What is a concept map?
A concept map, also called a conceptual diagram, is a graphical tool that shows how concepts or ideas relate to each other. It is a visual representation of knowledge or information, where ideas are represented as nodes or boxes, which are structured hierarchically and connected with lines or arrows. These connectors can include linking words and phrases that explain the connections between concepts.
By showing all the connections between different concepts, concept maps help people understand complex topics. While concept maps have many modern uses, they were originally developed to support meaningful learning. Therefore, it is still a perfect tool for students in their learning process.
20 Creative Concept Map Examples for Students
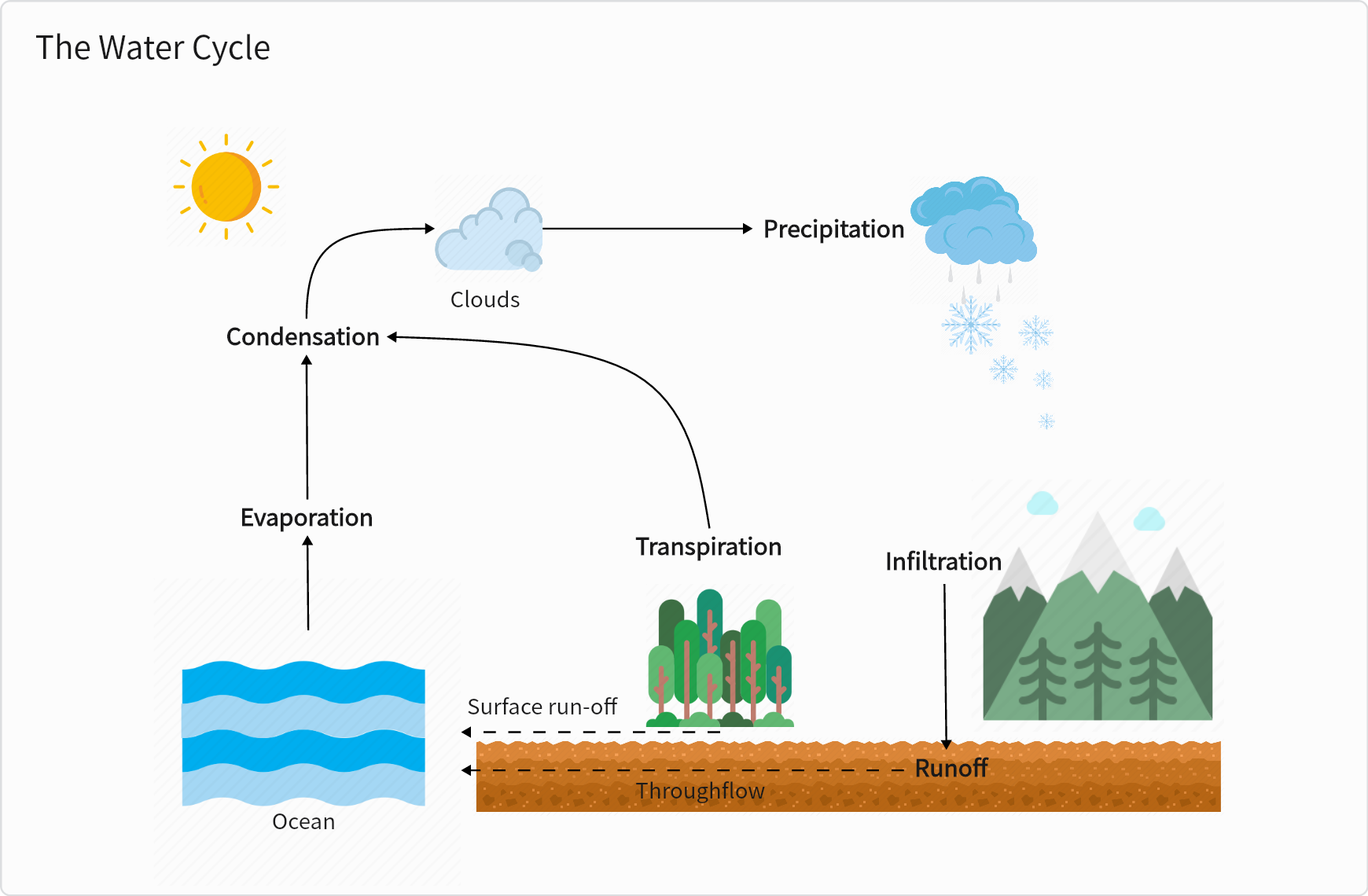
The Water Cycle
Below is a concept map example that contains the six basic processes of the water cycle, which describes where water is found on the earth and how it moves.
As shown in the diagram, evaporation refers to the conversion of liquid water into water vapor due to heat. At the same time, the release of water vapor by plants through their leaves also contributes to atmospheric moisture (transpiration). Then, water vapor will transform into tiny water droplets, forming clouds (condensation). The next process is precipitation, which refers to the release of condensed water droplets from clouds in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail. Then water will move into the ground, replenishing underground water sources (infiltration). Then, runoff is the next step that equate to the flow of excess water over the land surface into streams, rivers, and eventually oceans.
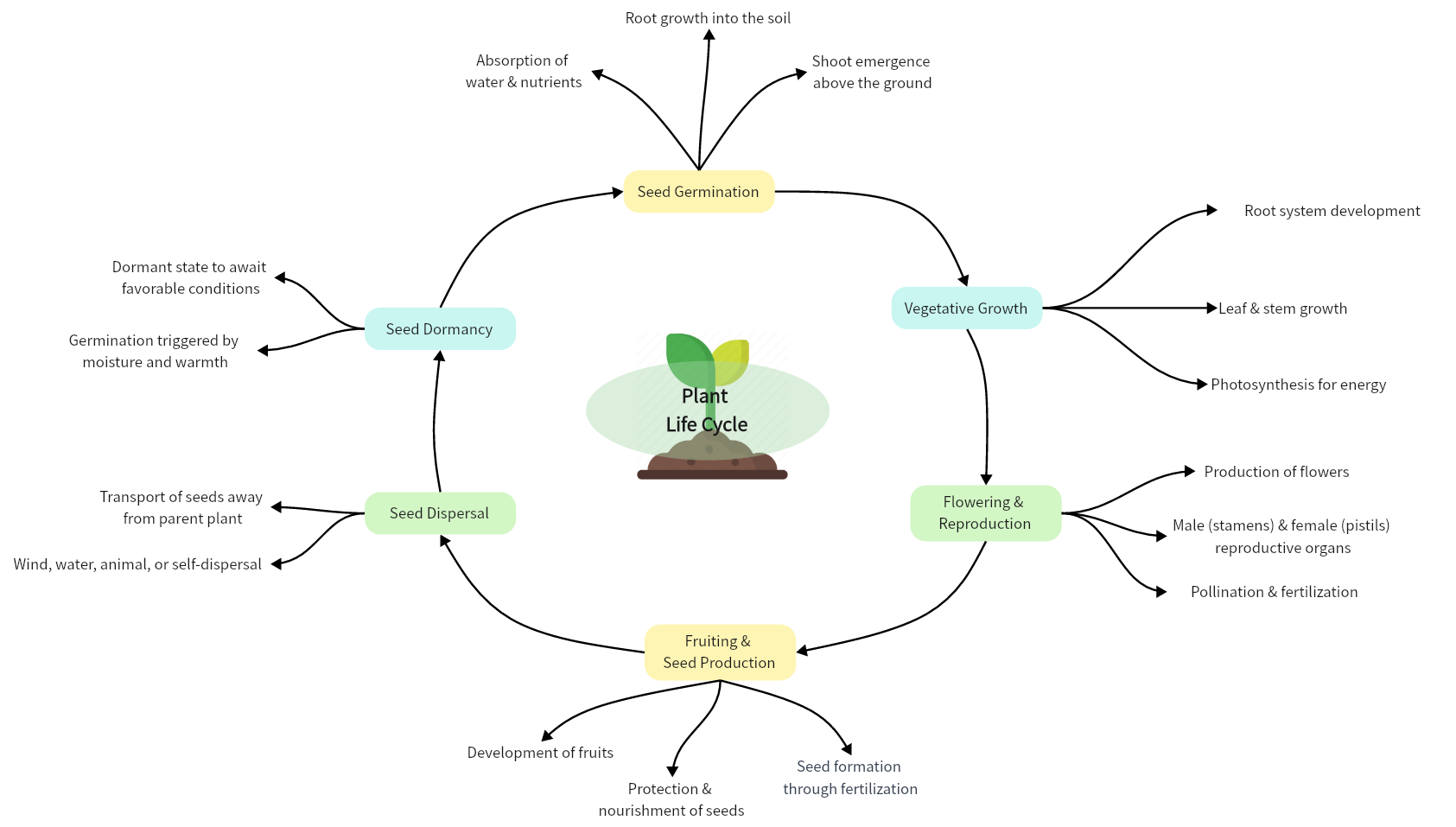
Plant Life Cycle
The life cycle of a plant is a continuous process, with seeds from one generation growing into mature plants that produce new seeds, thus perpetuating the cycle. The following concept map shows this cycle which includes six basic steps -- seed germination, vegetative growth, flowering and reproduction, fruiting and seed production, seed dispersal, as well as seed dormancy.
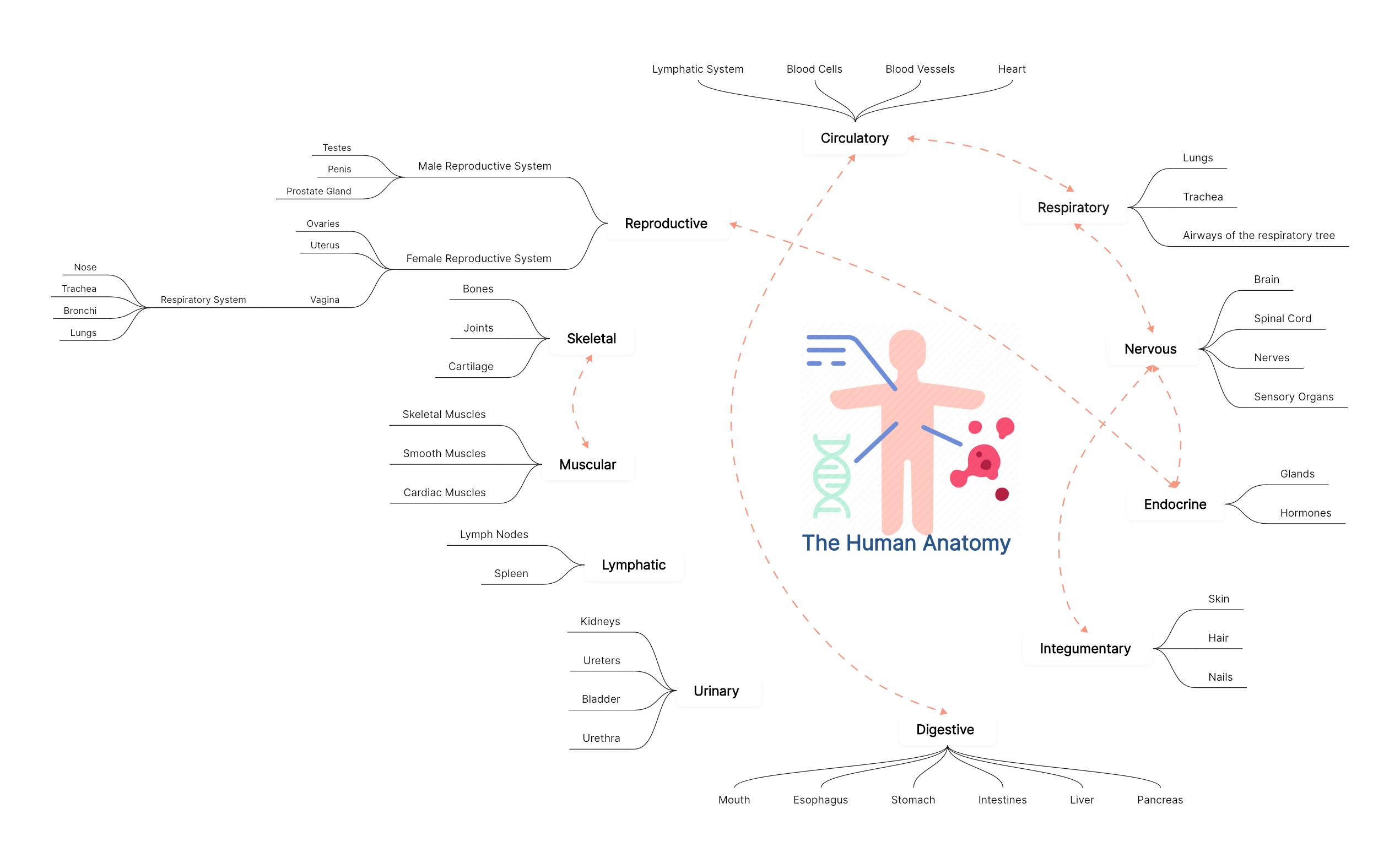
The Human Anatomy
Anatomy systems are groups of organs and tissues that work together to perform important jobs for the body. There are 11 major anatomy systems: Skeletal, Muscular, Circulatory, Digestive, Endocrine, Nervous, Respiratory, Lymphatic, Urinary, Reproductive, Reproductive, and Integumentary. These systems collaborate to keep the body in good health. For instance, the circulatory and digestive systems work together to deliver nutrients throughout the body. The dashed lines in the following diagram illustrate the connections between different systems. Except for the reproductive system, each is vital for survival.
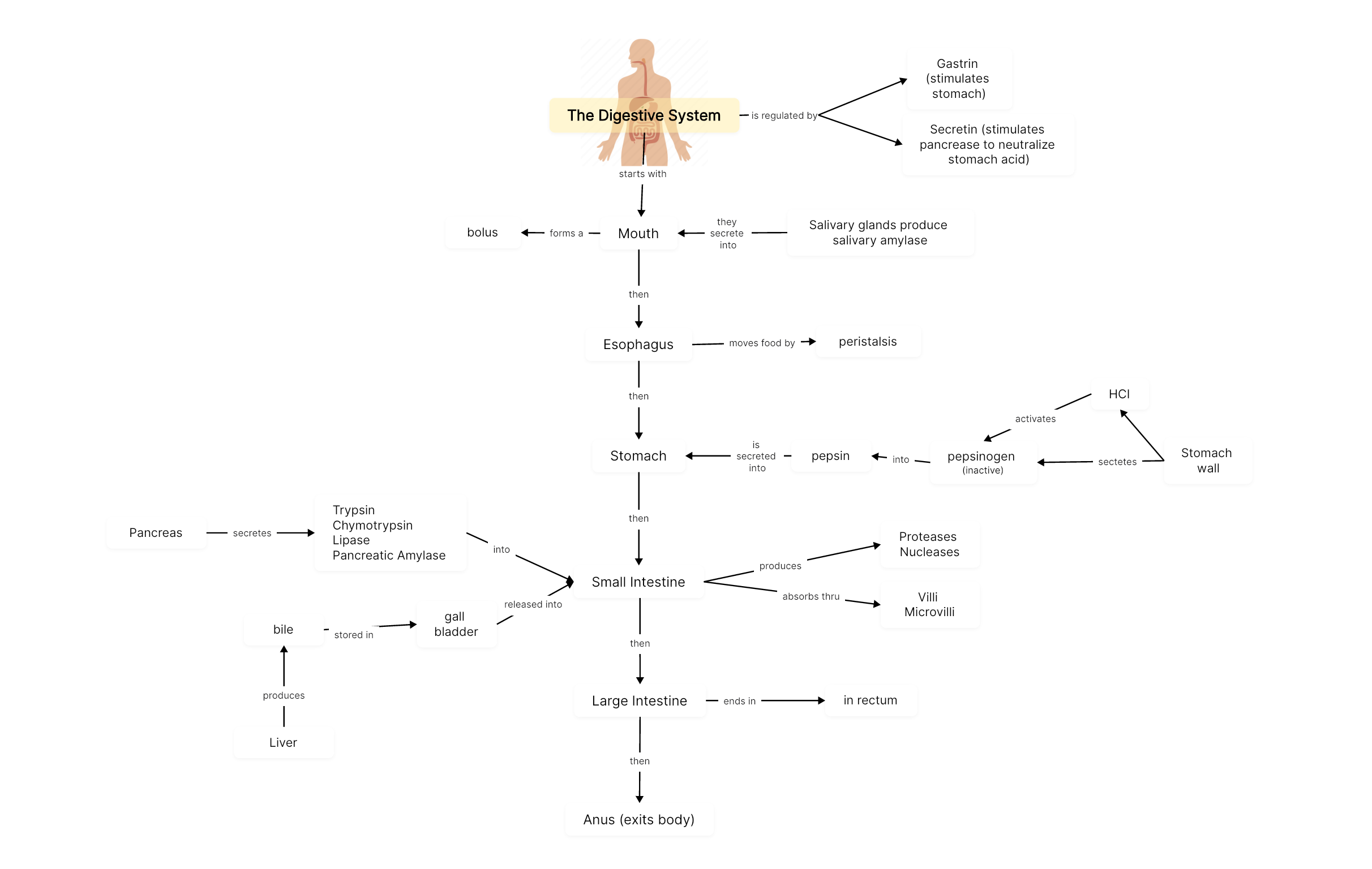
The Digestive System
Digestion is a network of organs that help you digest and absorb nutrition from your food. It includes your gastrointestinal (GI) tract and your biliary system. GI tract is a series of hollow organs that are all connected to each other, including mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus. The biliary system includes liver, gallbladder, pancreas and bile ducts, which deliver bile and enzymes through to the GI tract. Overall, the digestive system plays a crucial role in breaking down food, extracting nutrients, and eliminating waste to provide the body with the energy and essential substances it needs for proper functioning.
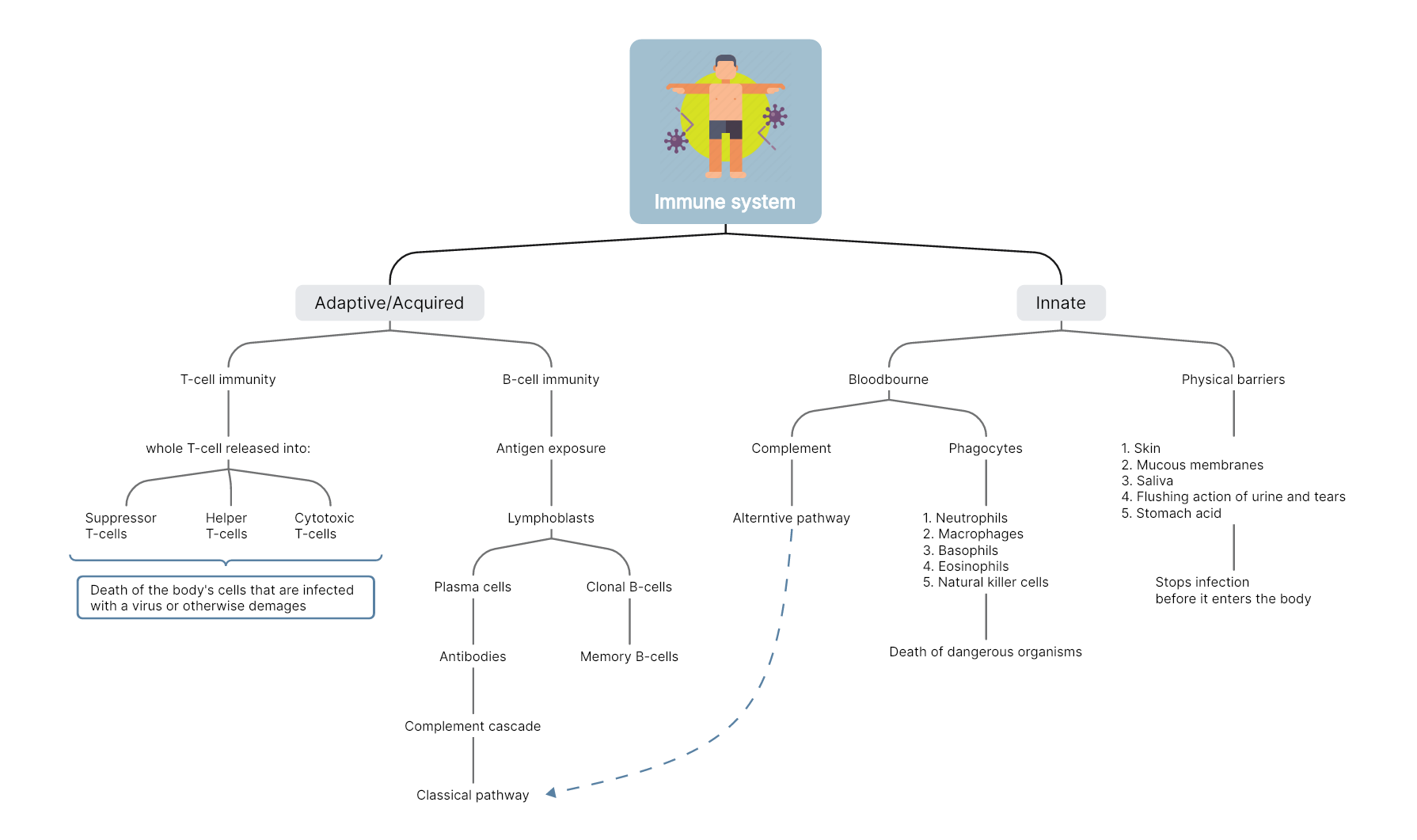
The Immune System
The immune system is a complex network of organs, cells and proteins that defends the body against infection, whilst protecting the body's own cells. It can be broadly categorized into two parts: the innate and the acquired immune system.
The acquired immune system is the immunity that we get throughout our lifestyle and diet. And the innate immune system is one that is provided by birth. The following concept map of the immune system illustrates the types of the immune system, how it is further branched out, and what every cell is supposed to do, which is designed for a better understanding and learning.
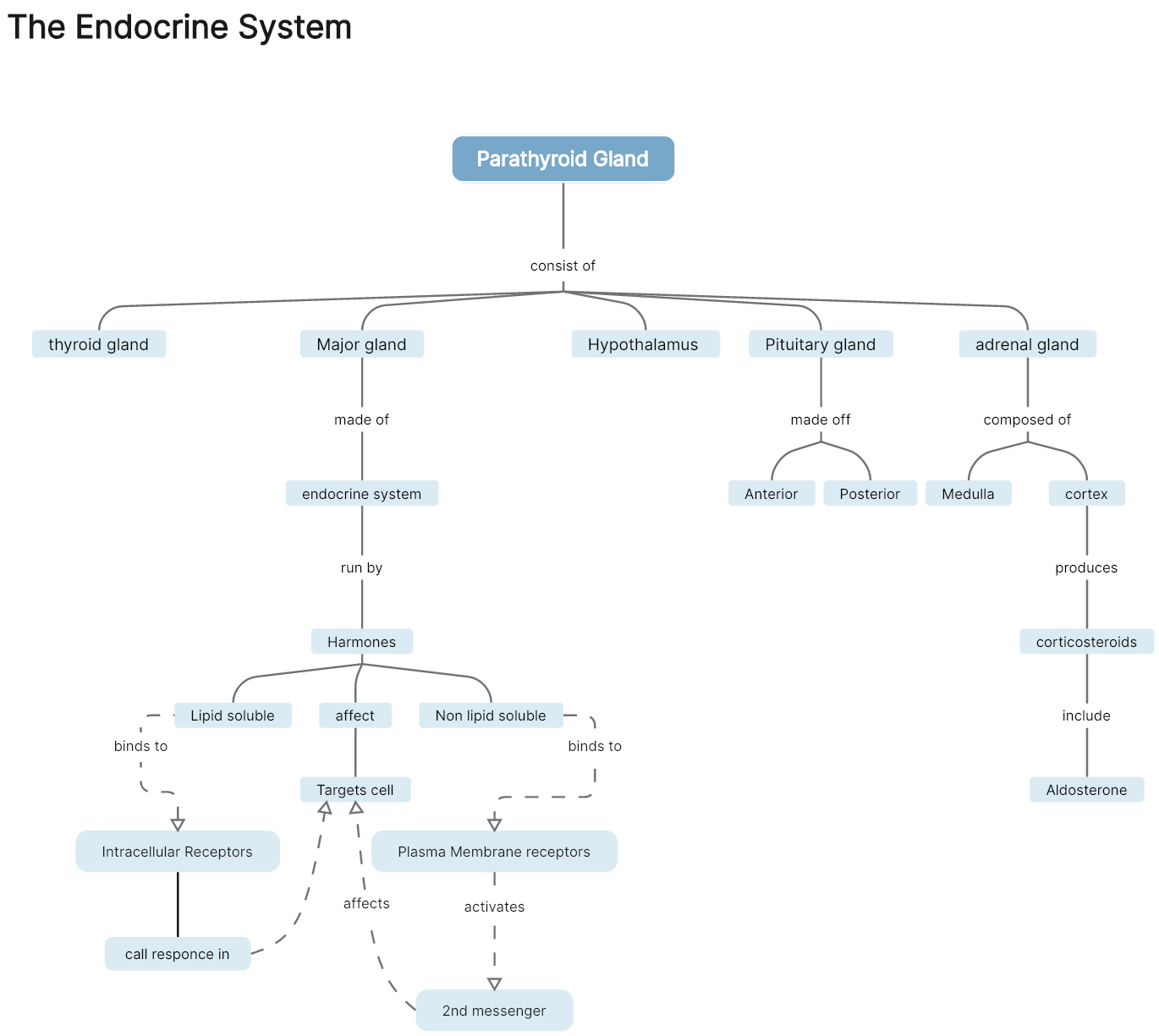
The Endocrine System
The endocrine system is made up of glands, which are organs responsible for producing and releasing different hormones that selectively affect various aspects within the body. This is a simple concept map illustrating the endocrine system, which mainly mentions the glands. While it does not explain what gland produces and what hormone, this diagram specifies several functions of the hormones and their kinds, which may boost understanding and learning for students.
The Parts of a Flower
The sole purpose of flowers is sexual reproduction, therefore ensuring the survival of the species. The male and female parts of the flower work together to facilitate pollination and fertilization. Pollen grains from the male parts (anther) are transferred to the female parts (stigma) either by wind, insects, birds, or other agents. Once pollen reaches the stigma, it travels down the style to reach the ovary, where fertilization can occur. After fertilization, the ovules develop into seeds within the ovary, ensuring the continuation of the plant species.
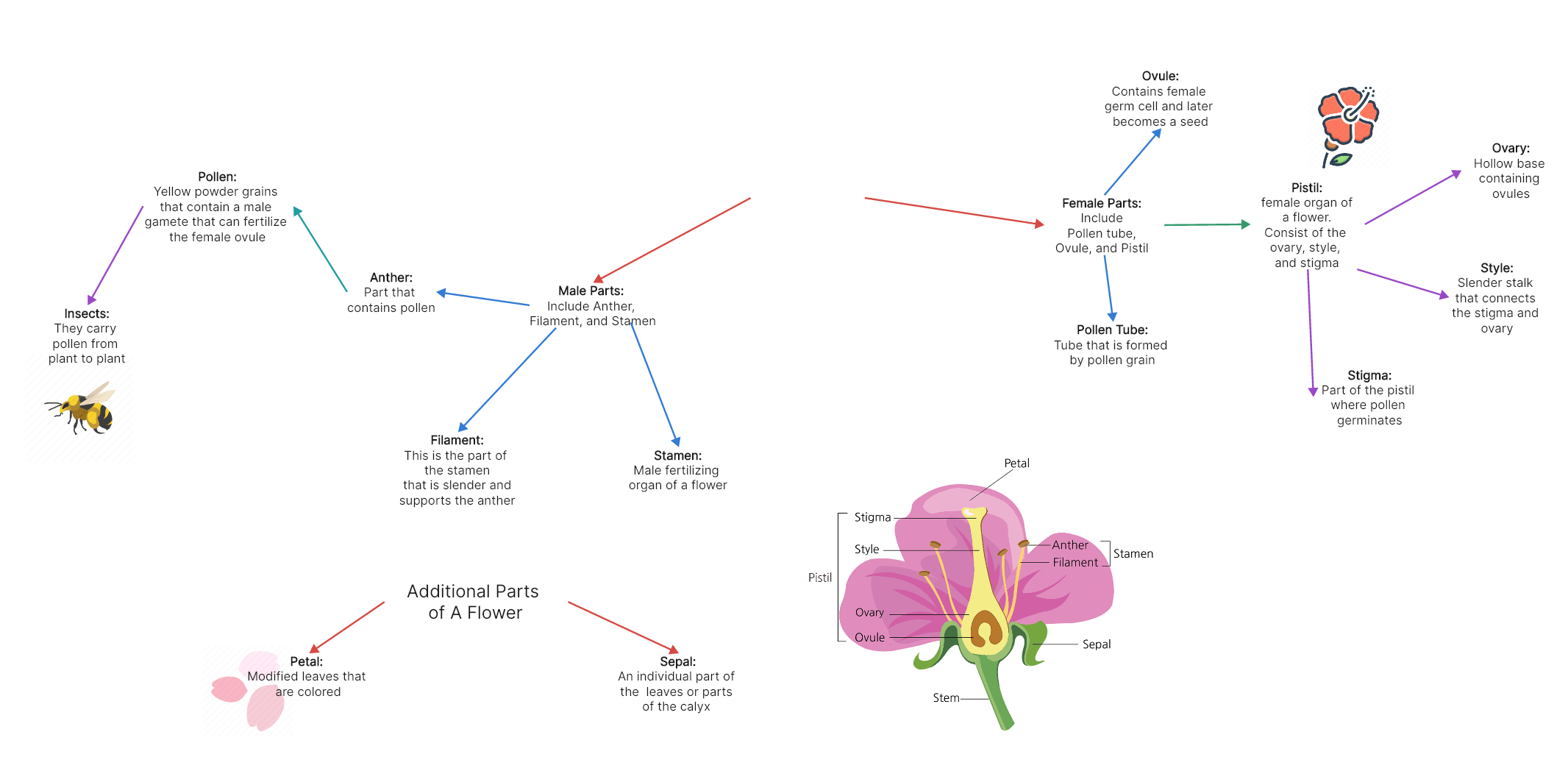
Reference: https://prezi.com/p/70u2oi7ibcj0/flower-concept-map/
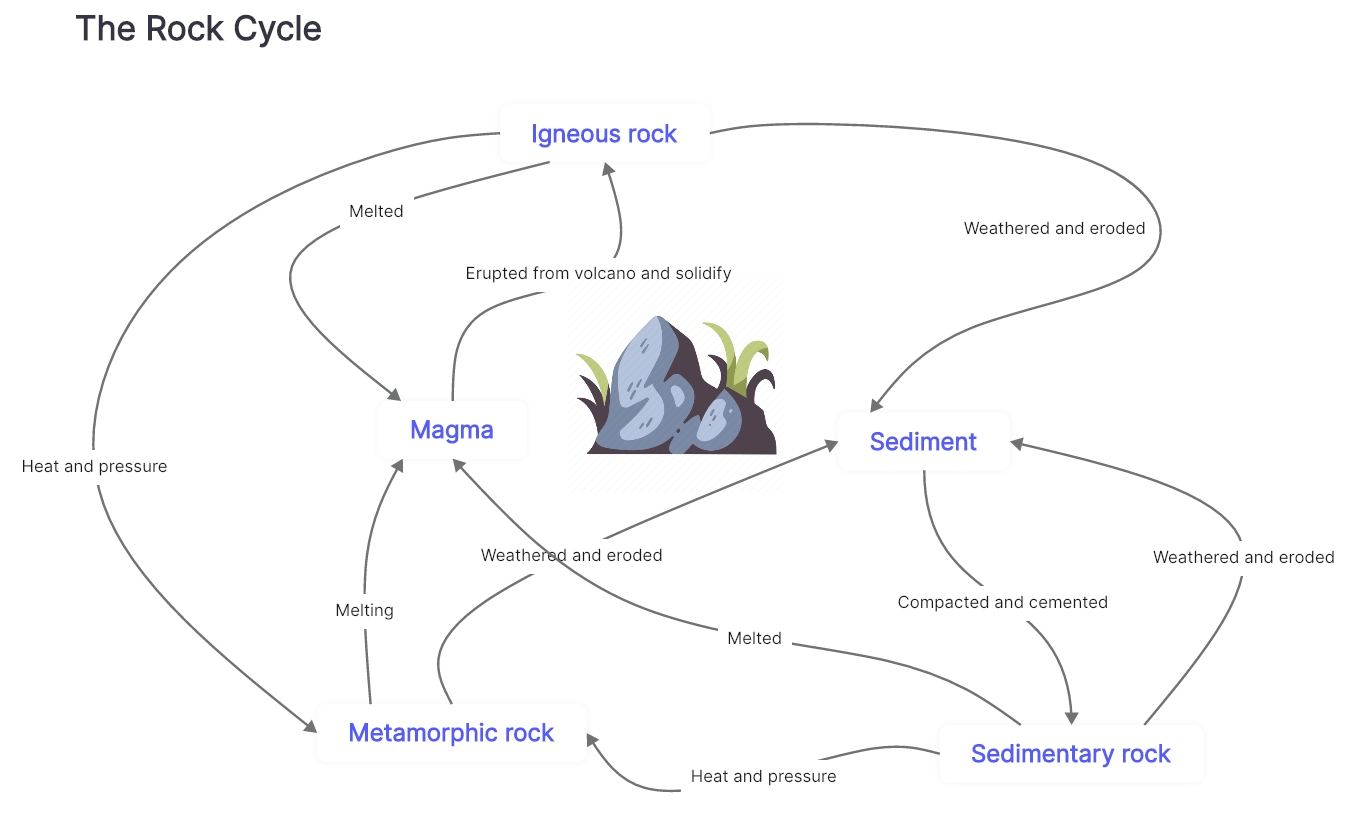
The Rock Cycle
The rock cycle illustrates how the three primary rock types (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) undergo transformations from one form to another. The creation, movement, and transformation of rocks are influenced by the Earth's internal heat, tectonic forces, as well as the impacts of water, wind, gravity, and biological activities, including human actions. The texture, structure, and composition of a rock provide insights into its formation conditions and offer valuable information about the Earth's past.
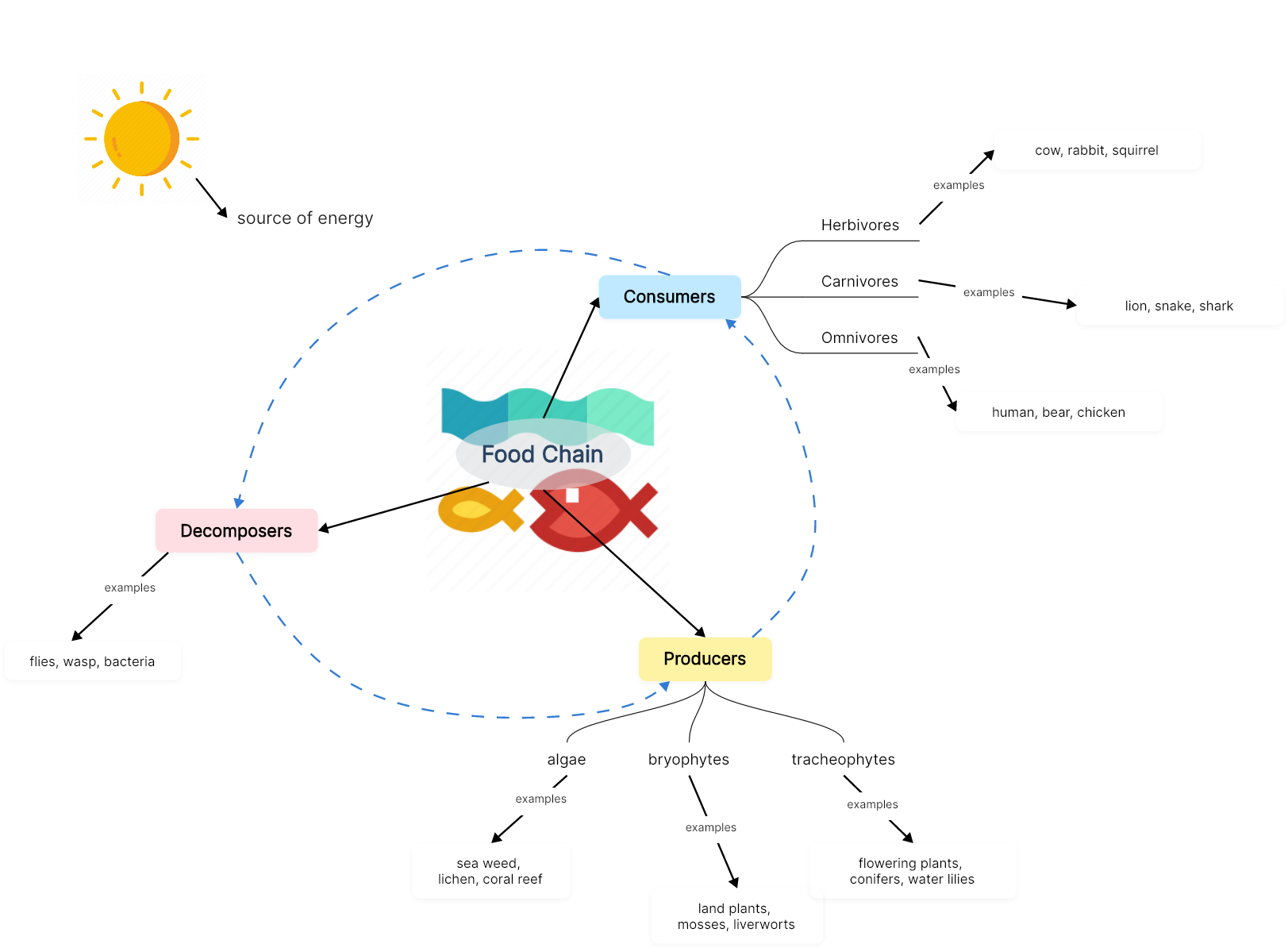
The Food Chain
A food chain is a linear sequence that depicts the transfer of energy and nutrients from one organism to another within an ecosystem. It represents the feeding relationships between different organisms, illustrating how energy flows through the ecosystem. The food chain consists of four major parts, namely the sun, producers, consumers and decomposers. The sun is the initial source of energy, which provides energy for everything on the planet. The connection between producers, consumers, and decomposers forms a continuous cycle of energy and nutrient flow in an ecosystem as illustrated in the following concept map. However, in reality, most ecosystems have complex food webs that involve multiple interconnected food chains, reflecting the diverse interactions and interdependencies among organisms in an ecosystem.
Ecosystems
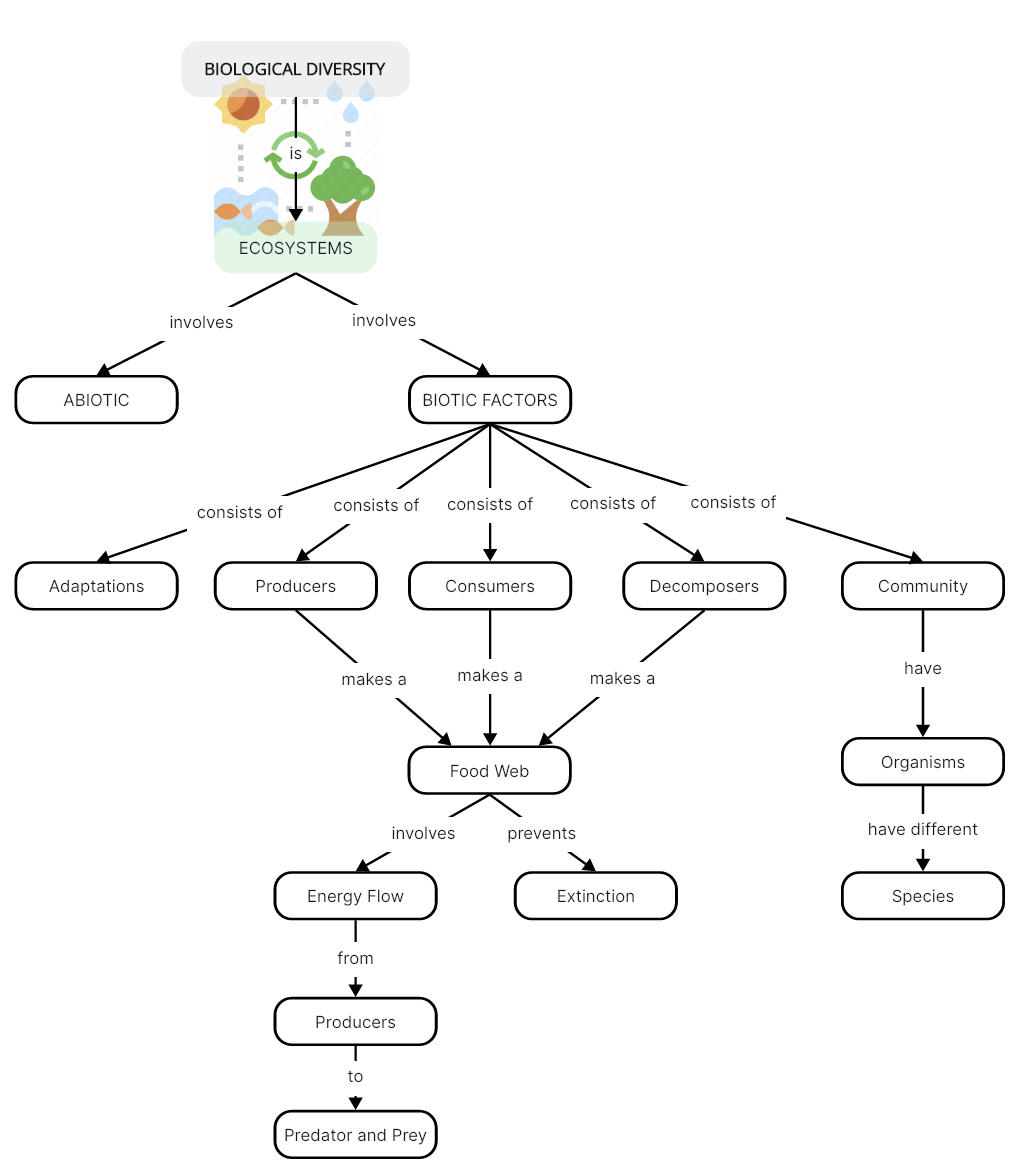
An ecosystem is a geographic area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, work together to form a bubble of life. Ecosystems contain both biotic and abiotic factors. Biotic factors are living or once-living components that influence the functioning and dynamics of the ecosystem, while nonliving components are referred to as abiotic factors.
Below is a concept map that mainly illustrates the biotic factors of the ecosystem, including key examples of adaptions, producers, consumers, decomposers, and community. Biotic factors are interconnected and influence one another in complex ways within an ecosystem. Understanding these factors is crucial for studying ecological relationships, conservation efforts, and maintaining the health and sustainability of ecosystems.
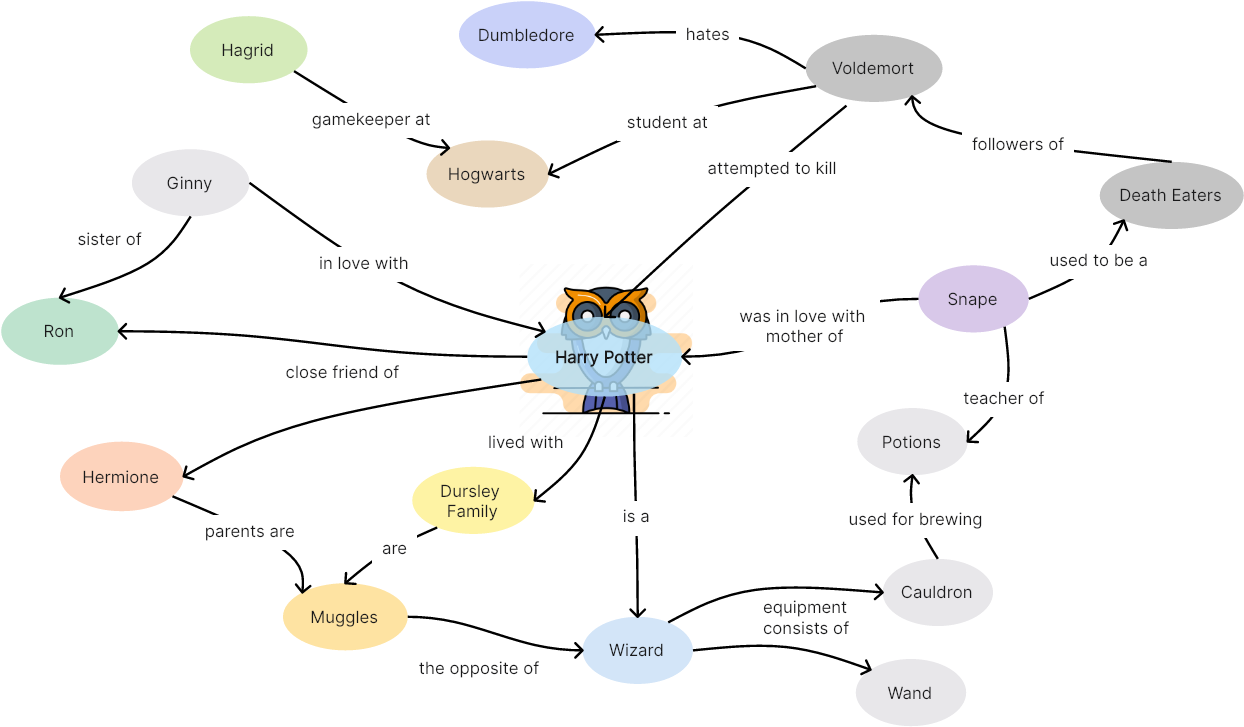
Character Relationship Map
Concept mapping is a useful tool for making a character relationship map, which visually represents the connections and interactions between various characters in a story. In the case of Harry Potter, the following map depicts the relationships among the main characters and their affiliations, friendships, rivalries, and other significant connections, centered around Harry Potter. However, these are just a few examples of the character relationships, and the full character relationship map would include many more characters other students at Hogwarts, professors, and various magical creatures.
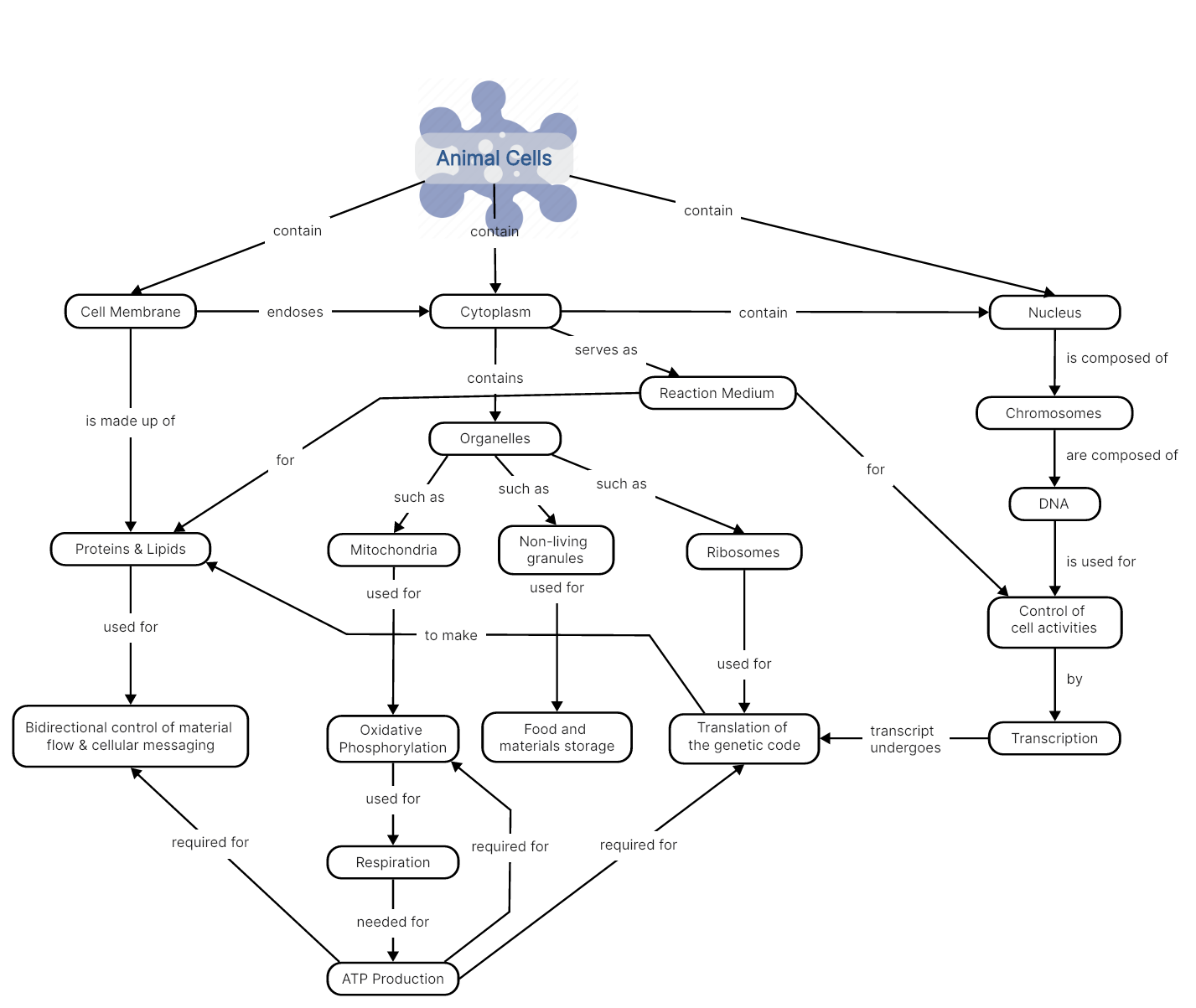
Animal Cells
An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall and has a true, membrane-bound nucleus along with other cellular organelles. The cell is the fundamental building block and structural unit of life, serving as the smallest and most fundamental biological unit within living organisms. Based on their cellular organization, cells can be categorized into eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. A typical animal cell contains three main cell organelles, namely, the membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
The concept of cells can be understood efficiently using a cell concept map. The following concept map depicts how these three components work together to maintain the structure, functionality, and integrity of the animal cell. Additionally, animal cells contain various other organelles, such as mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes, each playing specific roles in cell processes and functions.
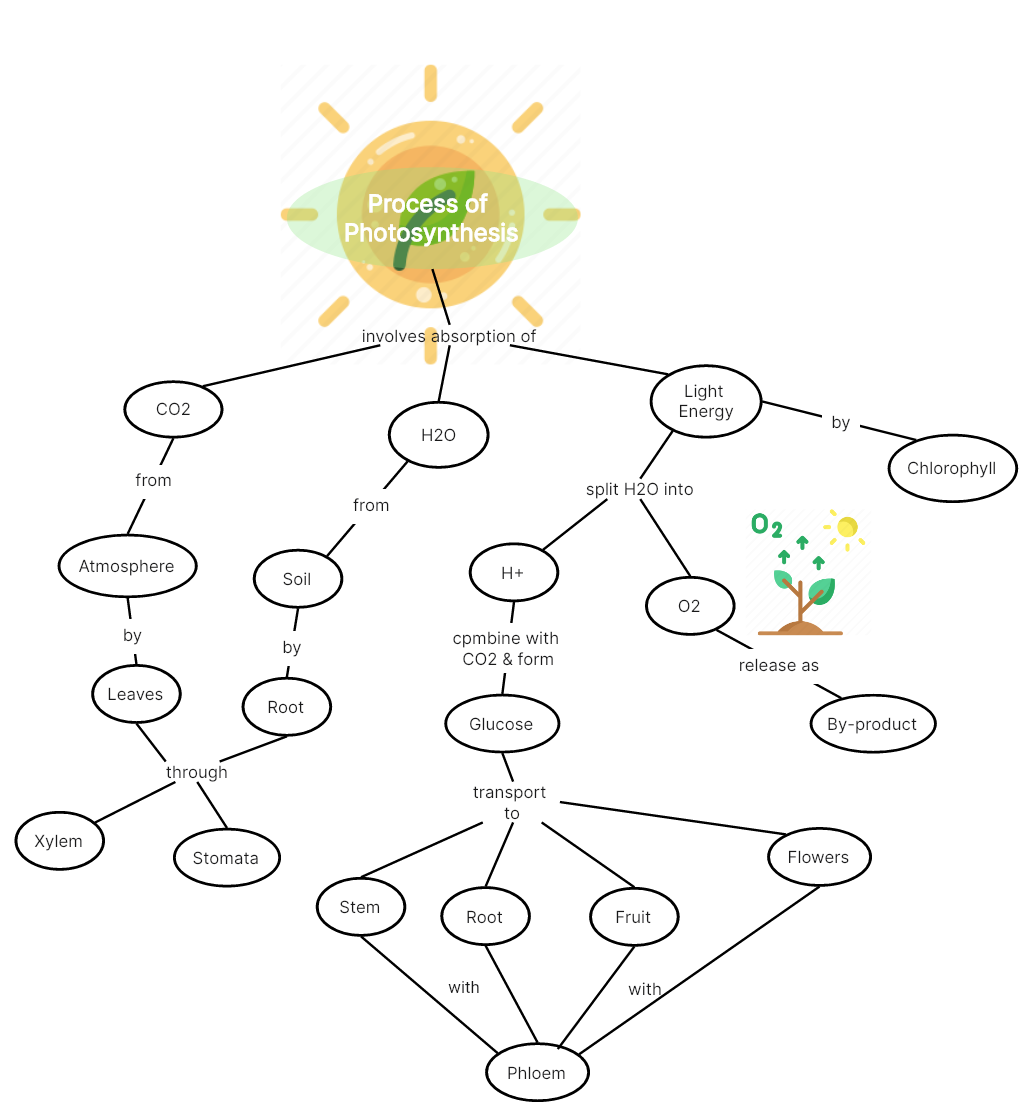
Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and certain other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, which is later used to fuel cellular activities. The process of photosynthesis requires solar energy, water and carbon dioxide, and oxygen is the by-product of this process. During photosynthesis, the plants create their food, and oxygen is liberated out into the environment which is utilized by humans, animals and other living species during the process of respiration. Therefore, photosynthesis is essential for the existence of all life on earth.
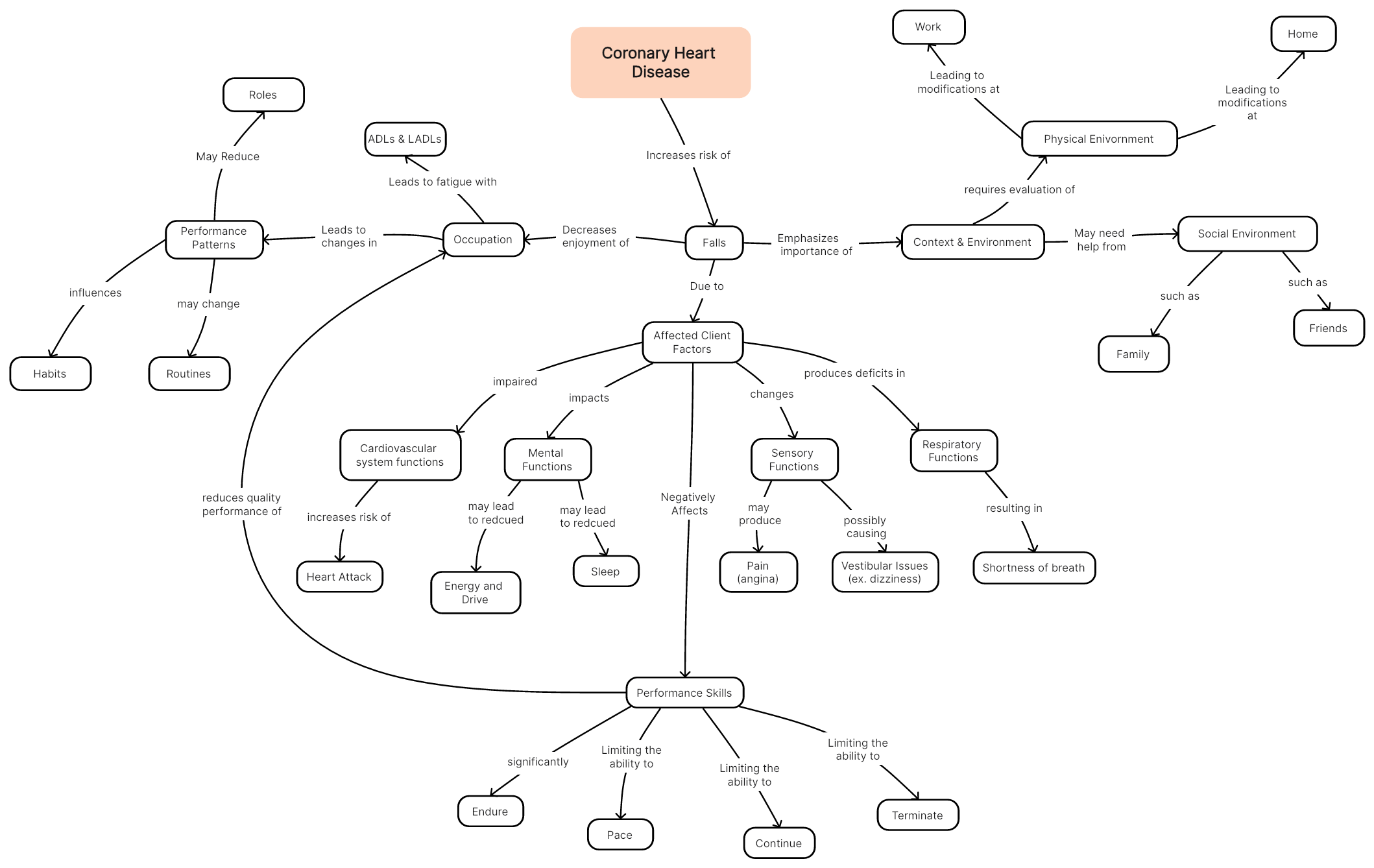
Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also known as coronary artery disease, is a common cardiovascular disorder characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. CHD develops due to the accumulation of plaque—a combination of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances—within the walls of the coronary arteries. This buildup, known as atherosclerosis, restricts blood flow and reduces the oxygen supply to the heart.
Below is a concept map that illustrates how such disease significantly impact an individual’s health and well-being. However, with proper medical management, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support, individuals with CAD can lead fulfilling lives and reduce the risk of complications associated with the disease.
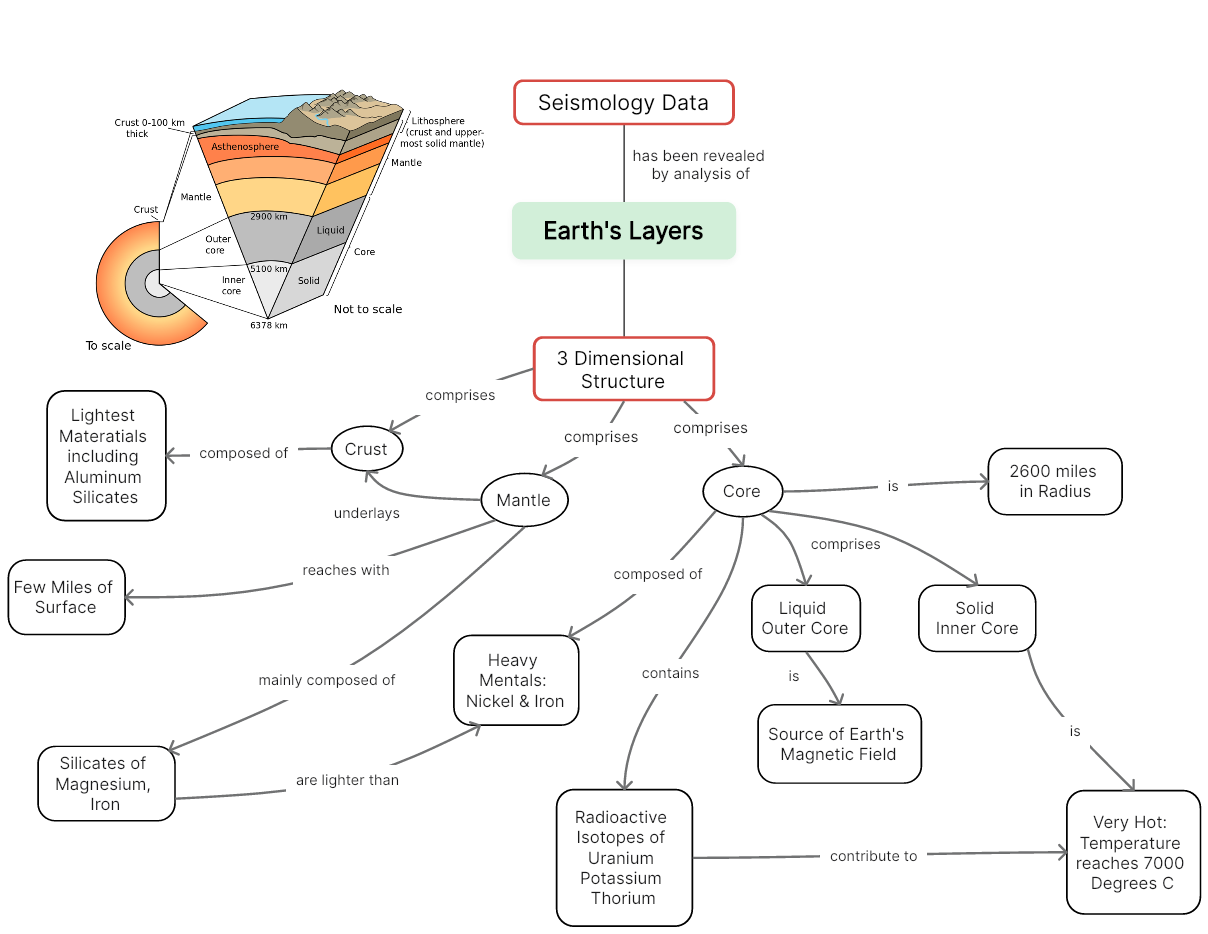
Layers of the Earth
The inner core, the outer core, the mantle and the crust are the four layers of the earth. Geologists believe that as the Earth cooled, the heavier and denser material sank into the centre, and the lighter ones rose towards the top. Due to this, the outermost layer is made of the lightest materials, such as rocks and granites, and the innermost layer consists of nickel and iron.
The layers of the Earth vary in terms of their composition, temperature, pressure, and physical state. These layers work together to shape the earth's structure, geologic processes, and overall dynamics.
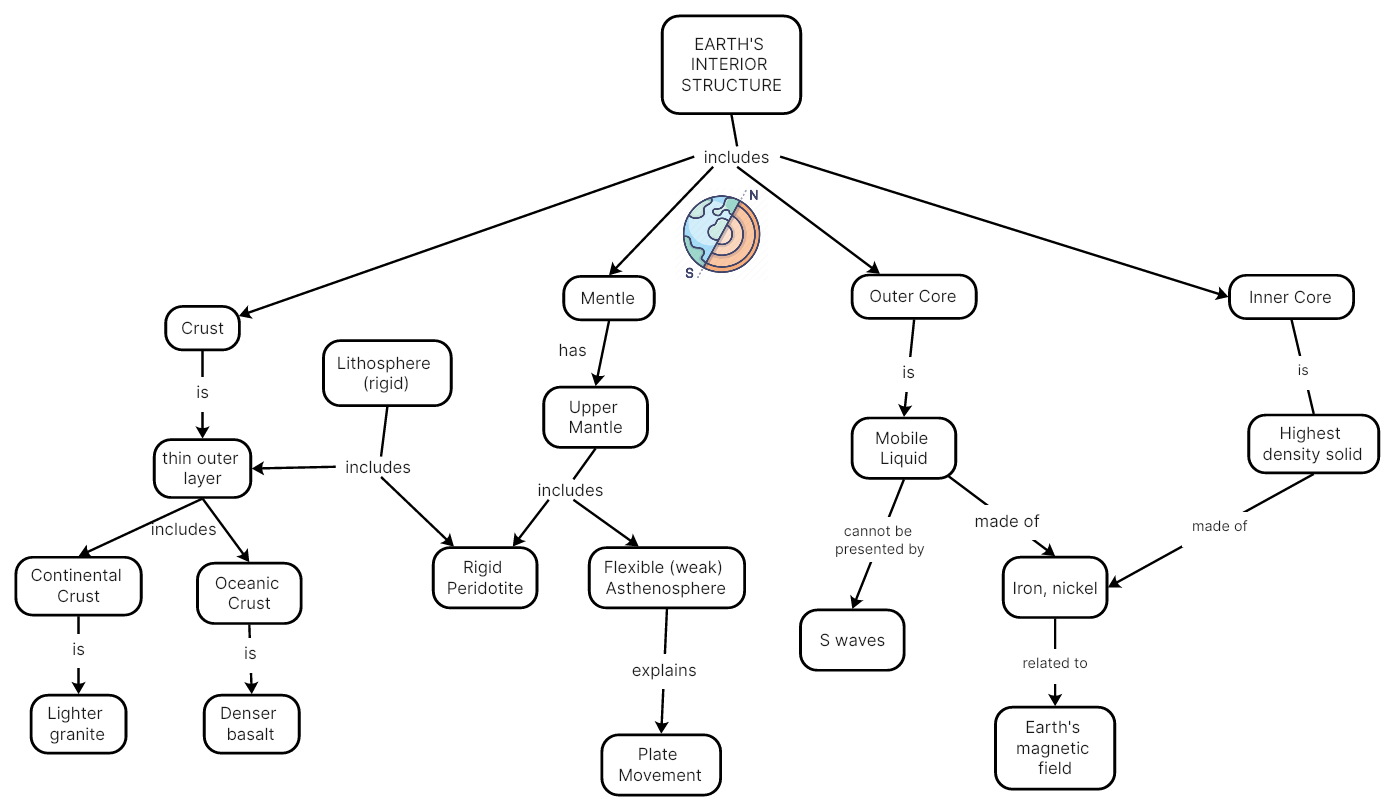
Earth’s Interior Structure
As we have mentioned in the last example, the earth comprises four separate layers -- the inner core, the outer core, the mantle and the crust. Below is a similar concept map that presents the earth’s inner structure, which also shows some related geographic phenomena, such as the plate movement, and the earth’s magnetic field.
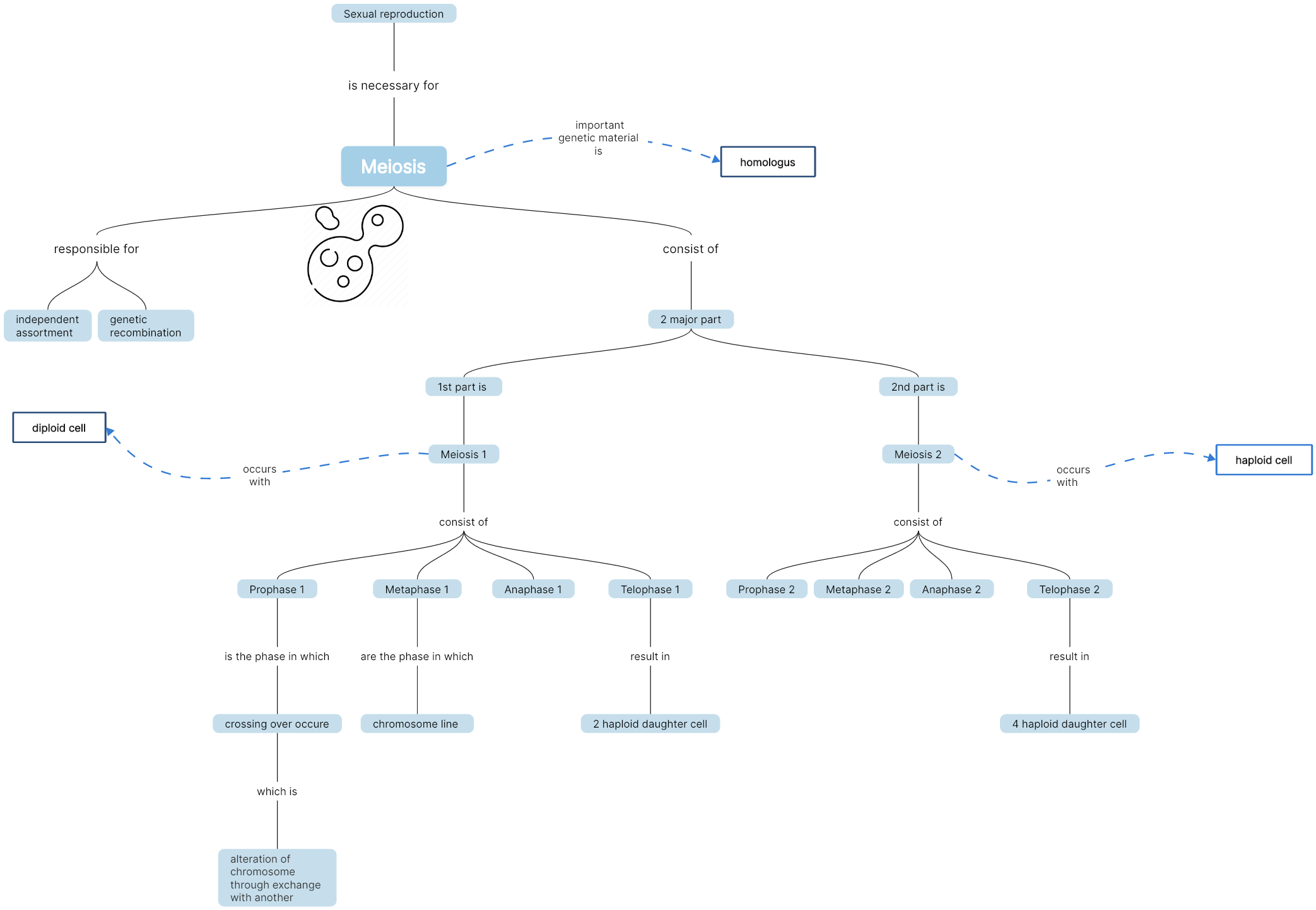
Meiosis
In meiosis, the cell has complex tasks. It needs to separate sister chromatids as in mitosis. But it must also separate homologous chromosomes, the similar but nonidentical chromosome pairs an organism receives from its two parents. These goals are achieved in meiosis using a two-step division process. Homologue pairs separate during a first round of cell division, called meiosis I. Sister chromatids separate during a second round, called meiosis II.
Since cell division occurs twice during meiosis, one starting cell can produce four gametes (eggs or sperm). In each round of division, cells go through four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The phases of meiosis can be understood efficiently using a cell concept map as shown in the following examples.
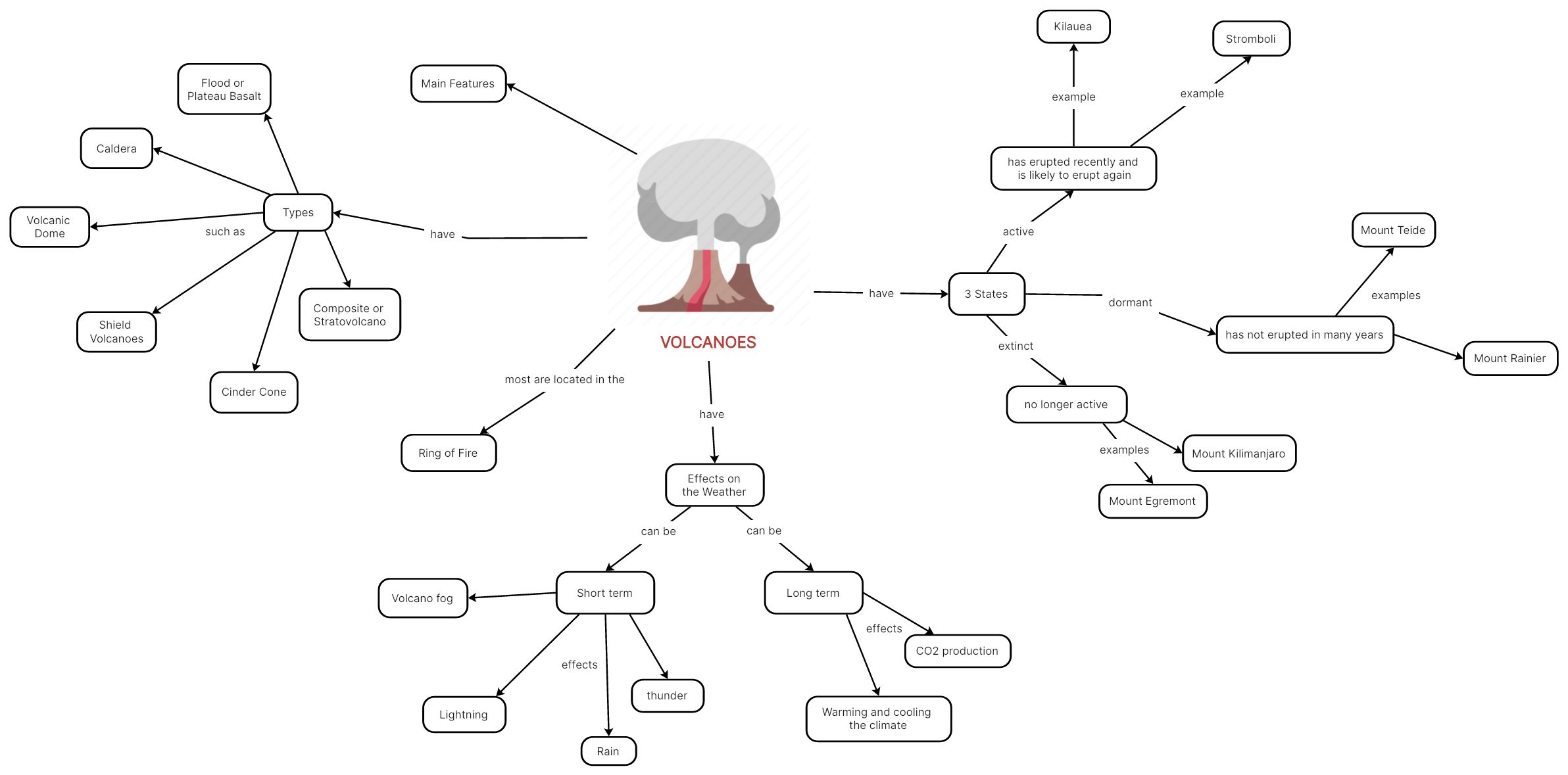
The Volcano
Volcanoes are awe-inspiring natural formations that result from the movement of molten rock, called magma, from beneath the earth's surface to the surface itself. These geological wonders are often characterized by their towering peaks, craters, and explosive eruptions. The following diagram maps out some basic facts about volcanoes, including the main features, types, effects, and the three states, which may be helpful in boosting your understanding of these captivating and dynamic natural phenomena. Moreover, volcanoes reminds us of the Earth's powerful forces and its ever-changing nature. They continue to inspire scientific inquiry, shape landscapes, and offer valuable insights into the inner workings of our planet.
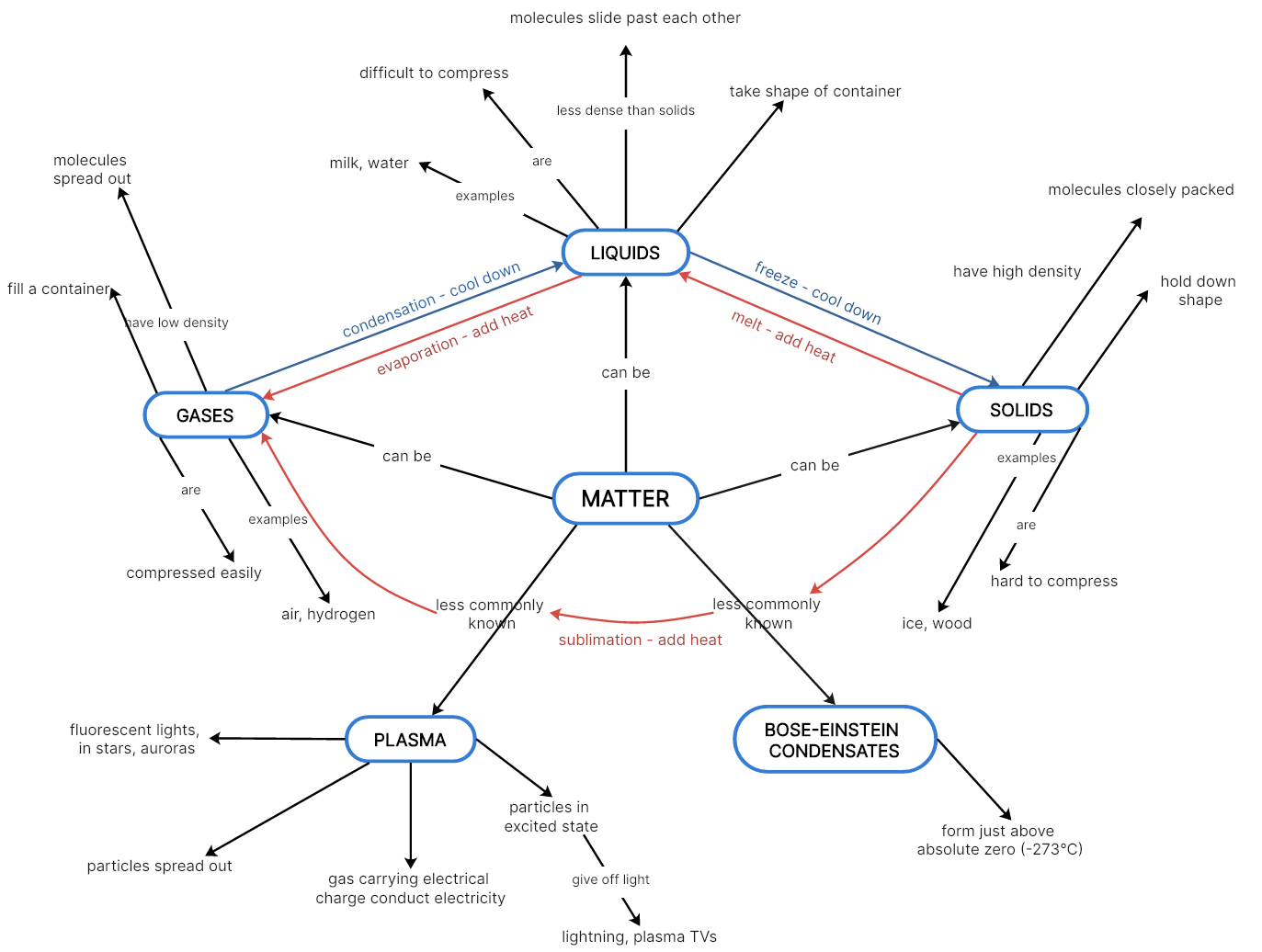
States of Matter
Matter can be classified into different categories based on the physical properties exhibited by them and the states in which they exist. Solids, liquids and gases are the basic three states of matter. Apart from the above mentioned three, there are 2 more states of matter which we do not see in our everyday life. They are Plasma & Bose-einstein condensate. In solids, the particles are tightly packed together. In liquids, the particles have more movement, while in gases, they are spread out. Particles in chemistry can be atoms, ions or molecules. States of matter are distinguished by changes in the properties of matter caused by external factors like pressure and temperature, which can be seen in the following concept map.
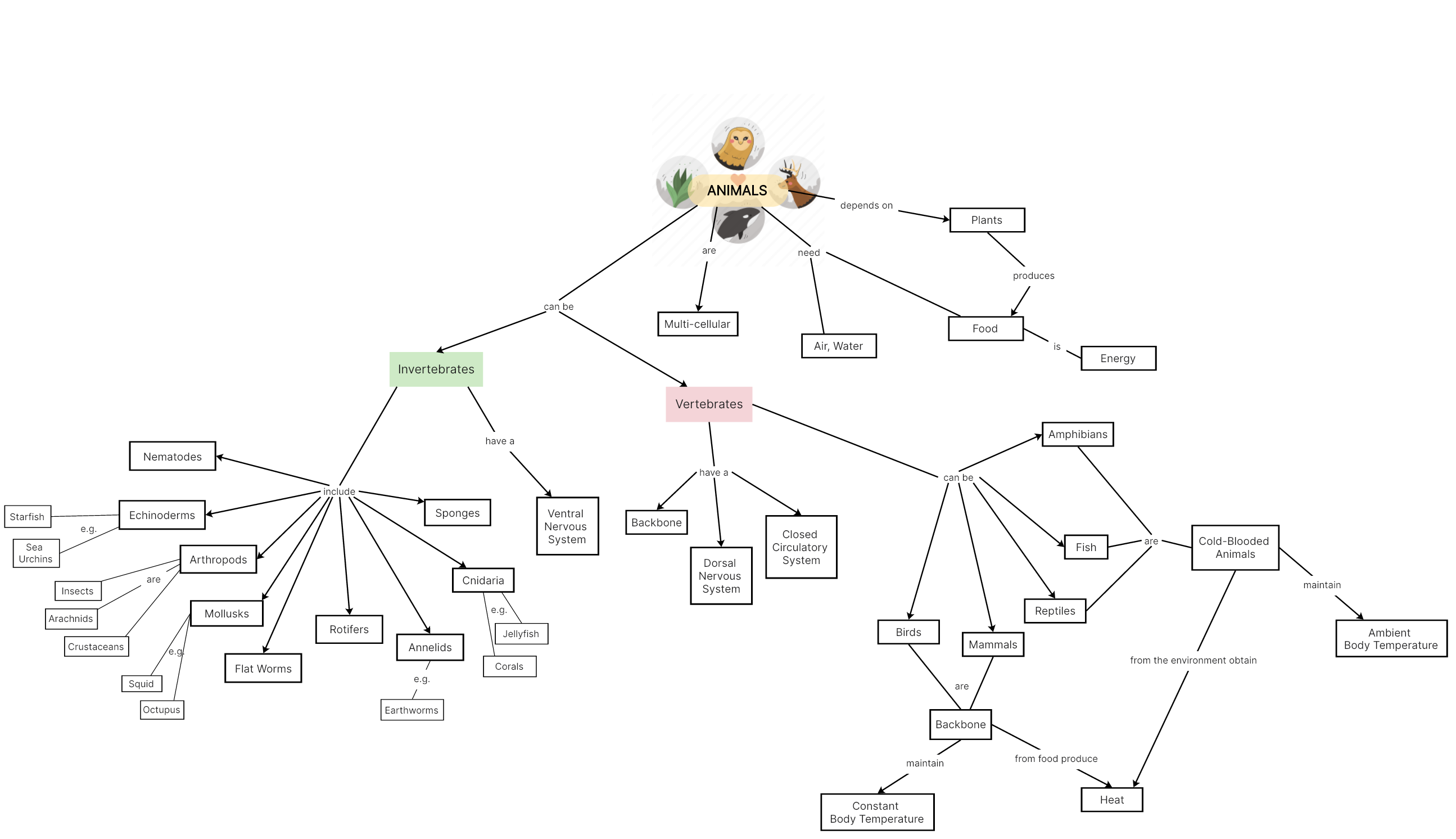
Types of Animals
One of the most well-known and primary methods of classifying animals is based on the presence or absence of the backbone or a spinal column. In this way, animals are classified into two main categories, namely vertebrates and invertebrates. Invertebrates are animals with no backbone, while vertebrates have a spine. Apart from this, there are more differences between vertebrates and invertebrates. Below is a concept map that shows the similarities and differences of these two animal types; it also lists out some typical examples of animals that fall into the two categories.
FAQs about concept maps
What is a concept map used for?
Concept maps can be used to define, explain and analyze complex systems of thought or processes by breaking a big idea into chunks, making it easier to understand. They are frequently employed in various domains and disciplines. For example, they are commonly seen in education, assisting in both teaching and learning processes. In the business field, concept maps are widely used to plot company goals and identify areas of improvement. Besides, they also play an increasingly important role in clinical settings and other situations.
How to create a concept map in Boardmix?
Boardmix is a powerful online collaborative whiteboard that integrates various tools to boost team efficiency and free team imagination. It offers a user-friendly interface that allows users to create, edit, and collaborate on a variety of digital boards. Due to its versatility, you can easily add text, images, lines, sticky notes, and multimedia elements to your boards. Hence, it is a effective tool to create and edit concept maps. Follow the steps below and get started!
Step 1: Gather the information needed. Brainstorm ideas, draw notes, and organize your information into categories. Create a list of the categories, and decide which ones are the most important. These can all be done on Boardmix whiteboard or a physical whiteboard if you prefer to write down things.
Step 2: Create a rough draft of the concept diagram on Boardmix whiteboard. You can choose the concept map template in the template center.
Step 3: Input your main ideas. To change the text in a box, simply click double-click the text, which will allow you to type or delete text.
Step 4: Add more details. You can try various tools by using the menu on the left side of the screen. Finally, review your concept diagram to ensure it is clear and concise.