Boardmix account.
Create a New Board: Set up a new board specifically for the exercise.
Preparing for the Exercise
Define Objectives: Clearly outline the goals and expected outcomes of the exercise. Inform participants about the purpose and process.
Gather Feedback: Collect preliminary feedback from team members using surveys or pre-meeting questionnaires if needed.
Setting Up the Board
Design the Board: Divide the board into three sections: Stop, Start, Continue. Use different colors or icons for visual clarity.
Populate the Board: Add sticky notes or cards for each identified action. Allow participants to add or move items during the exercise.
Facilitating the Exercise
Introduction: Welcome participants and explain the purpose of the exercise. Outline the process and expected outcomes.
Brainstorming Session: Collect inputs for each section. Use voting or prioritization techniques to identify the most critical actions.
Discussion and Consensus: Discuss each item and its implications. Reach consensus on which actions to stop, start, and continue.
Developing an Action Plan
Assign Responsibilities: Allocate tasks to specific team members. Set clear deadlines and deliverables.
Set Milestones: Define short-term and long-term goals. Establish regular check-ins to monitor progress.
Follow-Up and Review
Monitor Progress: Regularly review the status of actions identified in the Start Stop Continue exercise.
Adjust as Needed: Make necessary adjustments based on feedback and outcomes.
Celebrate Successes: Acknowledge and reward successful implementations.
5 Detailed Examples of Start Stop Continue Exercises
Example 1: Team Retrospective
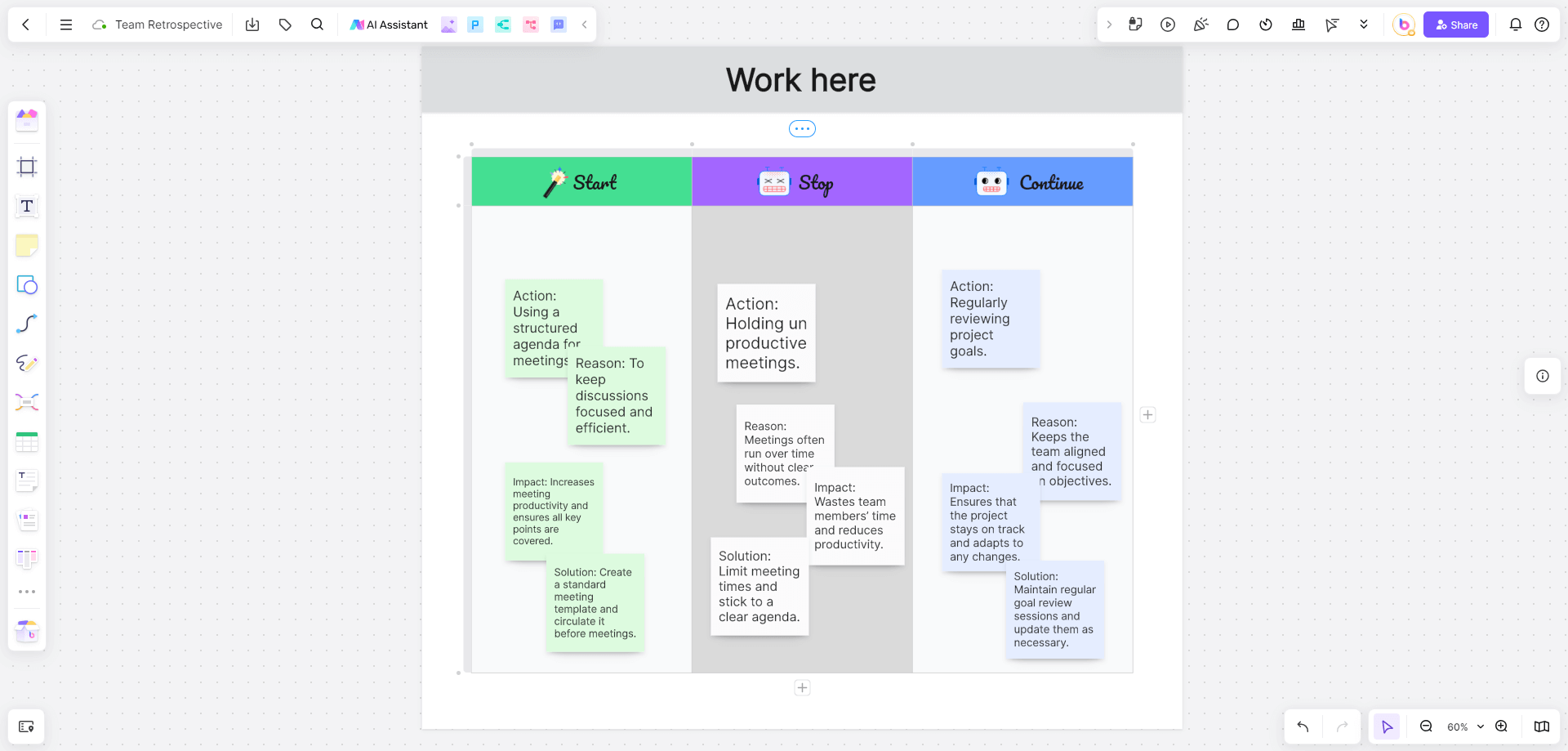
Context
A software development team conducts a retrospective at the end of each sprint to improve their processes.
Stop
Action: Holding unproductive meetings.
Reason: Meetings often run over time without clear outcomes.
Impact: Wastes team members’ time and reduces productivity.
Solution: Limit meeting times and stick to a clear agenda.
Start
Action: Using a structured agenda for meetings.
Reason: To keep discussions focused and efficient.
Impact: Increases meeting productivity and ensures all key points are covered.
Solution: Create a standard meeting template and circulate it before meetings.
Continue
Action: Regularly reviewing project goals.
Reason: Keeps the team aligned and focused on objectives.
Impact: Ensures that the project stays on track and adapts to any changes.
Solution: Maintain regular goal review sessions and update them as necessary.
Example 2: Personal Development
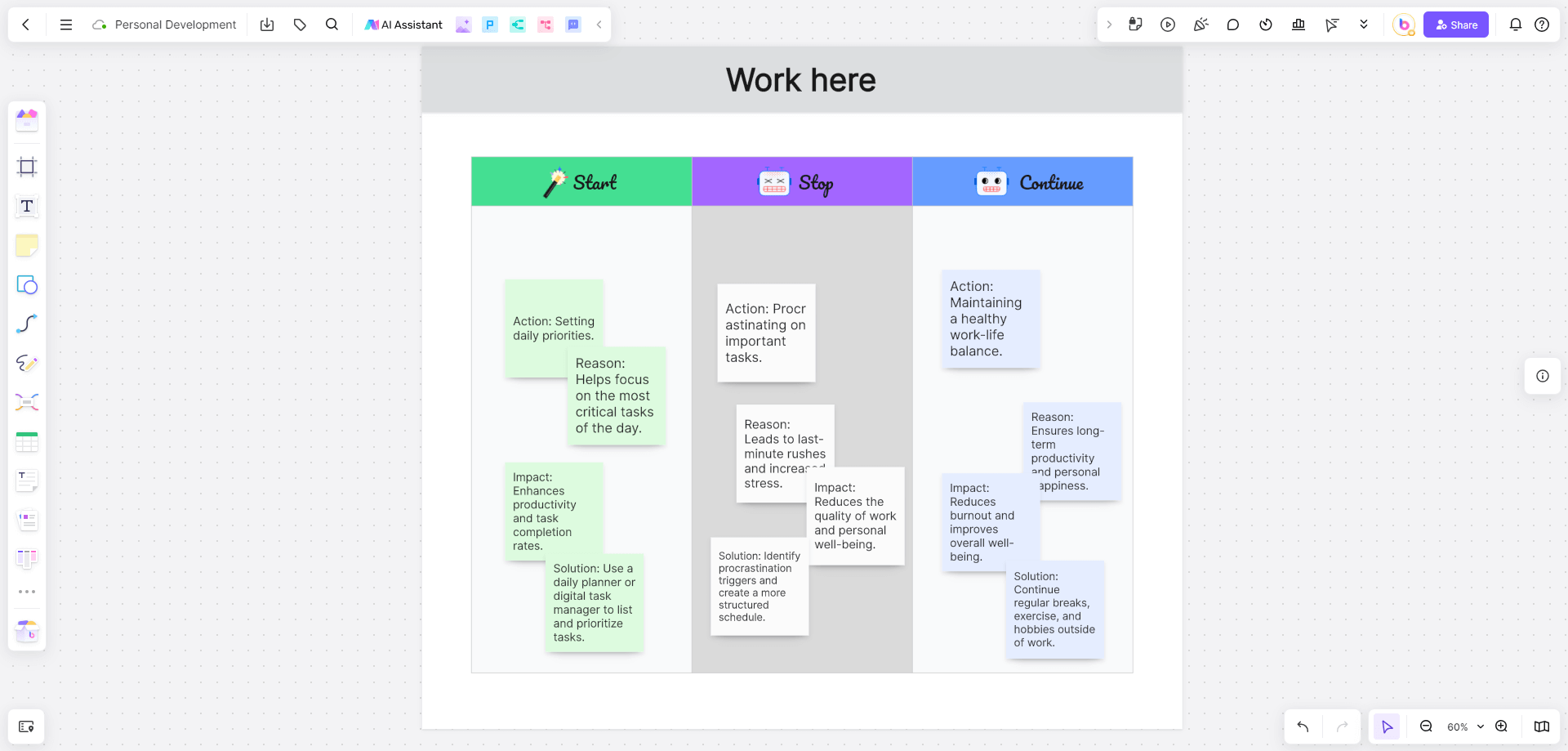
Context
An individual aims to improve their productivity and work-life balance.
Stop
Action: Procrastinating on important tasks.
Reason: Leads to last-minute rushes and increased stress.
Impact: Reduces the quality of work and personal well-being.
Solution: Identify procrastination triggers and create a more structured schedule.
Start
Action: Setting daily priorities.
Reason: Helps focus on the most critical tasks of the day.
Impact: Enhances productivity and task completion rates.
Solution: Use a daily planner or digital task manager to list and prioritize tasks.
Continue
Action: Maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
Reason: Ensures long-term productivity and personal happiness.
Impact: Reduces burnout and improves overall well-being.
Solution: Continue regular breaks, exercise, and hobbies outside of work.
Example 3: Customer Service Improvement
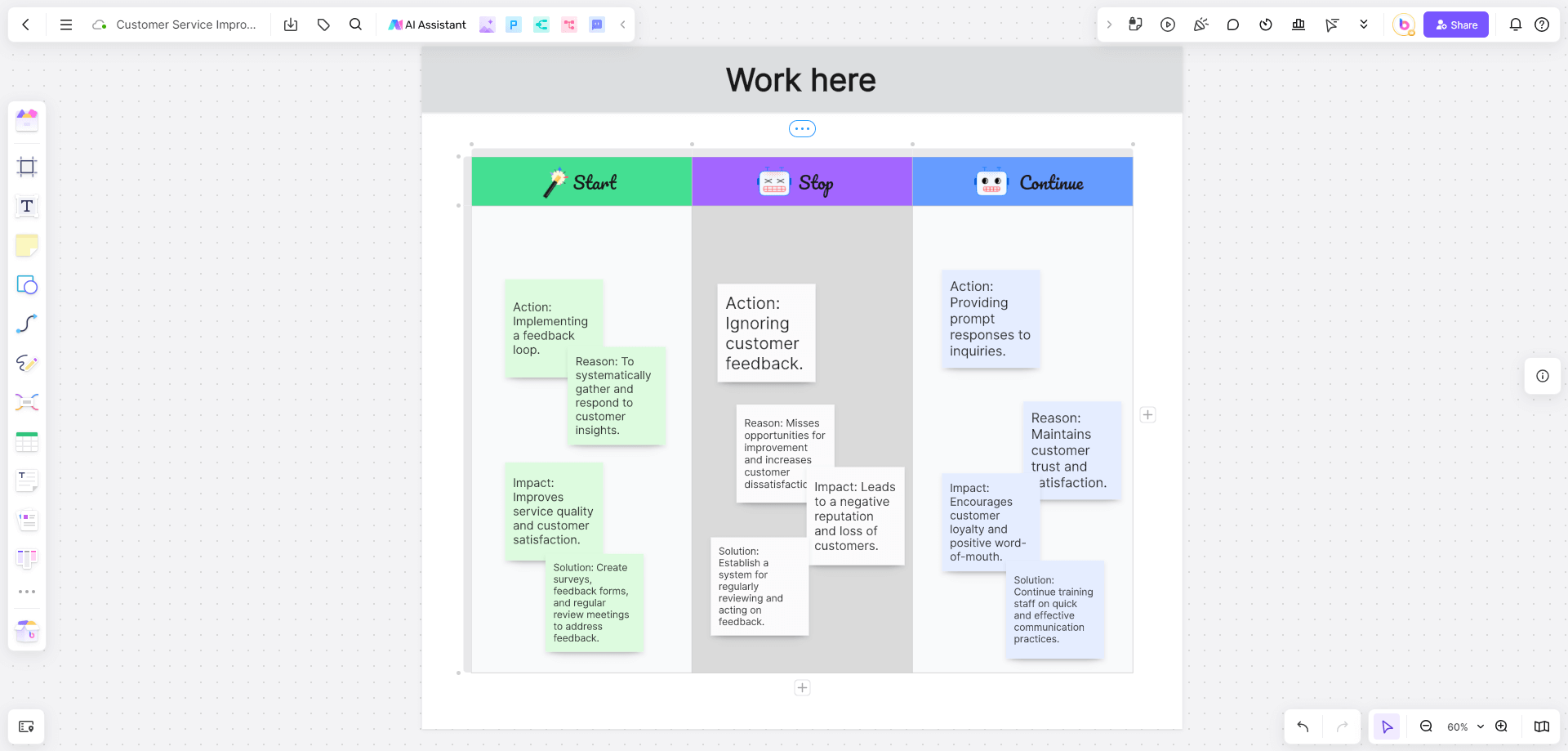
Context
A company wants to enhance its customer service experience.
Stop
Action: Ignoring customer feedback.
Reason: Misses opportunities for improvement and increases customer dissatisfaction.
Impact: Leads to a negative reputation and loss of customers.
Solution: Establish a system for regularly reviewing and acting on feedback.
Start
Action: Implementing a feedback loop.
Reason: To systematically gather and respond to customer insights.
Impact: Improves service quality and customer satisfaction.
Solution: Create surveys, feedback forms, and regular review meetings to address feedback.
Continue
Action: Providing prompt responses to inquiries.
Reason: Maintains customer trust and satisfaction.
Impact: Encourages customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
Solution: Continue training staff on quick and effective communication practices.
Example 4: Educational Setting
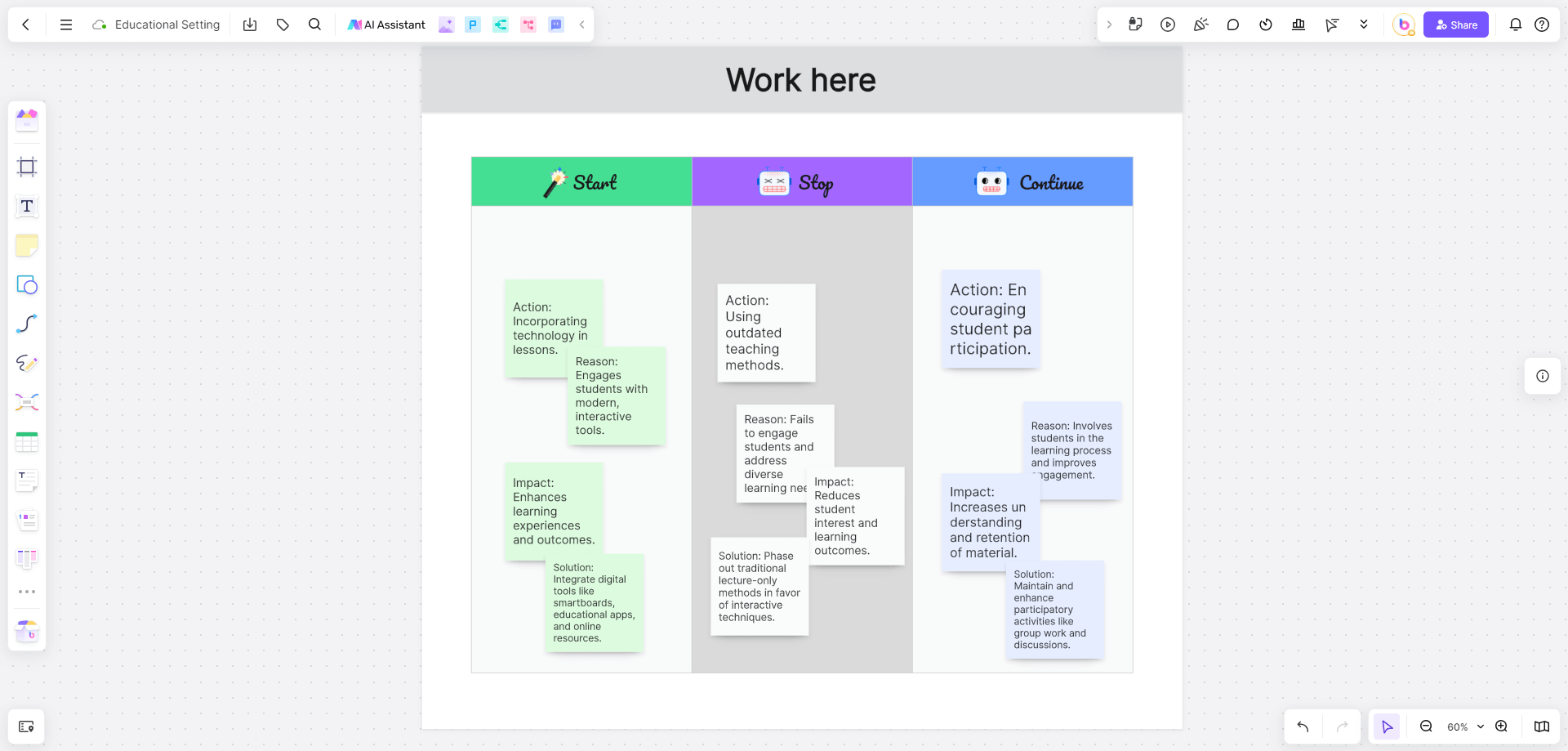
Context
A school aims to modernize its teaching methods to improve student engagement.
Stop
Action: Using outdated teaching methods.
Reason: Fails to engage students and address diverse learning needs.
Impact: Reduces student interest and learning outcomes.
Solution: Phase out traditional lecture-only methods in favor of interactive techniques.
Start
Action: Incorporating technology in lessons.
Reason: Engages students with modern, interactive tools.
Impact: Enhances learning experiences and outcomes.
Solution: Integrate digital tools like smartboards, educational apps, and online resources.
Continue
Action: Encouraging student participation.
Reason: Involves students in the learning process and improves engagement.
Impact: Increases understanding and retention of material.
Solution: Maintain and enhance participatory activities like group work and discussions.
Example 5: Organizational Change
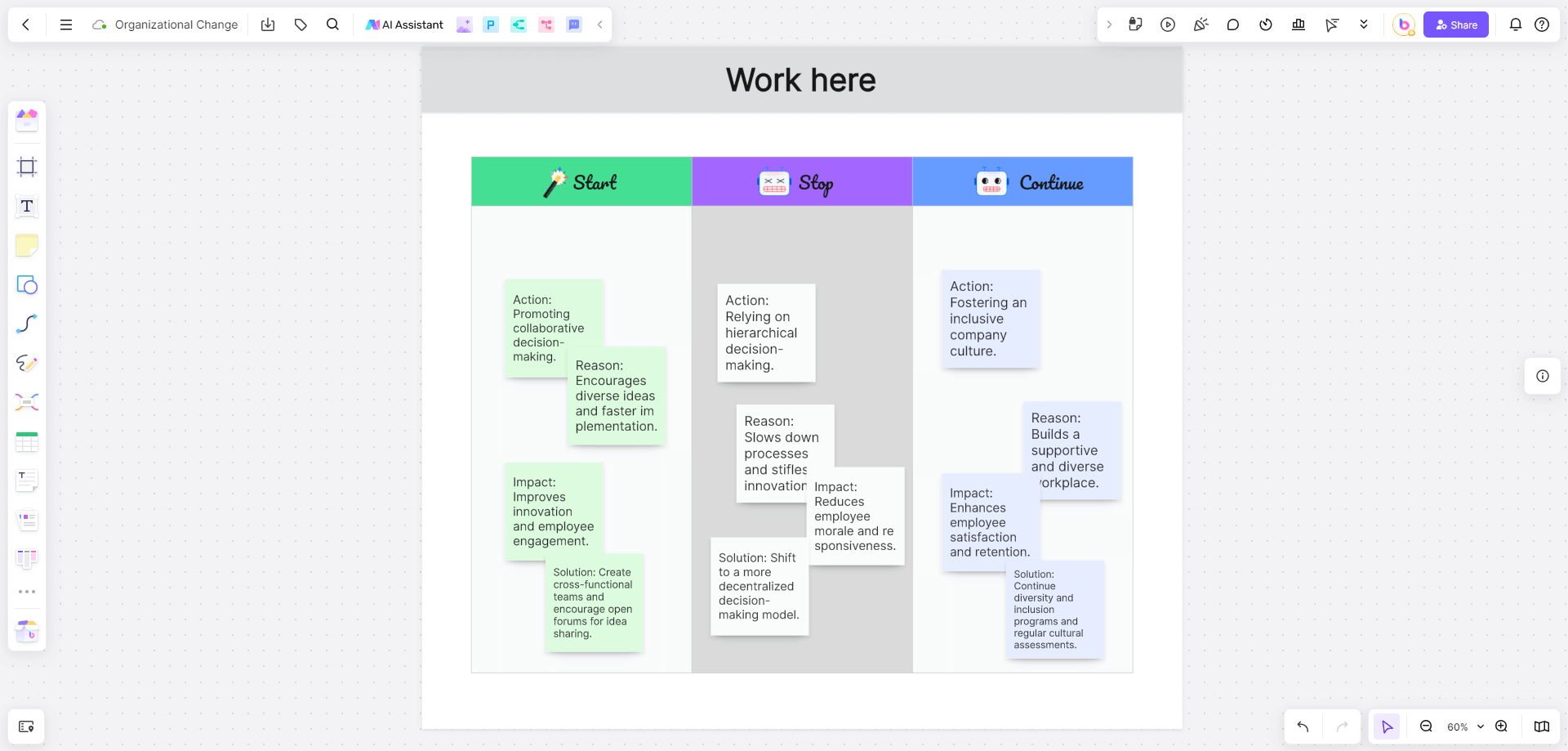
Context
A company undergoes a restructuring process to improve efficiency and culture.
Stop
Action: Relying on hierarchical decision-making.
Reason: Slows down processes and stifles innovation.
Impact: Reduces employee morale and responsiveness.
Solution: Shift to a more decentralized decision-making model.
Start
Action: Promoting collaborative decision-making.
Reason: Encourages diverse ideas and faster implementation.
Impact: Improves innovation and employee engagement.
Solution: Create cross-functional teams and encourage open forums for idea sharing.
Continue
Action: Fostering an inclusive company culture.
Reason: Builds a supportive and diverse workplace.
Impact: Enhances employee satisfaction and retention.
Solution: Continue diversity and inclusion programs and regular cultural assessments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key benefits of using the Start Stop Continue model?
The Start Stop Continue exercise simplifies the feedback process, enhances team collaboration, and drives continuous improvement by providing a structured framework for feedback and action.
How often should you conduct a Start Stop Continue exercise?
Ideally, the stop start and continue exercise should be conducted after each project phase or at regular intervals, such as monthly or quarterly, to ensure ongoing improvement and adaptation.
Can the Start Stop Continue model be used individually?
Yes, the Stop Continue Start feedback model is effective for personal development and self-assessment, helping individuals to regularly reflect and improve on their actions and behaviors.
What tools can be used to facilitate a Start Stop Continue exercise?
Tools that can facilitate a Start Stop Continue exercise include online whiteboards like Boardmix, Miro, and MURAL, physical whiteboards with sticky notes, and digital collaboration tools like Trello and Asana.
How do you ensure all voices are heard during the exercise?
To ensure all voices are heard during a Start Stop Continue exercise:
- Encourage a safe and open environment.
- Use anonymous inputs if necessary.
- Facilitate structured discussions and ensure equal participation from all team members.
By focusing on detailed examples and providing a comprehensive guide, this article aims to help individuals and teams effectively conduct Start Stop Continue exercises for continuous improvement and success. The use of stop start and continue exercise and stop continue start feedback throughout ensures a clear understanding of the model and its benefits.













