A professional GTM journey map can turn invisible service workflows into visual blueprints. It empowers teams to design purposeful, frictionless experiences that turn skepticism into loyalty. In this guide, we’ll break down step-by-step how to build a GTM journey map for services with free ready-made templates. No jargon, just actionable strategies to turn your service delivery into a competitive advantage.
1.What is a GTM Journey Map?
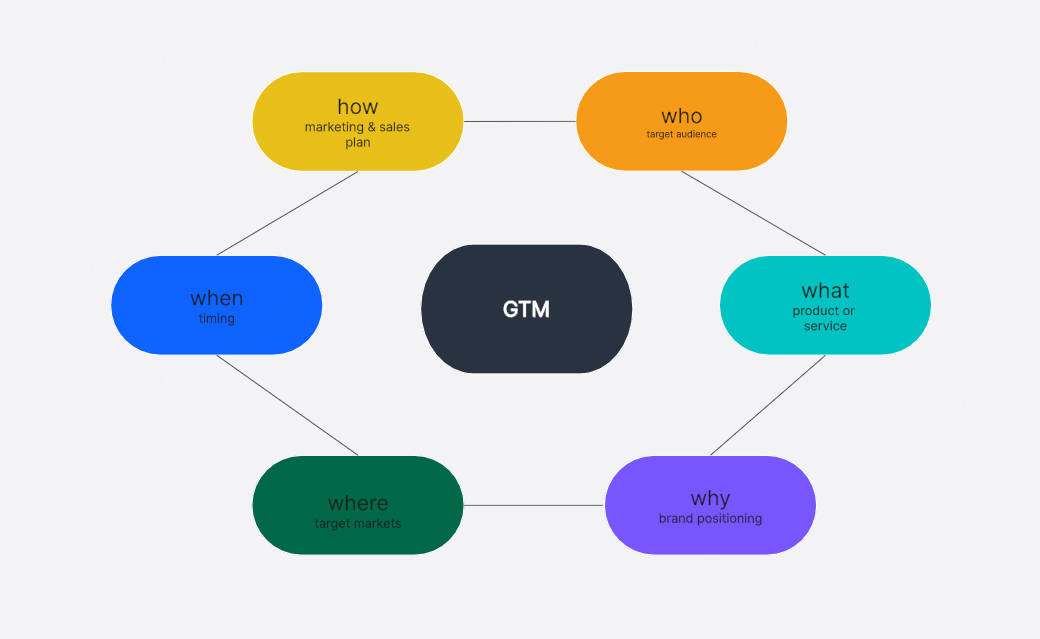
Imagine that you are going to travel to an unfamiliar place, but you don't have a map or navigation. You may get lost, take a long detour, or even miss the most important scenery. GTM (Go-To-Market) journey map is like a "travel guide" drawn for customers, except that the destination of this journey is the whole process of their unfamiliarity with your service to trust, from hesitation to purchase.
It uses a visual way to clearly show every key step from the first contact with your service (such as seeing an advertisement, receiving a sales call) to the final purchase or even becoming a loyal fan. At the same time, this GTM journey map will also tell you: what customers need and worry about at each stage, and how your team should respond to their needs
The GTM journey map for service is especially important. Because the service is "intangible", customers cannot touch the physical object before deciding like buying a mobile phone. For example, when you sign up for an online course, you may need to trust the quality of the course first.
2. Why Design a GTM Journey Map for Services?

The service industry has three inherent challenges:
- Intangibility: Customers cannot "try" the service in advance and can only place orders based on trust;
- Reliance on interpersonal interaction: A bad communication may directly lead to customer loss;
- Long delivery cycle: For example, a six-month corporate training, any mistake in the middle may make customers regret it.
These challenges make the service industry need a clear GTM map more than selling physical products. Here are its core values.
1. Reduce cognitive barriers: Let customers understand your service
When customers don't understand your service process, they will hesitate. For example, if a high-end gym only emphasizes "professional private training" but does not explain how the course is arranged and how the effect is evaluated, potential users may give up because they "can't understand".
The GTM map can help customers sort out the logic. From the first experience class to the customized plan, to regular feedback, each step is clearly displayed. This transparency can greatly reduce the decision-making pressure of customers.
2.Optimize customer experience: avoid bad experience and create surprises
The pain points in services are often hidden in the details. For example, an online education platform found that many users complained because they could not find the course entrance after paying. Through the journey map, they quickly added a striking "Learn Now" button on the payment success page and automatically sent a guidance email, and the complaint rate dropped by 60%.
3. Improve conversion rate: Guidance from interest to payment
When customers know clearly what to do next, they are more likely to act. For example, a design studio added a "3-step completion of demand submission" guide map on its official website:
- Fill out the design style questionnaire (5 minutes);
- Make an appointment for free telephone communication;
- Get customized solutions and quotes.
As a result, the customer's consultation conversion rate increased by 35%. Journey maps break down complex decisions into simple actions through "step-by-step guidance" to push customers forward.
4. Enhance team collaboration and stop fighting alone
Services require cooperation from multiple teams, but departments are often disconnected. For example, the marketing department is desperate to attract customers, but the sales department cannot respond to inquiries quickly; the after-sales team complains that "sales over-promises", which leads to customer dissatisfaction.
The GTM map can unify everyone's goals. This kind of collaborative rule allows customers to experience seamless service.
The GTM journey map turns vague experiences into clear paths and turns the chaos of the team into an orderly division of labor.
3. How to Create a GTM Journey Map for Service?
Next, I will take you through how to design a GTM journey map for a service step by step. The whole process is divided into 6 core steps. I will combine real cases in each step to let you see how the theory is implemented.
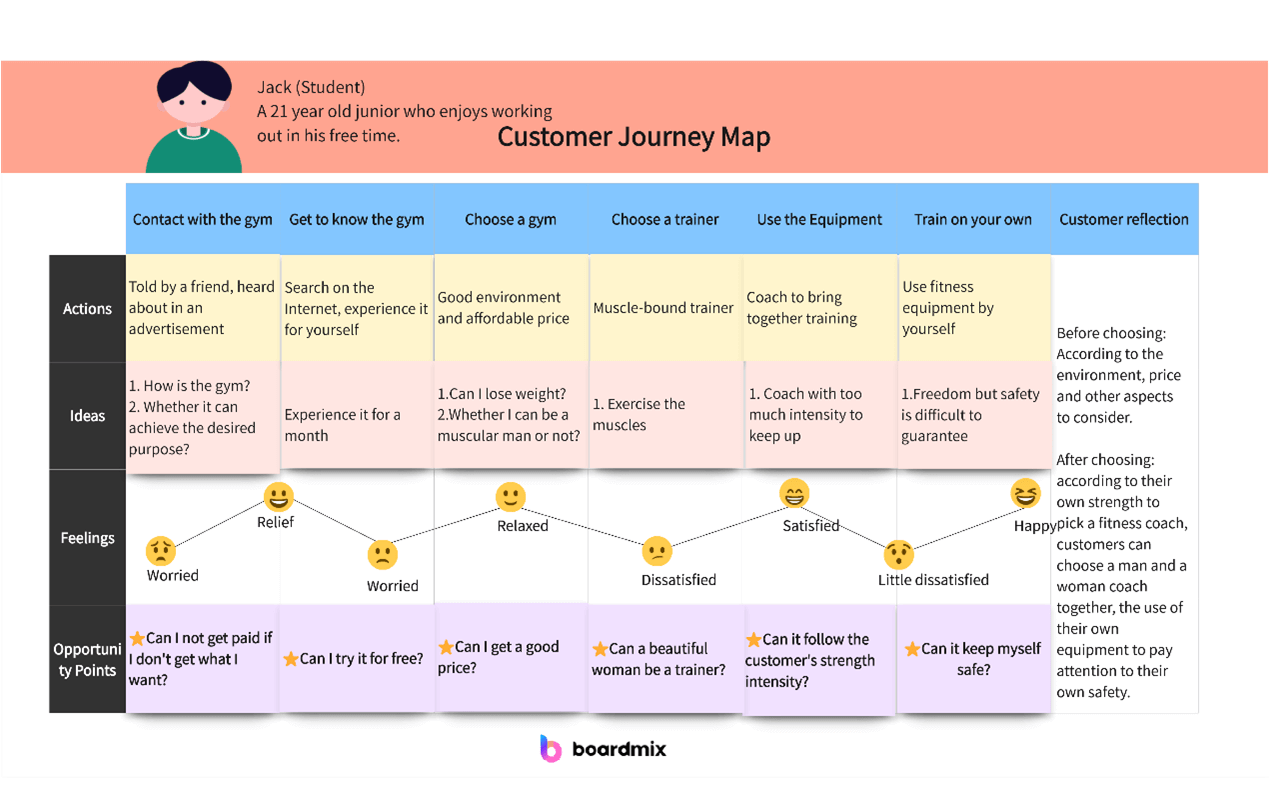
Take a company that provides enterprise-level SaaS services as an example. They want to optimize the entire journey of customers from first contact with the product to renewal recommendation.
Step 1: Define goals and scope your market
First, you need to answer two questions: "Who is the service object?" and "Where is the boundary of the journey?"
Let’s see this case. The core customers of this SaaS company are IT departments of small and medium-sized enterprises. They decided to scope the journey from "market awareness" to "renewal decision" for a total of 6 months.
Why is it important to define goals and scope for GTM journey maps? If the goals are vague, such as covering both B2B and B2C customers at the same time, the journey map will become confusing. The service industry especially needs to focus because different customers have huge differences in their needs for "delivery cycle" and "communication frequency".
What’s the Action:
- Define the goal in one sentence, for example: "Help IT managers of small and medium-sized enterprises understand the value of the product and make purchasing decisions within 3 months."
- Use the role card (Perona) to clarify the customer portrait, including position, pain points, and decision-making weight.
Step 2: Customer research and data integration
Services are intangible, so customer feedback and data are your compass.
Through customer interviews, this SaaS company found that the most anxious thing for IT managers is not the price, but "whether the operation and maintenance burden will increase after deployment." At the same time, background data shows that 70% of customers churn on the 14th day of the trial period because "key function configuration has not been completed."
How to do:
Quantitative data: Track page dwell time, customer service response speed, and service usage frequency.
Qualitative insights: Ask questions in customer interviews: "Which link makes you feel uneasy? Why?"
Especially for the service industry, in addition to NPS (net promoter score), pay attention to CES (customer effort). For example, how many times do customers need to find customer service to solve the problem?
Step 3: Map the customer journey stages
Now, you need to cut the customer journey into clear stages and mark the core touchpoints and emotional fluctuations of each stage.

The following are typical stages for drawing a customer journey map:
Awareness stage: seeing advertisements, industry white papers → Emotional keywords: curiosity, suspicion
Consideration stage: participating in product demonstrations, comparing competing products → Emotional keywords: entanglement, expectation
Decision stage: contract negotiation, service commitment → Emotional keywords: anxiety (fear of making the wrong choice)
Delivery stage: deployment training, first use → Emotional keywords: confusion or surprise
After-sales stage: troubleshooting, regular return visits → Emotional keywords: trust or disappointment
This SaaS company found a fatal touchpoint in the "delivery stage": after the customer logged in for the first time, the system's default interface was too complicated, causing users to be overwhelmed. So they added a "3-minute guide video" and increased the satisfaction of this link by 40%.
Remember that the touchpoints of the service industry are often hidden in "interpersonal interactions", such as the tone of a consulting conversation or the transparency of delivery.
Step 4: Identify pain points and opportunities
Next, you need to use the customer emotion curve to identify which links make them want to recommend you and which links make them want to escape. You can use Boardmix to draw an emotion curve chart, with the horizontal axis being the journey stage and the vertical axis being the emotion score (-5 to +5).
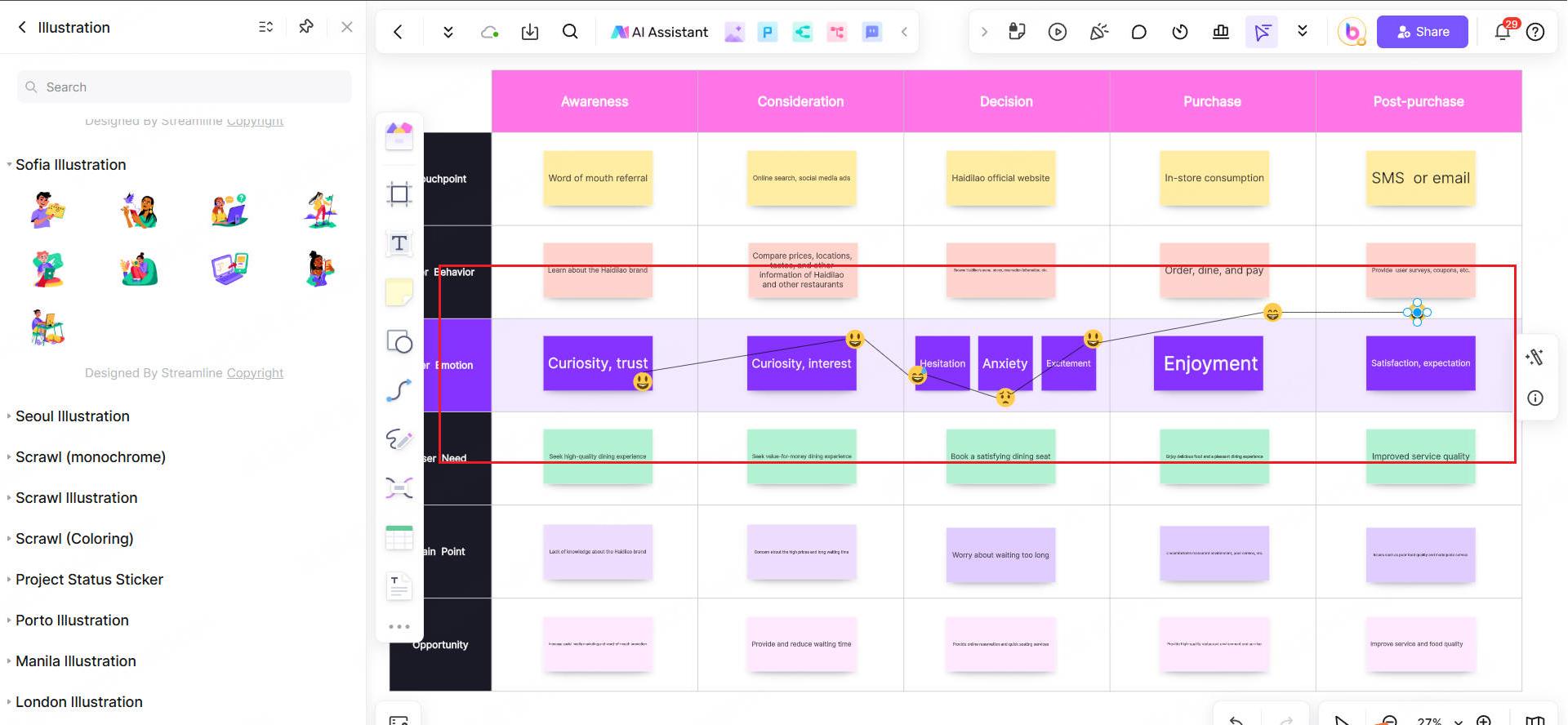
There are two common pain points in the service industry:
Information black box: customers do not know the progress of the service (such as "What stage has my contract reached?").
Response delay: after-sales consultation has not been responded to for more than 24 hours.
This is the solution for the service industry: insert "comforting actions" at the emotional low point, such as automatically sending progress notification SMS, or promising "2-hour response".
Step 5: Design key actions and resource allocation
The journey map is not for customers to see, but a battle map for internal teams.
The SaaS company found that the goals of the after-sales support team and the sales team conflicted sales pursued the number of signed orders, and after-sales pursued a low complaint rate. So they adjusted the KPI and included the "customer first configuration completion rate" in the sales assessment to align the interests of the team.
Step 6: Test and Iterate your GTM journey map
Finally, verify whether your design is effective with minimal cost. The SaaS company conducted an A/B test in the "trial period": Group A customers received a standard operating manual; Group B customers received a "1-on-1 configuration guidance appointment". The result was that the renewal rate of Group B was 3 times higher than that of Group A! So they solidified this as a standard process.
When iterating tasks, hold a "journey review meeting" every month to compare customer satisfaction data before and after optimization. Because the journey map of the service industry should be dynamic. Market changes, customer upgrades, and team adjustments may affect its effectiveness.
The key to designing a GTM journey map for a service is to implement abstract concepts into specific actions, and make timely adjustments based on data. Whether you are buying software or opening a restaurant, you can use the user journey map framework to find your customers‘ wow moments.
Tool and Template for Creating GTM Journey Map for Service
After understanding the value of GTM journey maps, the next key question is: "How to draw it efficiently?" Boardmix is an online whiteboard with a simple interface. It not only helps you easily draw professional maps, but also provides a free template library, which greatly reduces the design threshold.
Why choose Boardmix?
- One-stop visual collaboration platform
GTM maps in the service industry often require cross-team collaboration (marketing, sales, customer service), and Boardmix supports multi-person real-time online editing. Team members can add annotations, adjust processes, and assign tasks on the same whiteboard, completely saying goodbye to "version confusion" and "email bombing".
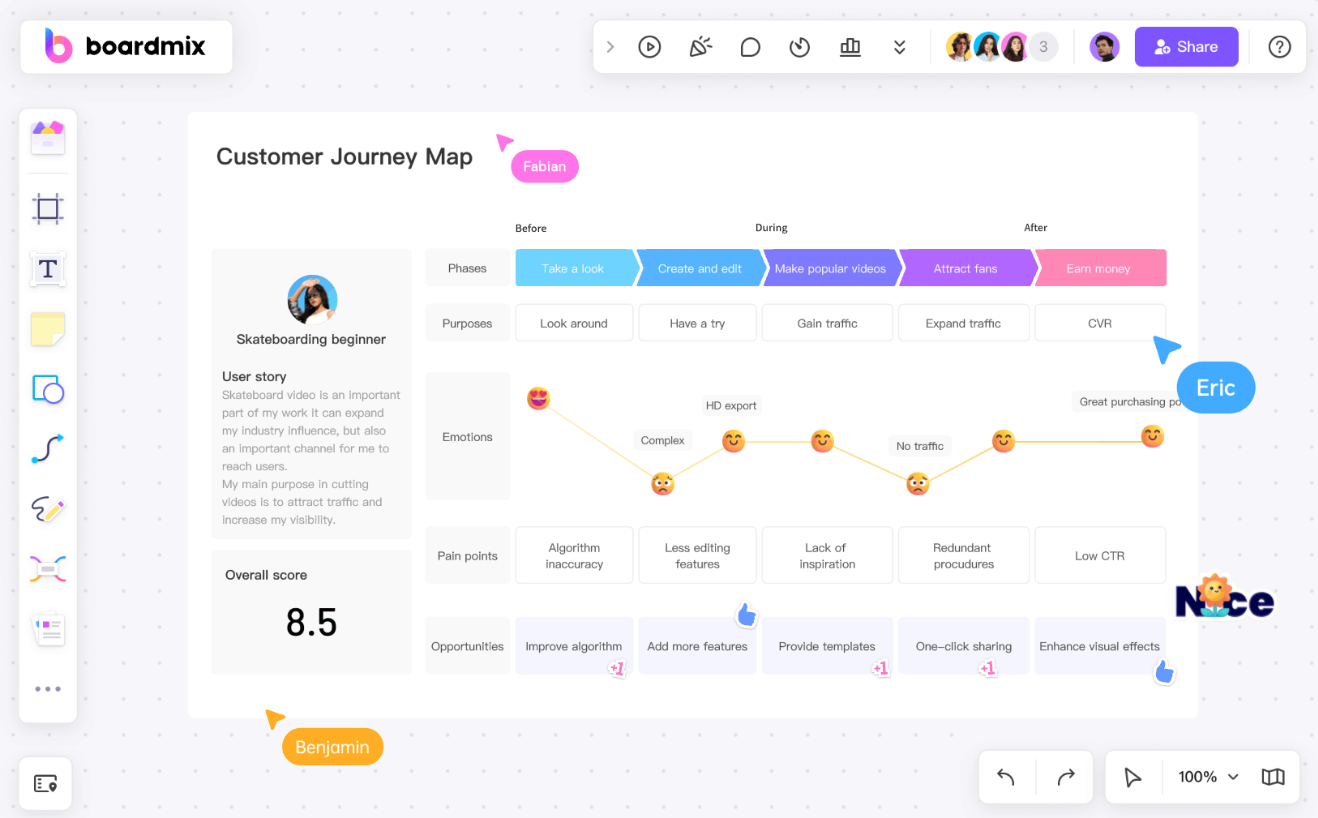
- Rich graphic library and template library
Preset service industry templates: Boardmix provides templates such as "User Journey Map" and "Customer Experience Map", which can be applied directly to get started quickly. For example, the template has preset typical stages (cognition→consideration→decision→delivery→retention), and you only need to replace it with your own business content.
Flexible drag and drop editing: From emotional curves, touch point icons to responsibility division labels, all elements can be freely combined to meet personalized needs.
- Deeply adapted to the needs of the service industry
Marking "invisible touchpoints": For example, use sticky notes to mark "trust-building words for the first telephone communication with customers", or use lines to show how "service progress notification text messages" can relieve customer anxiety.
Embed multimedia: Insert service flow charts, customer interview recordings, and even upload contract templates at key stages to make the map a "dynamic knowledge base".
- Completely free entry-level functions
For small and medium-sized service companies or start-up teams, the free version of Boardmix is enough to support basic map design and can be used without additional costs.
How to Create A GTM Journey Map with Boardmix?
Step 1: Log in to Boardmix and select a template
After visiting the Boardmix website, create an account online for free, then search for "user journey map" in the Boardmix template library and select a customer journey map template suitable for the service industry.
Step 2: Customize stages and touchpoints
Adjust stages: Add or delete stages based on business characteristics. For example, housekeeping services may need to add a "home inspection" link, while consulting companies may need to split "solution customization" and "contract negotiation".
Mark the emotional curve: Mark the peaks and troughs on the emotional axis of the template. For example, if the customer is anxious about the opaque progress in the "mid-term of service delivery", you need to add the "weekly progress report" touchpoint here.
Step 3: Assign responsibilities and resources
Use color labels to distinguish responsible departments (such as red = sales, blue = delivery, green = customer service);
Add notes next to the touchpoints to indicate the required resources (such as "need CRM system to automatically send service reminders").
Step 4: Team collaboration and iteration
Invite team members to comment online, such as customer service staff feedback: "Customers often ask 'what to do next' after payment, it is recommended to add a guide pop-up window";
Boardmix allows you to turn complex customer journeys into a clear, collaborative, and iterative visual blueprint. Whether it is optimizing customer experience or improving team efficiency, using tools and templates well can achieve twice the result with half the effort.
Conclusion
Creating a GTM journey map isn’t about making a perfect diagram, it’s about starting a conversation with your customers and your team. Start creating your GTM journey map today with a free template from Boardmix now!









