Mermaid is a text-based diagramming tool that’s changing how developers and teams create flowcharts and sequence diagrams. For beginners, it means generating clean, professional charts automatically with just a few lines of description—no mouse required. This guide will introduce you to Mermaid’s core value and walk you through its basic syntax for effortless code-to-diagram creation.
What is Mermaid?
Mermaid is a powerful diagramming and charting tool that uses text definitions to generate diagrams dynamically. Let's explore what it is, why it's useful, and where you can apply it.
What does Mermaid mean?
Mermaid is an open-source, JavaScript-based charting tool that uses a Markdown-inspired syntax. At its core, it's a rendering engine that converts text code into professional diagrams like flowcharts and timelines. In short: Write code = Generate diagrams!
Core Value of Mermaid
Goodbye, Drag-and-Drop: Stop struggling with dragging shapes and aligning connectors in traditional drawing software. Describe your diagram structure with concise code, and Mermaid renders it instantly. Updating a diagram is as fast as modifying a few lines of code.
Versatility: Whether you need an API flowchart for technical documentation, a project timeline (Gantt chart) for management, or a visual diagram for an educational presentation, Mermaid can handle it.
Primary Use Cases for Mermaid
Technical Documentation: Use Mermaid directly within tools like the Boardmix online whiteboard to generate flowcharts instantly. Share a live link with team members to improve technical communication and documentation efficiency.
Agile Project Management: Product managers can use Mermaid's Gantt chart syntax in Boardmix to outline sprint plans. Team members can then drag and adjust task nodes directly on the rendered chart for intuitive and efficient project tracking.
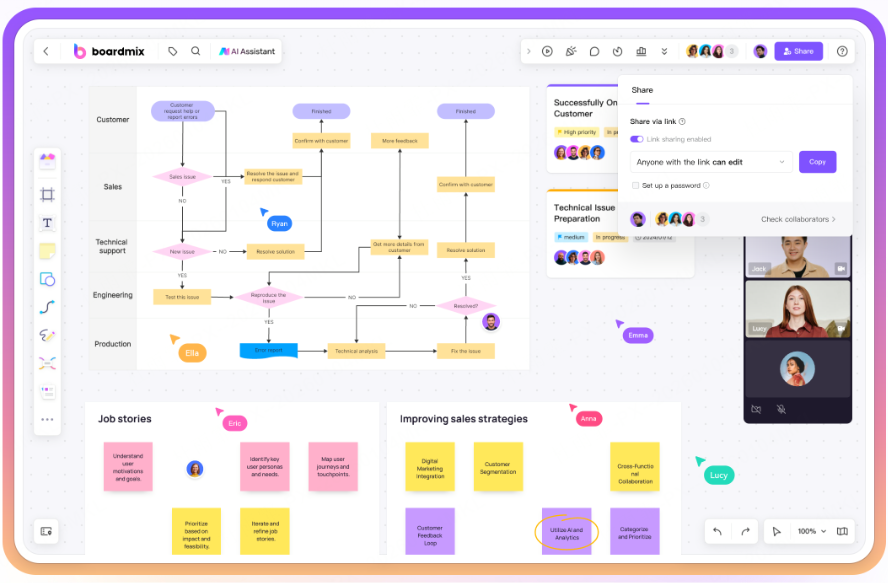
Mermaid Syntax Deep Dive
Mastering Mermaid syntax is key to creating diagrams with code. Its system covers directional controls, node definitions, message sequencing, and timeline settings for various chart types. Below, we break down the syntax rules with practical examples and tips for using them effectively in tools like Boardmix.
Flowchart Syntax
Direction Control: Use graph TD for a Top-Down layout (e.g., graph TD A-->B-->C) and graph LR for Left-to-Right (e.g., graph LR Start-->Process-->End).
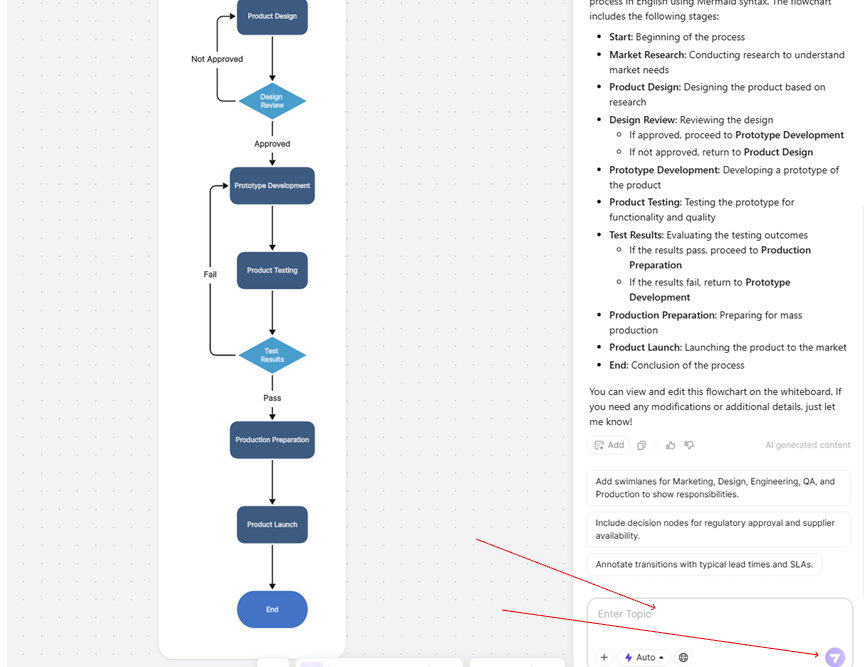
Node Syntax
- Rectangle: [Step Name]
- Diamond (Decision): {Condition}
- Rounded Rectangle (Start/End): (Label)
- Example: (Start)--> [Process Data]--> {Success?} creates a basic flow.
- Advanced Connectors:
- Labeled arrow: -->|API Call|
- Asynchronous link: -->>
- Thick link: ==>
- Example: A-->|Login| B-->> C==> D
Practical Tip: In Boardmix, use the AI Assistant or code block to input this syntax, and it will render a clear flowchart automatically.
Sequence Diagram Syntax
- Defining Participants: Declare roles using participant Client and participant Server.
- Message Types: Synchronous: ->>, Asynchronous: -->>, Self-loop: ->.
- Control Structures: Loop: loop Daily Tasks on a new line, followed by indented messages like Client->>Server: Submit Data, ending with end.
- Alternative (if/else): alt Login Successful on a new line, indented Client->>Server: Redirect to Home, then else Login Failed, indented Client->>Server: Show Error, ending with end.
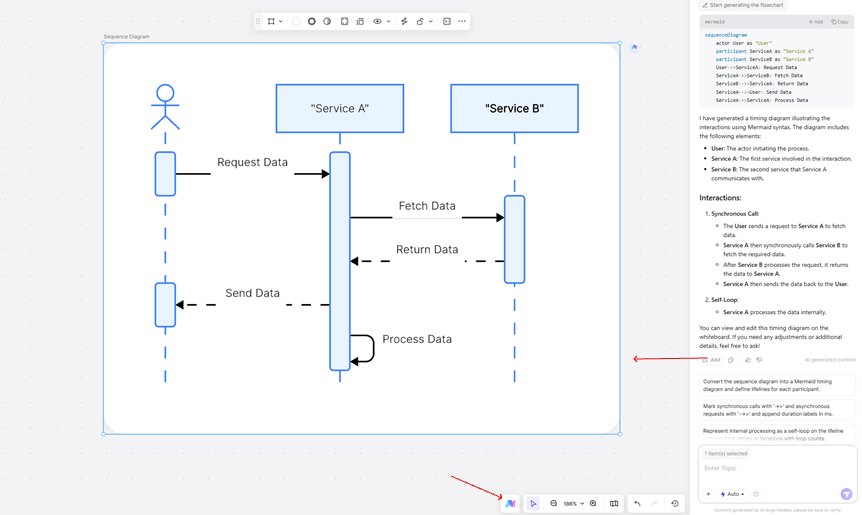
Gantt Chart Syntax
- Timeline Setup: Define the format with dateFormat YYYY-MM-DD. Use section Phase 1 to group tasks.
- Task Dependencies: Syntax like TaskB :after TaskA, 3d means Task B starts 3 days after Task A finishes. In Boardmix, you can drag these tasks to adjust timelines directly on the chart.
Practical Tip: Input your task plan code into Boardmix's editor to generate an interactive Gantt chart.
Other Diagram Types
- Class Diagram (classDiagram): Use <|-- for inheritance (e.g., ChildClass <|-- ParentClass) and ..|> for interface realization (e.g., Class ..|> Interface).
- State Diagram (stateDiagram-v2): Define transitions with State1 --> State2 : Event. For example: LoggingIn --> LoggedIn : Validation Passed.
Common Mermaid Syntax Errors & Fixes
Beginners often encounter rendering issues due to minor syntax mistakes. Here are common pitfalls:
- Handling Special Characters: If node text contains symbols like [ ] { }, wrap the entire text in double quotes. Example: A["[Alert] System Error"].
- Indentation Sensitivity: The content inside control structures (loop, alt, opt, par) or subgraph blocks must be indented (typically with 2 spaces or a tab). Incorrect indentation causes rendering failures.
- Rendering Compatibility: Some connector styles are specific to certain diagrams. For instance, --o (circle-ended arrow) is valid only in flowcharts and may not work as expected in sequence or class diagrams. Always refer to the official syntax guide for your diagram type.
Practical Applications of Mermaid
Once you've mastered the syntax, you can leverage Mermaid across various scenarios.
Visualizing Technical Docs
Embed a Mermaid code block in your documentation (e.g., graph LR Client-->|API /query| Server), and it renders as a clean API flowchart. Teams can export documentation with embedded, version-controlled diagram code, eliminating the hassle of manual updates in traditional drawing tools.
Agile Development & Collaboration
Use Gantt chart syntax for Scrum sprint planning. After defining tasks (e.g., section Frontend TaskA: 2025-06-01, 5d), your team can collaboratively drag and adjust task nodes in real-time on a Boardmix whiteboard, making sprint planning flexible and progress delays immediately visible.
Educational Use Cases
When teaching algorithms or system workflows, instructors can generate flowcharts (loop...end) or state diagrams in real-time with Mermaid. Students can copy the code block, modify parameters in their own workspace, and immediately see how the AI-rendered diagram changes.
Boost Team Efficiency with Mermaid + Visual Collaboration Tools
While Mermaid works anywhere that supports it (like GitLab Markdown or note-taking apps), pairing it with a powerful visual collaboration tool multiplies its effectiveness.
Pain Points of Traditional Workflows:
- Manual code preview refreshing.
- Single-file lock for collaboration.
- Needing to export static images for docs.
- Difficulty mixing multiple diagram types in one view.
The Modern Solution: Boardmix
Boardmix is an AI-enhanced online whiteboard built for real-time collaboration, featuring deep integration for Mermaid. It supports mixed-format creation, including mind maps, flowcharts, and more on one infinite canvas.
Key Advantages for Team Efficiency:
- True Real-Time Collaboration: Multiple team members can view, edit, and comment on the same board simultaneously—even dragging task nodes on a live-rendered Gantt chart—without conflicts or locks.
- Hybrid Creation Workspace: Combine Mermaid technical diagrams with mind maps, user story maps, freehand sketches, and document cards on a single canvas. This bridges the gap between technical design and business discussion.
- End-to-End Workflow: Go from code input → diagram generation → comment/annotation → exporting developer documentation in one seamless toolchain. No more context switching.
- Team Asset Management: Save frequently used Mermaid chart snippets as reusable team templates. Enterprise plans offer private deployment and granular permissions for secure knowledge management.
Conclusion
Mermaid offers an efficient, flexible, and maintainable solution for creating professional diagrams through its concise code syntax. Its potential is fully unlocked when combined with a multiplayer visual collaboration tool like Boardmix. Together, they empower teams to generate diagrams from code and collaborate on them in real-time, making visual documentation faster and more dynamic.
Ready to visualize with code and collaborate in real-time? Try creating your first Mermaid diagram in Boardmix today.








