A SWOT analysis is a powerful strategic tool that helps hospitals understand their internal and external environments. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, healthcare institutions can develop effective strategies to enhance patient care, optimize operations, and achieve organizational goals.
This guide delves into the specifics of conducting a SWOT analysis for hospitals, providing insights on how to leverage strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats. Whether you're a hospital administrator or a healthcare consultant, mastering SWOT analysis is essential for driving continuous improvement and ensuring long-term success.
What is a SWOT Analysis on Hospital?
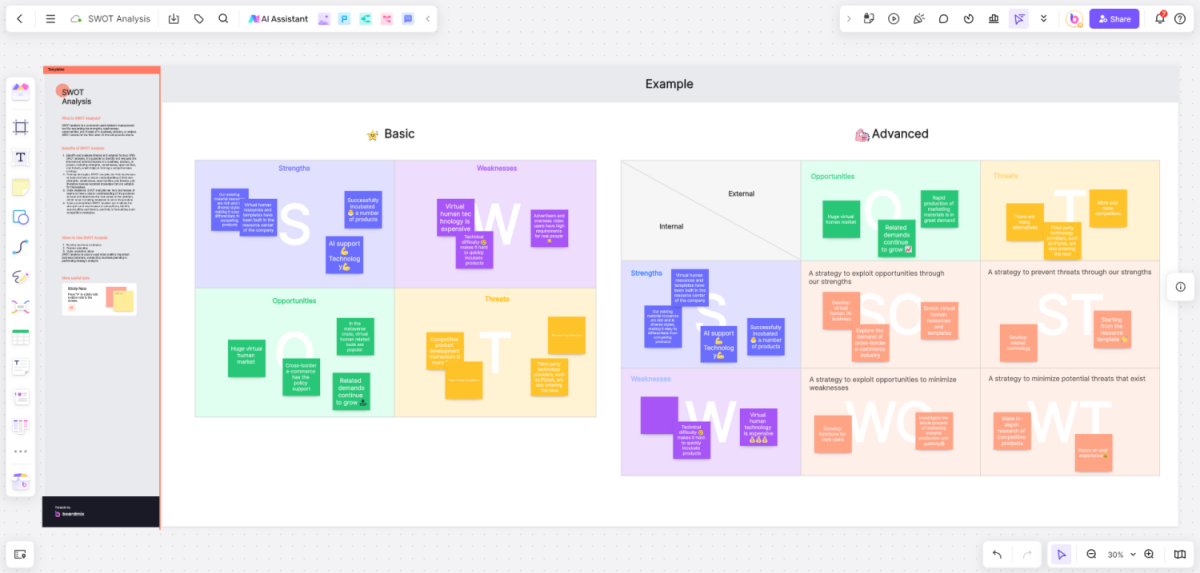
A SWOT analysis of the hospital is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats involved in healthcare delivery. This analysis involves specifying the objectives of the hospital and identifying the internal and external factors that are favorable or unfavorable to achieving those objectives.
Basic Components of a SWOT Analysis
The components of a SWOT analysis for a hospital can be broadly categorized as follows:
1. Strengths (Internal)
These are the attributes that give the hospital an advantage over others. Examples might include specialist medical staff, state-of-the-art medical equipment, or a strong brand reputation.
2. Weaknesses (Internal)
These are the areas where the hospital might lack or where it could improve. Examples might include high employee turnover, lack of specific expertise, or outdated facilities.
3. Opportunities (External)
These are elements in the environment that the hospital could exploit to its advantage. Examples might include increasing demand for certain medical services, regulatory changes allowing for expansion, or partnerships with health insurance companies.
4. Threats (External)
These are elements in the environment that could cause trouble for the hospital. Examples might include tightening of healthcare regulations, emerging competition, or budget cuts.
The ultimate goal of conducting a SWOT analysis for a hospital is to form actionable strategies that capitalize on its strengths and opportunities while mitigating its weaknesses and threats. It enables decision-makers to create a realistic, future-oriented plan for organizational stability and growth.
What are Patient Strengths in a Hospital SWOT Analysis?
In a hospital's SWOT analysis, patient strengths typically refer to the positive aspects of a hospital's patient care, satisfaction levels, and other benefits that patients might receive. These can provide the hospital with a competitive edge, drive patient loyalty, and increase its reputation within the healthcare sector. Identifying and leveraging these strengths can help hospitals deliver better care and improve overall performance.
Identifying and Evaluating Patient Strengths
It's important for hospitals to continuously identify and evaluate their patient strengths. This process might involve:
1. Conducting regular patient satisfaction surveys to understand what aspects of care patients appreciate the most.
2. Analyzing online reviews and ratings for additional insights into patients' perceptions of their care.
3. Interacting with patients regularly through feedback sessions or community outreach programs to understand their needs better.
Examples of Patient Strengths in a Hospital
Here are some examples of patient strengths that might be highlighted in a hospital's SWOT analysis:
1. High Quality of Care
If a hospital provides high-quality medical care resulting in successful treatments and recoveries, this can be a significant strength. This could be due to specialist expertise, advanced medical technology, or efficient processes.
2. Excellent Patient Experience
This could include factors like short waiting times, comfortable hospital facilities, supportive staff, clear communication from doctors, or seamless admission and discharge procedures.
3. Comprehensive Services
If the hospital offers a wide range of services that cater to various patient needs – from preventive care to rehabilitation – this is an asset.
4. Trust and Reputation
Having a strong reputation for patient safety and trustworthiness is crucial in healthcare. This is often built on consistent performance and positive patient outcomes over time.
5. Innovation and Research
A hospital known for cutting-edge research and innovative treatments can attract patients seeking the latest therapies not available elsewhere.
6. Accessibility
Offering convenient accessibility, either through multiple locations or telemedicine options, is another significant strength.
Impact of Patient Strengths on Overall Hospital Performance
Patient strengths impact a hospital's overall performance in several ways:
1. Increased Patient Satisfaction: High levels of patient satisfaction often lead to repeat visits and long-term loyalty.
2. Improved Reputation: Positive patient experiences contribute to a hospital’s reputation, which can attract more patients.
3. Better Patient Outcomes: High-quality care often leads to better health outcomes, reinforcing the hospital’s reputation for effective treatment.
4. Greater Competitive Edge: Leveraging patient strengths can help differentiate a hospital from its competitors, driving growth and success in the long run.
Understanding and capitalizing on patient strengths is a key aspect of strategic planning for hospitals. It not only boosts the quality of healthcare provision but also plays a pivotal role in shaping the hospital’s brand image and future growth potential.
What are Common Weaknesses in a Hospital SWOT Analysis?
A SWOT analysis helps hospitals identify their weaknesses, which are internal factors hindering their performance or affecting their reputation. It's crucial for healthcare institutions to regularly conduct these analyses to pinpoint areas of improvement and develop strategies to address them.

Identifying and Improving Weaknesses
To identify weaknesses, hospitals can:
1. Analyze patient feedback and complaints to understand which areas are causing dissatisfaction.
2. Monitor hospital operations to identify inefficiencies or areas that are causing delays or unnecessary costs.
3. Review clinical outcomes to identify any recurring issues, such as high readmission rates or infections.
Once weaknesses are identified, hospitals can create a targeted action plan for improvement. This could involve training staff, investing in new equipment, or improving communication procedures.
Examples of Common Weaknesses in a Hospital:
Here are some common weaknesses that might be highlighted in a hospital's SWOT analysis:
1. Staff Shortages
If a hospital consistently faces a lack of sufficient staff, this can lead to longer wait times, increased workloads, and decreased patient satisfaction.
2. Outdated Equipment
The use of outdated or inefficient equipment can negatively impact the quality of care provided.
3. Poor Communication
Inadequate communication between hospital departments or between staff and patients can lead to misunderstandings and mistakes.
4. Inefficient Processes
Processes that are unnecessarily complicated or outdated can cause delays and inefficiencies.
5. Financial Constraints
Limited budgets can restrict the hospital's ability to invest in new equipment, hire more staff, or offer competitive salaries.
Success Stories of Hospitals Overcoming Weaknesses
Here are a couple of examples of hospitals overcoming their weaknesses:
1. Addressing Staff Shortages
A regional hospital faced ongoing staff shortages. To resolve this issue, they introduced a comprehensive staff recruitment and retention program, which included competitive salaries, training programs, and employee benefits. As a result, they saw a significant decrease in staff turnover and an improvement in patient satisfaction levels.
2. Upgrading Equipment
A local hospital had outdated equipment that was limiting its ability to provide high-quality care. After conducting a SWOT analysis, they prioritized funding for new equipment. This not only improved the quality of care but also attracted more specialized medical professionals to their facility.
It is crucial to recognize and address weaknesses for any hospital's growth and success. It allows them to continuously improve their patient care, efficiency, and overall performance. Conducting regular SWOT analyses is an essential part of this continuous improvement process.
What are External Opportunities Examples for Hospitals?
In a hospital's SWOT analysis, external opportunities are elements in the broader healthcare environment that a hospital could exploit to its advantage. These can include evolving patient needs, changes in technology, shifts in health policies, and even demographic trends.

External Opportunities Examples for Hospitals
Here are some common external opportunities examples that hospitals might consider:
1. Advances in Medical Technology
Rapid advancements in medical technology often present opportunities for hospitals to improve their services. Whether it's the latest imaging equipment, surgical robotics, telemedicine platforms, or EHR systems, these advancements can enhance patient care and efficiency.
2. Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaborations with other healthcare providers, academic institutions, research bodies, or tech companies can create mutual benefits. Such partnerships can lead to shared resources, research collaborations, enhanced service offerings, or improved patient access.
3. Changes in Healthcare Policies
Shifts in health policies and regulations could present new opportunities. For instance, policies supporting integrated care models could encourage hospitals to form alliances with primary care providers, specialist clinics, and community health programs.
4. Population Health Trends
Demographic changes and disease trends in the hospital's catchment area can highlight new service needs. For instance, an aging population might indicate a need for more geriatric services. Likewise, rising chronic disease rates might point to a need for better preventive care and disease management programs.
5. Increasing Health Awareness and Demand for High-Quality Care
As people become more health-conscious and demand higher-quality care, hospitals have an opportunity to differentiate themselves by offering patient-centered care, holistic health programs, advanced treatments, and excellent service experiences.
Leveraging Opportunities to Enhance Hospital Services and Management
Leveraging these external opportunities requires strategic planning, informed decision-making, and sometimes, significant investments. Here's how hospitals can make the most of these opportunities:
1. Stay Informed: Keeping up-to-date with healthcare trends, technological advancements, and policy changes can help hospitals identify relevant opportunities early.
2. Strategic Planning: Once an opportunity is identified, it's essential to evaluate its feasibility and fit with the hospital’s mission and capabilities. This includes conducting cost-benefit analyses and developing detailed implementation plans.
3. Invest in Resources: Implementing new opportunities often requires investing in resources - be it new medical equipment, staff training, IT infrastructure, or marketing efforts.
4. Build Partnerships: Forming alliances with relevant partners can facilitate resource-sharing and broaden the hospital's capabilities.
5. Monitor Progress: Finally, it's crucial to monitor the implementation progress and evaluate the outcomes against predefined objectives. This feedback allows for continuous improvement and fine-tuning of strategies.
Understanding external opportunities and strategically leveraging them can significantly enhance a hospital's services, reputation, patient satisfaction, and overall success.
What Threats Do Hospitals Face in a SWOT Analysis?
In a hospital's SWOT analysis, threats typically refer to external factors in the broader healthcare environment that could potentially harm the hospital's performance or growth. It's crucial for healthcare institutions to proactively identify these threats and develop strategies to mitigate their potential impacts.

Identifying and Addressing Threats
To identify threats, hospitals can:
1. Monitor healthcare industry trends and forecasts to anticipate potential future challenges.
2. Keep abreast of changes in health policies, regulations, and standards that could impact their operations.
3. Conduct competitor analyses to understand their strategic moves and potential threats they could pose.
Once threats are identified, hospitals can develop strategies to address them. This could involve risk management measures, strategic alliances, diversification strategies, or advocacy efforts.
Examples of Threats in a Hospital's SWOT Analysis
Here are some common threats that might be highlighted in a hospital's SWOT analysis:
1. Competitive Pressure
The healthcare industry is highly competitive. New hospitals, specialized clinics, or telemedicine platforms can pose threats by drawing away patients or staff.
2. Changes in Health Policies or Regulations
Changes in health policies or regulations could introduce new compliance requirements, restrict certain practices, or affect funding. This could disrupt hospital operations and impose additional costs.
3. Technological Disruptions
While technological advancements can present opportunities, they can also pose threats. For instance, hospitals that fail to keep up with digital health trends could lose out to more tech-savvy competitors.
4. Economic Factors
Economic downturns or changes in health insurance policies can affect patients' ability to afford care, potentially leading to lower hospital revenues.
5. Public Health Crises
Epidemics or public health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic can drastically increase demand for healthcare services, strain resources, and disrupt regular operations.
Examples of Hospitals Successfully Addressing Threats
Here are a couple of examples of how hospitals have successfully addressed threats:
1. Combating Competitive Pressure
A community hospital was facing competitive pressure from larger hospitals and specialist clinics. They differentiated themselves by focusing on personalized care, community outreach, and building strong relationships with local primary care physicians. As a result, they managed to maintain their patient base and enhance their reputation in the community.
2. Adapting to Technological Disruptions
A traditional hospital was struggling to keep up with digital health trends. They tackled this by investing in telemedicine platforms and electronic health record (EHR) systems, training their staff to use these technologies, and promoting these new capabilities to their patients. These efforts helped them improve efficiency, patient satisfaction, and competitiveness.
While external threats can pose significant challenges, proactive identification and strategic management can help hospitals mitigate their impacts and turn potential threats into opportunities for growth and improvement.
How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis for a Hospital?
A SWOT analysis can provide a powerful tool for hospitals to assess their current situation, identify opportunities for growth and improvement, and address potential threats. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a SWOT analysis for a hospital.
Steps to Conduct a Hospital SWOT Analysis
1. Assemble the Team
Before beginning the SWOT analysis, gather a diverse group of individuals who can bring various perspectives to the process. This team could include hospital executives, medical staff, administrative personnel, and even patients or community members.
2. Define the Purpose:
Identify the purpose of your SWOT analysis. Is it to develop a strategic plan, improve patient satisfaction, or address specific challenges? Having a clear purpose will guide your analysis and help you focus on relevant factors.
3. Conduct Internal Analysis - Strengths and Weaknesses
Analyze internal aspects of your hospital that affect its performance. Strengths could include experienced staff, state-of-the-art equipment, or strong community ties. Weaknesses could be staff shortages, outdated technology, or inefficient processes.
4. Conduct External Analysis - Opportunities and Threats
Examine external factors that might affect your hospital's future. Opportunities might be technological advancements, partnerships, or healthcare policy changes. Threats could be increased competition, regulatory changes, or economic instability.
5. Prioritize and Analyze
Once you have a comprehensive list of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, prioritize them based on their impact and urgency. Analyze how these factors interrelate and what they mean for your hospital's strategic direction.
6. Develop Strategies
Use your SWOT analysis to develop strategies for your hospital's future. Strengths and opportunities should guide where to invest and expand. Weaknesses and threats indicate areas that need improvement or risk mitigation strategies.
Tools and Resources for Effective SWOT Analysis
Several tools and resources can help make your SWOT analysis more effective:
1. SWOT Analysis Templates: These templates provide a structured format for organizing your findings and insights from the SWOT analysis.
2. Industry Reports: These reports can provide valuable information on trends, developments, and challenges in the healthcare industry that could influence your SWOT analysis.
3. Patient Feedback: Patient satisfaction surveys, online reviews, and direct feedback can provide insights into strengths and weaknesses from a patient's perspective.
4. Employee Feedback: Interviews or surveys of hospital staff can offer insights into internal strengths and weaknesses that management might overlook.
5. Competitor Analysis Tools: Tools like Porter's Five Forces or PESTLE analysis can complement your SWOT analysis by providing more in-depth insights into the competitive environment or macro-environmental factors.
In conclusion, conducting a thorough SWOT analysis can provide a robust foundation for your hospital's strategic planning, decision-making, and performance improvement efforts.
Boardmix: An Online Whiteboard Tool for SWOT Analysis
If you're looking to conduct a comprehensive SWOT analysis for your hospital, Boardmix could be an excellent tool to consider. It is an online whiteboard tool that allows you to create visual, collaborative SWOT analyses effortlessly.
Features of Boardmix
1. Free SWOT Analysis Templates: Boardmix provides free SWOT analysis templates, eliminating the need to start from scratch. These templates provide a structured framework for you to populate with your analysis findings.
2. AI-Powered Features: What sets Boardmix apart is its integration of AI functionalities. It can quickly generate SWOT analysis diagrams, saving you time and enhancing the quality of your analyses.
3. Unlimited Data Gathering: With Boardmix, you can not only conduct your SWOT analysis but also integrate various sources of information onto the same canvas. It allows for effective industry report research, competitor analysis, and collection of patient and employee feedback.
4. Online Collaboration: Boardmix facilitates seamless online collaboration, allowing multiple users to work together in real time on the same SWOT analysis. This feature enhances teamwork and ensures that all perspectives are considered, leading to a more comprehensive and well-rounded analysis.
How to Use Boardmix for Your Hospital's SWOT Analysis
1. Select a Template: Start by choosing a SWOT analysis template that suits your needs. The templates come with predefined sections for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
2. Use AI Capabilities: Utilize the Boardmix AI feature to generate diagrams and perform quick analyses based on your inputs.
3. Incorporate Data: Collect and integrate data from various sources directly onto the Boardmix canvas. You can pull in industry reports, competitor data, or patient and employee feedback all in one place.
4. Collaborate with Your Team: Invite your team members to join the board and collaborate in real-time. This feature enables diverse input, robust discussions, and consensus-building.
5. Analyze and Strategize: Once you've completed the SWOT analysis on Boardmix, use it as a foundation to prioritize areas of focus, devise strategies, and make informed decisions about your hospital's future direction.
In conclusion, Boardmix is a powerful tool that can significantly simplify and enhance the process of conducting a SWOT analysis for your hospital. Its user-friendly interface combined with its AI features and collaborative functionalities make it an excellent choice for strategic planning. So why stop? Try it now!








