Recalling vast amounts of information poses a common challenge, especially for students absorbing new knowledge daily. Memorizing information from lectures and readings can be daunting. This process is made extra difficult because of the Ebbinghas forgetting curve, which demonstrates how people have a strong tendency to forget newly acquired information quickly unless they take special steps to remember consciously.
What Is the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve?
The Ebbinghaus forgetting curve is the natural tendency of people to forget information as time goes by, especially during the short period immediately after they have learned the information. These first few minutes or hours after the learning show the steepest drop in the rate of retention, as can easily be seen in the visual image of the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve in graph format.
After this, the retention rate becomes stable. In essence, the information retained after the initial stage will likely endure for a considerable time. Nevertheless, as time passes, only a small fraction of the original knowledge we were meant to learn remains intact, following the natural course of forgetting. But the good news is that the forgetting curve can become a lot less steep with the help of proven methods.
Memory retention can also improve significantly with the help of memory-strengthening techniques, like regular reviews. These reviews need not be continuous though. It has been found that leaving gaps between the reviews, which is called spaced learning, produces much better results.
History of the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve
The forgetting curve was discovered by and named after the German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus, sometime between 1880 and 1885. He had written about the procedures and theories he used as well as the results of his experiments in great detail in his published work, Memory. Ebbinghaus also made numerous contributions to research on learning and memory, in which he was one of the pioneers.
As the first psychologist to dedicate his studies to memory, Ebbinghaus did not have a lot of resources to work with and so had to conduct numerous memory experiments, mostly on himself. Most of his tests involved the use of nonsensical groups of letters in the CVC or consonant-vowel-consonant format. He would make himself memorize these “words” and go about his other activities. He would then test his knowledge of these words periodically over the next few days, plotting the results on a graph.
Ebbinghaus summarizes the results of his studies with the equation R = e^(-t/s) where R is one’s recall readiness, s is the strength of one’s memory, t is the period that has elapsed from the time of learning to the time of testing, and e is Euler’s number. This is a mathematical constant that equals approximately 2.71828.
Complex as it all sounds, these very valuable studies have eventually revealed what we know today as the forgetting curve.
What Is the Purpose of the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve?
The initial purpose of the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve was to simply figure out why people forgot pieces of information and to demonstrate the diminishing rate of retention and how it changes over time. Today, though, the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve serves as a tool to improve memory by reminding people to regularly review newly learned information and to consolidate it to boost the rate of retention.
Why Is the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve Important?
The Ebbinghaus forgetting curve is very important because it enables people to learn more and to remember what they have learned for a very long time. It emphasizes that to truly learn new information or new skills, you need to review and retrieve this information several times. Otherwise, it will all just fall into the natural forgetting curve and disappear from your memory as if you did not do any learning in the first place.
Over the years, several methods and strategies have been developed to deal with the learning curve. Knowing that it exists has prodded people to take steps to consciously strengthen memory instead of just relying on initial learning, which has proven to be not very effective in the long run.
A thorough understanding of the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve is very important so that you can combat it properly, and use ways that will be most effective for you. Although its principles are certainly applicable to many situations, including most professions or lines of work, as well as in personal situations, they are particularly valuable for individuals who need to absorb and retain huge amounts of information for long-term use.
How to Combat the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve
It is a naturally occurring phenomenon in everyone, which makes the forgetting curve a bit overwhelming. Combatting it would be like going against nature, and that is not going to be easy. It is certainly a challenge but one that can quite easily be overcome, given the right mindset, attitude, and tools.
In one of the most significant discoveries that Ebbinghaus made during his studies, it became clear that regular reinforcement played a very important role in strengthening memory. The most crucial period is in the hours immediately after learning. During this time, you need to constantly review the information to boost the chances of it sticking to your mind.
Clarity
Information that is clear, concise, and easily understandable is easier to remember than long and complex ideas. Therefore, it will help a lot in fighting the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve if you can simplify information as much as possible before you attempt to learn it.
Relevance
If a piece of information is not personally relevant, likely, the person trying to learn it will still eventually forget it. This can be avoided by finding meaning in the information by relating it to a personal experience perhaps. Admittedly, this strategy is not always easy and might even seem impossible in some cases but if you can relate to even a small part of the information, it will be easier for you to remember it.
Interactivity
Active involvement is a great aid in learning. Take a seminar or class lecture, for example. The audience will learn better if there are interactive elements like games or even just a simple question-and-answer portion, rather than if they just sit there and listen while the speaker drones on the entire time.
Accessible Training
In the corporate setting, training is frequently held to improve the skills of employees. But the traditional once-a-month training does not cut it when you consider the points raised in the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve. A day or two after the training, the participants would most likely just forget what they have learned, unless there are frequent follow-throughs and open access to continued training and learning.
Thus, when holding training sessions or seminars, companies need to take advantage of technology to allow employees to continue their learning whenever they can. Mobile learning, for instance, makes it much easier for learners to accomplish the constant repetition and review that is a vital part of overcoming the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve.
Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve Templates in Boardmix
Our comprehensive set of templates is designed to help you leverage the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve to optimize learning and retention in diverse contexts. By understanding and applying the principles of spaced repetition and systematic review, you can significantly enhance memory retention and improve overall performance. Here are five templates we’ve crafted to guide you in utilizing the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve effectively in the Boadmix Community.
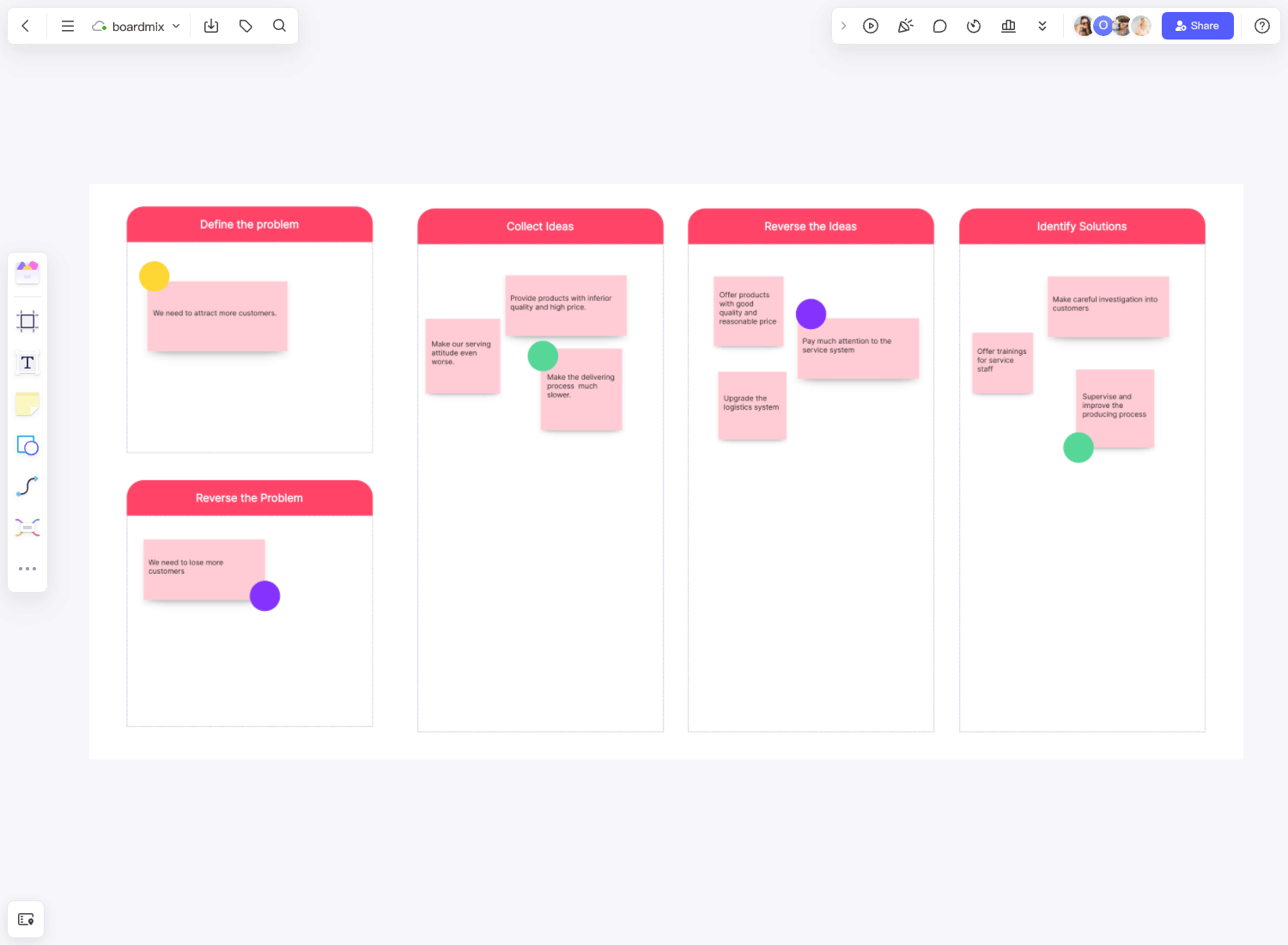
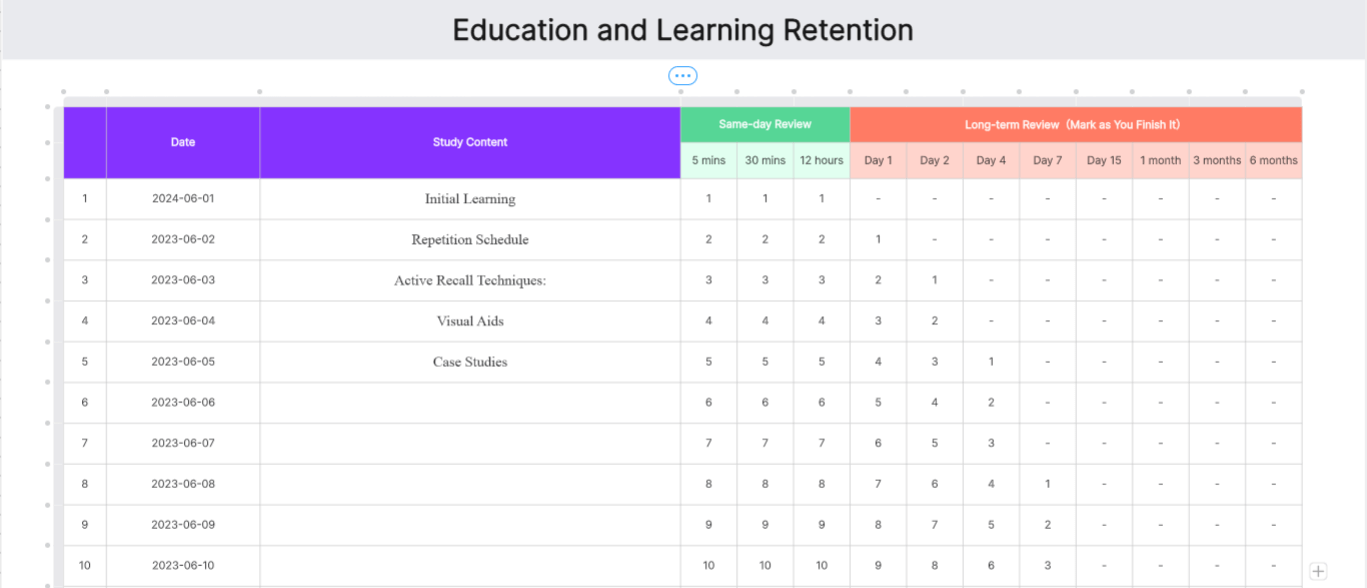
Education and Learning Retention
In the education area, teachers can use the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve to help students improve their memory and grades. This template focuses on educational settings, providing strategies for teachers to help students retain information more effectively. It includes detailed plans for initial learning, spaced repetition schedules, and active recall techniques to create a dynamic and engaging learning environment.
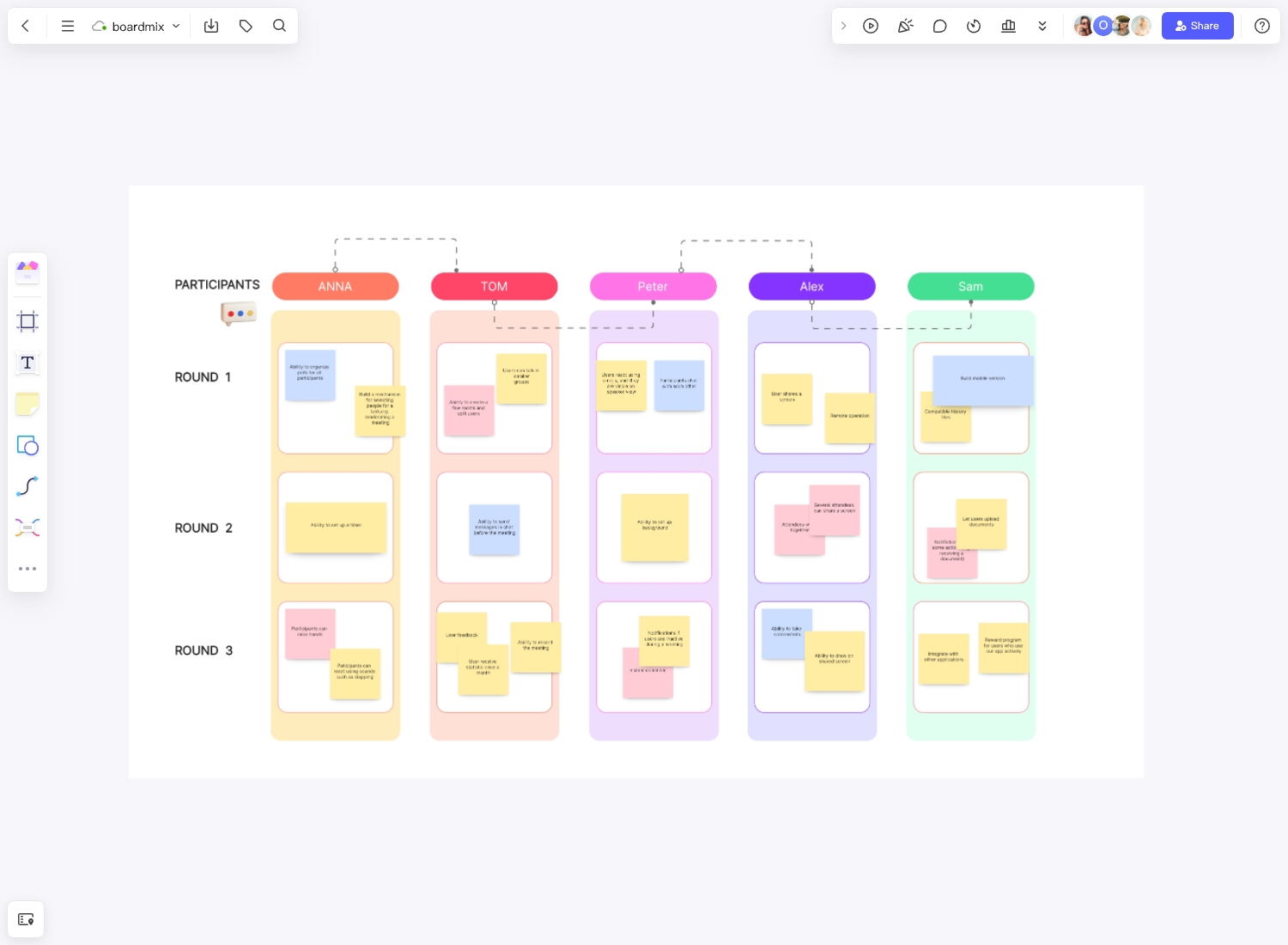
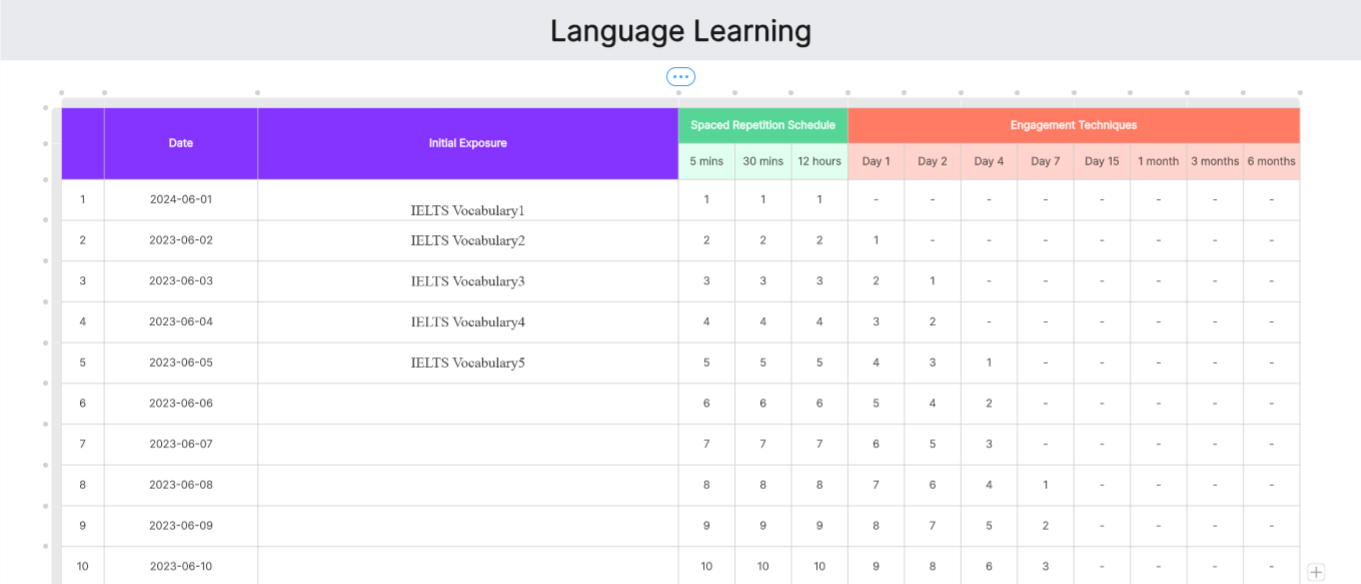
Language Learning
Language learners can benefit from this Ebbinghaus forgetting curve by following its guidelines on how to apply spaced repetition to vocabulary and grammar acquisition. The template offers practical tips on initial exposure, review schedules, and engagement techniques to facilitate long-term language retention.
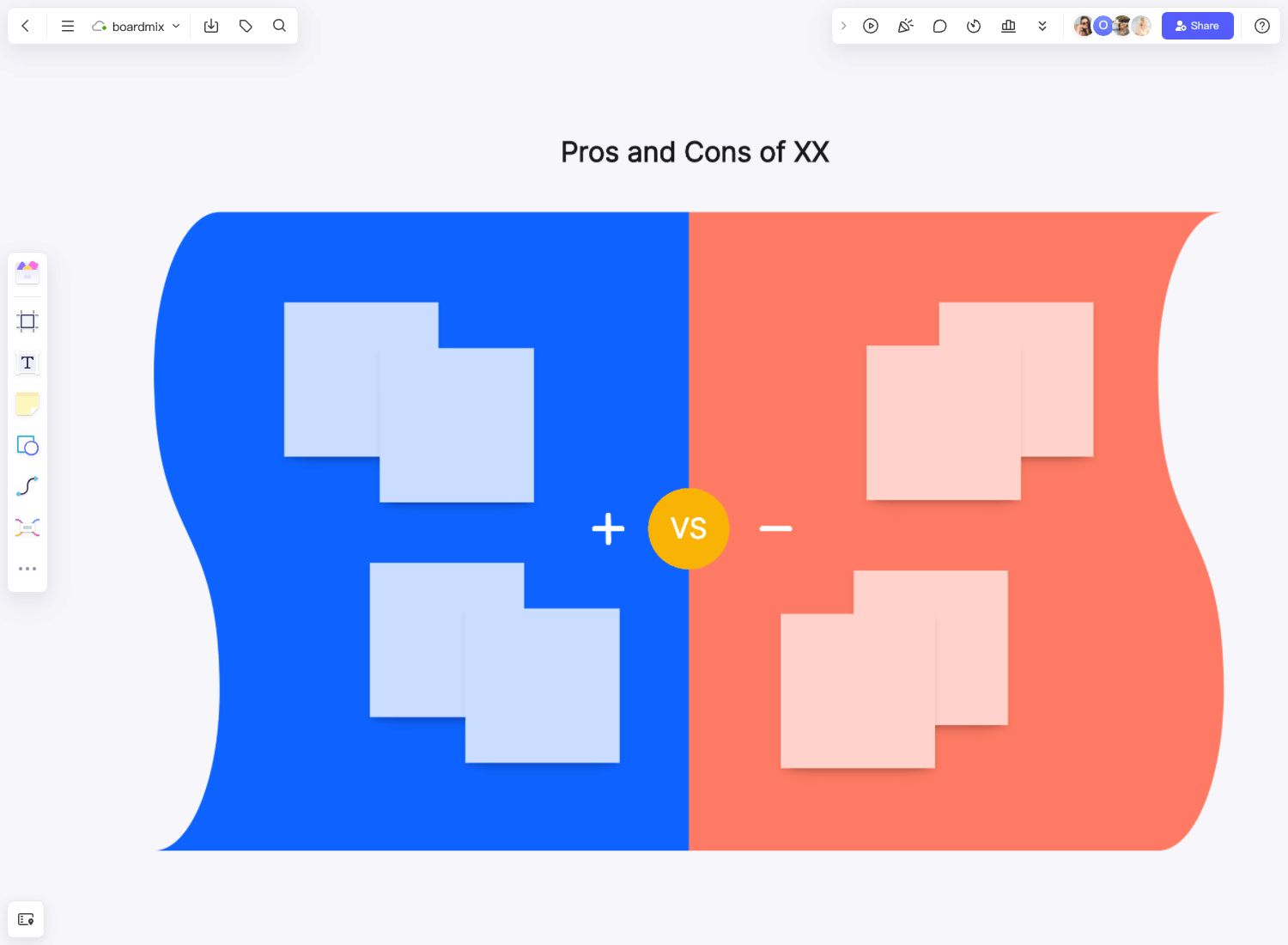
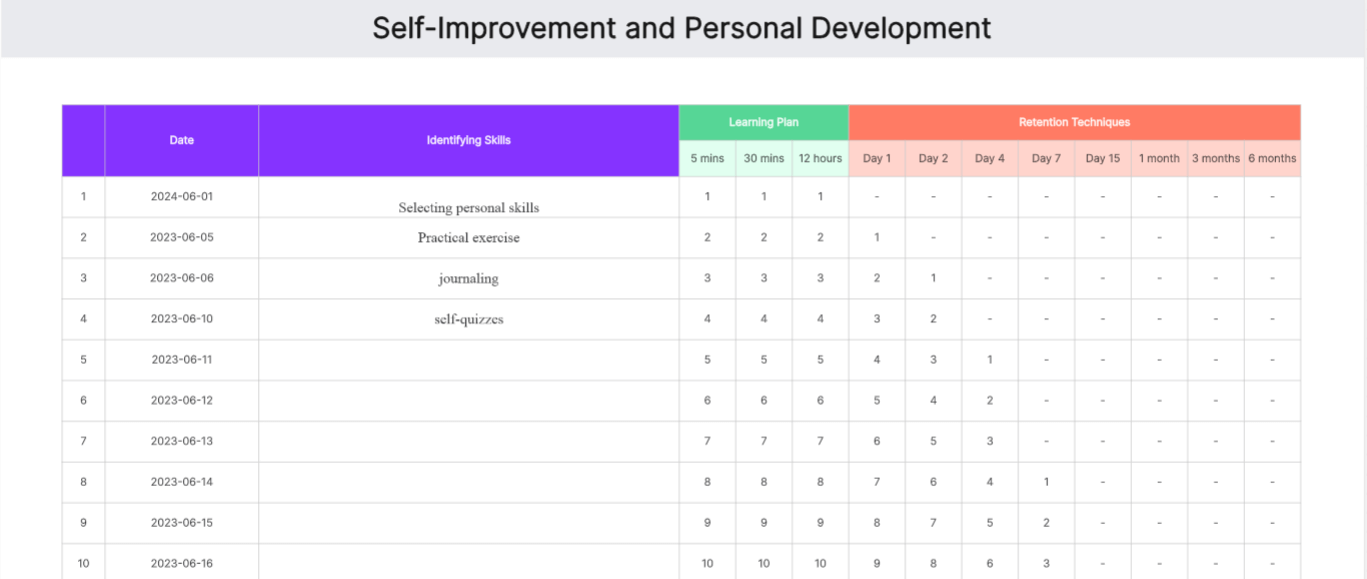
Self-Improvement and Personal Development
Personal development is geared towards individuals seeking to improve personal skills and knowledge. It guides users through the process of setting learning goals, developing a review schedule, and using retention techniques to achieve continuous personal improvement.
How to Use the Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve – 21-Day Schedule Template
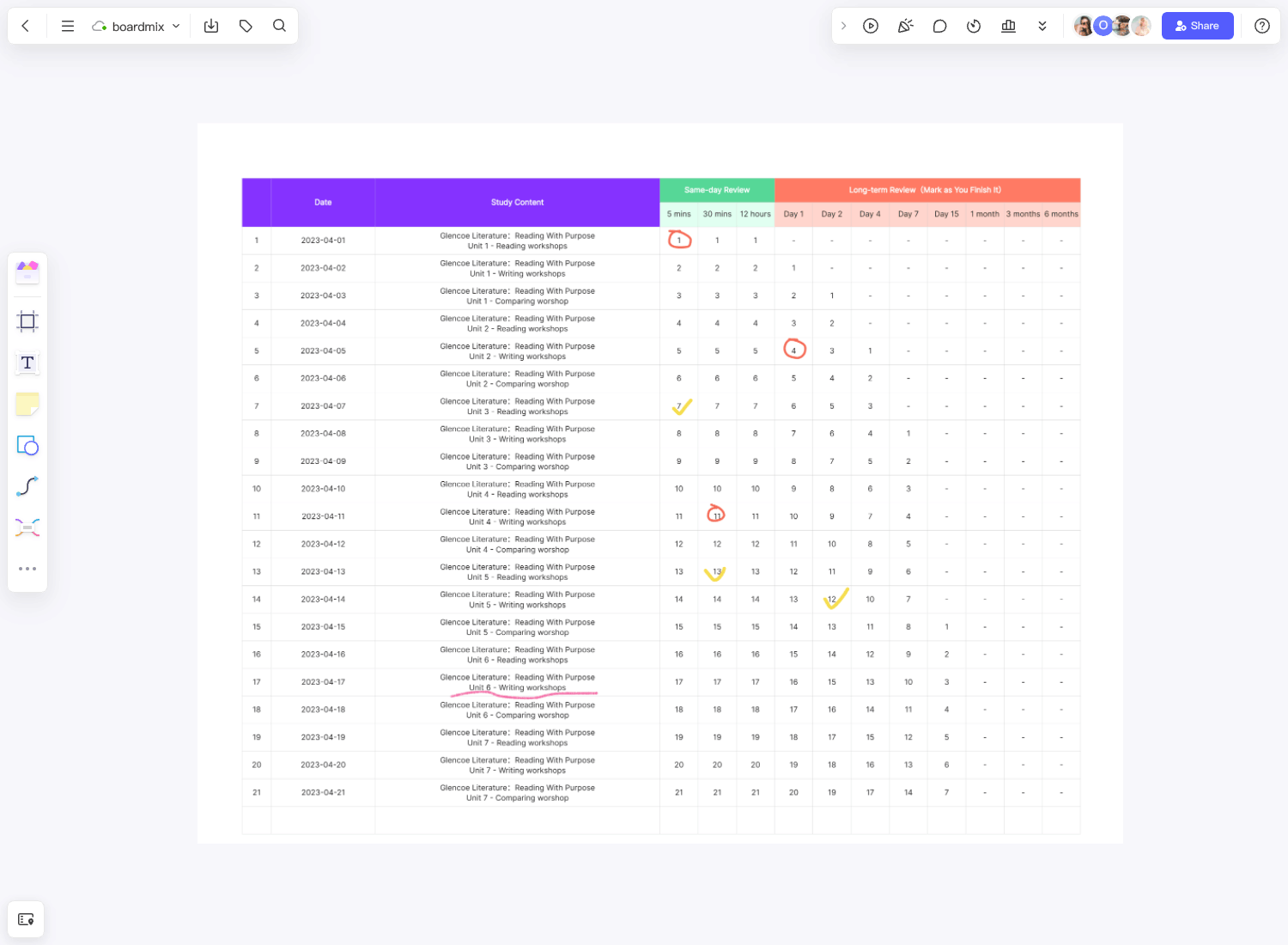
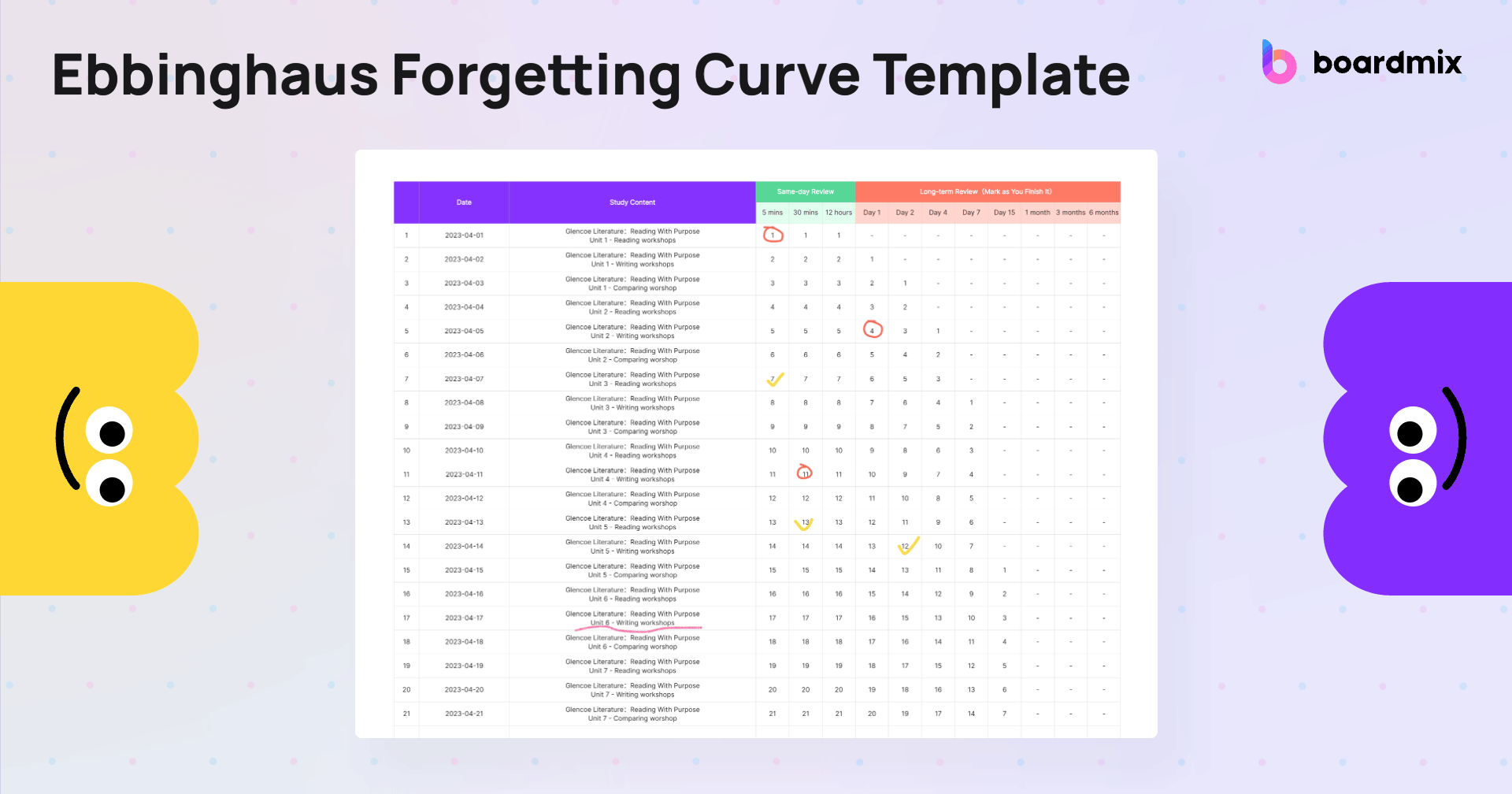
The Ebbinghaus forgetting curve has been known for more than a century and as mentioned, many methods have been developed to try and fight it. One of the most effective techniques for long-term learning is the 21-day schedule, and that is the basis of the template that we have here at Boardmix.
The template consists of 21 rows corresponding to the 21 days of the schedule. For each row, there is a column for the study content, as well as two separate sets of columns for same-day review and long-term review.
The same-day review section has columns for 5 minutes, 30 minutes, and 12 hours, which are the prescribed intervals during which you must review the information for optimal retention. As for the long-term review, there are columns for days 1, 2, 4, 7, and 15, followed by columns for months 1, 3, and 6. You need to mark each entry accordingly as you finish the review for that particular session.
Step 1: Log in to Your Boardmix Account
To begin, you'll need to access your Boardmix account. Go to the Boardmix website and enter your login credentials. If you don't have an account yet, you can sign up for a new one for free.
Step 2: Search and Choose Ebbinghaus Forgetting CurveTemplate
Once you're logged in, head over to the Template library. You can find this in the main dashboard. Search for the Activity Planning Template and click to use it for free.
Step 3: Customize and Edit Your Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve
Now that you've chosen the template, it's time to customize it according to your needs. You can use shapes, lines, drawing pens, icons, and other tools to decorate your template. The Activity Planning Template comes with several sections that you can fill out.
Step 4: Save Your Work, Share and Collaborate
When customizing your Ebbinghaus forgetting Template, Boardmix autosaves your progress, but it's good practice to manually save before exiting.
Next, share your Ebbinghaus forgetting curve to collaborate with your team. Click on the "Share" button on the top right corner of the screen, copy the sharing link, and send it to anyone whom you want to collaborate with. People can join this file to edit and collaborate on this file in real-time by clicking this sharing link. We encourage your team to leave comments, suggest edits, or ask questions online so you can adjust it in time.