Creating a Point-to-Point Network Topology Diagram can be compared to connecting dots in a constellation. It's about linking each node directly to another, forming a network that ensures secure and efficient data transmission. Harnessing the power of Boardmix to create diagrams that are not only precise but also visually engaging. So, how does Boardmix assist you in crafting these diagrams effectively? What features does it offer to streamline your network visualization process? Let's delve into these questions together, exploring the realm of Point-to-Point Network Topology Diagrams through the lens of Boardmix.
What is the Point-to-Point Network Topology?
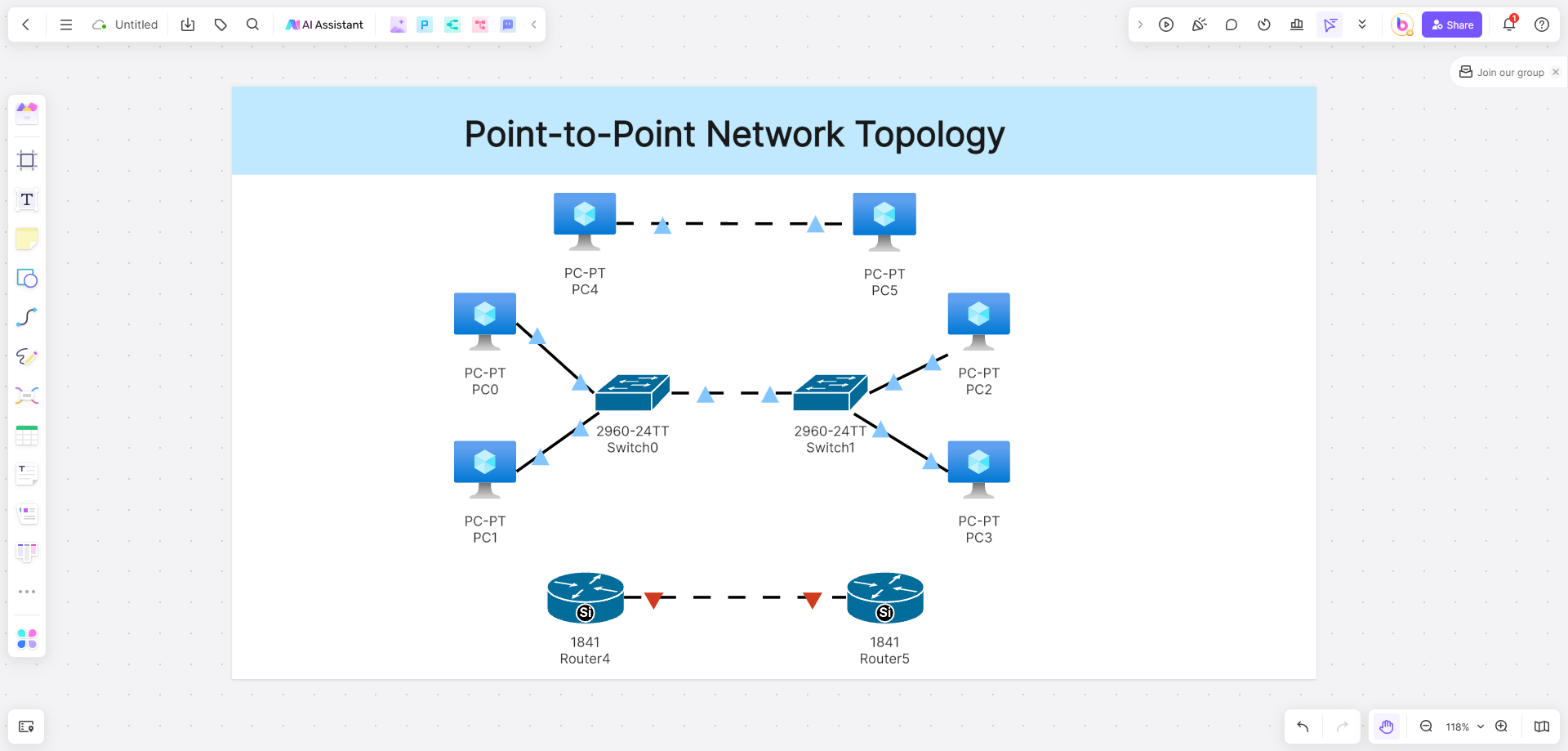
Point-to-Point Network Topology is a type of network architecture where each device in the network is connected directly to another device. In this topology, there is a dedicated communication channel between each pair of devices, allowing for efficient and reliable communication. This topology is commonly used in situations where the network needs to have high bandwidth and low latency, such as in telecommunications and data centers. It provides a direct and secure connection between devices, eliminating the need for data to pass through intermediate devices. Point-to-Point Network Topology is also known for its simplicity and scalability, as new devices can be easily added to the network without affecting the existing connections.
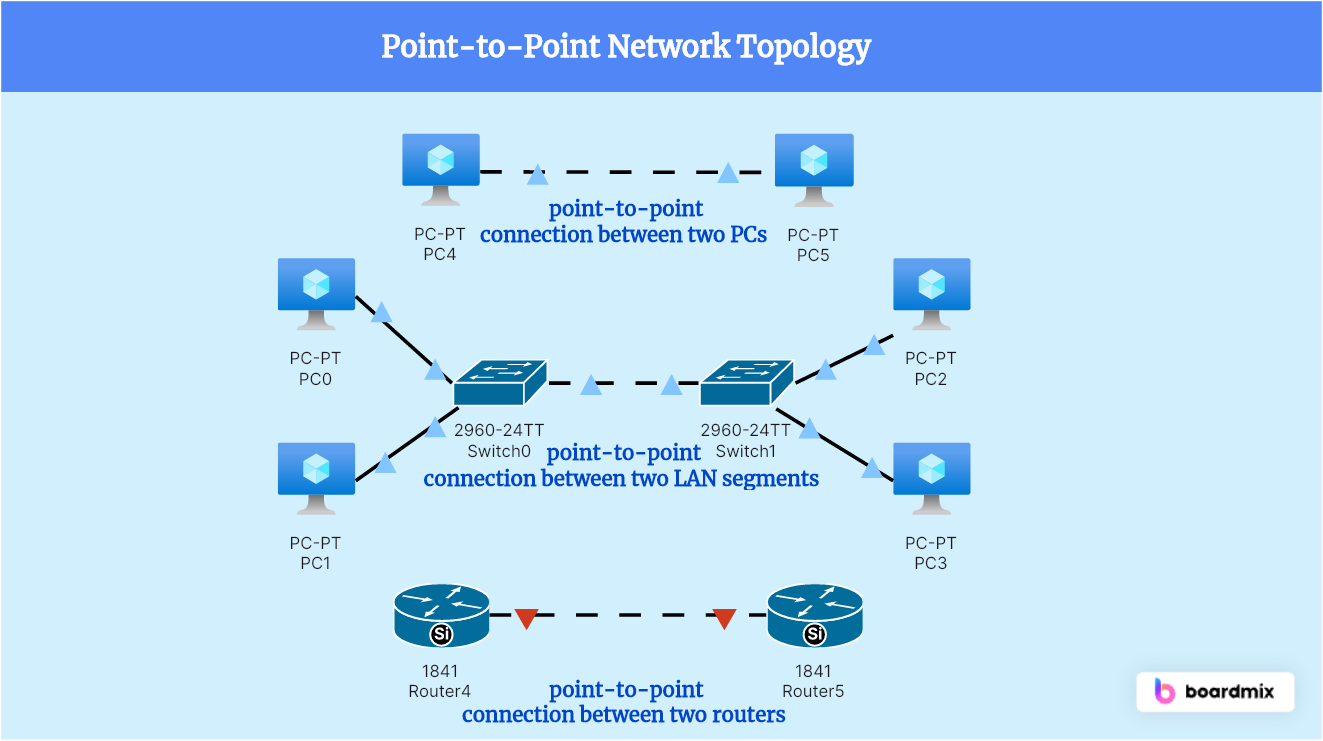
Key Components and Connections of Point-to-Point Network Topology
By understanding these key components and connections of Point-to-Point Network Topology, you can effectively design and implement this type of network architecture for your specific needs. Here are the key components and connections of Point-to-Point Network Topology.
- Devices: The main components of a Point-to-Point network are the devices that are connected directly to each other. These devices can include computers, servers, routers, switches, or any other network-enabled devices.
- Communication Channel: In Point-to-Point Network Topology, there is a dedicated communication channel between each pair of devices. This channel can be a physical cable, such as Ethernet or fiber optic cables, or it can be a wireless connection, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
- Connectors: Connectors are used to physically connect the devices to the communication channel. Common connectors include RJ45 connectors for Ethernet cables or optical connectors for fiber optic cables.
- Data Transmission: Point-to-Point Network Topology allows for efficient and reliable data transmission between the connected devices. Data can be transmitted in a half-duplex or full-duplex mode, depending on the capabilities of the devices and the communication channel.
- Data Encryption: To ensure the security of data transmitted over a Point-to-Point network, encryption techniques can be used. This can include protocols such as SSL/TLS for secure web browsing or IPsec for secure communication between networks.
- Scalability: Point-to-Point Network Topology is highly scalable, as new devices can be easily added to the network without affecting the existing connections. This makes it suitable for expanding networks or adding new devices in the future.
- Reliability: Point-to-Point Network Topology provides a reliable connection between devices, as there are no intermediate devices that can cause interruptions or delays in communication. This ensures that data is transmitted efficiently and without loss.
- Flexibility: Point-to-Point Network Topology allows for flexibility in network design and configuration. Different devices and communication channels can be used depending on the specific requirements of the network, making it adaptable to different environments.
How Boardmix Enhances Visualization and Clarity in Point-to-Point Networks
Point-to-point network diagrams can sometimes be complex and difficult to understand, especially when there are multiple devices and connections involved. Boardmix is a powerful tool that can help optimize these diagrams and make them more visually appealing and easier to interpret.
1. Customizable Design Options
Boardmix provides a wide range of customizable design options, allowing you to create point-to-point network diagrams that align with your specific requirements. You can choose from different shapes, colors, and sizes for devices, connectors, and communication channels, making it easier to differentiate between them and understand the overall network topology.
2. Clear Labeling and Annotations
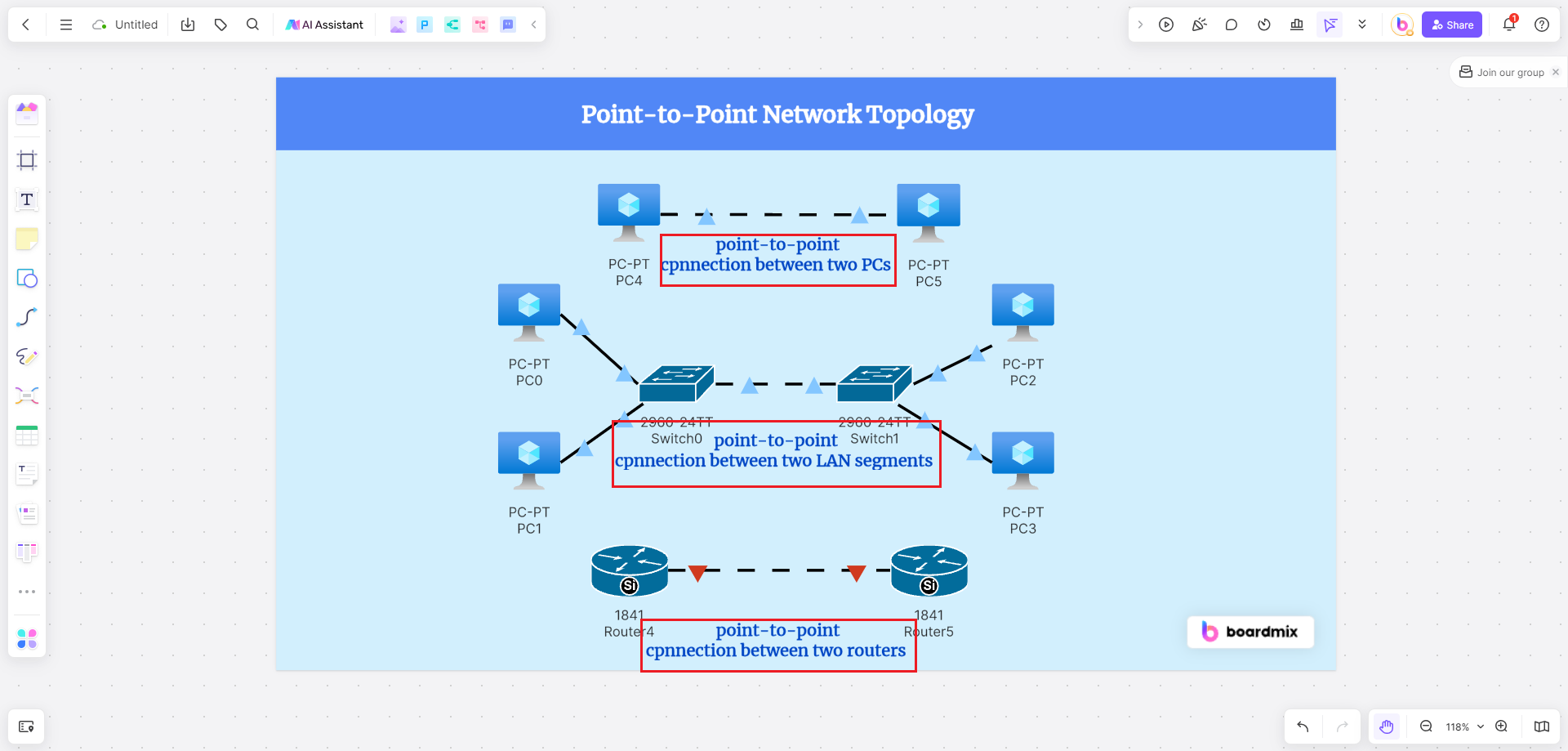
In point-to-point network diagrams, clear labeling and annotations are crucial for providing additional context and information about each device and connection. Boardmix allows you to easily add labels, text boxes, and callouts to your diagrams, ensuring that important details are clearly communicated and easily understood.
3. Simplicity and Intuitive Interface
Boardmix offers a user-friendly and intuitive interface that simplifies the process of creating point-to-point network diagrams. With drag-and-drop functionality and an extensive library of pre-designed shapes and icons, you can quickly build professional-looking diagrams without the need for complex technical skills.
4. Interactive Features
Boardmix also includes interactive features that enhance the user experience and make it easier to navigate through complex point-to-point network diagrams. You can add clickable elements, hyperlinks, or tooltips to provide additional information or links to external resources, allowing users to access more detailed information as needed.
5. Collaboration and Sharing
Collaboration is often a key aspect of working with point-to-point network diagrams. Boardmix enables real-time collaboration, allowing multiple users to work on the same diagram simultaneously. You can share your diagrams with team members or clients through various sharing options, ensuring everyone has access to the latest version of the diagram.
By utilizing the features offered by Boardmix, you can enhance visualization and clarity in your point-to-point network diagrams. This will not only improve understanding and communication but also streamline network management and troubleshooting processes.
How to Use Boardmix to Create a Point-to-Point Network Diagram?
Creating a point-to-point network diagram using Boardmix is a straightforward process. Here's a step-by-step guide to get you started:
1. Sign in to your Boardmix account or create a new one if you don't have an account already.
2. Click on "Create New Board" and search for the "topology" template from the available options.
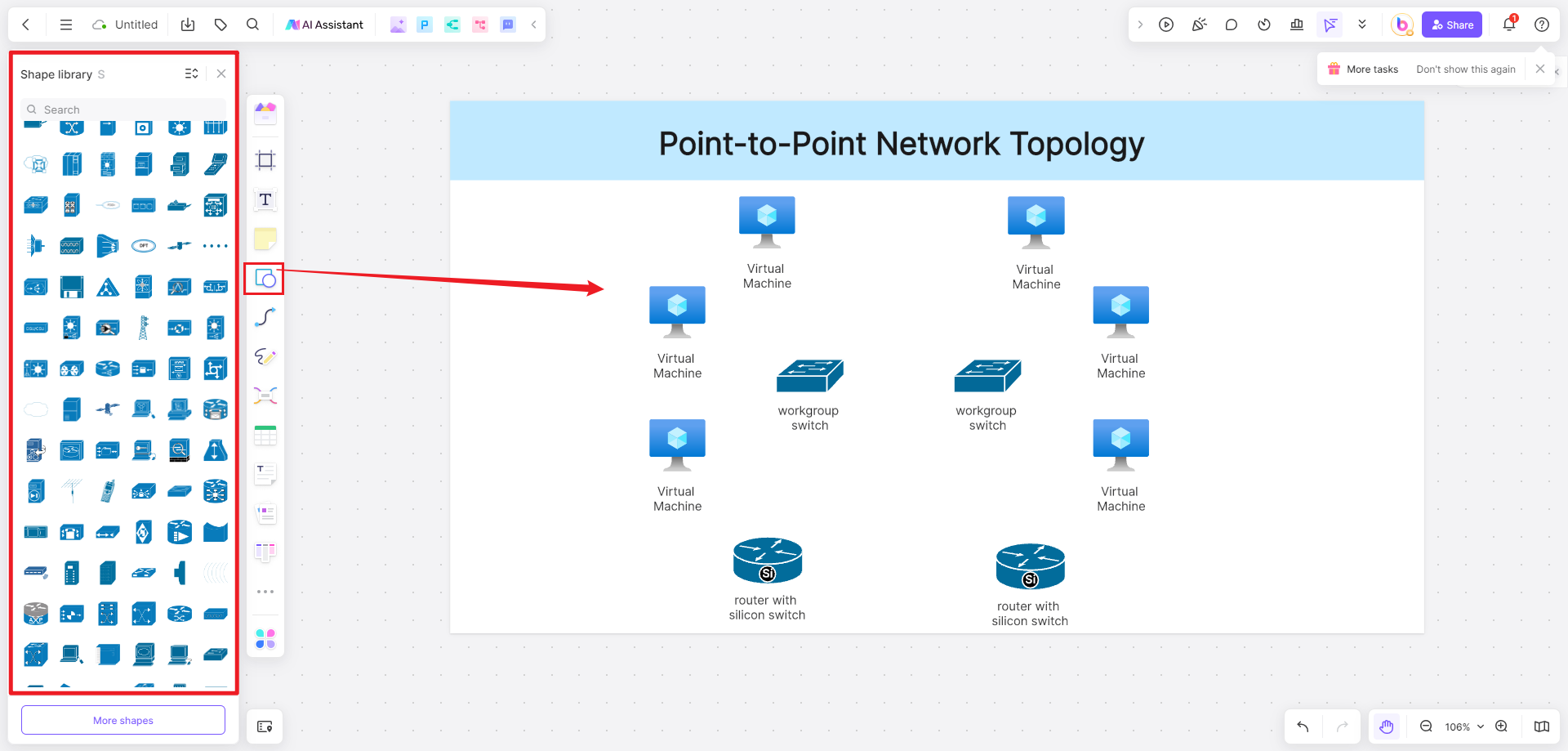
3. Begin by dragging and dropping device icons onto the canvas to represent the devices in your network. You can customize the icons by selecting different shapes, colors, and sizes.
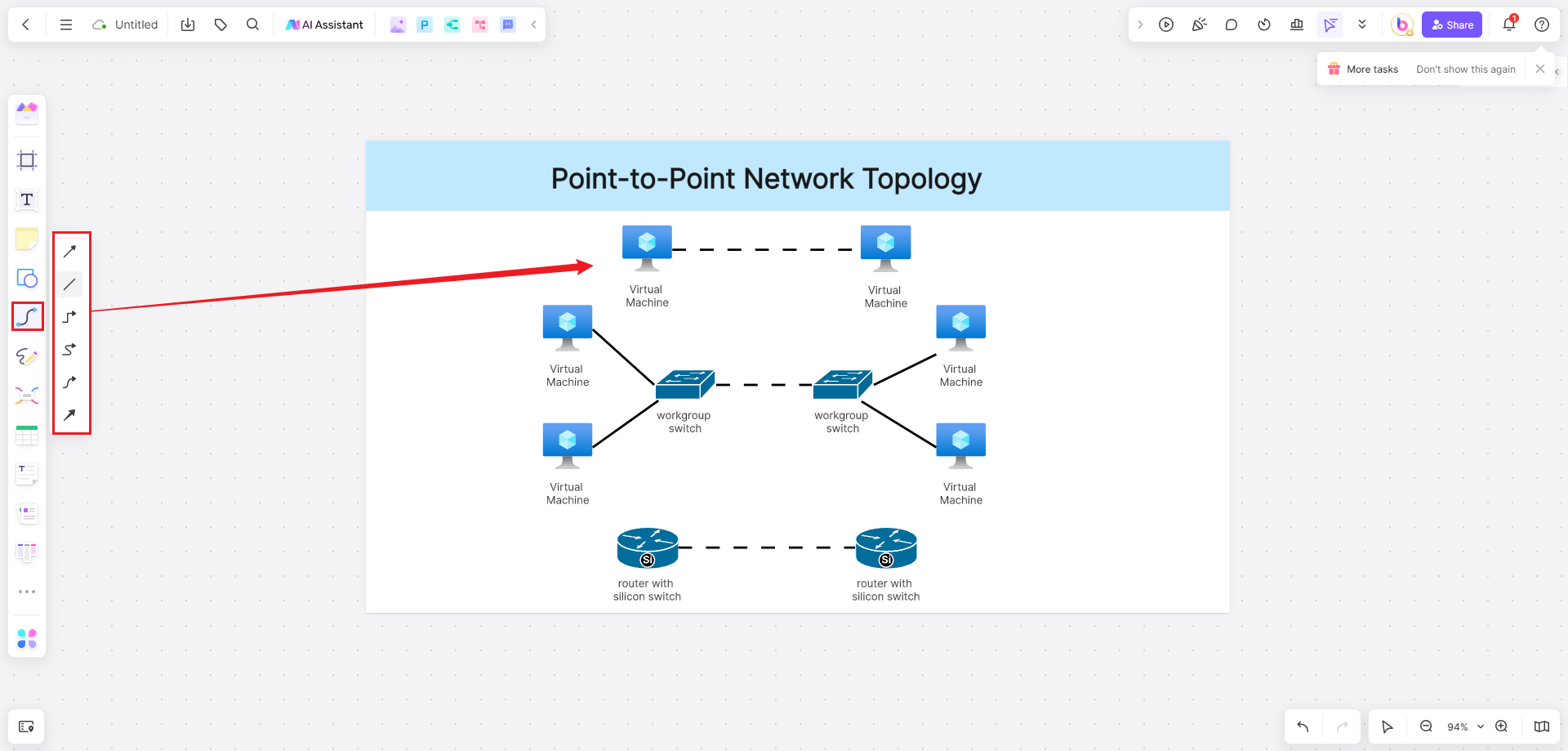
4. Use connectors to establish connections between the devices. You can choose from various connector styles such as straight lines or curved lines.
5. Label each device and connection by adding text boxes or callouts. Be sure to provide clear and concise labels that accurately describe each element.
6. Customize the overall design of your diagram by selecting different themes, layouts, or background images.
7. Add any additional annotations, explanations, or tooltips as needed to provide further information or context.
8. Once you're satisfied with your diagram, save it and share it with others by generating a shareable link or exporting it in different file formats.

Boardmix simplifies the process of creating point-to-point network diagrams while ensuring visual clarity and ease of understanding. By following these steps and utilizing the customizable features offered by Boardmix, you can create professional-looking diagrams that effectively communicate your point-to-point network architecture.
Tips and Best Practices for Point-to-Point Diagrams
For tips and best practices for creating effective point-to-point diagrams, here is some guidance.
1. Design Principles for Effective Point-to-Point Network Diagrams
- Keep the design clean and uncluttered by using a minimalistic approach. Use simple shapes and lines to represent the devices and connections in the diagram.
- Use consistent and easily recognizable symbols for different network devices such as routers, switches, and servers. This will make it easier for the viewers to understand the diagram.
- Logically organize the diagram, with devices and connections arranged in a way that reflects the actual network topology.
- Use colors sparingly and purposefully to highlight important elements in the diagram. Avoid using too many colors as it can make the diagram visually overwhelming.
- Use labels and annotations to provide additional information about the devices and connections in the diagram. This will make it easier for viewers to understand the diagram.
2. Utilizing Colors and Icons for Improved Understanding
- Use colors to differentiate between different types of connections or network segments. For example, you can use different colors to represent wired and wireless connections.
- Use icons or symbols to represent common network devices such as routers, switches, and servers. This will make the diagram more visually appealing and help viewers quickly identify different elements.
3. Ensuring Scalability and Accessibility in Point-to-Point Visualizations
- Consider the scalability of the diagram by using scalable vector graphics (SVG) format. This will ensure that the diagram can be easily resized without losing clarity or quality.
- Make sure that the diagram is accessible to people with visual impairments by providing alternative text descriptions for images and using high-contrast colors.
- By following these design principles and best practices, you can create effective and visually appealing point-to-point diagrams that are easy to understand and navigate.
Advantages and Limitations of Point-to-Point Networks
By considering the advantages and limitations, you can make an informed decision about whether a point-to-point network is suitable for your specific needs.
Advantages of Point-to-Point Networks
- Enhanced Security: Point-to-point networks offer a higher level of security compared to other types of networks. Since the connection is established between two specific endpoints, it is less vulnerable to unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Dedicated Bandwidth: In point-to-point networks, the entire bandwidth is dedicated to the communication between the two endpoints. This ensures fast and reliable data transfer without the risk of congestion or network slowdowns.
- Flexibility: Point-to-point networks provide flexibility in terms of network design and configuration. They can be easily set up and customized to meet specific requirements, allowing for efficient communication between different locations or devices.
- Reduced Latency: Since point-to-point networks eliminate the need for data to travel through multiple intermediate devices, they offer lower latency and faster response times. This is particularly important in real-time applications where immediate data transfer is crucial.
- Improved Performance: Point-to-point networks generally offer better performance compared to shared networks, as the bandwidth is not shared among multiple users. This ensures consistent and high-quality data transfer.
Limitations of Point-to-Point Networks
- Cost: Implementing a point-to-point network can be more expensive compared to other network configurations, especially for long-distance connections. The cost includes the installation of dedicated lines or equipment, which can add up significantly.
- Scalability: Point-to-point networks may face challenges when it comes to scalability. Adding additional endpoints or expanding the network may require additional resources and infrastructure changes, making it less flexible in terms of accommodating growth.
- Maintenance and Management: Point-to-point networks require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal performance. Any issues with the network components or connections may require troubleshooting and can cause downtime.
- Limited Coverage: Point-to-point networks are designed for communication between two specific endpoints, which means their coverage is limited to those endpoints. Connecting multiple locations or devices may require additional point-to-point connections, increasing complexity and cost.
Conclusion
Point-to-point network topology diagrams play a crucial role in network management. They offer a clear visual representation of connections, aiding communication with stakeholders. In troubleshooting, these diagrams are invaluable for swiftly identifying and addressing issues. Moreover, they assist in planning network expansion, highlighting potential improvements. As essential documentation, they serve as a reference point for future configurations, ensuring consistency and accuracy in network management.
Boardmix is a powerful tool that promotes enhanced visual communication in point-to-point networks. Integrated seamlessly with other collaboration tools, Boardmix simplifies workflows, offering remote access for improved efficiency. Its user-friendly interface makes it accessible to both technical and non-technical users, encouraging widespread adoption of superior visual communication in point-to-point networks. Try Boardmix today and make your point-to-point topology diagram more visualizable and make it easier!