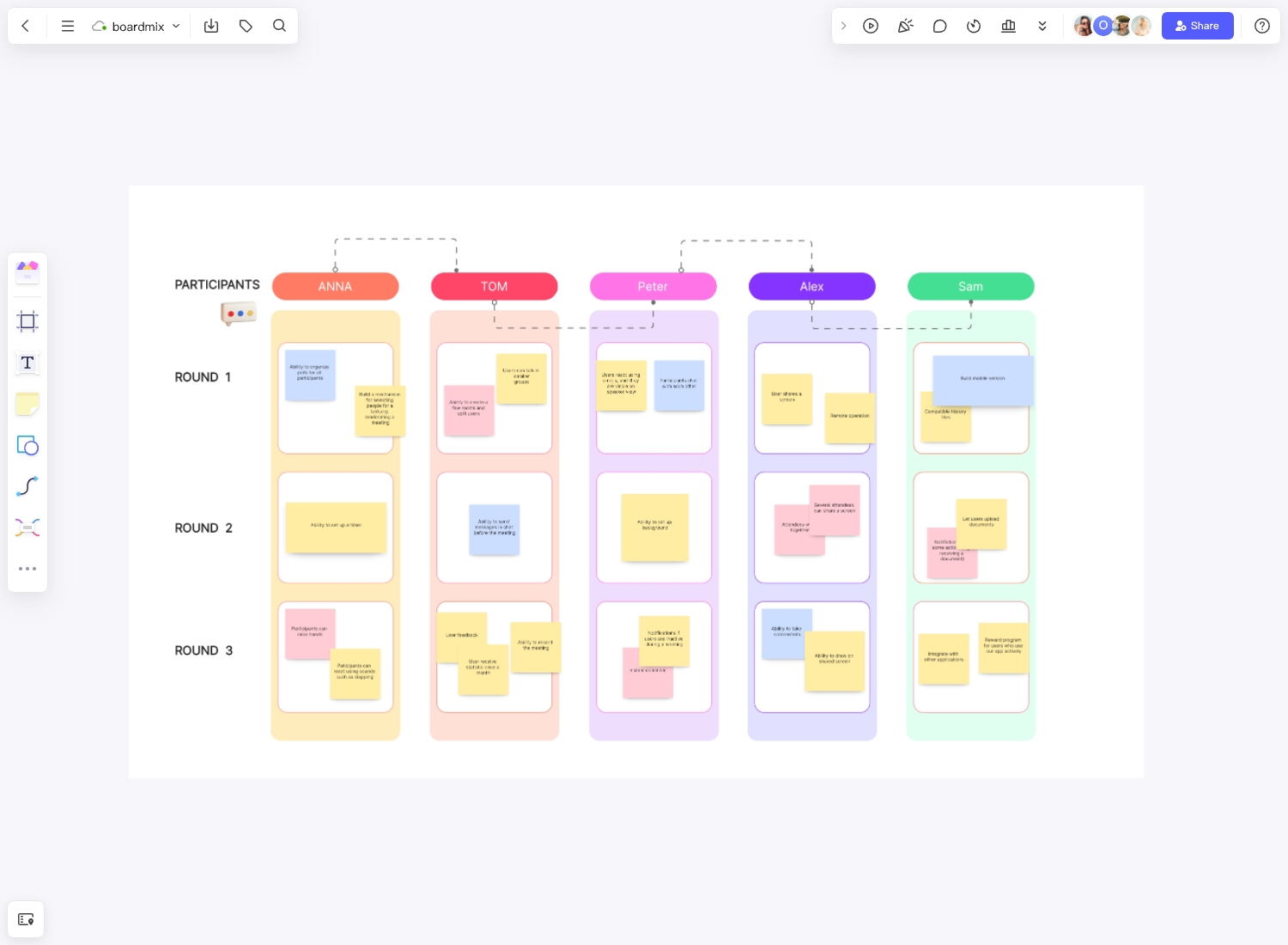
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a strategic planning discipline that helps organizations align IT assets, business processes, and strategies to achieve their business objectives. This article provides a comprehensive understanding of EA, including its definition, significance, and how to draw an EA diagram. Plus, it offers a variety of templates to kick-start your EA journey. Unleash the power of strategic alignment with EA and drive your organization toward success.
What Is an Enterprise Architecture Diagram?
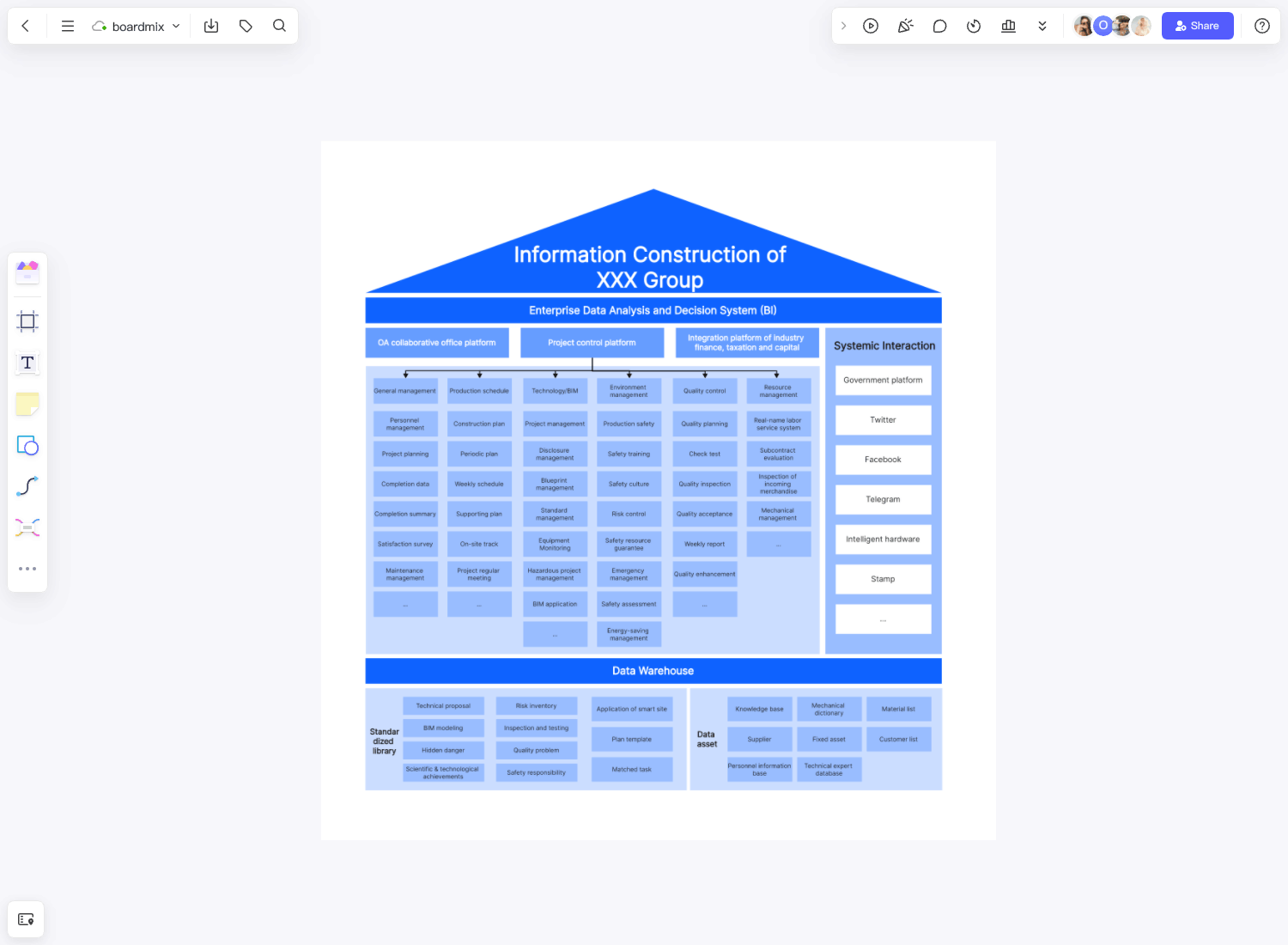
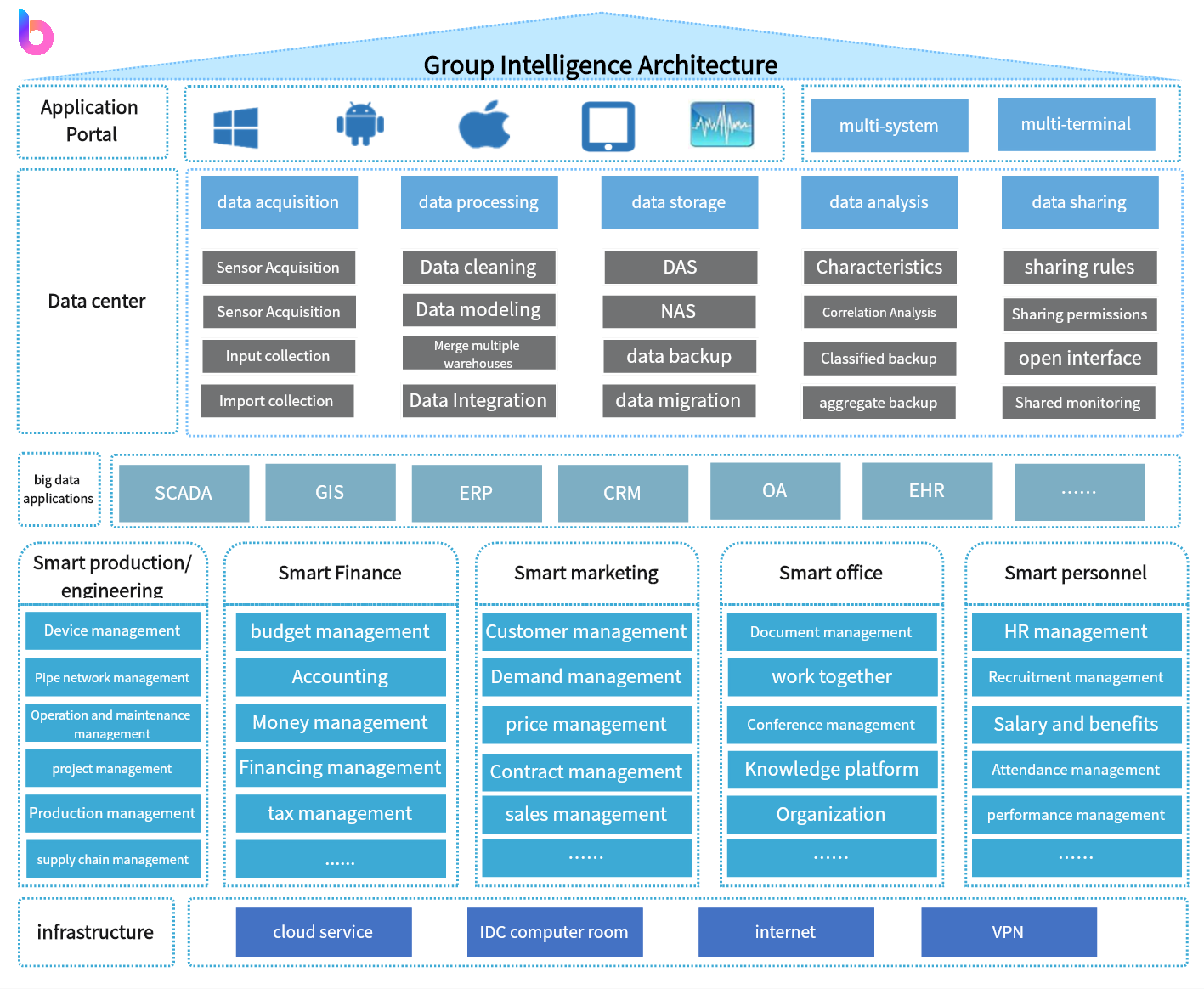
Enterprise architecture is a framework of a business or organization, consisting of the structure, processes, systems, IT infrastructure, and many other components of the business. It serves a multitude of purposes, but the primary function is to help identify ways and strategies to achieve present and future business goals.
Build Enterprise Architecture for Free
Businesses started using enterprise architecture in the 1980s when a rapid influx of technology advancements created the need for businesses to be more adaptable and therefore stay relevant and competitive in their respective industries amidst the modern changes. Back then, EA was focused only on IT but over the years, it began to encompass all the other areas of an enterprise. Today, enterprise architecture planners use the fundamental EA principles for the entire business, ensuring that the enterprise presents a seamless environment where innovative applications and legacy processes can be used together in the successful execution of business strategies.
What are the 4 Main Types of Enterprise Architecture?
Enterprise architecture is a holistic view of an organization's key business process and IT strategy. It's a well-defined practice for conducting enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation, using a comprehensive approach at all times, for the successful development and execution of strategy. The four main types of enterprise architecture include:
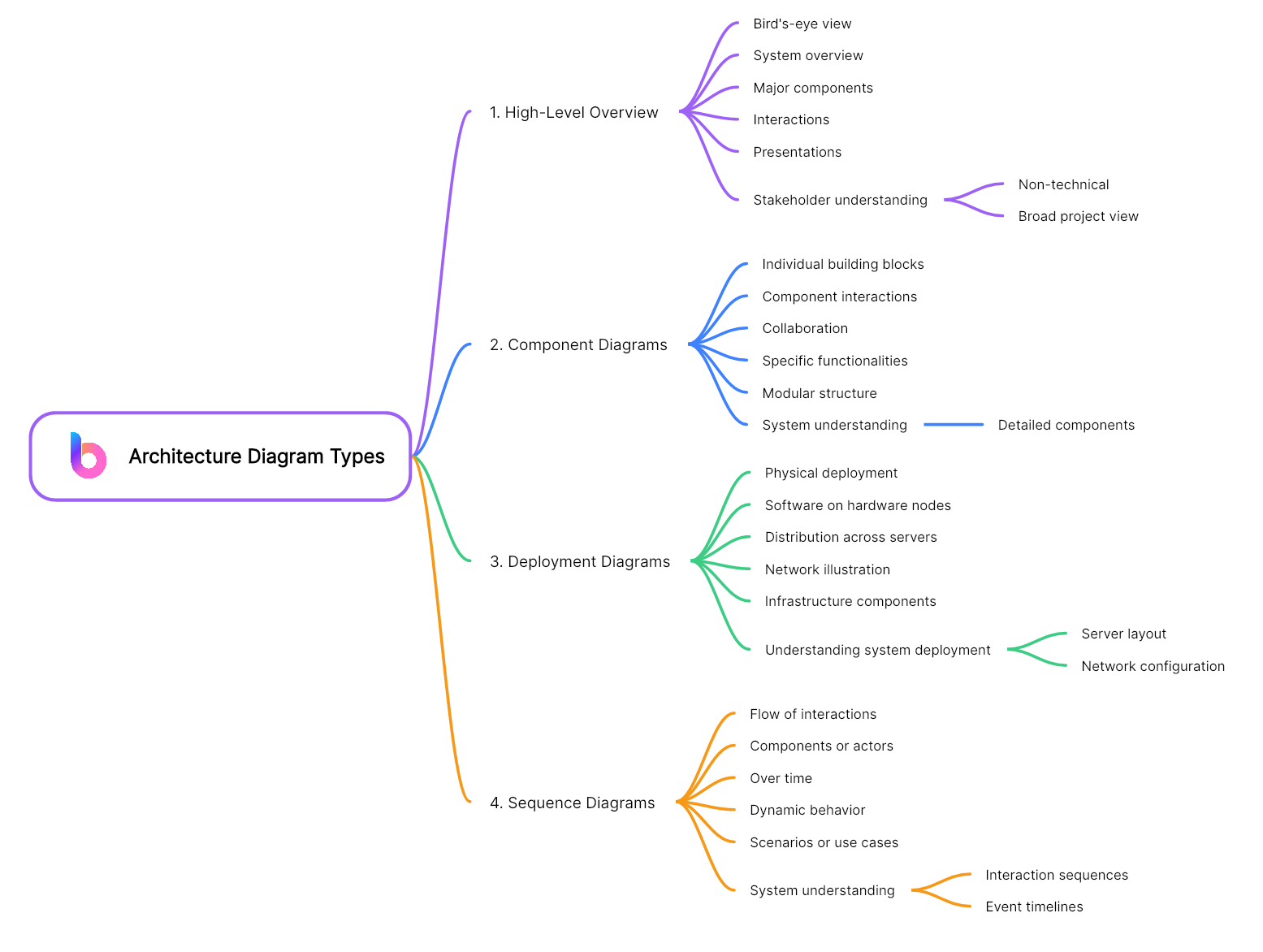
Business Architecture
In this section, you will find a comprehensive overview of the business, covering its offered services and products, organizational structure, goals, strategies, and the factors that contribute to its goal attainment. Moreover, it outlines the interrelationships between various components, providing a holistic view of the business.
Application Architecture
This part lists and describes the applications and other IT assets of the enterprise, including how they are integrated into the overall business flow, how they function with one another, and the role they play in the delivery of products, services and processes.
Information Architecture
This component describes the data model of the enterprise, as well as its various information requirements. This part is crucial in ensuring the proper and sufficient management of data towards the achievement of business goals. Through data analytics, all other areas of the system can be improved and it ultimately promotes optimal IT performance and adaptability.
Technology Architecture
In this component, all software and hardware technology used in implementing the business, application and information side of the enterprise, as well as other business operations are identified and described. It also details how these technologies are deployed in support of data and applications.
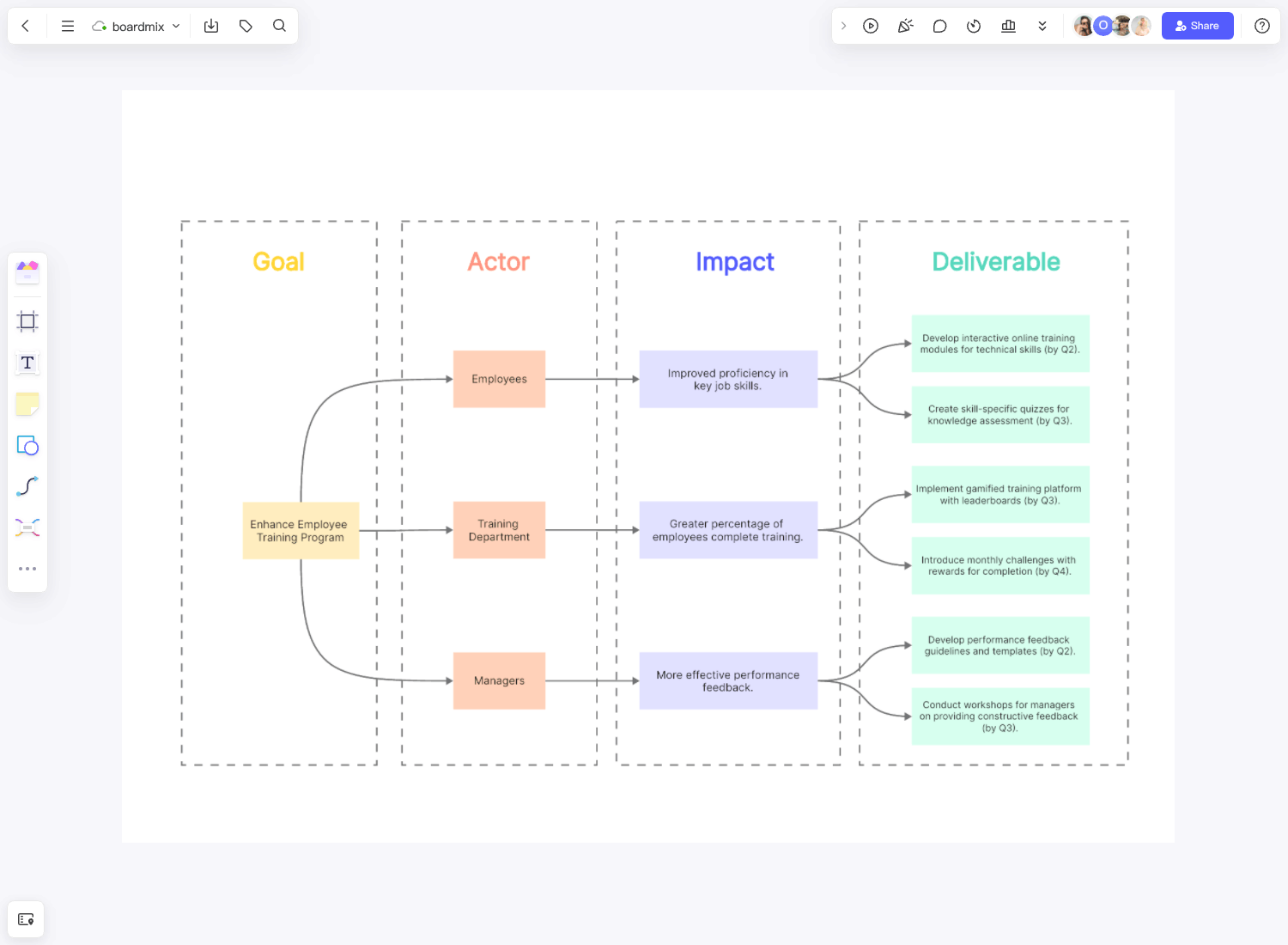
How do you create an enterprise architecture diagram?
Creating an enterprise architecture diagram involves several steps.
Here is a general guide:
-
Define the Purpose: The first step in creating an enterprise architecture diagram is to define its purpose. Do you want to map out the current architecture of your enterprise or are you planning for the future? The purpose will guide the creation process.
-
Identify Components: Depending on the type of diagram you're creating, you need to identify all the components that will be included in it. This could include business processes, IT infrastructure, data flow, applications, users, etc.
-
Choose a Framework: There are several enterprise architecture frameworks available like TOGAF, Zachman or FEAF. These provide a structured way of creating your diagram and can be very helpful.
-
Draw the Diagram: Using an appropriate tool, begin drawing your diagram. Start with high-level components and then drill down into more detail as necessary. Be sure to clearly label all components and relationships.
-
Review and Refine: Once you have a draft of the diagram, review it for accuracy and completeness. Get feedback from stakeholders and refine as necessary.
-
Communicate: Once your diagram is complete, use it as a communication tool. It can help everyone in the organization understand how various elements work together and how changes can impact them.
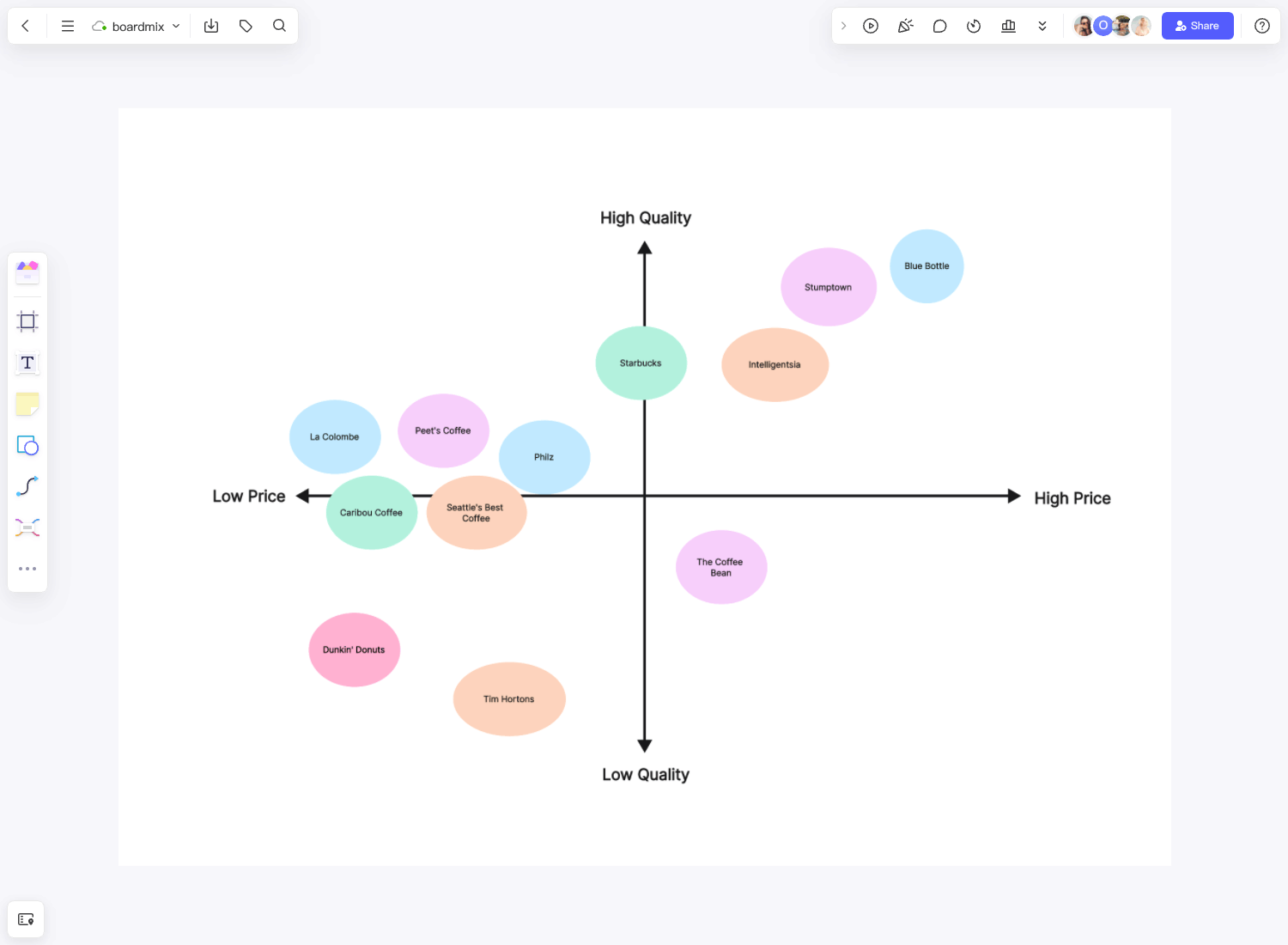
Enterprise Architecture Examples Templates
Enterprise architecture templates can provide a clear framework and guidance during the implementation of enterprise architecture. Here are some common Enterprise Architecture example templates.
1. Business Architecture Template
This template focuses on the organization's business strategy, key performance indicators (KPIs), and business processes. This helps to clarify the organization's business goals and how to achieve these goals.
2. Information Architecture Template
The information architecture template can help organizations better understand and manage their data assets. It includes elements such as data definitions, data flow, and data management.
Build Enterprise Architecture for Free
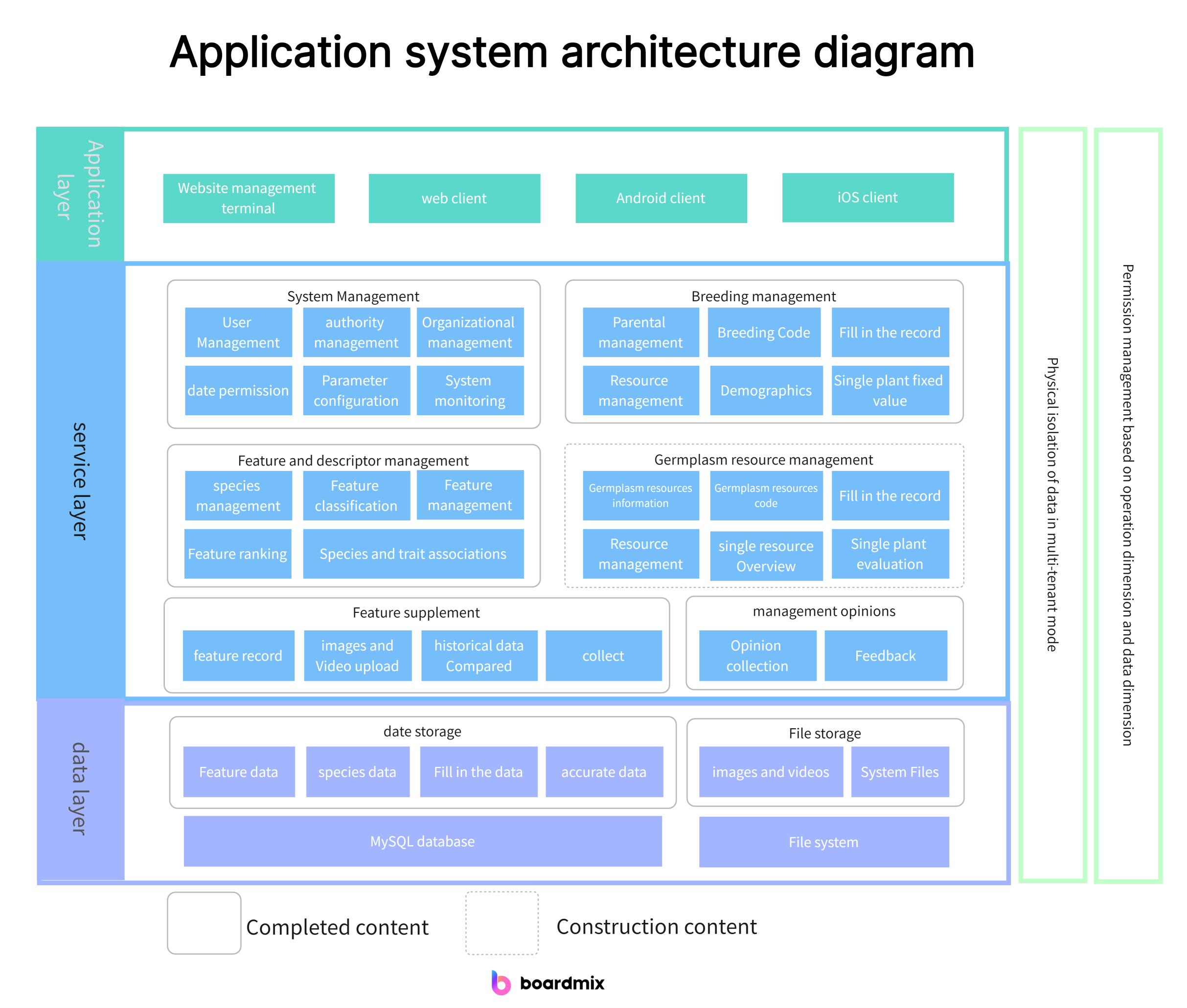
3. Application Architecture Template
The application architecture template describes the application systems used by the organization and how these systems support business processes.
4. Technology Architecture Template
The technology architecture template focuses on infrastructure, such as hardware, software, networks, and how these technologies support the organization's applications and data.
Build Enterprise Architecture for Free
How to use BoardMix's Enterprise Architecture Template
Using Boardmix's Enterprise Architecture Template is a straightforward process that can help you visualize and map your organization's structure, processes, and systems. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Access the Template: First, log in to your BoardMix account. If you don't have one, you'll need to create it. Once logged in, navigate to the template section and search for the "Enterprise Architecture" template.
Open the Template: Click on the template to open it. You'll be presented with a new board containing the template.
Customize the Template: The beauty of BoardMix's templates is that they're fully customizable. Start by adding your company name and any other details you want to include in the header or title area.
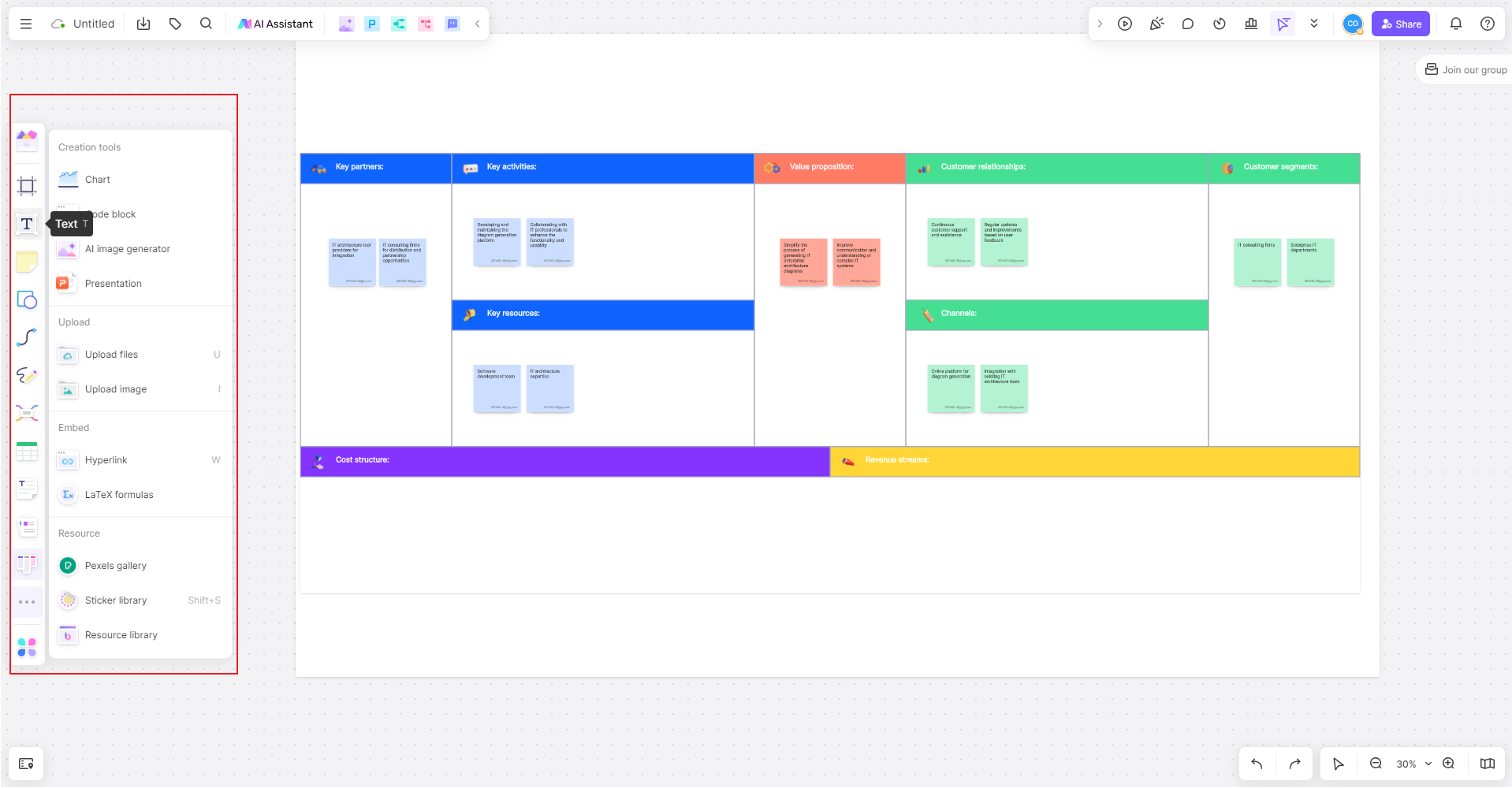
Identify Components: Start identifying the components of your enterprise architecture that you want to include in your diagram. These could be business processes, IT infrastructure, data flow, applications, users, etc.
Add Components to the Diagram: Drag and drop shapes from BoardMix's shape library onto your board to represent these components. You can customize these shapes with different colors and labels.
Connect Components: Use arrows or lines from BoardMix's shape library to connect these components where necessary to show relationships or data flow between them.
Add Notes: You can add notes or comments to any part of your diagram by using BoardMix's text tool or comment feature. This can be useful for providing additional information or context.
Collaborate and Share: Invite team members to collaborate on your diagram by clicking on the "Share" button at the top right of your screen. You can also export your diagram as a PDF or image file for sharing outside of Boardmix.
Review and Update: Regularly review and update your enterprise architecture diagram as changes occur within your organization.
Benefits of Using Enterprise Architecture
Most businesses today use enterprise architecture primarily to aid in digital transformation, but there are a multitude of other benefits that a well-designed EA can bring to the different aspects of your business.
Flexible Design Planning
With the operations and infrastructure of the business laid out, it is easy to analyze the structures and components and to implement design changes should they become necessary, like in the event of a merger or acquisition, or if there is a reshuffling in the organizational structure of the company, and so on.
Improved Business Efficiency
Enterprise architecture helps standardize processes, promote better consolidation, minimize redundancy due to new technology, and facilitate asset integration. All this contributes greatly toward improving the overall efficiency of the business.
Better Project Management
A laid-out EA is very helpful for project management, particularly in work prioritization and the use of data modeling to make faster and more viable decisions when it comes to project investments. It also promotes stakeholder communication and collaboration.
Faster Solutions
The very organized blueprint of an EA allows for the easy identification of lapses or the need for certain business or technology requirements. Once these potential problems have been discovered, the search for a suitable solution can begin right away, and the problem will be solved promptly.
Minimized Redundancies
As new technology arrives and is integrated into the system, it may create redundancies, which generate unnecessary and removable costs. With an efficient EA, you can be quickly notified of such redundancies and they can be eliminated, ultimately making the IT infrastructure not only much simpler but also more cost-efficient.
Reduced Business Risks
Risks are an inherent part of business and cannot completely be eliminated. However, once you implement an EA plan, this can drastically reduce the likelihood of business risks caused by system failures or security glitches. The issues that lead to these business risks can be identified and corrected early, keeping them from turning into massive setbacks.
What Are the Purposes of Enterprise Architecture?
The primary purpose of enterprise architecture is to present an organized and complete representation of the structure of an organization. Although it is a conceptual framework, it can easily be represented visually with the help of a good enterprise architecture template.

With such tools, the EA becomes a blueprint of the organization, showing everything from the hierarchical structure to the business processes and many more. Many EA diagrams are also very adaptable and easily accommodate upgrades or the addition of new components, making it a very helpful tool for companies that are undergoing digital transformation.
Other than painting a picture of the business operations, EA is also an invaluable guide for planning and the continuous achievement of long-term business objectives. In creating an EA, you should aim for it to also meet the following purposes.
Create an Effective Workflow
An EA eliminates unnecessary twists and turns in the business workflow that only causes delays and also unnecessary spending. With proper implementation, the EA leaves you with the most effective workflow, with no redundancies or delays.
Promote Efficient Use of Resources
In addition to the elimination of redundancies, an EA also allows systems to share or reuse resources, which saves a lot of time and money for the business. It also encourages more collaboration across the system.
Facilitate Smooth Transition between Technologies
Most businesses still use a lot of legacy technology. EA makes it easier to use these older systems alongside modern ones, while also identifying when there is an absolute need to move forward by upgrading or replacing certain components.
Ensure Continuity
In the event of a system failure, network disruption, or even a natural disaster, businesses rely heavily on their disaster recovery and continuity plan to survive. But to better your chances of continuously running your critical operations even further, the standardized business process from an EA will be very valuable.
Enterprise Architecture Stakeholders and Their Concerns
One of the objectives of an EA is to show the overall structure of an organization, including all its components, the relationship between these components, and its numerous intricacies. The EA processes directly affect a lot of individuals, groups, and other organizations. These affected entities are known as the stakeholders, and they play a significant role in the architecture.
Enterprise Architects
They create and implement the architecture processes that are vital for keeping the model properly aligned with business strategies.
Portfolio Managers
They take care of the management and streamlining of portfolios for technology, applications, and so on.
Business Architects
They create efficient and functional business models, making sure that the value streams are in perfect alignment with what customers are expecting to receive.
Solution Architects
They are in charge of a range of technology solutions that will help achieve business goals, especially when it comes to infrastructure, service, and application.
Security Architects
They conduct tests and present solutions to make sure that the security strategies of the new EA meet industry standards and are by the security policy of the company.
Business Analysts
Their job is to make improvements, if any are needed, to the existing processes to elevate business performance and also to comply with regulations. They are also the ones that identify areas that can be automated to reduce costs and improve overall efficiency.
Information Architects
Also sometimes called the chief data officers, their job is centered on the management of data and information. This includes storage, privacy, regulation, intelligence, and other data-related activities.
Compliance Managers
They are in charge of evaluating risk levels across different areas of the business and checking for compliance with regulations.
As you can see, there are so many stakeholders with various specific concerns in the enterprise. These concerns lead them to ask different sets of questions relevant to the enterprise. The business analyst might want to know what applications support a particular process, and what methods they can use to automate the process. A security architect, on the other hand, will be more interested in whether a proposed solution would meet security standards, or if would leave the system vulnerable to certain threats.
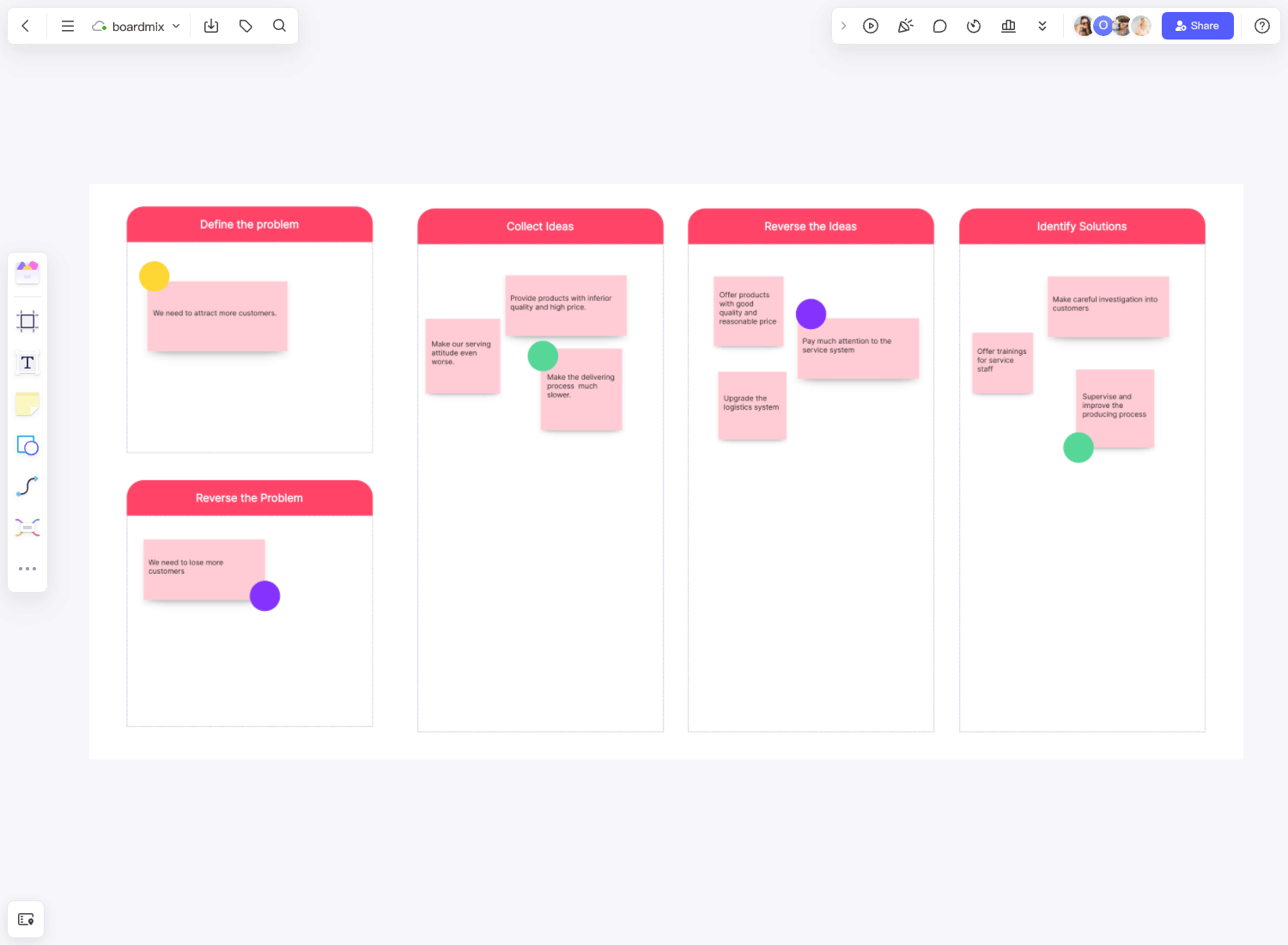
Best Practices of Enterprise Architecture
Creating an enterprise architecture for a business can become much faster and simpler with the help of a good enterprise architecture template. But even the most carefully crafted template won’t do much good unless you follow some best practices that will help ensure that you produce a successful EA plan.
First of all, the enterprise architect must have a thorough understanding of all the components of the business, from the company strategies and goals to the various project delivery methods, to be successful. With that being said, here are the best practices that the architect should strive to follow.
- Start by making a clear outline of what the EA is expected to do for the business, including its purpose, vision, and other vital components that are to be included in the initiative.
- Formulate and implement a comprehensive communications plan.
- The EA addresses both current and future situations of the company, but it is better to start with the future and work your way backward.
- Set realistic expectations.
- Assess your progress regularly using an objective measurement tool.
- As much as possible, direct the focus on strategic planning and business outcomes.